Animals in the Anthropocene II: The case of amphibians
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Amphibian ecological roles
Key environmental indicators: Ecosystem health indicators due to their sensitivity to environmental changes.
Crucial Ecological Roles: Dual roles in food webs as predators and prey, contributes to ecological balance and offering vital ecosystem services i.e. pest control
Diversity and Vulnerability: Amphibians have specific habitat needs and narrow preferences make them particularly vulnerable to rapid environmental changes.

Origins
Ancestor with lobe-finned fishes
Key evolutionary adaptions: development of lungs, limbs and the ability to live both in water and on land.
Survived the Permian Extinction ‘‘Great Dying’’ of anoxia, OA and warming.
Tiktaalik roseae. “Fishapod” 375 MYa
Lepospondyli - Diplocaulus. Late Carboniferous
300MYa

Clades
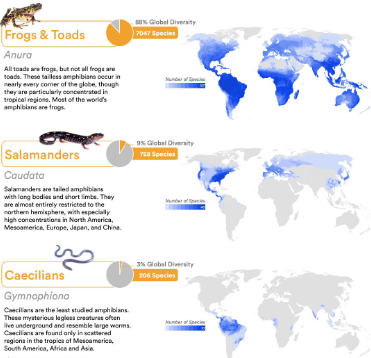

Anura
Example: for unique adaptions
Skin and gastric brooding
Sexual selection and displays
Aposematism*

Caudata
Some salamander speices are arboreal
May possess Tetrodotoxin
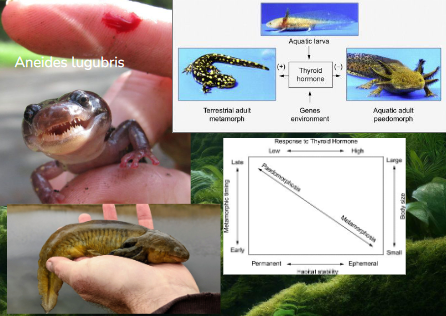
Facultative paedomorphosis
Adults retain larval characteristics
In stable habitats that don’t require migration
Gymnophiona
Skull adapted for subterranean lifestyle
Little known, it’s difficult to find them
Some species provide parental care
Oviparous species
Skin feeding
Milk provisioning
Viviparous species
Oviduct lining feeding


Morphological diversity
Amphibians are very diverse
Sizes
Calls
Colors
Behaviours such as gliding

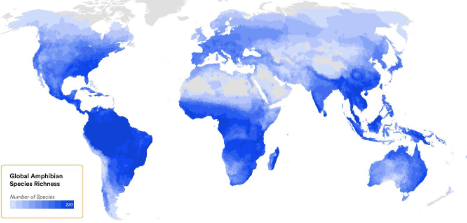
Distribution
Globally distributed but absent in Antarctica
Over 8,600 amphibian species
Common in humid tropical environments
Some adapt to extremes, from deserts to Arctic tundras
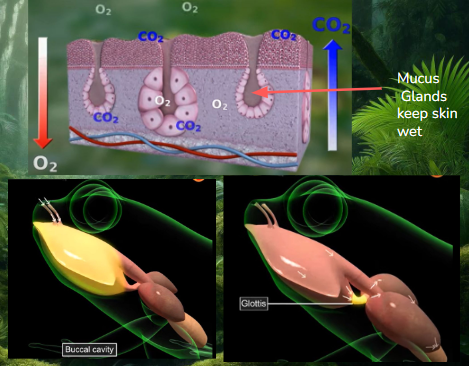
Amphibian respiratory adaptions
Three types of respiration
Cutaneous
Buccopharyneal
Pulmonary (paired lungs)
Tadpoles, lungless and paedomorphic salamanders & during hibernation: cutaneous only
Amphibian reproduction
Aquactic vs terrestrial egg deposition
Egg-laying vs direct development (29%)
Diverse parental care
Tadpole transport
Guarding
Mosturising clutch

Amphibian physiological adaptions
Nocturnal activity
conserve moisture
low metabolic rate
Hibernation and estivation
Freeze tolerance
Lung loss in plethodontids*
embryos initally develop lung rudiments, which regress through apoptosis*

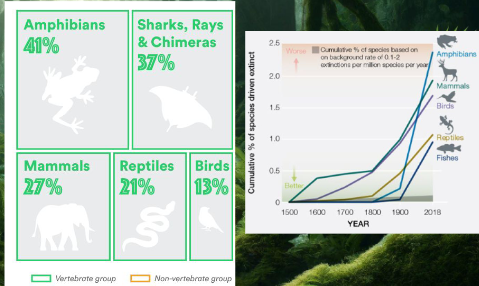
Amphibian decline
Habitat destruction and fragmentation
Disease, specifically chytridiomycosis
Climate change impacts
Pollution and pesticides
Invasive species

Threats to Amphibians
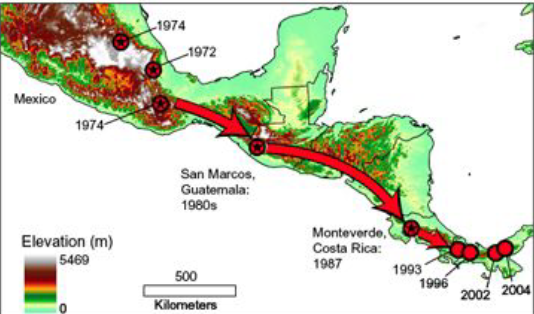
1985: Dr. Karen Lips studies tree frog ecology in Costa Rican cloud forest.
1996 return: Found all frogs disappeared from the site, similar disappearances in a western site
Suspected an unknown disease might be the cause of disappearances, prompting further investigation westward
Arrival in Panama: Found frogs initially present
Observed frogs dying rapidly in the following days
Dr. Joyce Longcore determined deaths were due to Chytridiomycosis (Bd), new fungal disease

Threats to Amphibians 2 (salamanders)
Bd declines in frog slowly
New disease since 2010s: Bsal Batrachochytrium salamandrivorans
Affects salamanders in Europe
Spreading rapidly, assessments are underway


Threats to Amphibians 3
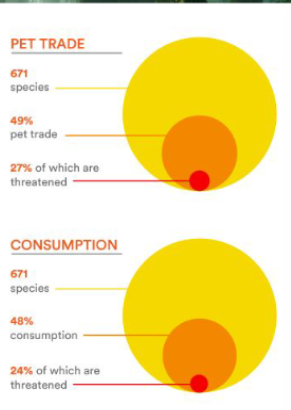

Global and local initiatives (conservation)
Global and local conservation initiatives
Combating disease
Captive breeding and reintroduction programme
Habitat restoration and protection
Citizen science and community involvement

The impact of amphibian conservation

GAA2 Conservation priorities 1
Global monitoring needed
Expand habitat protection, especially at high elevation to provide migration buffers and corridors
Conservation breeding programmes
Active management of protected areas


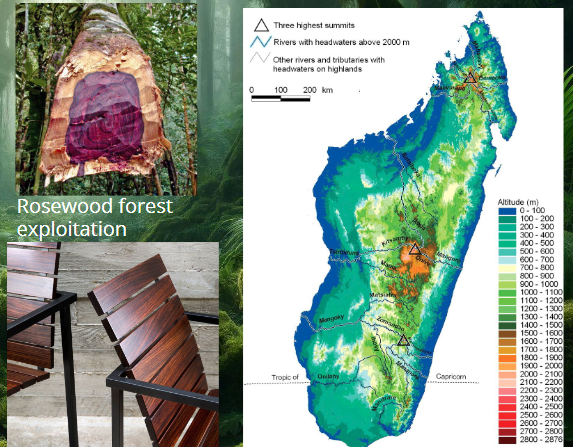
Madagascar
Development index:
Country rank 142 of 176
Severe deforestation
High amphibian endemism and species richness
Where do which species occur?
Microendemism
Which areas to conserve?

Madagascar images
