Neurons and Neuroglia Histology
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
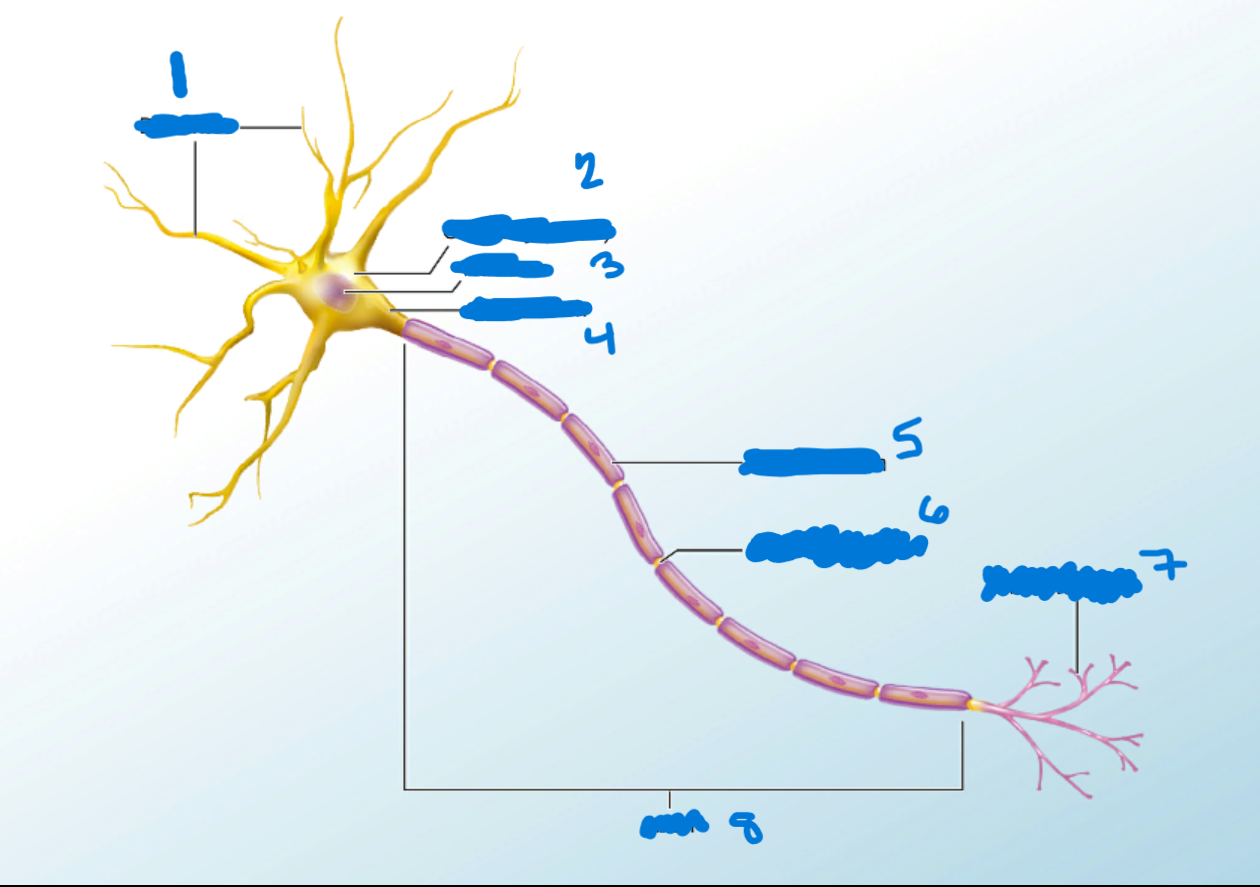
Dendrites
What is #1?
Branchlike processes that extends from the neuron cell body and functions as a contact for incoming signals (synapses) from other neurons or sensory cells.
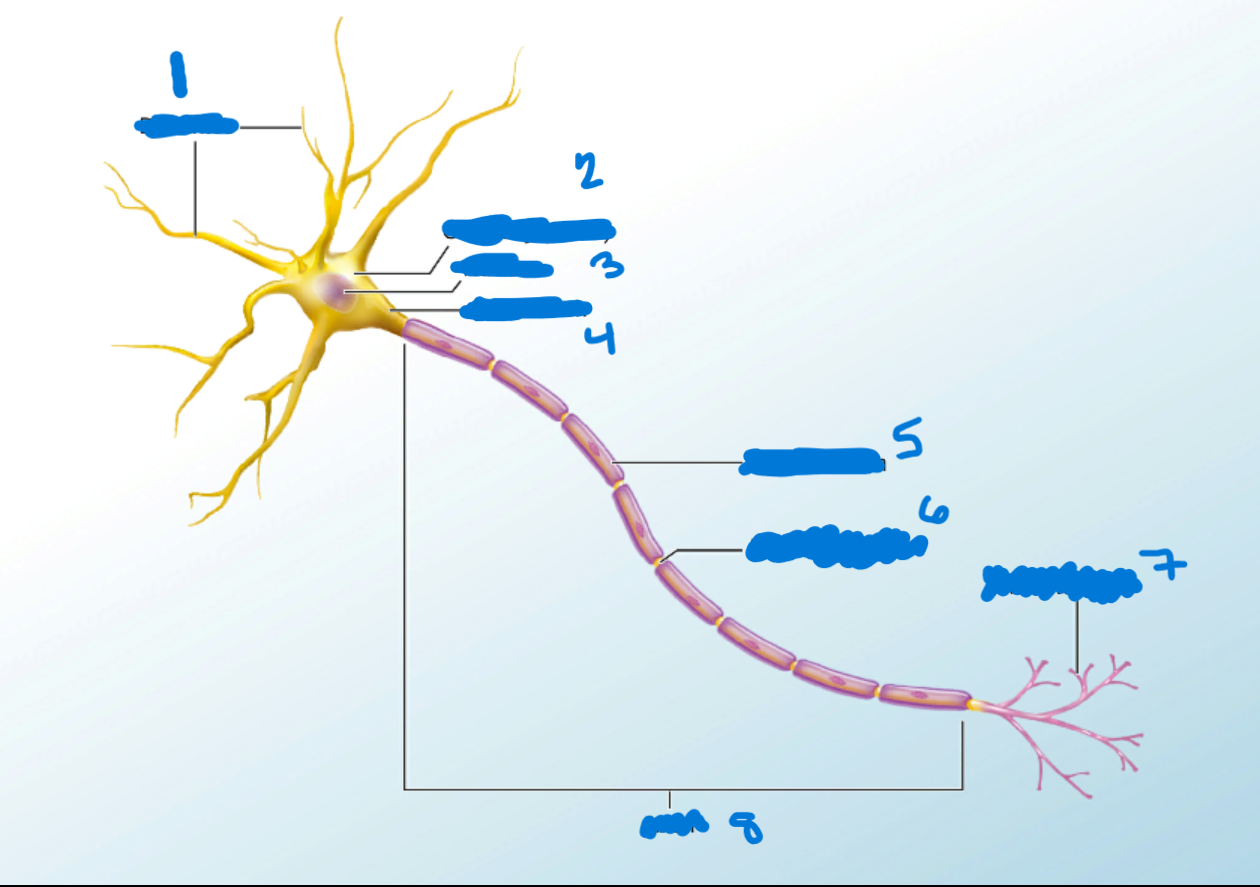
Soma
What’s #2?
Portion of the cell that contains the nucleus; the cell body as opposed to the cell processes (axon and dendrites)
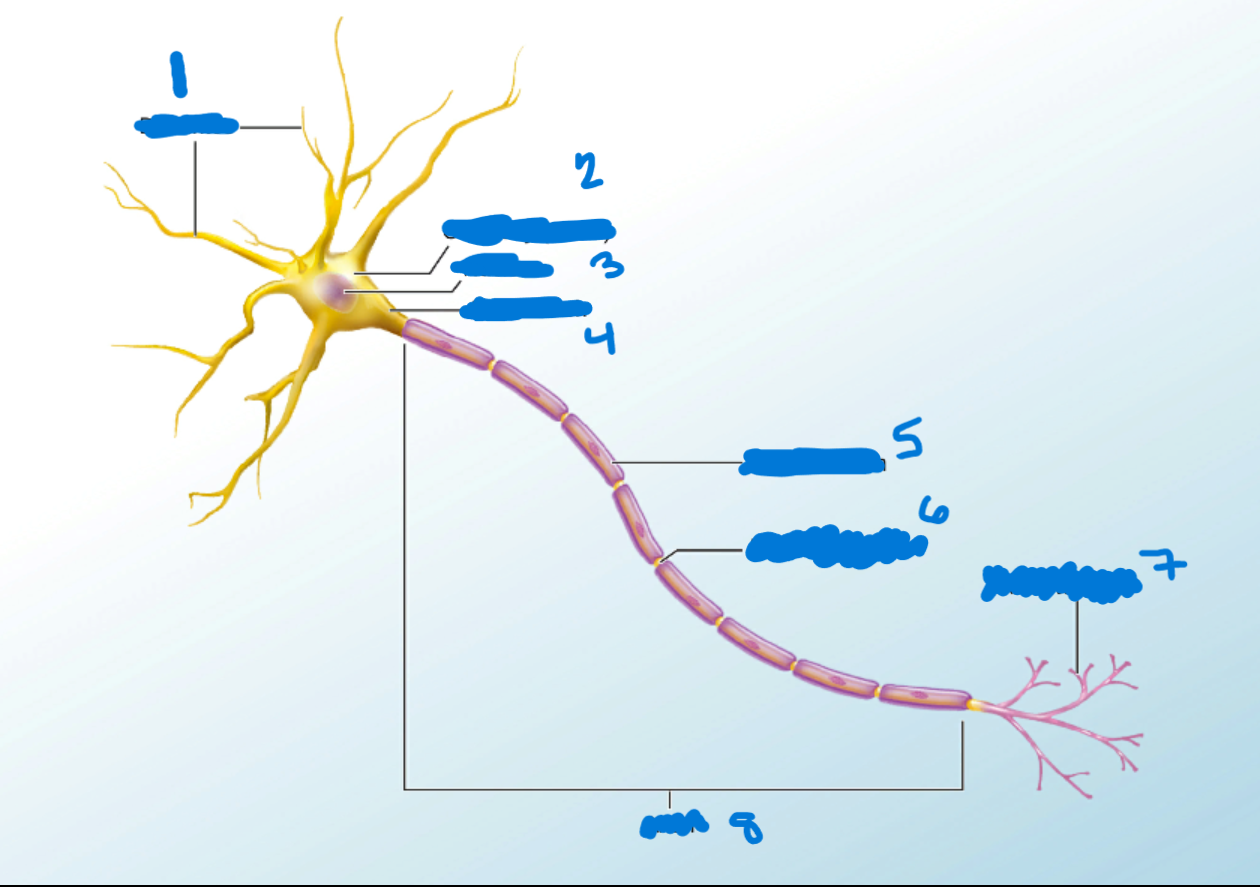
Nucleus
What’s #3?
A localized collection of neuron cell bodies that are functionally related; a “center” of neural function.
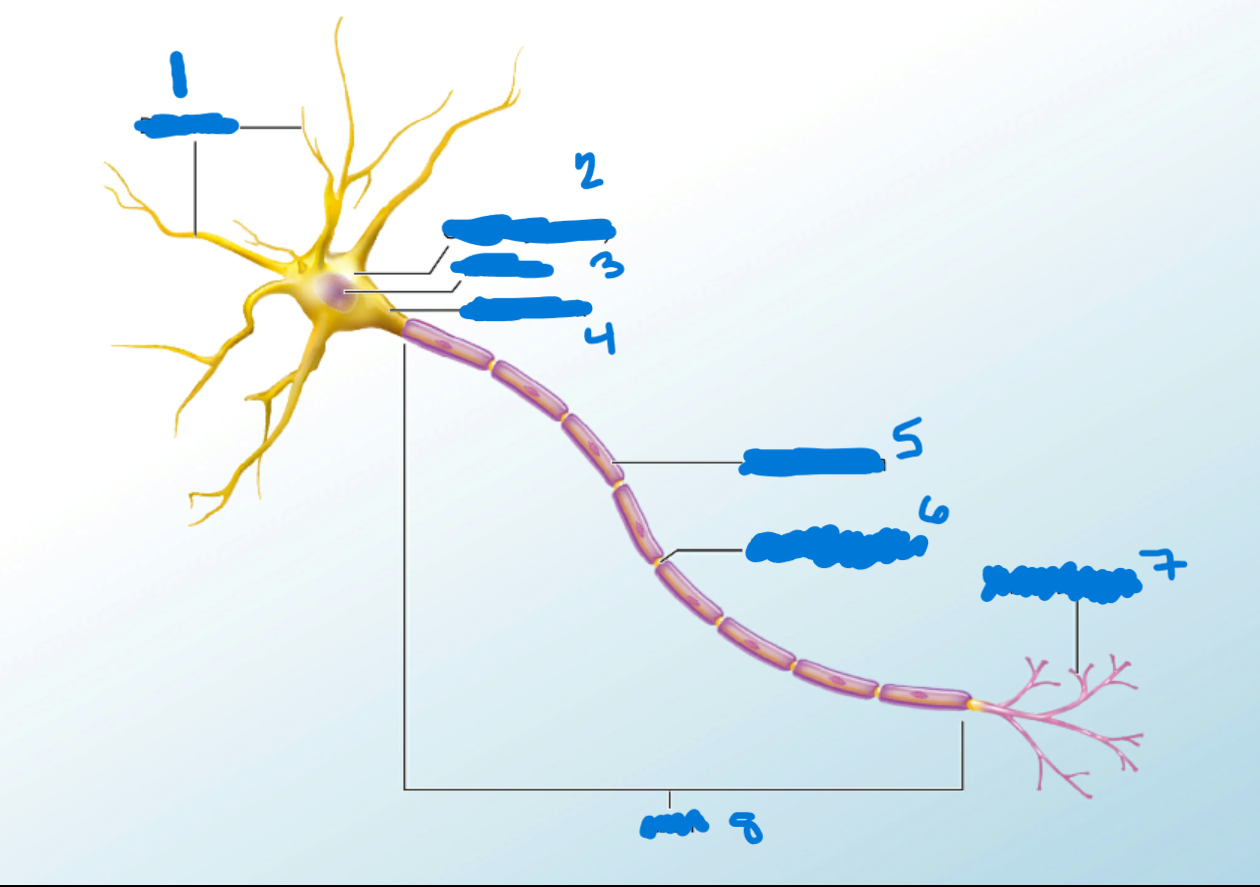
Myelination
When a neuron has a myelin sheath.
Axon Hillocks
What’s #4?
Tapering of the neuron cell body that gives rise to the axon.
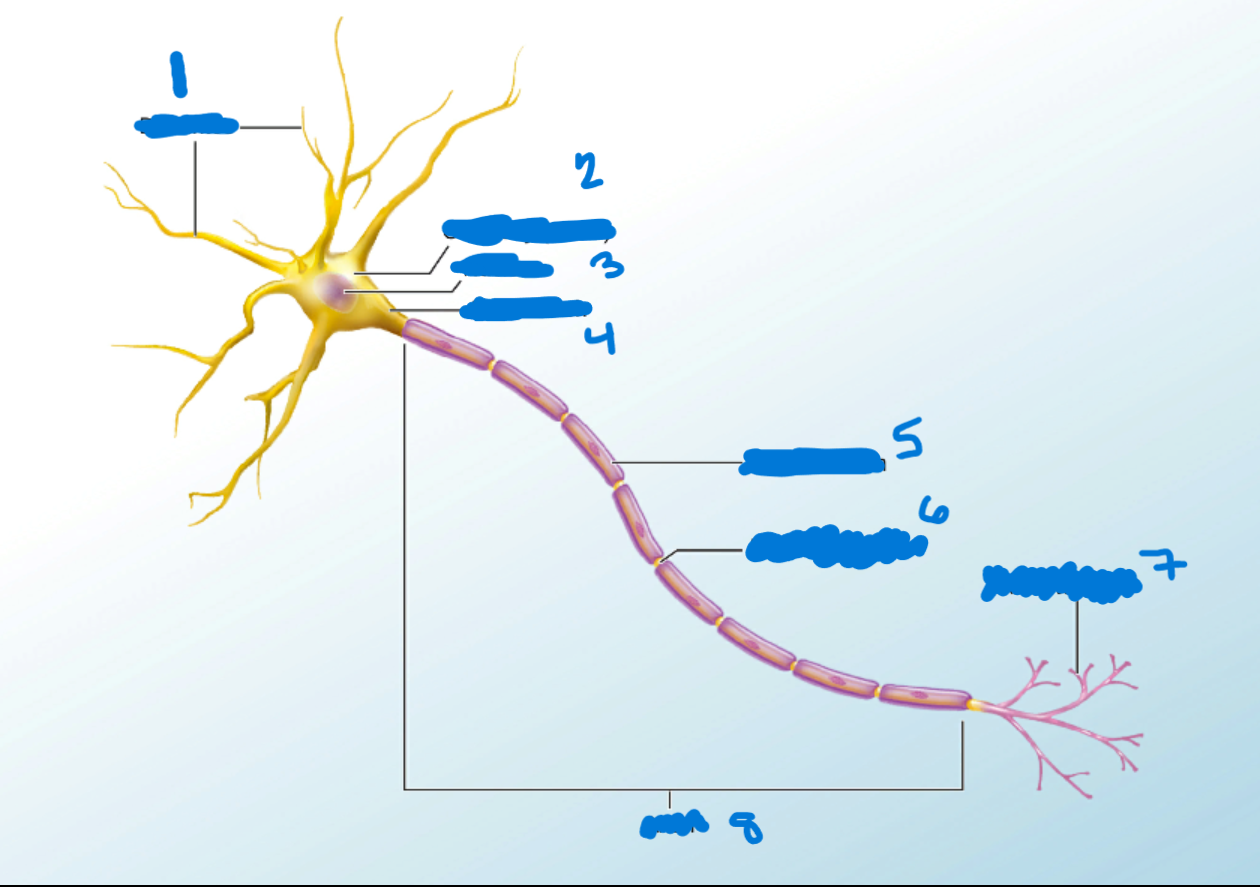
Myelin Sheath
What’s #5?
Lipid-rich layer of insulation that surrounds an axon, formed by oligodendrocytes in the CNS and Schwann Cells in the PNS; facilitates the transmission of electrical signals.
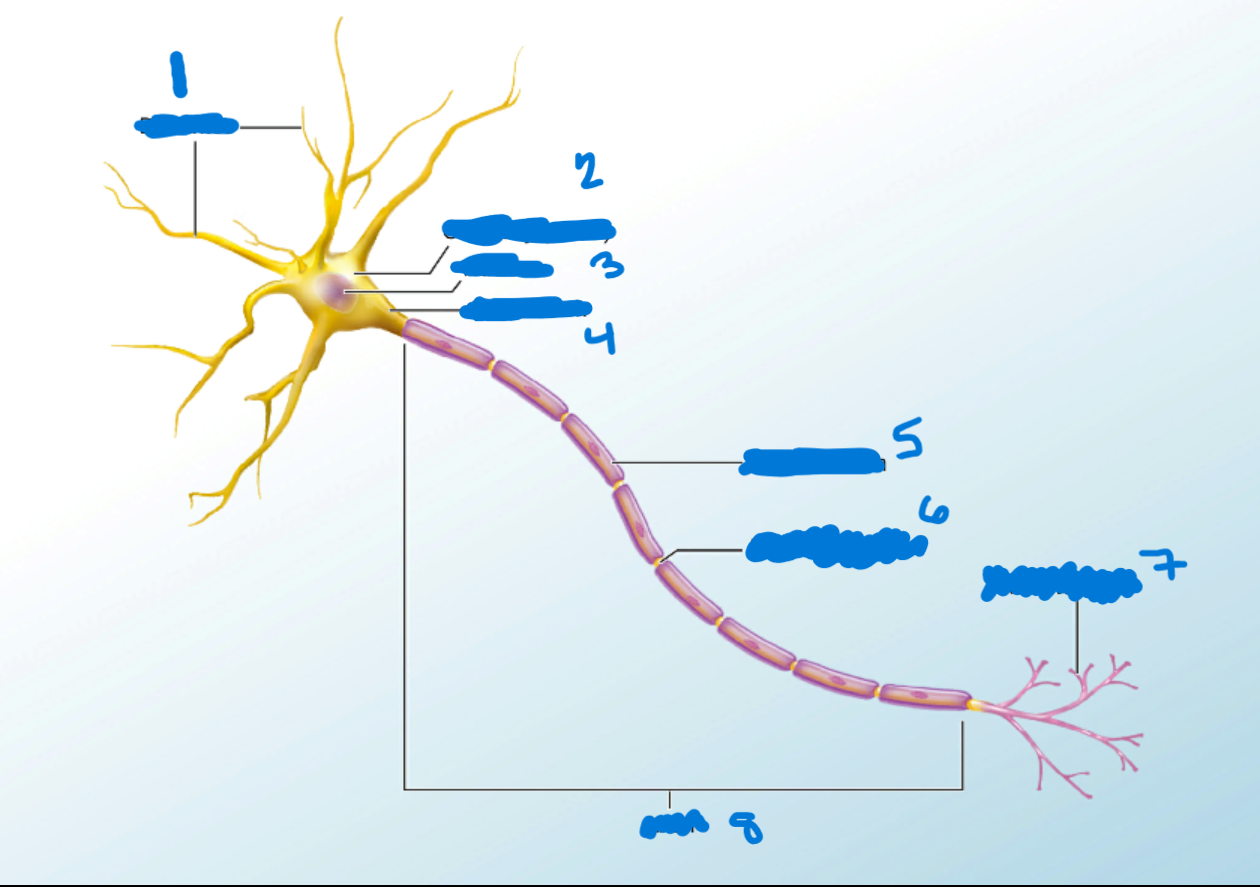
Node of Ranvier
What’s #6?
Gap between two myelinated regions of an axon, allowing for strengthening of the electrical signal as it propagates down the axon.
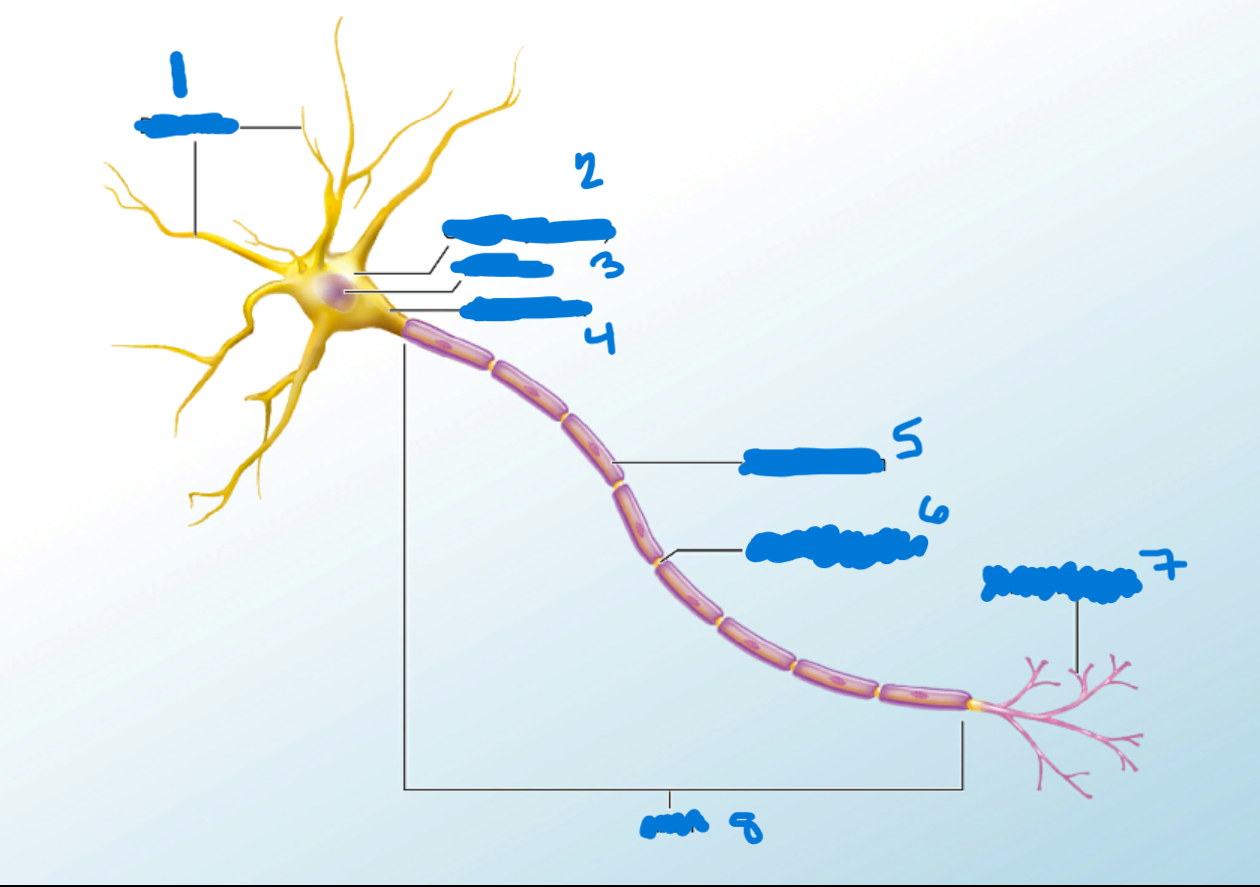
Axon Terminal
What’s #7?
End of the axon, where there are usually several branches extending toward the target cell.
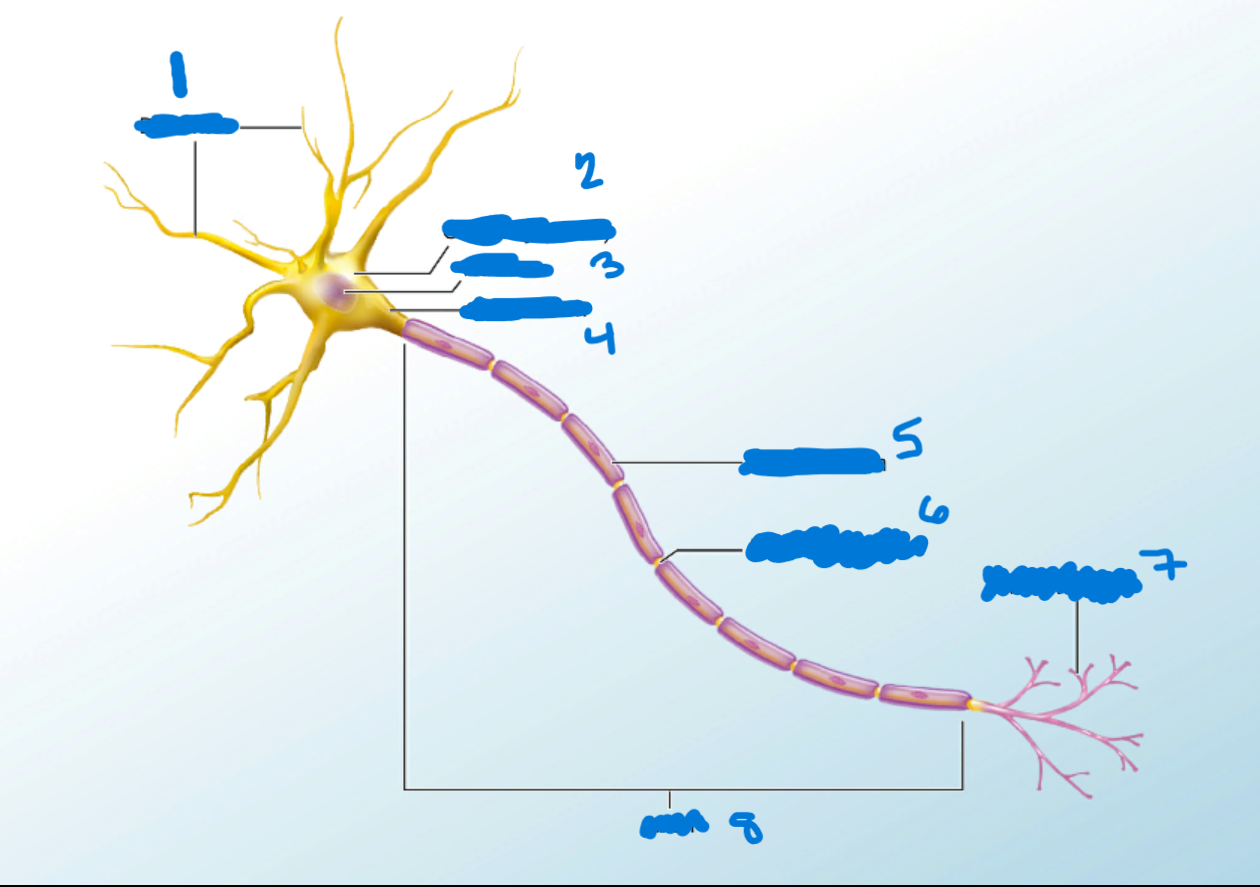
Axon
What’s #8?
Single process of the neuron that carries an electrical signal (action potential) away from the cell body toward a target cell.
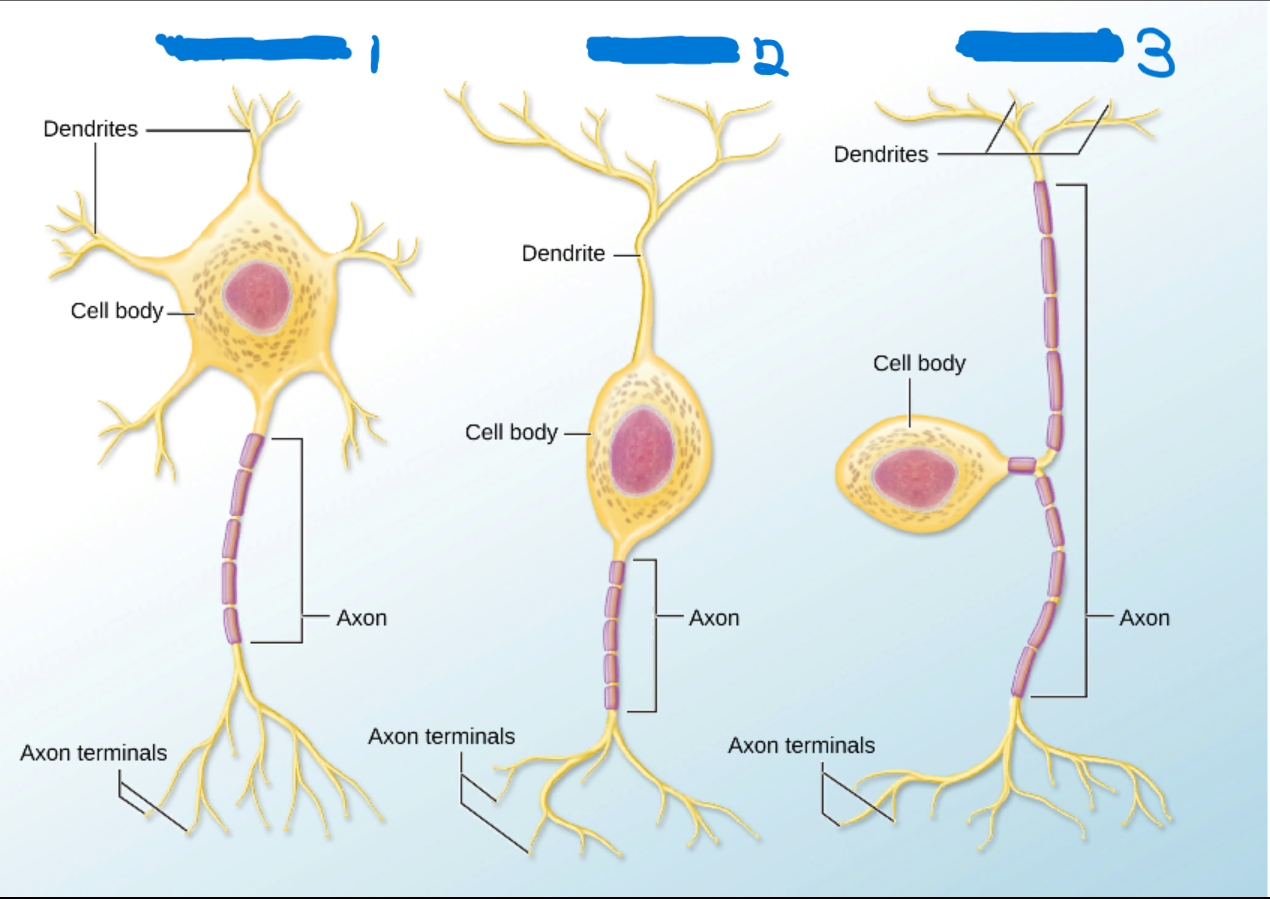
Multipolar
What’s #1?
1 Axon
Many dendrites
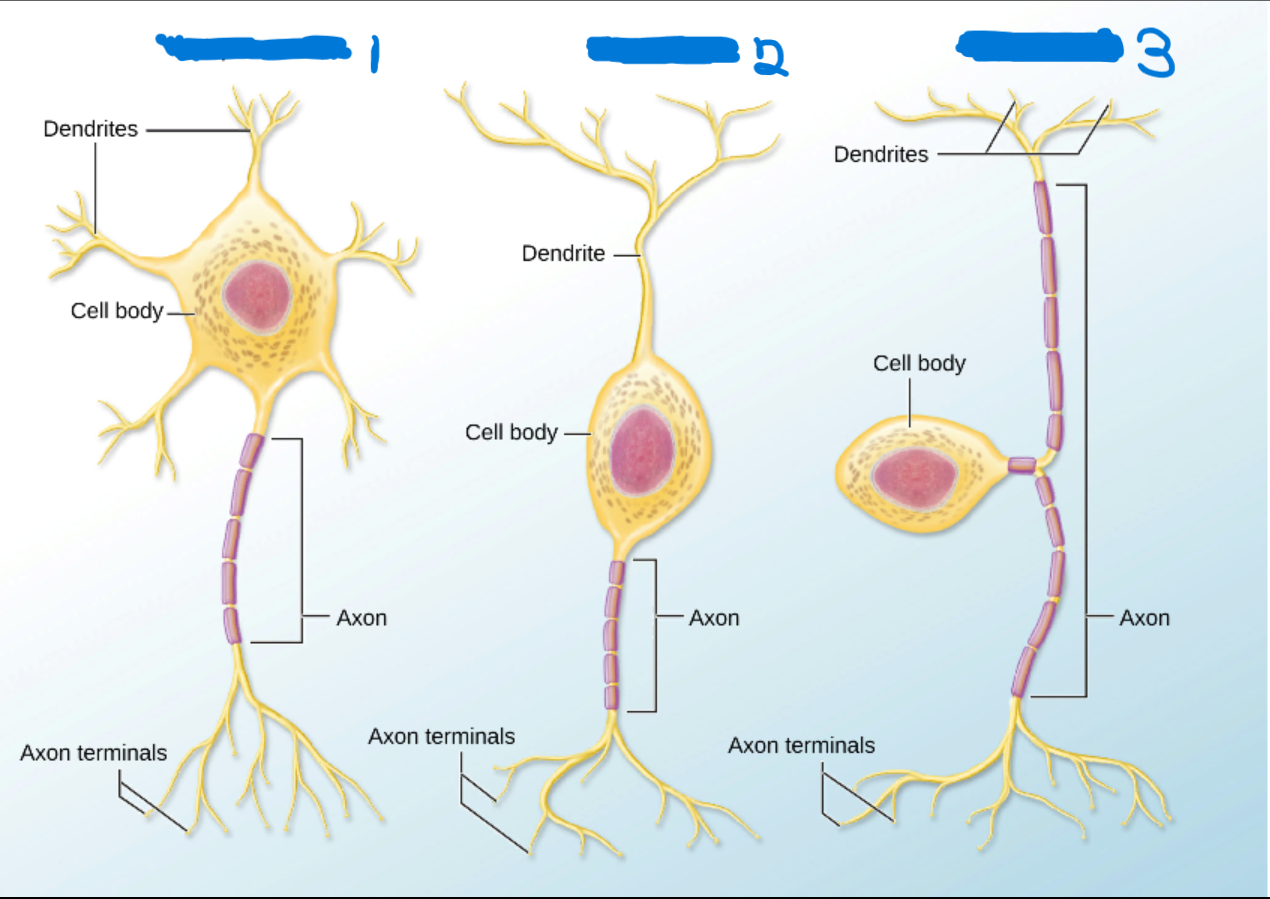
Bipolar
What’s #2?
1 Axon
1 Dendrites
Sensory Organs
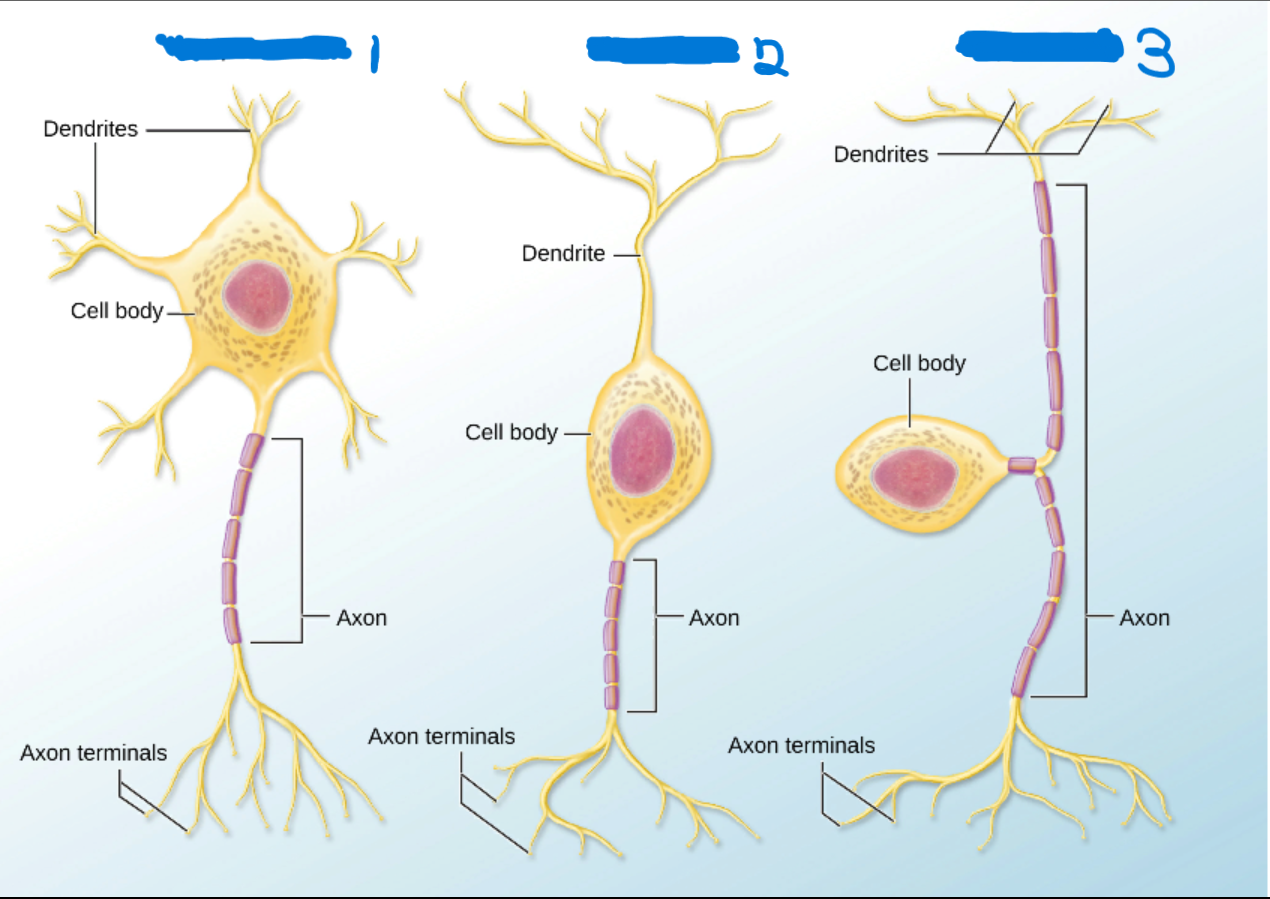
Unipolar
What’s #3?
Axon splits into two branches that attach to the cell body.
Sensory Neuron
Neuron
Excitable neural cell that transfer nerve impulses.
Astrocytes
What’s #2?
Connect neurons to blood supply capillaries and help provide support.
CNS
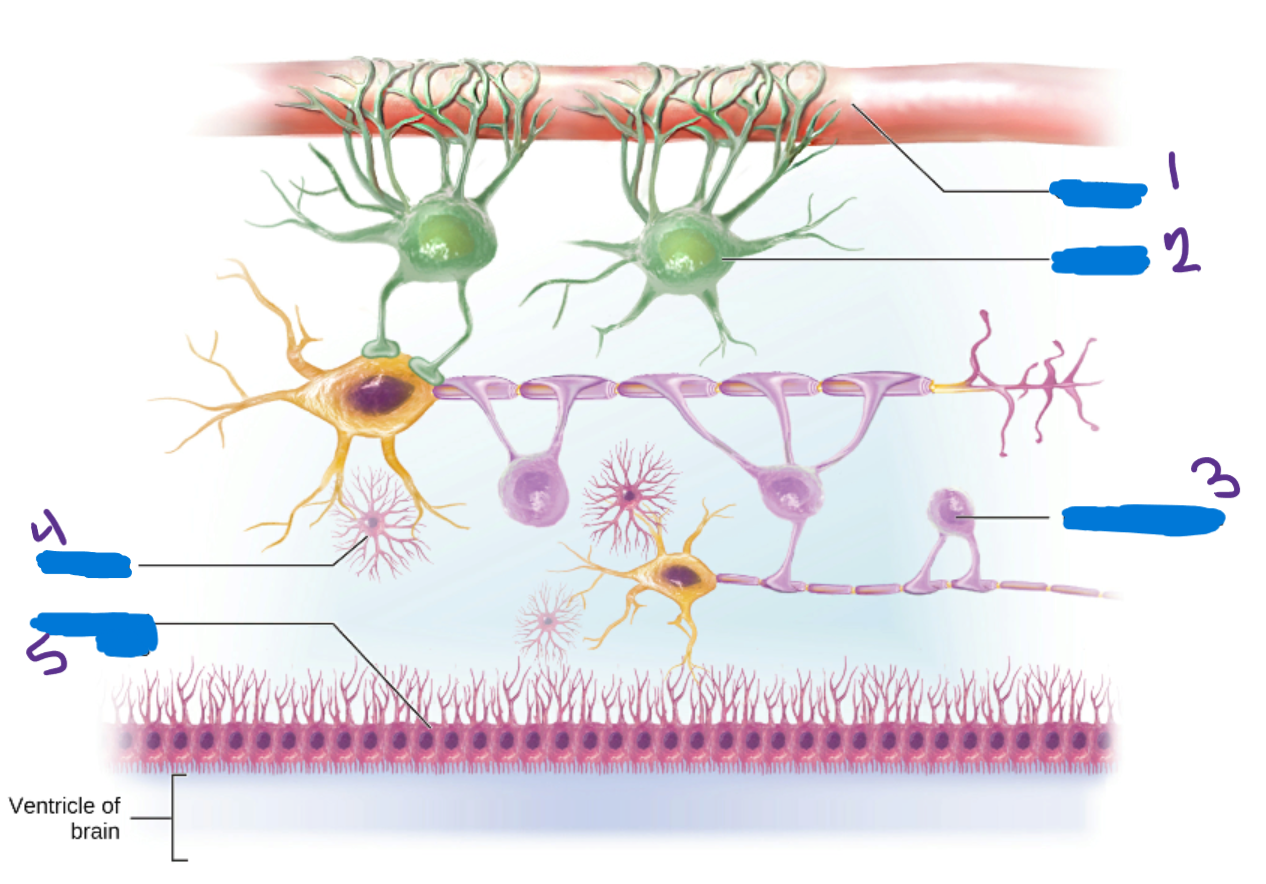
Oligodendrocytes
What’s #3?
in the CNS create myeline sheaths that protect neurons and increase the conduction speed of the neural impulse
CNS
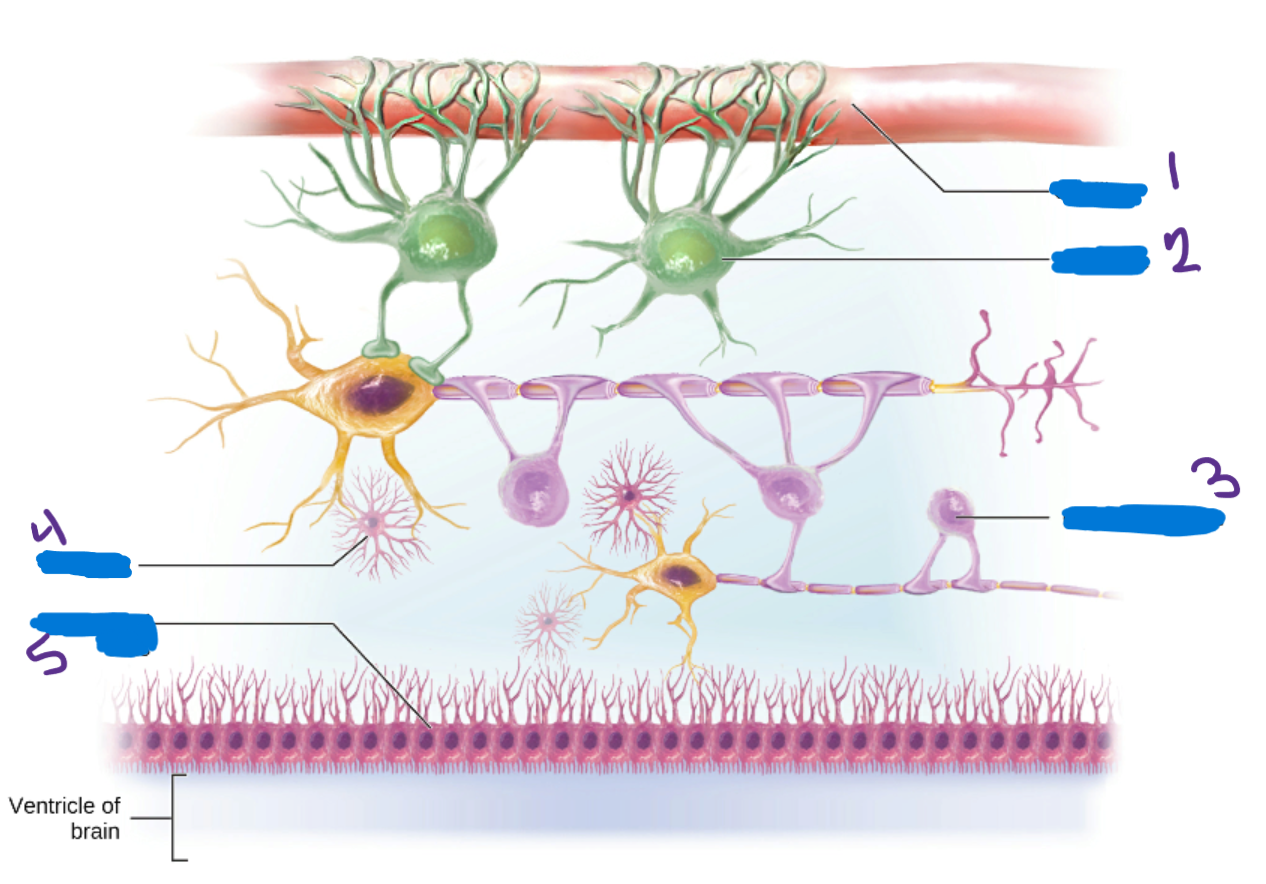
Microglia
What’s #4?
Provide immune system support by removing pathogens that pass through the blood-brain barrier
CNS
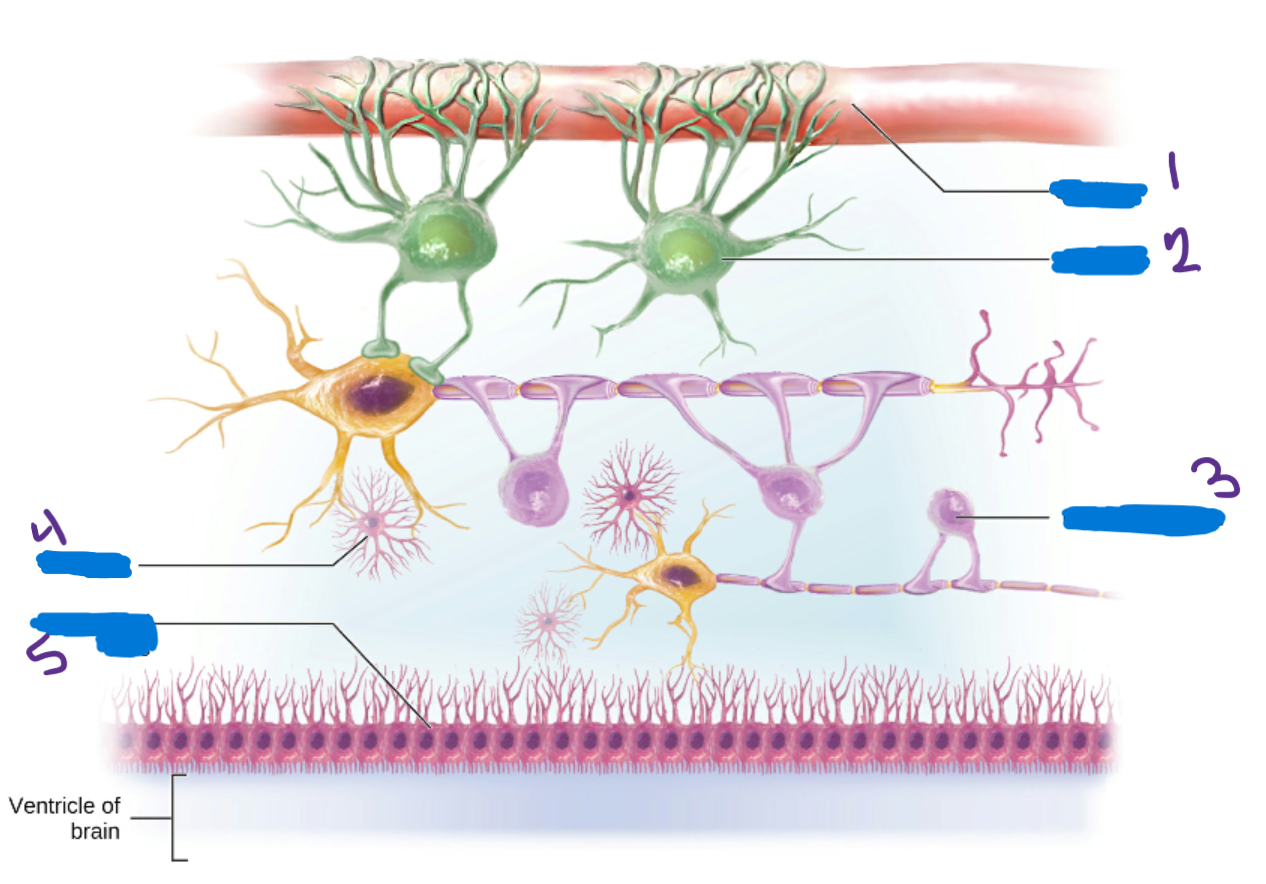
Ependymal Cells
What’s #5?
Cells help produce and circulate cerebrospinal fluid
CNS
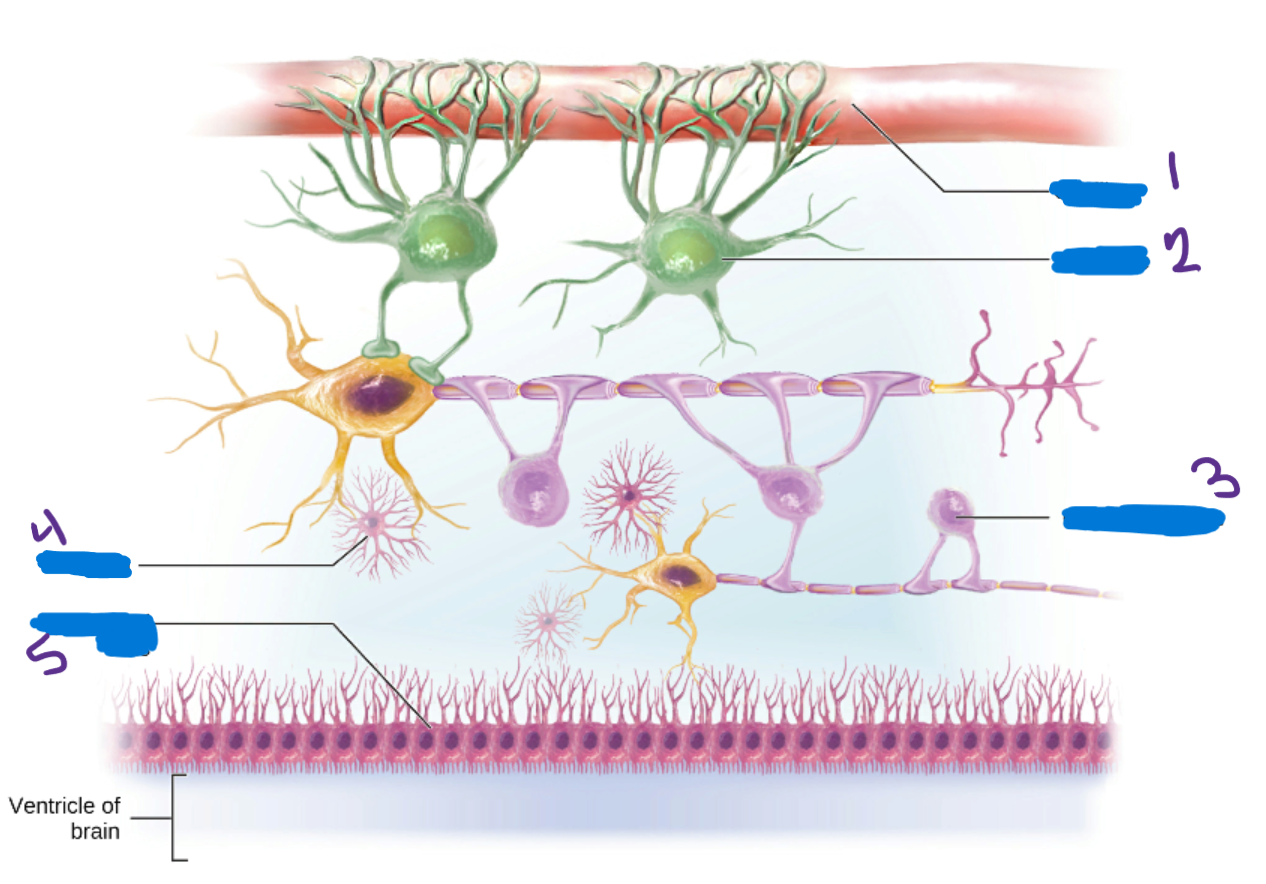
Schwann Cells
Produce the myelin sheaths in the PNS
Satellite Cells
Glial cell types in the PNS provide support for neurons in the ganglia.
Neuroglia
Nervous Tissue
Support Neurons
Ependymal Cells
Oligodendrocytes
Astrocytes
Microglia
Surround and protect neurons in the CNS.
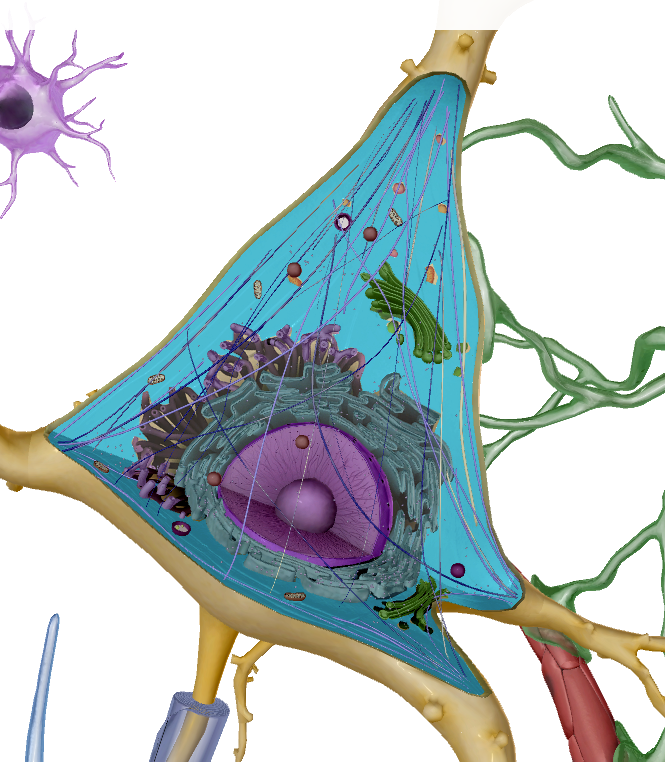
Nucleolus
What is this?
Contains genetic information of the cell
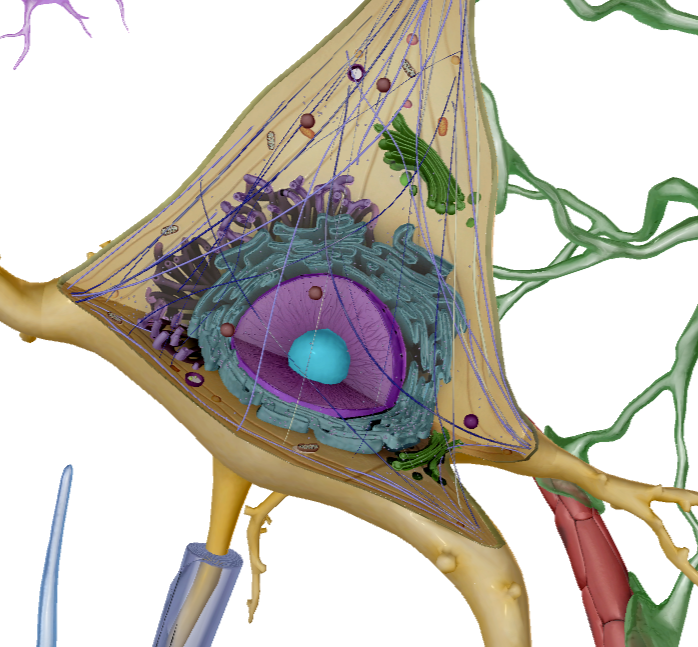
Mitochondria
What is this?
Creates energy known as ATP
Nissi Bodies
What is this?
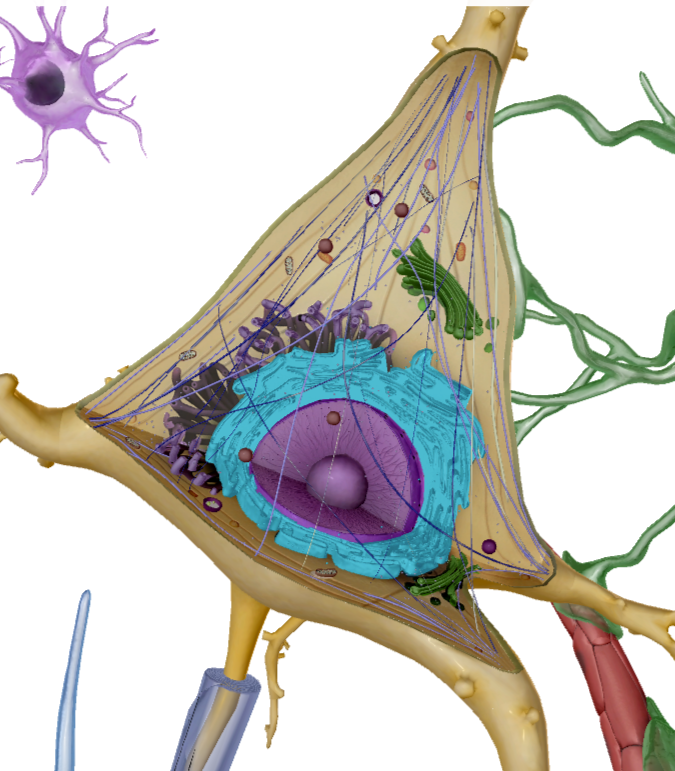
Cytoplasm
What is this?