BB ch 15
1/199
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
200 Terms
Glycogen
A highly branched glucose polymer that functions as the main storage form of carbohydrate in animal cells.
Glycogen Granule
Cytosolic particle that houses glycogen β-particles together with the associated enzymes for its synthesis and degradation.
Glycogen β Particle
Basic spherical unit of glycogen (~21 nm, up to 55 000 glucose units with 2 000 non-reducing ends).
Glycogenin
Core protein that autoglucosylates a Tyr residue to initiate and anchor the growing glycogen molecule.
Nonreducing End
The terminus of a glycogen chain where glycosyl residues are removed or added; lacks a free anomeric carbon.
Glucose Residue
Individual glucose unit covalently linked within glycogen or other polysaccharides.
Glycogen Phosphorylase
Key enzyme that catalyzes phosphorolytic cleavage of α(1→4) bonds at glycogen non-reducing ends to release glucose-1-phosphate.
Phosphorolysis
Bond cleavage by inorganic phosphate attack rather than water, conserving energy as a sugar phosphate.
Sugar Phosphate
Glucose or other sugar molecule esterified to inorganic phosphate, often an immediate metabolic substrate.
Pyridoxal Phosphate
Vitamin-B6-derived cofactor required by glycogen phosphorylase for catalytic activity.
Debranching Enzyme
Bifunctional protein with transferase and α(1→6) glucosidase activities that removes branch points during glycogen breakdown.
Oligo(α1→6 to α1→4) Glucan Transferase
Activity of the debranching enzyme that moves a short trisaccharide from a branch to a nearby chain.
α(1→6) Glucosidase
Debranching enzyme activity that hydrolyzes the single glucose remaining at a branch point.
Glucose-1-Phosphate
Product of glycogen phosphorolysis; can enter glycolysis or be converted to glucose-6-phosphate.
Phosphoglucomutase
Enzyme that reversibly converts glucose-1-phosphate to glucose-6-phosphate via a glucose-1,6-bisphosphate intermediate.
Glucose-6-Phosphate
Central glycolytic intermediate produced from glucose-1-phosphate or hexokinase action on glucose.
Glucose-6-Phosphatase
ER-membrane enzyme in liver and kidney that hydrolyzes glucose-6-phosphate to free glucose for export to blood.
G6P Transporter (T1)
Translocase that moves glucose-6-phosphate from the cytosol into the ER lumen for dephosphorylation.
Pi Transporter (T3)
ER membrane protein that exports inorganic phosphate generated by glucose-6-phosphatase back to the cytosol.
GLUT2
High-capacity, low-affinity glucose transporter on hepatocyte plasma membranes and pancreatic β-cells.
UDP-Glucose
Uridine diphosphate-activated form of glucose that donates glucosyl units for glycogen synthesis.
Sugar Nucleotide
Nucleotide-linked sugar that serves as an ‘activated’ donor in biosynthetic reactions (e.g., UDP-glucose).
UDP-Glucose Pyrophosphorylase
Enzyme that forms UDP-glucose from glucose-1-phosphate and UTP, driven by pyrophosphate hydrolysis.
Glycogen Synthase
Key anabolic enzyme that elongates glycogen chains by adding glucose from UDP-glucose to α(1→4) positions.
Oxonium Ion Intermediate
Carbocation-like transition state formed during glycosyl transfer by glycogen synthase.
Amylo(1→4→1→6) Transglycosylase
Branching enzyme that creates α(1→6) links by transferring terminal segments to form new branch points.
Branching Enzyme
General term for amylo(1→4→1→6) transglycosylase that introduces branches into a growing glycogen molecule.
Advanced Glycation End Products (AGEs)
Irreversible protein modifications arising from non-enzymatic reactions of sugars with amino groups, implicated in diabetic complications.
Schiff Base
Reversible imine linkage formed between an aldehyde (e.g., glucose C-1) and an amino group on proteins.
Amadori Rearrangement
Transformation of a Schiff base to a more stable ketoamine intermediate in non-enzymatic glycation.
Glycated Hemoglobin
Hemoglobin A1c; hemoglobin irreversibly modified by glucose, used to monitor long-term blood glucose control.
Glycogen Storage Disease
Inherited metabolic disorder caused by defects in enzymes of glycogen synthesis or degradation.
Von Gierke’s Disease (Type I)
Deficiency of glucose-6-phosphatase (or its translocase) leading to hepatomegaly and severe hypoglycemia.
Pompe’s Disease (Type II)
Lysosomal α-glucosidase deficiency causing glycogen accumulation in muscle and heart; often fatal in infancy.
Cori’s Disease (Type IIIa)
Debranching enzyme deficiency producing abnormal glycogen and hepatomegaly.
Andersen’s Disease (Type IV)
Branching enzyme deficiency resulting in abnormal unbranched glycogen and liver cirrhosis.
McArdle’s Disease (Type V)
Muscle glycogen phosphorylase deficiency leading to exercise-induced cramps and myoglobinuria.
Hers Disease (Type VI)
Liver glycogen phosphorylase deficiency causing hepatomegaly and mild hypoglycemia.
Tarui’s Disease (Type VII)
Muscle phosphofructokinase-1 deficiency producing exercise intolerance and hemolytic anemia.
Phosphorylase Kinase
Enzyme that phosphorylates and activates glycogen phosphorylase in response to cAMP-dependent signaling.
Protein Phosphatase 1 (PP1)
Ser/Thr phosphatase that dephosphorylates and inactivates glycogen phosphorylase while activating glycogen synthase.
Glycogen Phosphorylase a
Phosphorylated, catalytically active form of glycogen phosphorylase.
Glycogen Phosphorylase b
Dephosphorylated, less active form of glycogen phosphorylase.
Glycogen Synthase I (GS a)
Active, dephosphorylated form of glycogen synthase.
Glycogen Synthase D (GS b)
Phosphorylated, less active form of glycogen synthase; can be allosterically activated by glucose-6-phosphate.
AMP
Allosteric activator of glycogen phosphorylase, signaling low energy status.
Glucagon
29-residue peptide hormone from pancreatic α-cells that raises blood glucose by stimulating glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis.
stim glycogen breakdown and inhibit glycogen synthesis
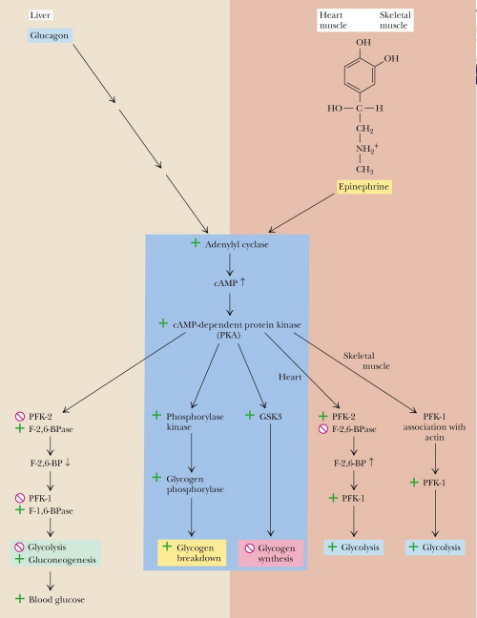
Epinephrine
Adrenal medulla hormone that triggers rapid mobilization of glycogen and activates the fight-or-flight response.
stim glycogen breakdown and inhibit glycogen synthesis
Calcium Ions (Ca²⁺)
Second messenger that activates phosphorylase kinase in muscle during contraction.
ATP
Allosteric inhibitor of glycogen phosphorylase, indicating high cellular energy levels.
Caffeine
Methylxanthine that antagonizes glycogen phosphorylase activation and cAMP breakdown.
Insulin
Pancreatic β-cell hormone released in response to high blood glucose, promoting glycogen synthesis and glucose uptake.
Protein Kinase B (PKB/Akt)
Ser/Thr kinase activated by insulin signaling; phosphorylates and inhibits GSK3, activating glycogen synthase.
GSK3 (Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3)
Kinase that phosphorylates and inactivates glycogen synthase; inhibited by insulin-activated PKB.
IRS-1
Insulin receptor substrate protein that propagates insulin signaling via PI-3K activation.
PI-3 Kinase
Enzyme that converts PIP₂ to PIP₃, initiating a kinase cascade downstream of insulin.
PIP₃
Phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate lipid second messenger generated by PI-3K.
PDK-1
Protein kinase that activates PKB upon binding to PIP₃ at the membrane.
GLUT4
Insulin-regulated glucose transporter stored in vesicles that translocate to muscle and fat cell membranes.
Portal Vein
Vessel that carries nutrients and pancreatic hormones directly from the gut to the liver.
Hepatocyte
Liver parenchymal cell responsible for glycogen storage, gluconeogenesis, and detoxification.
Adipose Tissue
Fat storage tissue where glucagon acts sparingly; lacks glucose-6-phosphatase.
Skeletal Muscle
Contractile tissue with high glycogen stores; lacks glucose-6-phosphatase and responds to epinephrine, not glucagon.
Fight-or-Flight Response
Physiological reaction to stress mediated by epinephrine, increasing glucose and ATP availability.
Gluconeogenesis
Pathway that synthesizes glucose from non-carbohydrate precursors, activated in liver by glucagon.
Glycolysis
Cytosolic pathway that converts glucose to pyruvate with ATP production.
Lipid Synthesis
Anabolic process stimulated by insulin involving fatty acid and triacylglycerol formation.
Protein Synthesis
Formation of polypeptides, promoted by insulin’s overall anabolic signaling.
Active Transport
Energy-dependent movement of molecules across membranes, enhanced by insulin signaling.
Glycogenolysis
Overall process of glycogen breakdown to glucose-1-phosphate and glucose.
Blood Glucose Homeostasis
Maintenance of blood glucose between 70-110 mg/dL through hormonal regulation.
Second Messenger Cascade
Intracellular signaling sequence that amplifies hormone binding into multiple phosphorylation events.
Phosphorylase Cascade
Amplification pathway where hormonal signals activate PKA, phosphorylase kinase, then glycogen phosphorylase.
Phosphorylation
Covalent addition of phosphate to proteins, modulating their activity.
Dephosphorylation
Removal of phosphate groups from proteins by phosphatases like PP1.
Allosteric Activation
Regulation where a metabolite binds at a site other than the active site to increase enzyme activity.
Covalent Modification
Reversible chemical change (e.g., phosphorylation) that alters protein function.
Reciprocal Control
Coordinated regulation where glycogen synthase and phosphorylase are activated in opposite phosphorylation states.
Hexokinase II
Muscle isozyme induced by insulin to phosphorylate glucose for glycolysis or glycogen synthesis.
PFK-1
Rate-limiting glycolytic enzyme activated by insulin and inhibited by glucagon signaling.
Pyruvate Kinase
Glycolytic enzyme whose liver isoform is inhibited by glucagon to conserve glucose.
FBPase-2
Domain of the bifunctional PFK-2/FBPase-2 enzyme; activated by PKA to lower fructose-2,6-bisphosphate levels.
PFK-2
Kinase domain that synthesizes fructose-2,6-bisphosphate; inhibited by PKA during glucagon signaling.
Fructose-2,6-Bisphosphate (F26BP)
Potent allosteric activator of PFK-1 and inhibitor of FBPase-1, regulating glycolysis/gluconeogenesis.
cAMP
Cyclic nucleotide second messenger produced by adenylate cyclase in response to glucagon and epinephrine.
Protein Kinase A (PKA)
cAMP-dependent kinase that phosphorylates multiple targets, promoting glycogen breakdown and inhibiting synthesis.
Trans Double Bond
Configuration of a carbon–carbon double bond with substituents on opposite sides, common in partially hydrogenated fats.
Partially Hydrogenated Oils
Food fats produced industrially that contain trans fatty acids linked to cardiovascular risk.
Tyrosine Residue
Amino acid side chain on glycogenin (Tyr-194) accepting the first glucose in glycogen priming.
Glucosyltransferase Activity
Ability of glycogenin to attach glucose from UDP-glucose to itself.
Chain-Extending Activity
Glycogenin-mediated addition of up to 7–8 glucose residues before glycogen synthase takes over.
Glycogen Primer
Short glucan chain covalently linked to glycogenin that serves as the foundation for glycogen assembly.
Glucose-1,6-Bisphosphate
Reaction intermediate in phosphoglucomutase-mediated conversion between G-1-P and G-6-P.
ER Lumen
Intracellular compartment where glucose-6-phosphatase dephosphorylates G-6-P in liver cells.
High-Molecular-Weight Granule
Large aggregated structure of many glycogen β-particles forming visible rosettes in cells.
α(1→4) Glycosidic Bond
Linkage between C1 of one glucose and C4 of another in glycogen’s main chains.
α(1→6) Linkage
Branch point bond in glycogen connecting C1 of one glucose to C6 of another.
Nonenzymatic Glycation
Spontaneous reaction of sugars with protein amino groups forming Schiff bases and AGEs.
Lysine Side Chain
Protein amino group frequently involved in Schiff base formation with glucose.
Oxidative Stress
Cellular condition where ROS accumulation can accelerate AGE formation and tissue damage.