Biology biological molecules 3.1.1&2
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Card 8 is 3.1.2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
the biochemical basis of all life
carbon hydrogen nitrogen oxygen. this is proof of evolution.
what are monomers
basically smaller units from which larger molecules are made.
what are polymers
basically molecules that are made from a large number of monomers
examples of monomers
amino acids, nucleotides and monosaccharides, such as ALPHA GLUCOSE AND BETA GLUCOSE.
Example of a polymer
cellulose, glycogen, and dissaccharides.
a condensation reaction
joins tomolecules together which form a bond and involves the elimination of a molecule of water
A hydrolysis reaction
this breaks a chemical bond between two molecules and involves the use of a water molecule
mono saccharides
they are sugar molecules, they are monomers which make up larger disaccharides and polysacchardies
glucose
c6 h12 o6( hexase)
the monosaccharides
glucose, fructose and galactose
sucrose
glucose+ fructose. sucrose is not a reducig sugar
disaccharides
they are know as nonredcing sugars
Glycosidic bond
this is formed between two monosaccharides. Eg Maltose is made from two alpha glucose joined together by a condensation reaction. these are formed between the OH groups of the C1 and C4
lactose
glucose+galactose.
maltose
alpha glucose +alpha glucose
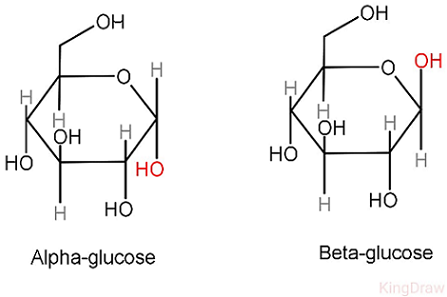
isomers
Basically molecules with the same molecular formula a different arrangement of atoms withthin the molecule for instance the alpha and beta glucose molecule.
image of isomer on the right.
covelent bonding
when atoms share pairs of electronds in their outer shell and a more stable compound called a moecule isformed
Apolarised molecule
when the charges ar are not spread evely aroudnd the loecule also known as uneven distribution of electrons.
carbohydrates
the carbon atoms readily form bonds with other carbon atoms. therefore a sequence of lengths of carbon atoms are built. these form a “backbon that other atoms can be attache. this permits a large number of different sizes and types of molecules to be based on carbon.
mono saccharides
they are sweet tasting SOLUBLE SUBSTANCES. they have the forula ( CH20)n where n has a range of 3-7
why would a colorimeter improve repaetability
because colour is subjunctive
percentage error
uncertainty/ volume) x100
test for reducing sugars
add solution in test tube. then add benedicts solution, heat for 4 mins and a red precipitate shoud be formed.
test for non reducing sugars
the first biochemical test willl be negative for non-reducing sugars. they need to be neutraised first, which means, the a put in a test tube, then added an acid or HCL . once it stops fizzing sodium hydrogen carbonate (NaHCO3). the beenedicts solutin is added and then placed ina water bath. this is because the disaacharide has been hydrolysedinto monosacchardides.
starch
made from alpha glucose molecules which form a glycosidic bond. they form a helix structure which makes it compact and good for storage. it has branched and unbranched chain. the OH groupp be pointing inwards which form hydrogen bonds that keep them in shape. it is made from amylopectin and amolose
properties of starch
they are large molecules and thereforecannot diffuse out of the cell memebran. the are large molecules therefroe insoluble.so this does not affect their water potential. when hydrolyesed, it easily transported and readily used for respiration. Has many ends so that they are acted on by enzyme acticity. also glucose is released easily. it is also stored in storage organs and seeds, and is found in plants.
glycogen is very
Has very similar to starch but found in ANIMAL CELLS. it is stored in small granues and is shorter and highly branched. ithese granules are found muscles, and liver cells.
celllulose
made of beta glucose molecules arranged parallel to each other and are straight chains with unbranched chains which then form hydrogen bonds that are adjacent and form a linkage between these chains that have collective strength, this makes the cell wall very turgid and non-woody parts of the plant semi turgid.