Bonding Unit 5 - Chemistry
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What are the four main ways atoms bond?
Ionic bonding, Covalent bonding, Metallic bonding, and Network Covalent bonding.
How does metallic bonding cause properties like ductility, malleability, and conductivity?
The freely moving electrons in the electron sea model allow flexibility in the solid metal and conduct electricity.
What are the 7 diatomic molecules?
Hydrogen (H2), Nitrogen (N2), Oxygen (O2), Fluorine (F2), Chlorine (Cl2), Bromine (Br2), Iodine (I2).
What is the Octet Rule?
The octet rule refers to the tendency of atoms to bond until 8 valence electrons surround the atom.
How many electrons are shared in a double bond?
4 electrons (2 pairs).
How many electrons are shared in a triple bond?
6 electrons (3 pairs).
How is bond length related to the number of bonds in a covalent molecule?
The more bonds that hold 2 covalently bonded atoms together, the shorter the bonds will be.
How is bond energy related to bond length?
The longer the covalent bond, the less energy it will hold.
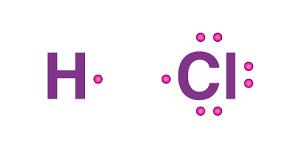
What is the lewis structure for HCl?
How many bonds does Oxygen usually form according to the HONC rule?
2 bonds.
How do structural formulas and Lewis structures differ from space-filling models and ball-stick molecules?
Structural formulas and Lewis structures are 2D while space-filling models and ball-stick models are 3D.
What is a resonance structure?
The same set of atoms as another molecule but the bonds are in a different location.
What is an electron domain and how does it affect molecular geometry?
An electron domain is a region around an atom where electrons are most likely to be found, causing different molecule shapes due to their negative charge.
Draw a lewis structure and ball-stick model for NH3. Name its geometry.
Trigonal pyramidal.

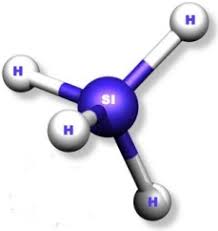
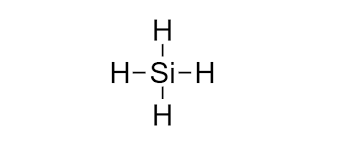
Draw a lewis structure and ball-stick model for SiH4. Name its geometry.
Tetrahedral.
What is the difference between a polar and nonpolar molecule?
A polar molecule has an uneven distribution of charge (e.g., H2O), while a nonpolar molecule has an even distribution of charge (e.g., CH4).
What is a polarity or dipole arrow?
A polarity arrow illustrates which atom is the most electronegative in a polar covalent bond.
Identify the polarity of H2, HCl, CO, and CO2.
H2 - nonpolar, HCl - polar, CO - polar, CO2 - nonpolar.
Why is a trigonal pyramidal molecule polar?
It has an asymmetrical shape due to lone pairs of electrons pushing atoms to one side, resulting in molecular polarity.
What shape is water and why is it polar?
Water is bent and polar because lone pairs on oxygen push hydrogen atoms to one side, causing an uneven distribution of electronegativity.
What is the difference between intramolecular forces and intermolecular forces?
Intramolecular forces occur within a molecule, while intermolecular forces occur between different molecules.
How do intermolecular forces affect melting and boiling points?
Stronger intermolecular forces cause higher melting and boiling points because molecules have a harder time separating.
How does a hydrogen bond form?
A hydrogen bond forms when a hydrogen atom is covalently bonded to a highly electronegative atom like F, O, or N.
Which is the weakest type of intermolecular force?
Dispersion force.
Which is the strongest type of intermolecular force?
Hydrogen bonding.
What type of intermolecular forces can exist between polar molecules?
Dispersion forces, dipole-dipole forces, and possibly hydrogen bonding.
What type of intermolecular forces can exist between nonpolar molecules?
Dispersion forces only.