UTA Plant Science Exam 1
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
114 Terms
Bryophyte characteristics
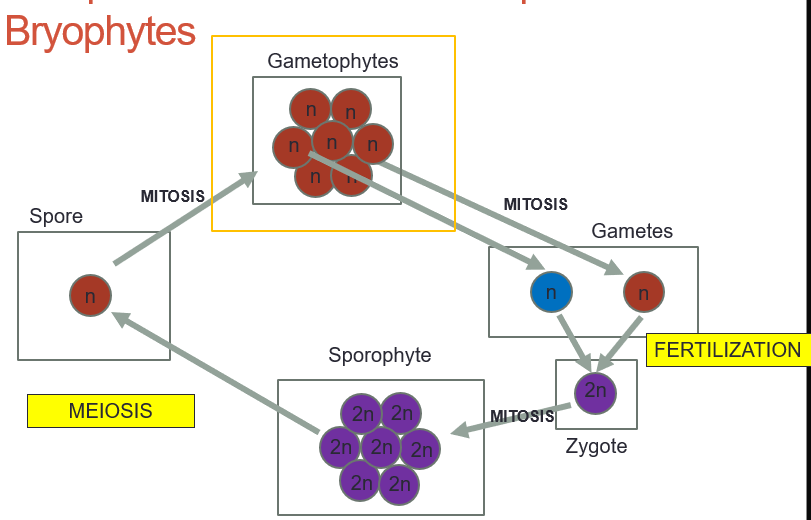
nonvascular (no leaves, roots, or shoots) , gametophyte dominant, motile sperm that require water for fertilization, SEEDLESS
hydroids
bryophyte water conducting tissue, NOT lignified
thalloid (thallus)
leaf-life structures used for uptake of water and gas exchange
bryophyte solution to no stems
cuticle with structures analogous to stomata (gas exchange)
rhizoids
bryophyte “roots” used to Anchor but NOT FOR WATER TRANSPORT
where do bryophytes absorb water
absorption of water and ions occur directly and rapidly throughout the [gametophyte]
dominant generation of bryophytes
gametophyte
gametophyte
gamete producing generation
sporophyte
spore producing generation
alternation of generations diagram
antheridium
male gametangia, either unicellular or multicellular, consists of: Stalk (antheridiophore), Sterile Jacket Layer (single cell layer), Spermatogenous Tissue (each spermatogenous cell forms one biflagellated sperm cell)
archegonium
female gametangia, multicellular, consists of: Neck and Neck canal cells, Venter (surrounds single egg), fertilization occurs inside here
fertilization in bryophyes
occurs in archegonium, neck canal cells disintegrate forming a fluid-filled tube, sperm travels down archegonium and down to the neck, fuses with egg to form zygote, zygote remains in archegonium, undergoes mitosis to generate the embryo, eventually becomes mature sporophyte
embryophytes
term for ALL plants
matrotrophy
embryo gets nutrients and protection from maternal gametophyte, “placenta” between the two generations facilitate the transfer of nutrients
mature sporophyte
unbranched, has single sporangium (Foot, Seta, Capsule), spores are released when conditions are favorable
elaters
from mature sporangium, are elongated cells, contain moisture absorbing wall thickenings, when capsule dehisces, elaters dry and undergo twisting motion that helps disperse spores
sporopollenin
impregnates spore walls, decay/chemical resistant, survival during air transport
protonemata (protonema)
spores germinate to often form this juvenile stage of the gametophyte, formed in ALL mosses, and some liverworts
phylum marchantiophyta
liverworts
phylum anthocerophyta
hornworts
bryophyta
mosses
[Liverworts]
[Marchantiophyta], no hydroids, single celled rhizoid, sporophyte embedded in gametophyte, consists solely of spherical capsule, gametophytes unisexual, gametophores produce gametangia, some are capable of asexual reproduction, gemmae are multicellular and produce multicellular gametophyte, dispersed by splashes of rain
[Hornworts]
[Anthocerotophyta], no hydroids or leptom, unicellular rhizoid, nostoc cyanobacterium nitrogen fixing in gametophytes, sporophytes have cuticle, lack seta (meristem instead), elongates sporangium when favorable conditions, pseudoelaters ribbonlike dehiscence
Bryophyta: Sphagnidae
peat mosses, unusual protonema (budlike, divides in three), peculiar gametophyte (mop head, hyaline cells), lack rhizoids, water holding up to 20x their dry weight, explosive spore dispersal (operculum and pseudopodium), used in horitculture, antiseptic, peatlands 1-3% of earth, carbon cycle
Bryophyta: Andreaeidae
granite mosses, protonema stage, split create slits to disperse spores when dry,
Bryophyta: Bryidae
“true mosses”, protonema juvenile, multicellular rhizoids, hydroids are like tracheids (dead at maturity), not lignified, leptoids in some, unbranched sporophyte => embedded in gametophyte placenta, have stomata, peristome uncurl in dry air, curl in moist
what do bryophytes and vascular plants have in common?
multicellular matrotrophic embryo, heteromorphic alternation of generations, trace back to green algae
adaptations of vascular plants
lignin: grow large on land, conducting tissue, vertical support
apical meristem: allows for branching
dominant sporophyte
branched sporophyte: multiple sporangia
evolution of vascular plant body
gametophyte becomes REDUCED and dependant on the sporophyte
tracheary elements
conducting cells of xylem, contain lignin, resistant to degradation, provides stem support
tracheids
Silurian and Devonian, only type of water-conducting cells in most plants, trend in thickening from annular rings to pitted
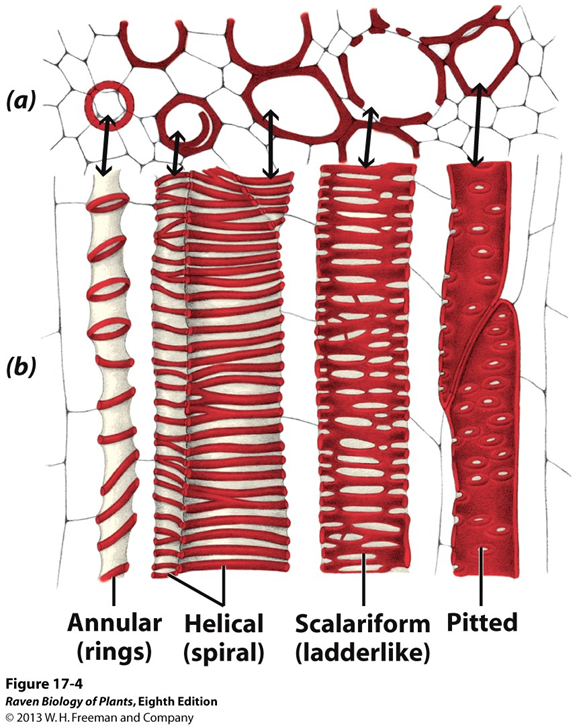
vessel elements
principle water-conducting cells in angiosperms, evolved independently (convergent evolution)
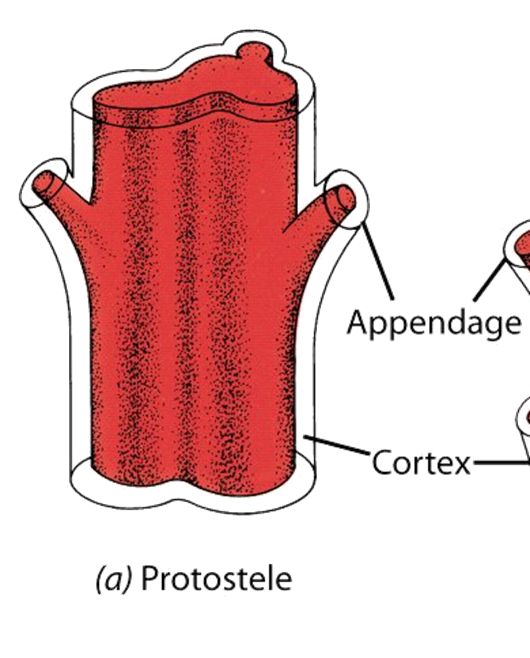
stele
central cylinder of tissue composed of primary vascular tissue and sometimes pith (vascular cylinder)
protostele
ANCIENT, found in most roots, solid cylinder of vascular tissue, no pith, extinct seedless vascular plants, in some living vascular plants
siphonostele
central pith surrounded by vascular tissue, most species of seedless vascular plants, convergent from protostele
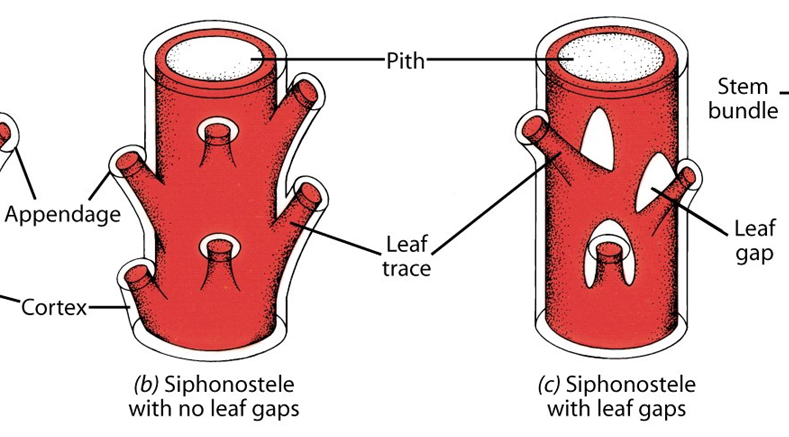
eustele
discrete strands around a pith, almost ALL seed plants, evolved directly from protostele (i.e., none of the seedless vascular plants with living representatives gave rise to the seed plants)
evolution of roots
believed to evolved from subterranean portions of axis of ancient vascular plants
evolution of leaves
arise as leaf primordia from apical meristem
microphylls
megaphylls
microphylls
one strand of vascular tissue or vein, characteristic of lycophytes, associated with protosteles
megaphylls
each blade has complex system of branching veins, associated with siphonosteles or eusteles
evolved through 3 transformations
overtopping: formation of determinate lateral branches
plantation: development of “flattened” branch systems
webbing: fusion of planated branches with lateral growths of photosynthetic mesophyll tissue to form blade
homosporous
free living gametophyte, relies on water to transfer sperm, produce one kind of spore from meiosis, bisexual spore, turns into bisexual gametophyte, gametophyte develops outside the spore wall, some lycophytes, fern allies, and almost all ferns
heterosporous
two spores types in two different types of sporangia
microspores (n) borne in microsporangia (2n)
megaspores (n) borne in megasporangia (2n)
result in unisexual gametophyte
reduced in size, develops within spore wall
reduced gametophyte retained in spore wall, dependent on sporophyte for nutrition
gametophyte reproductive evolution
trend towards smaller, simpler gametophytes
phylum rhyniophyta
extinct, terminal sporangia, homosporous, sporophyte dominant, alternation of isomorphic generations, simple dichotomously branching stems, Cooksonia oldest vascular plant
phylum zosterophyllophyta
extinct, leafless, dichotomously branched, stems with cuticle, only upper stems had stomata, homosporous, downward growing branches function like roots supporting lateral growth
phylum trimerophytophyta
extinct, larger more complex, leafless, homosporous, ancestral to both ferns and pro-gymonosperms, large vascular strand => taller
phylum lycopodiophyta
1200 living species, all herbaceous, differentiated into roots, stems, leaves, all possess microphylls
family lycopodiaceae
club mosses, sporophyte, stem and root are protostelic, sporangia found on sporophylls (fertile microphylls), grouped in to strobili, homosporous, bisexual spores => bisexual gametophytes, requires water for fertilization, sporophyte becomes independent
family selaginellaceae
spike mosses, microphylls, stem and root are protostelic, tropical, sporophyills arranged in strobili, heterosporous:
megasporangia are borne on megasporophylls
microsporanga are borne on microsporophylls
water required for fertilization, resurrection plant
phylum monilphyta
horsetails, oldest surviving genus, scouring rushes, jointed stems and rough texture, microphylls, homosporous, free-living gametophytes, bisexual,
fiddleheads, abaxial sporangia, siphonostelic rhizomes, megaphylls, circinate vernation => protects embryonic leaf tip during development, possess sori (sporangia clusters), free-living, bisexual gametophytes, prothallus - heart shaped and has rhizoids, water required for sperm,
eusporangiate
having a sporagnium developed from a group of cells rather than a single cell
oogamous
condition in which small sperm that travels (or is conveyed) to Egg
strobili
sporophylls clustered into cone-like structures
all seed plants are ________
heterosporous
megasporocyte/microsporocyte
specific cells that undergo meiosis to produce spores
housed in their respective sporangium
megaspore/microspore => mitosis => megagametophyte/microgametophyte
evolution of the seed
production of seed is extreme form of heterospory
megasporangia and megaspore are modified to form an ovule which develops into a seed
ovule
baby seed, consists of megasporangium which contains megasporocytes that produce megaspores, surrounded by integuments
develops into seed
seed
mature ovule that contains an embryo, food stores, and coat
gymnosperm
naked seed, ovules and seeds exposed on surface of sporophylls
contain megagametophyte
no water for fertilization required
male gametophyte (pollen) transfered to female gametophyte (pollenation)
microgametophyte
develop as pollen grains, transferred to vicinity of megagametophyte = pollination
produce a pollen tube that brings non-motile sperm directly to egg via micropyle (opening)
NO NEED FOR WATER TO FERTILIZE!
phylum coniferophyta
cones, drought-resistant
genus pinus
seedlings: needlelike leaves in spiral, single, then in bundles (fascicles), leaves adapt for low moisture, thick cuticle, hypodermis, sunken stomata, retain leaves for 2-4 years, xylem primarily tracheids
pinus life cycle
takes up to 2 years, separate cones for male (lower) female (higher), meiosis in early spring
pinus male reproductive
microsporangia on sporophylls
microsporocytes (microspore mother cells)
produce 4 haploid microspores => each undergoes mitosis to become pollen grain
two prothallial cells
one generative cell
one tube cell
this is the immature male gametophyte (microgametophyte)
4 celled pollen grain (mature)
pinus female reproductive
megasporangiate (ovulate), seed scale complex (modified branch system) includes:
ovuliferous scale with two ocules on upper surface
subtending sterile bract
multicellular nucellus (megasporangium) that contains one megasporocyte (megaspore mother cell)
massive integument with opening (micropyle)
after meiosis, only one megaspore is functional
pinus pollination
occurs in spring, scales on ovulate cones widely separated, pollination drops secreted by ovulate sticks to pollen and draws in pollen grain, scales close after pollination
tube cell elongates, produces 1 sterile cell + 1 spermatogenous cell
spermatogenous cell later divides to make 2 sperm cells
pinus fertilization
~15 months after pollination, pollen tube reaches egg cell in archegonium
one sperm will fertilize the egg
pinus seed
usually shed in fall of 2nd year
most winged (wind dispersal)
some pines need fire to open
some require birds
other important conifers
Cupressaceae: redwoods, sequoia sempervirens, juniper (cedars), bald cypress, pond cypress,
phylum cycadophyta
palmlike plants, tropical subtropical, zamia integrifolia,
coralloid roots: grow upwards and branch dichotomously near soil surface
highly toxic, unisexual reproductive units
phylum gingkophyta
gingko biloba, fan shaped leaves, unisexual, female seeds stinkay, doug russell park
phylum gnetophyta
gnetum, ephedra, welwitschia, resemble angiosperms, produce “nectar”, double fertilization, strobili look like flower clusters
ephedra
branched shrubs with small, scalelike leaves, arid regions, only genus of gentophytes found in US
welwitschia
one species, two leaves only but split into several parts when growing, mostly buried in sand, coastal desert of southwestern Africa
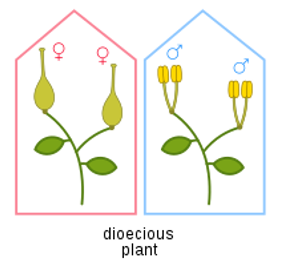
dioecious
angiosperms
flowering plants, double fertilization! one phylum anthophyta
monocot (monocotyledons)
one cotyledon
fibrous roots
scattered vascular system
parallel veins in leaf
flowers are in multiples of 3
grasses, lilies, irises, orchids, palms
dicot (eudicotyledons)
two cotyledeon
tap roots (thick main)
ringed vascular system
net-like veins in leaf
flowers are in multiples of 4 or 5
most trees, shrubs, many herbs
myco-heterotrophs
lack chlorophyll, obligate relationship with fungi, “mycorrhizal cheater” (steals from fungi)
the flower
determinate shoot that bears sporophylls
inflorescences
flower bearing branches of plant
peduncle
fat meaty main stalk
pedicel
small part, stalk of individual flower on clustered inflorescences
spike inflores
simple umbel inflores
compound umbel inflores
head inflores
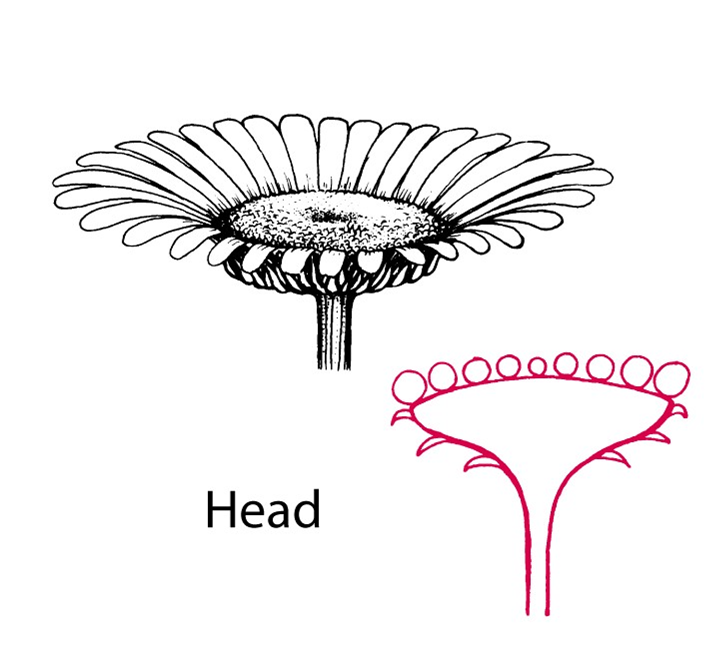
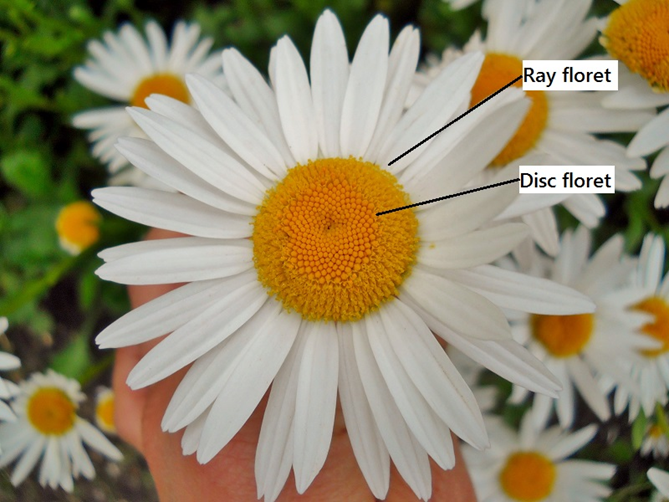
disc vs. ray flowers
disc: small
ray: big

the four whorls
sepal
petal
stamen (male)
carpel (female)
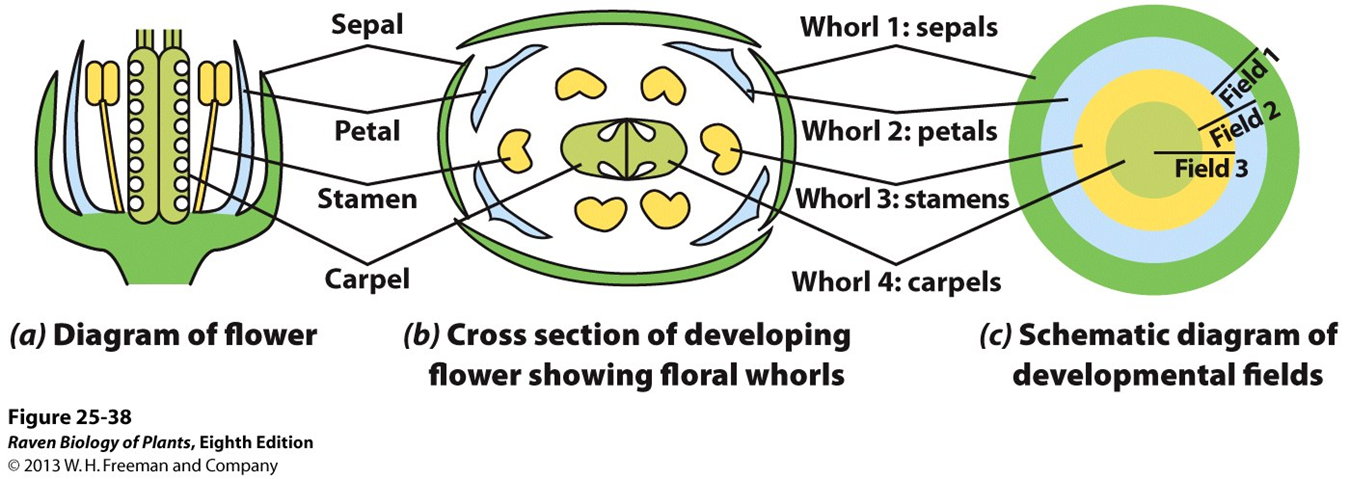
2 sterile whorls (perianth)
1. calyx - made of sepals
2. corolla - made up of petals
toyota corolla has “pedals”
2 fertile whorls
androecium: made of stamen
microsporophylls
filament
anther containing pollen sacs two pairs
gynoecium: made of carpels
megasporophylls
ovary: houses ovule
style: connects stigma to ovary
stigma: pollen receptacle
complete vs incomplete
all four whorls (sepals, petals, stamen, carpel) present
if any missing it is Incomplete
based on number of whorls ONLY!
perfect vs imperfect
perfect contains both female and male parts
imperfect: unisexual, one sex only
staminate flower: male
carpellate flower: female
based on sex ONLY!
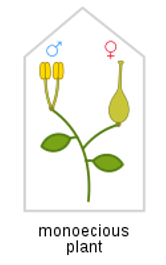
monoecious
plant has both male and female flowers (doesn’t have to have both parts on one flower)
dioecious
plant has either male OR female, but not both
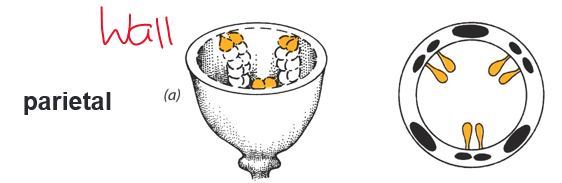
parietal
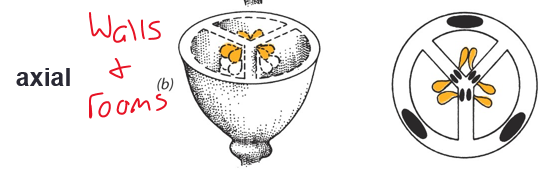
axial
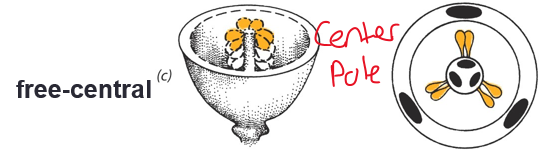
free-central
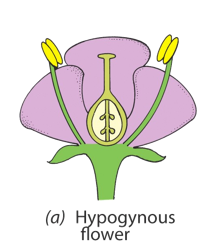
hypogynous
insertion point below ovary