ITEC 3230 - L5: Design Process: Prototyping
1/177
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
178 Terms
Prototyping
Creating preliminary models of user interfaces.
Conceptual Model
High-level description of system organization.
Metaphors
Familiar concepts used to explain interfaces.
Interaction Types
Different methods of user-system interaction.
Instructing
Issuing commands and selecting options.
Conversing
Interacting as if having a conversation.
Manipulating
Interacting with objects by manipulation.
Exploring
Moving through virtual or physical environments.
Interface Styles
Various methods for user interaction with systems.
Command Language
User types commands in an artificial language.
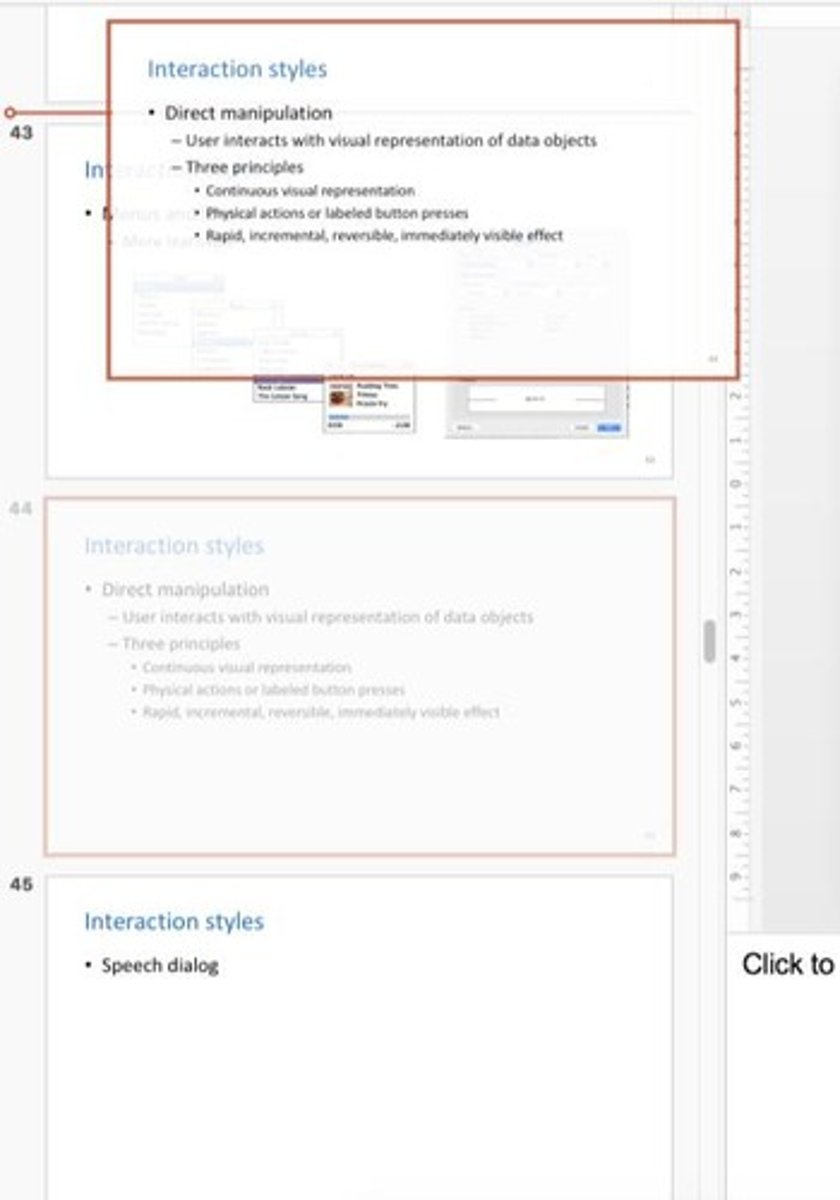
Direct Manipulation
Physical actions replace complex command syntax.
Menus and Forms
Structured options for user selection.
Voice Interaction
Using voice commands for system interaction.
Graphical User Interface (GUI)
Visual interface allowing user interaction.
Augmented Reality
Overlaying digital information on the real world.
Gesture Interaction
Using body movements to control interfaces.
Undo Functionality
Allows users to reverse actions taken.
Recycle Bin
Temporary storage for deleted items.
Wizards
Guided interfaces for user tasks.
Chat Bots
Automated systems for conversational interaction.
Recognition vs Recall
Recognition aids memory; recall requires retrieval.
Prototyping
Creating preliminary models for design evaluation.
Interaction styles
Different ways users interact with systems.
Speech dialog
Natural language communication between user and system.
User involvement
Engaging users in the design process.
Participatory design
Collaborative design approach with user participation.
Usability testing
Evaluating a product by testing it with users.
Field testing
Testing in real-world environments.
High fidelity prototyping
Detailed and functional prototypes resembling final product.
Low fidelity prototyping
Basic prototypes using simple materials for concepts.
Task-centered system design
Design focused on user tasks and goals.
Heuristic evaluation
Expert review of usability based on principles.
User-centered design
Design approach prioritizing user needs and experiences.
Iterative test and redesign
Repeated testing and refining of designs.
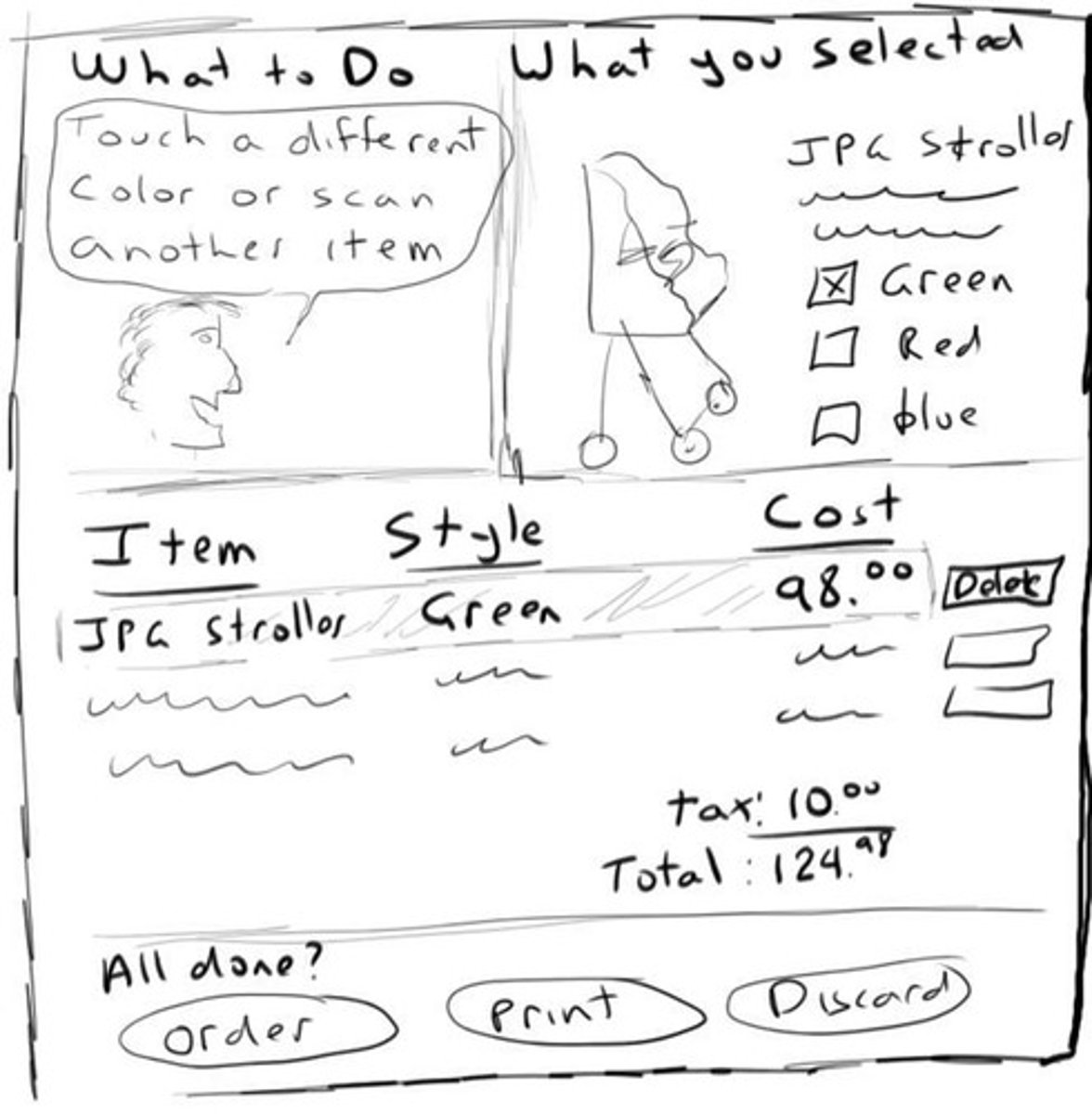
Mockups
Visual representations of design concepts.
Needs analysis
Identifying user requirements for effective design.
Task analysis
Breaking down user tasks for better understanding.
Function allocation
Deciding which tasks are performed by users or systems.
System layout
Organizing components for optimal user interaction.
Graphical screen design
Visual layout of user interface elements.
Acceptance testing
Final evaluation to ensure user satisfaction.
Evaluation stages
Assessing design effectiveness at various phases.
Psychology of everyday things
Understanding user behavior and expectations in design.
Throw-away paper prototypes
Temporary models used for quick feedback.
Sketching
Low-fidelity representation of design ideas.
Low-fidelity prototype
Basic mock-up for early design concepts.
Medium-fidelity prototype
Computer-based simulation with limited features.
High-fidelity prototype
Detailed and functional representation of final design.
Vertical prototyping
Focus on specific features in isolation.
Horizontal prototyping
Broad overview of multiple features at once.
Scenario prototyping
Simulates user interaction in specific contexts.
Storyboarding
Series of sketches illustrating user interaction.
PICTIVE
Collaborative design using sticky notes and overlays.
Task-centered walkthrough
Evaluates user tasks through interface exploration.
Heuristic evaluation
Expert review to identify usability issues.
Usability testing
User testing to assess interface effectiveness.
Alpha test
Initial testing phase with limited users.
Beta test
Testing phase with broader user group.
Attributes of sketches
Quick, disposable, and exploratory design tools.
Crude sketches
Focus on high-level concepts rather than details.
Interface style
Visual design elements of a user interface.
Screen design
Arrangement of visual elements on a display.
User reactions
Feedback from users on design concepts.
Design modifications
Changes made based on user feedback.
Limited field testing
Testing in real-world conditions with constraints.
Interaction demonstration
Showcasing how users interact with prototypes.
Management perception
Risk of stakeholders believing prototypes are final.
Vertical Prototype
Focuses on in-depth functionality of few features.
Horizontal Prototype
Simulates full interface without underlying functionality.
Throw-away Prototype
Rapidly created to elicit user feedback.
Incremental Prototype
Built as separate components, tested individually.
Evolutionary Prototype
Iteratively altered to incorporate design changes.
Scripted Simulation
User follows a tight script for interaction.
Interface Builders
Tools for designing layouts of common widgets.
Figma
Design tool for creating user interfaces.
Axure
Prototyping tool for interactive wireframes.
Balsamiq
Rapid wireframing tool for low-fidelity prototypes.
Invision
Platform for creating interactive prototypes from designs.
Proto.io
Mobile prototyping platform for interactive designs.
Wizard of Oz
Testing method simulating a non-existent system.
Storyboard
Visual sequence illustrating user interaction scenarios.
Media Tools
Software used to create interactive storyboards.
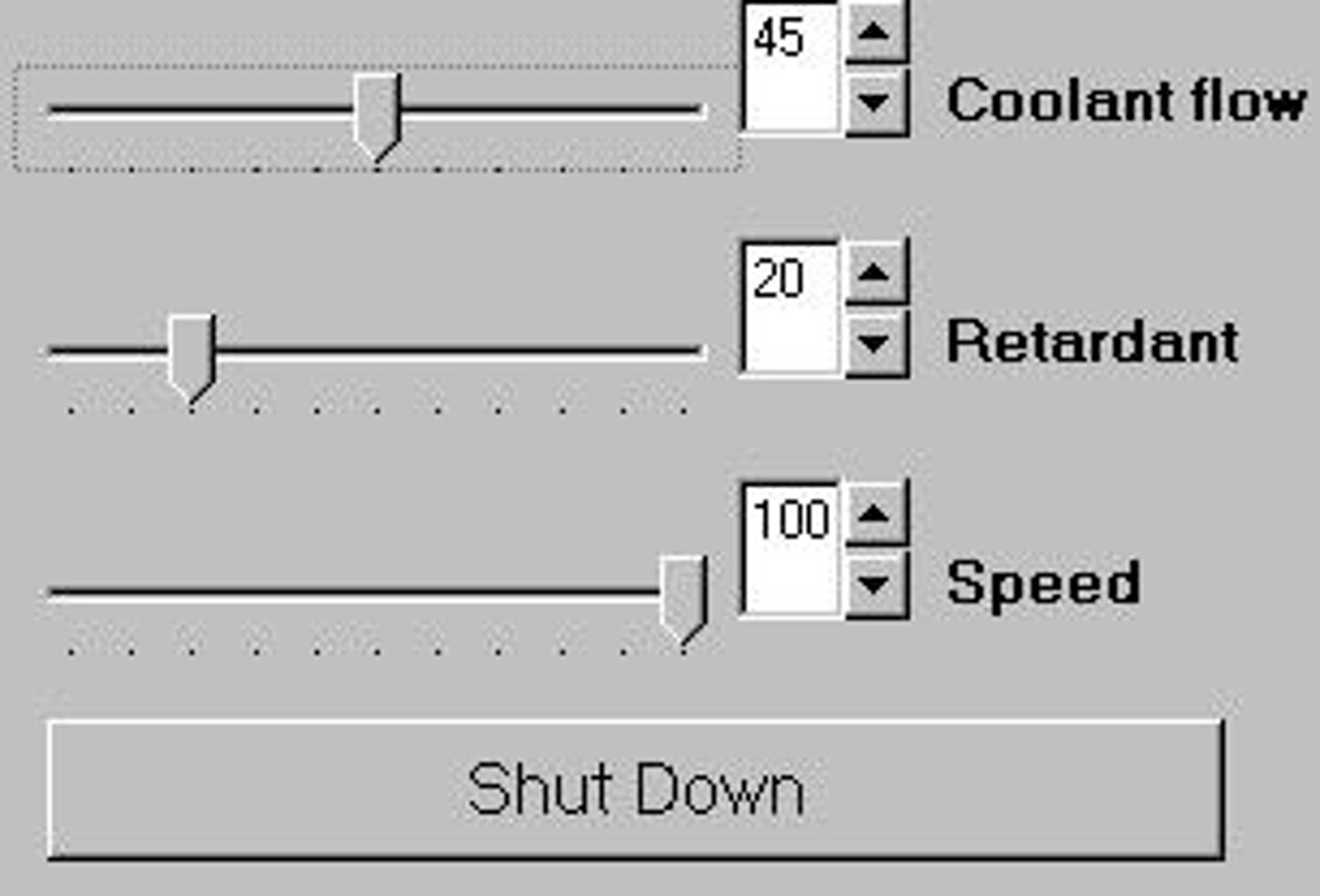
Control Panel
Interface for managing system operations and settings.
User Inputs
Actions taken by users to interact with prototypes.
Simulation
Imitation of real system behavior for testing.
Rich Graphical Interfaces
Complex interfaces with advanced visual elements.
Fixed Uses
Predefined scenarios with no allowed deviations.
Coolant Flow
Measurement of coolant percentage in a system.
Retardant
Substance used to slow down a process.
Wizard of Oz
Human simulates system response for testing.
Human Wizard
Interprets user input via an algorithm.
Mock Interface
Simulated interface used in testing scenarios.
Vertical Functionality
Simulated features for complex system testing.
Design Principles
Guidelines for creating effective user interfaces.
Simplicity
Design should be straightforward and clear.
Learnability
Ease with which users can learn the system.
Affordances
Design elements suggesting their usage.
Mapping
Relationship between controls and their effects.
Feedback
User responses indicating system status or actions.
Visibility
Clarity of available actions in the interface.