Day 2 - Enzymes (Catalytic Proteins)
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
What are enzymes?
- biochemical catalysts
- very specific for reactions and substrates (lock and key)
- most are proteins
- not used up in the reaction
- speed up reaction, but do not change outcome
- lower EA
- influenced by temperature, pH, substrate concentration, inhibitors
How are enzymes affected by temperature? (3)
- they have an optimum temp
- activity increases with temp until optimum temp, then activity declines
- enzymes will denature and lose activity

What three amino acids participate in catalytic reactions (especially in the active site)?
histidine
glutamate
cysteine
What is the optimum pH for cytosolic enzymes?
7-8

Is the optimal pH for lysosomal enzymes acidic or basic?
acidic

What is the optimum pH for pepsin?
1.5-2 (gastric)

What is the optimum pH for trypsin and chymotrypsin?
8-9 (pancreatic juice)

Does the Lyases (synthases) class of enzymes require ATP?
Does the Ligases (synthetases) class of enzymes require ATP?
yes
no
Think: Lyases = has a 'y' = yes ATP
Enzymes increase the rate at which a reaction will achieve ______________.
equilibrium

Do enzymes affect Keq (ratio of products to reactants at equilibrium)?
No

What is free energy?
energy available to do useful work (aka can it be used to make ATP)

What is entropy?
measure of disorder or randomness of a system

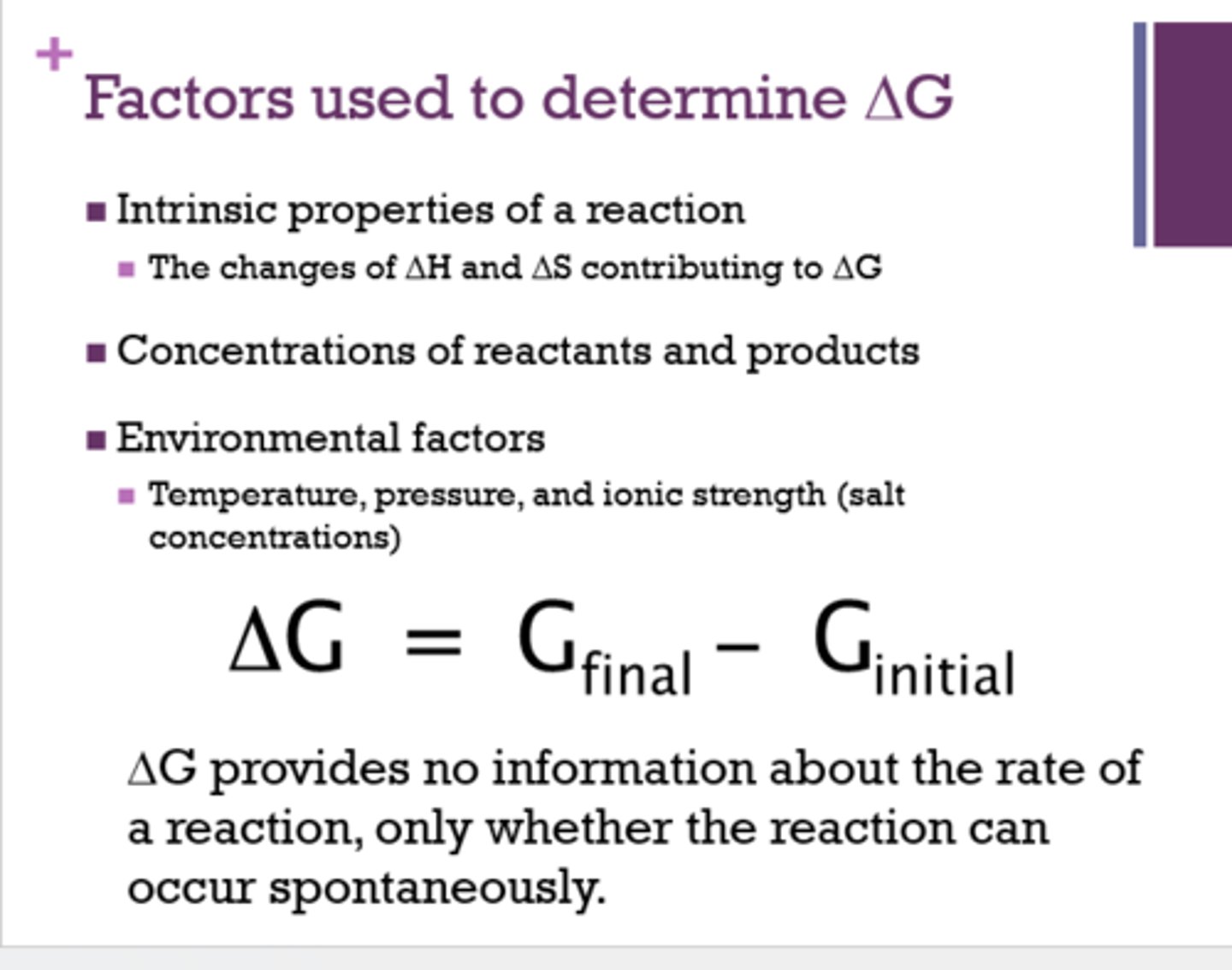
What is the equation for △G?
△ G= △H - T(△ S)

What is △H?
change in enthalpy

What is △S?
change in entropy

What must △G be in order for the reaction to be spontaneous?
negative

What factors are used to determine △G?
- intrinsic properties of a reaction
- concentration of reactants and products
- environmental factors
What are standard conditions?
temp =
pressure =
conc =
pH =
temp = 298K (25C)
pressure = 1 atm
conc = 1M
pH = 7 (living cells)
Note: "Biological reactions occur at concentrations much less than 1 M"

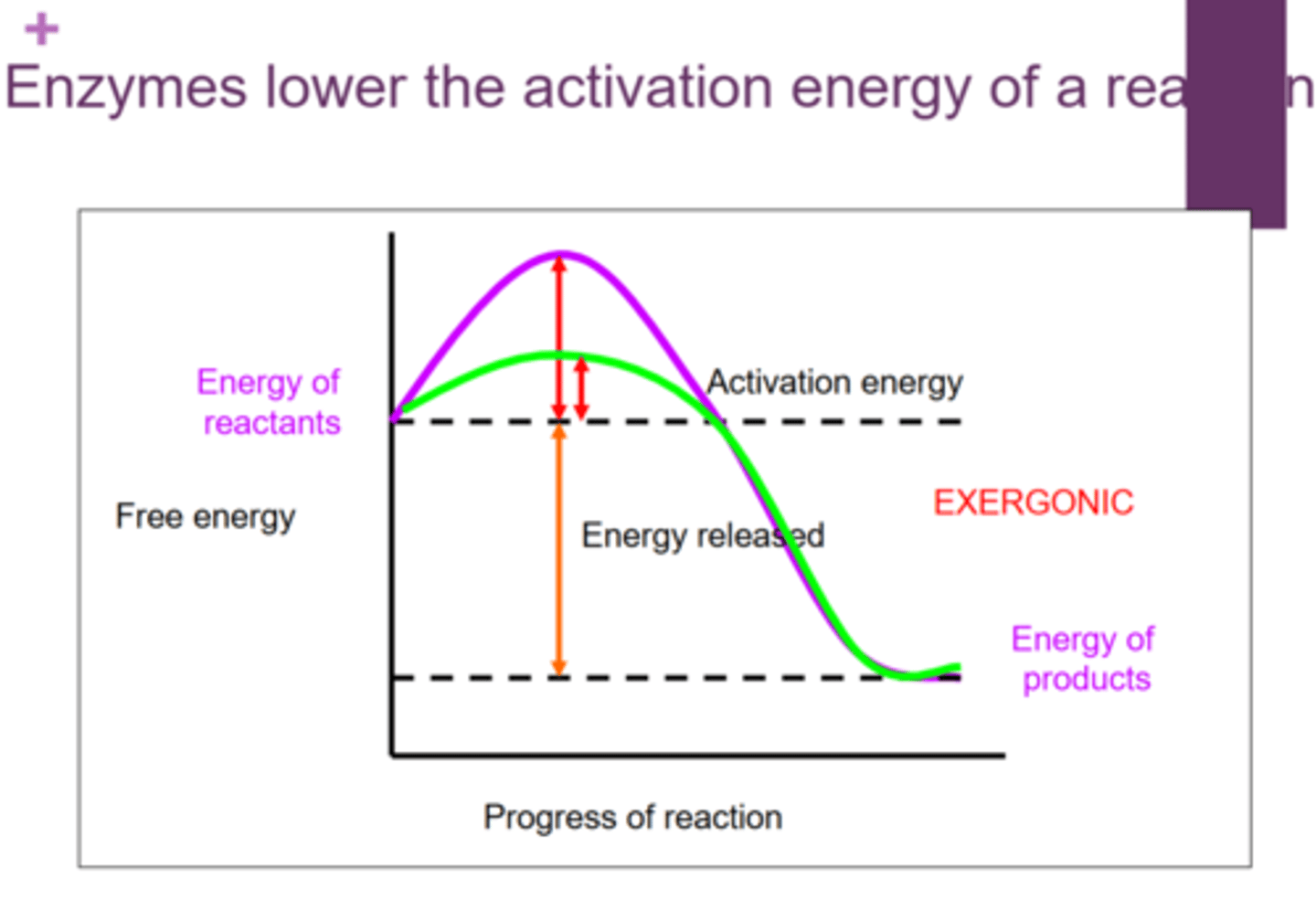
Breaking bonds results in a release of _______.
Cells capture energy released from bonds that are _______.
energy
broken
Which type of reactions release free energy?
exergonic
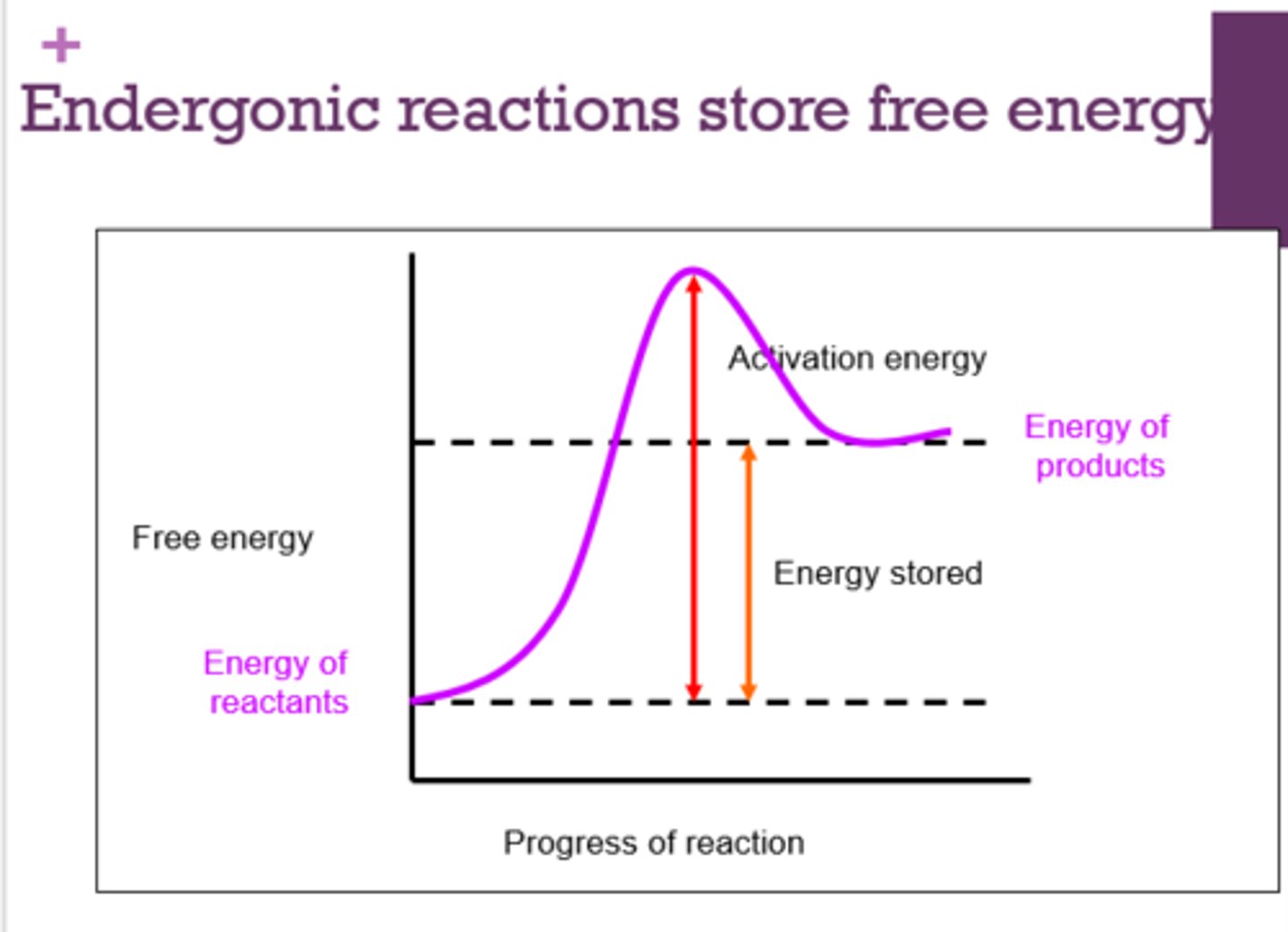
What type of reactions store free energy?
endergonic
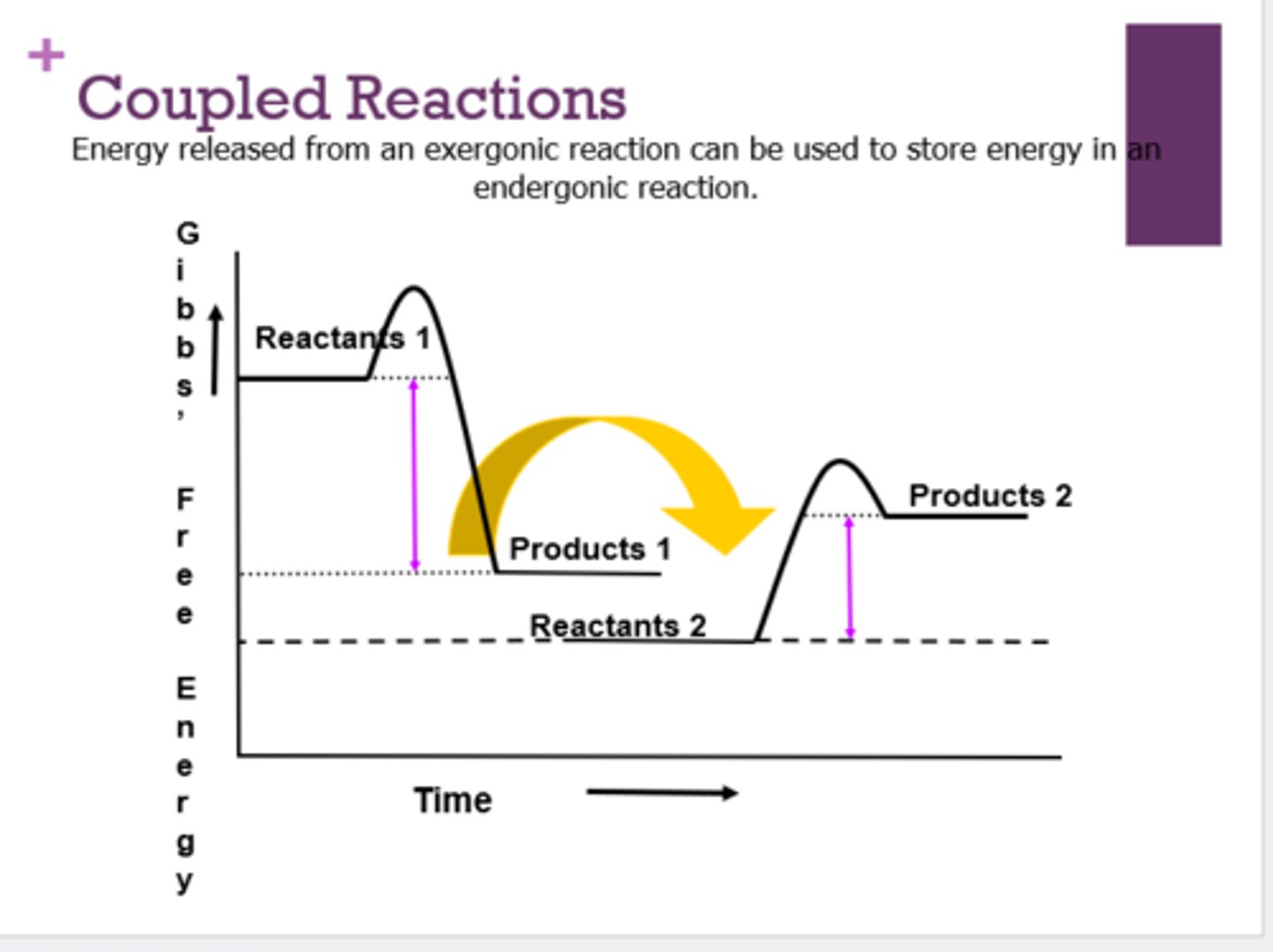
What are coupled reactions?
energy released from an exergonic reaction can be used to store energy in an endergonic reaction
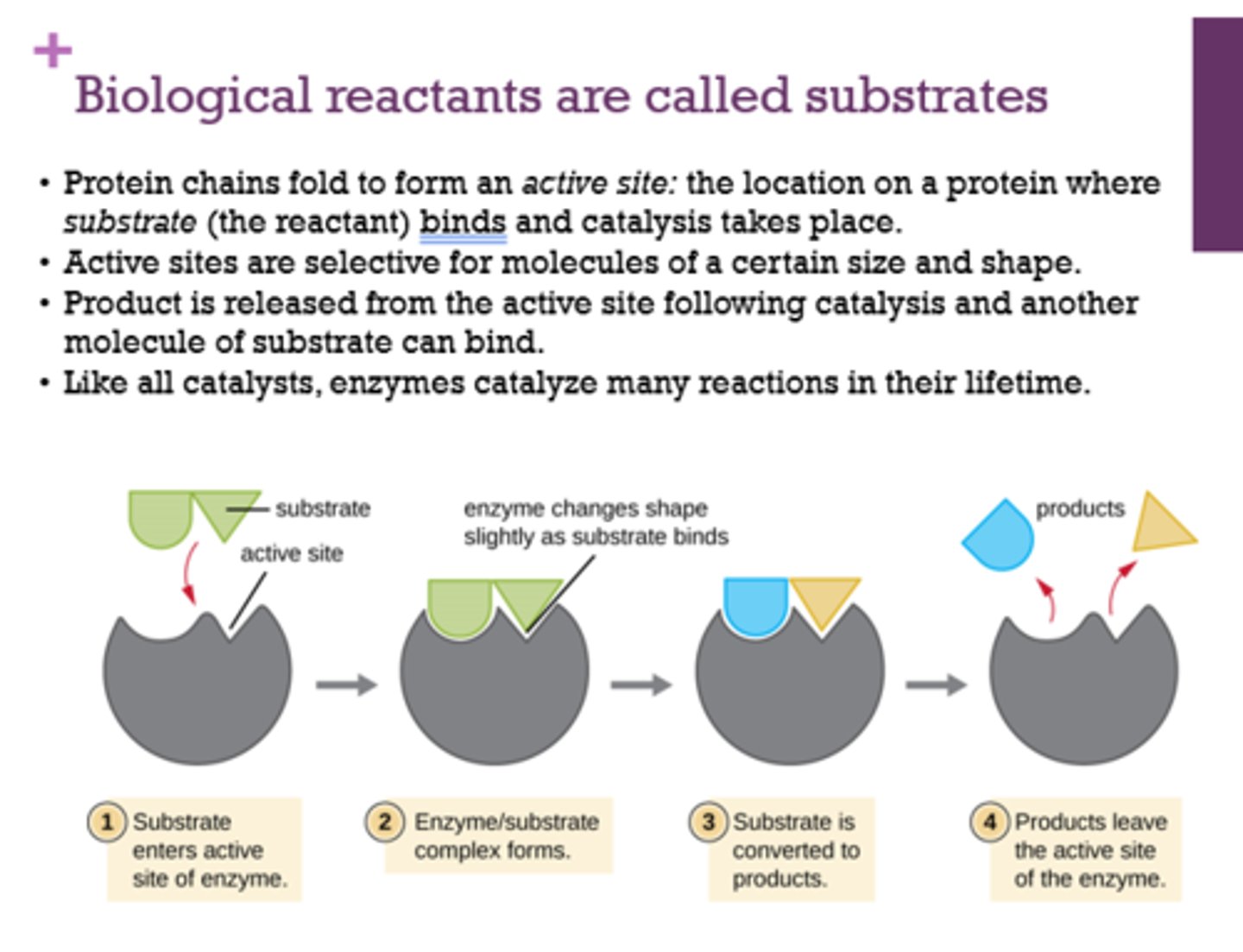
What amino acid most often makes up the active site of protein enzymes?
histidine

What is the active site?
location on a protein where substrate binds and catalysis takes place
Coenzymes join with an __________ to form a ___________.
- apoenzyme
- holoenzyme

How do coenzymes work?
either work with oxidoreductases by donating or accepting hydrogen atoms or electrons OR transfer groups other than hydrogen

What are the general characteristics of coenzymes?
heat stable, low molecular weight

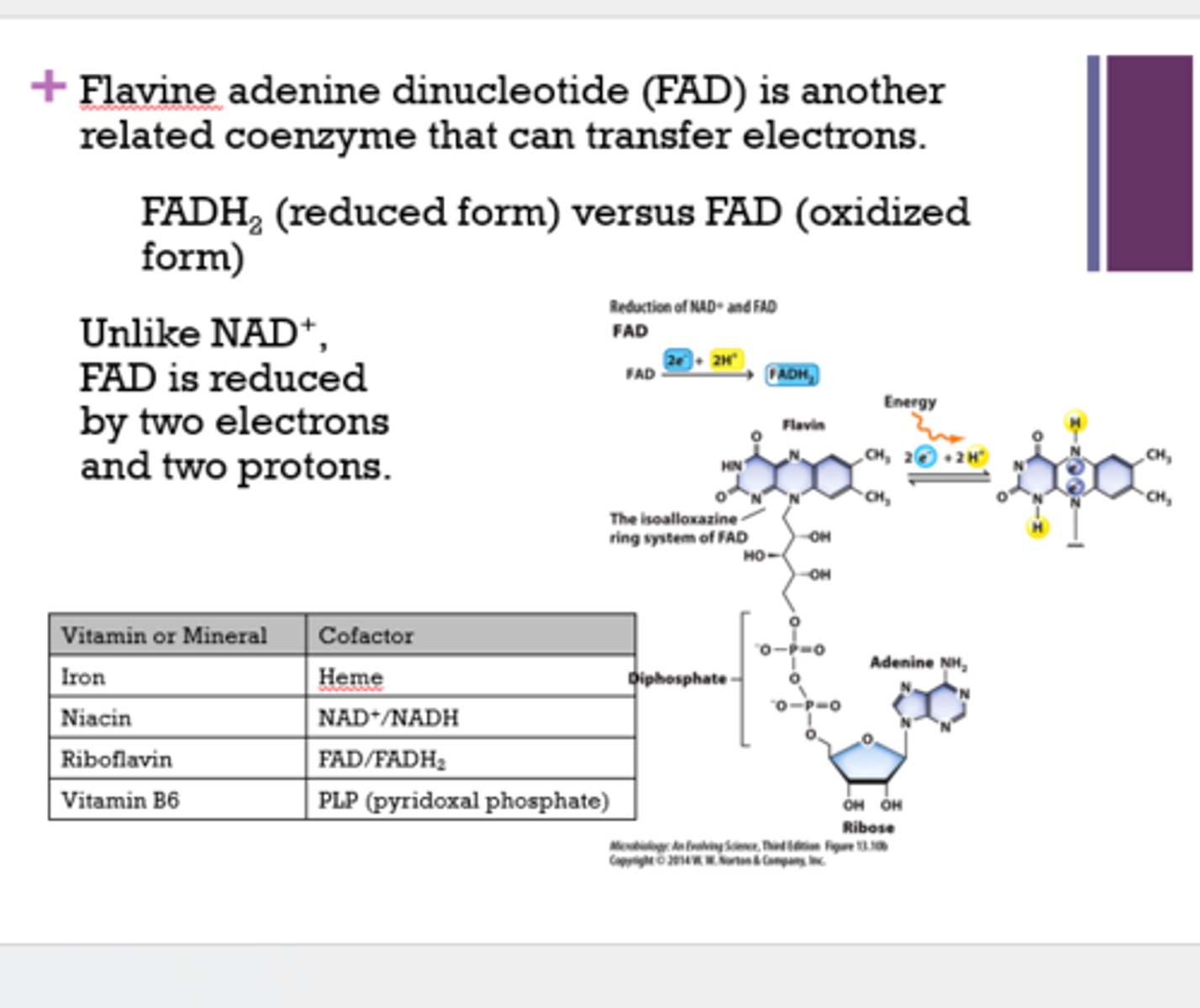
How many electrons and protons does FAD carry?
How many electrons and protons does NAD+ carry?
2 electrons and 2 protons
2 electrons 1 proton
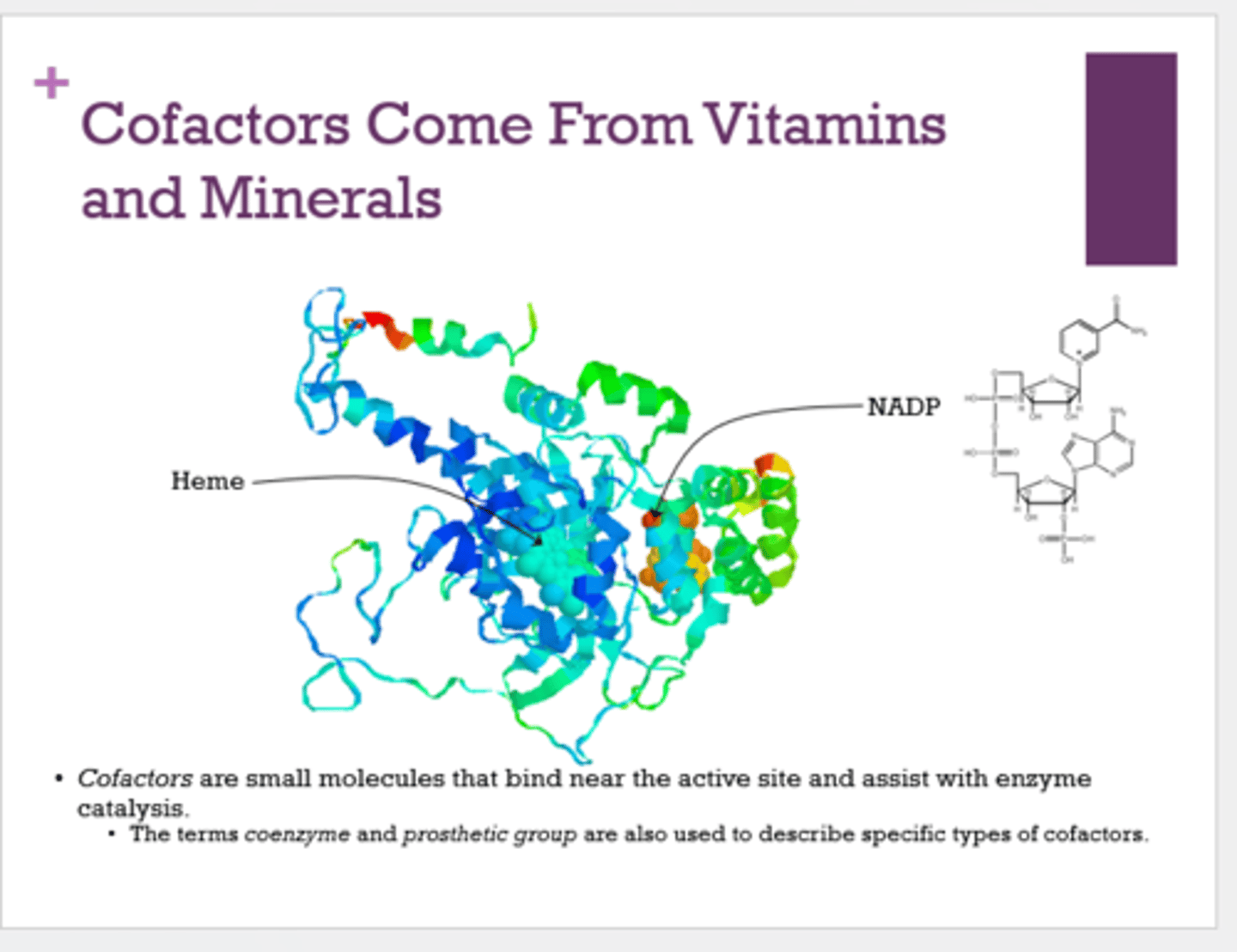
Where do cofactors come from?
vitamins and minerals
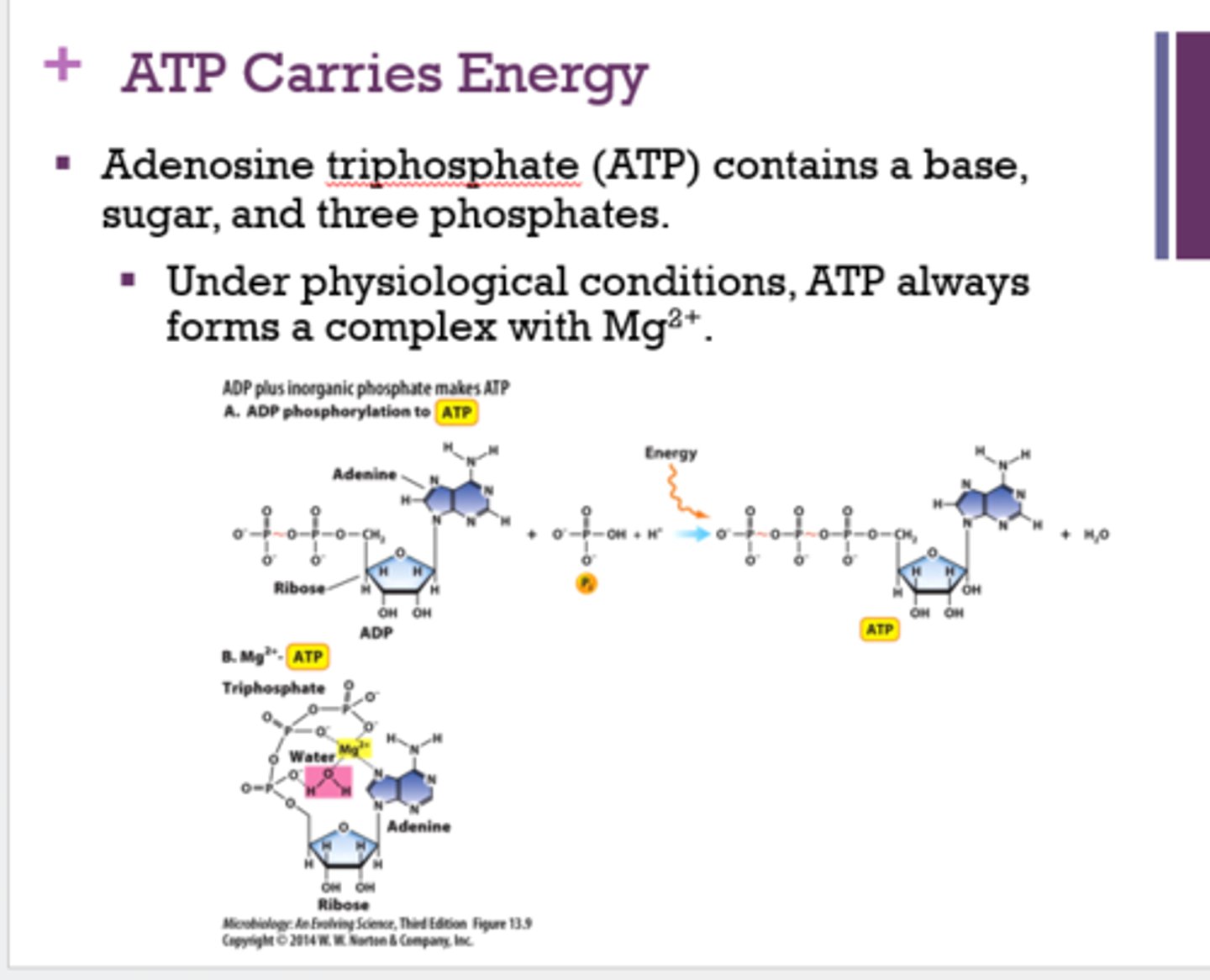
What are the 3 parts of ATP?
base, sugar, 3 phosphates
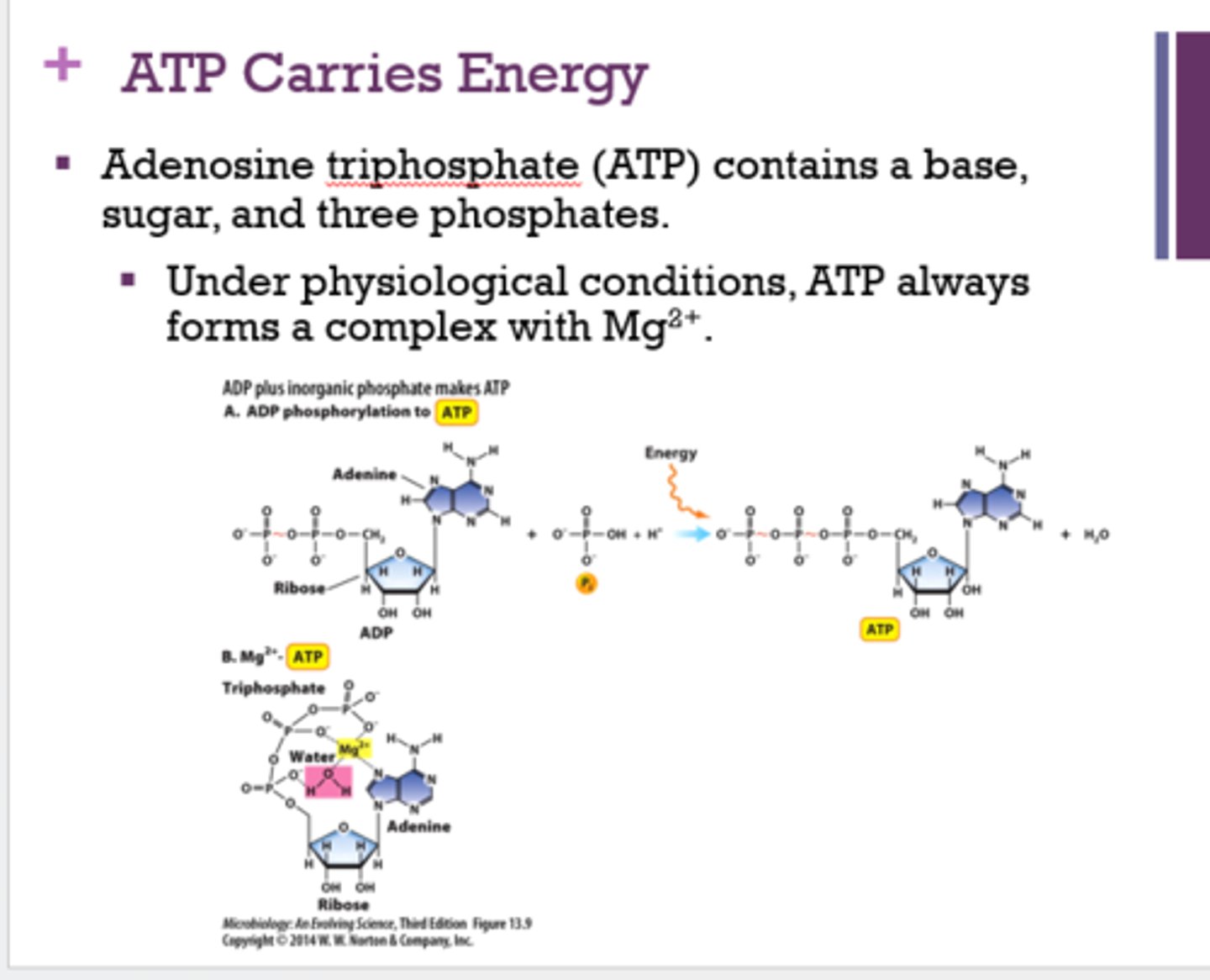
Under physiological conditions, what does ATP always form a complex with?
Mg2+
What are the 3 ways ATP can transfer energy to cell processes?
1. hydrolysis-releasing phosphate
2. hydrolysis-releasing pyrophosphate
3. phosphorylation of an organic molecule

What the 2 digestive enzymes in the oral cavity?
- alpha-amylase (secreted in saliva, cleaves glycosidic bonds)
- lingual lipase (secreted from tongue, removes free fatty acids from dietary triglycerides)

What antimicrobial enzymes are in the oral cavity?
- lysozyme (in saliva, breaks glycosidic bones in peptidoglycan)
- lactoperoxidase (in saliva, helps form hypothiocyanite ions)

What potentially pathogenic enzymes are located in the oral cavity?
- collagenases
- glucosyltransferases

What enzymes are found in enzyme tooth pastes?
dentrifice enzymes (lysozyme, lactoperoxidase)

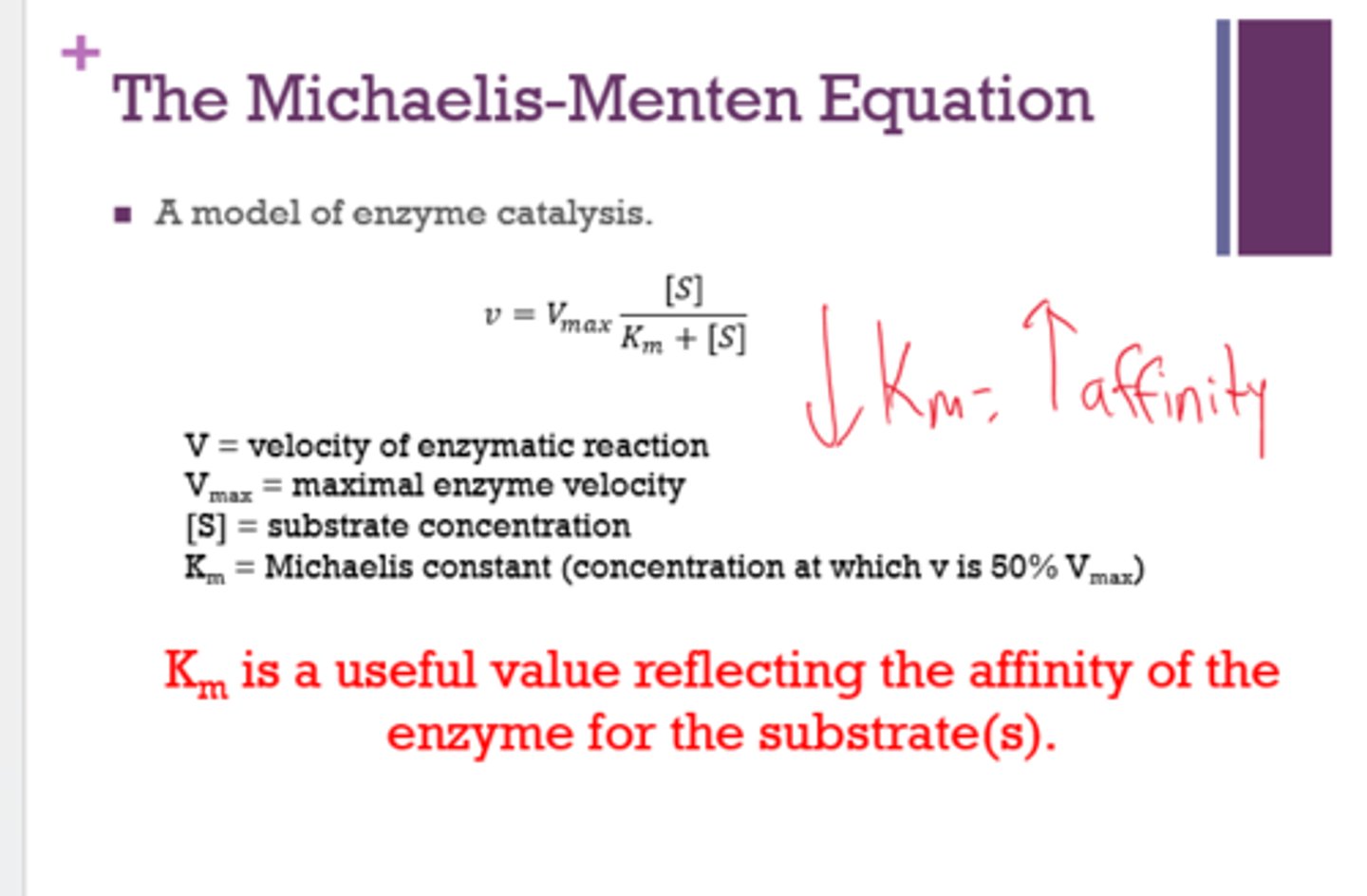
What does the Michaelis-Menten equation do?
- models enzyme catalysis
- calculates Km and Vmax
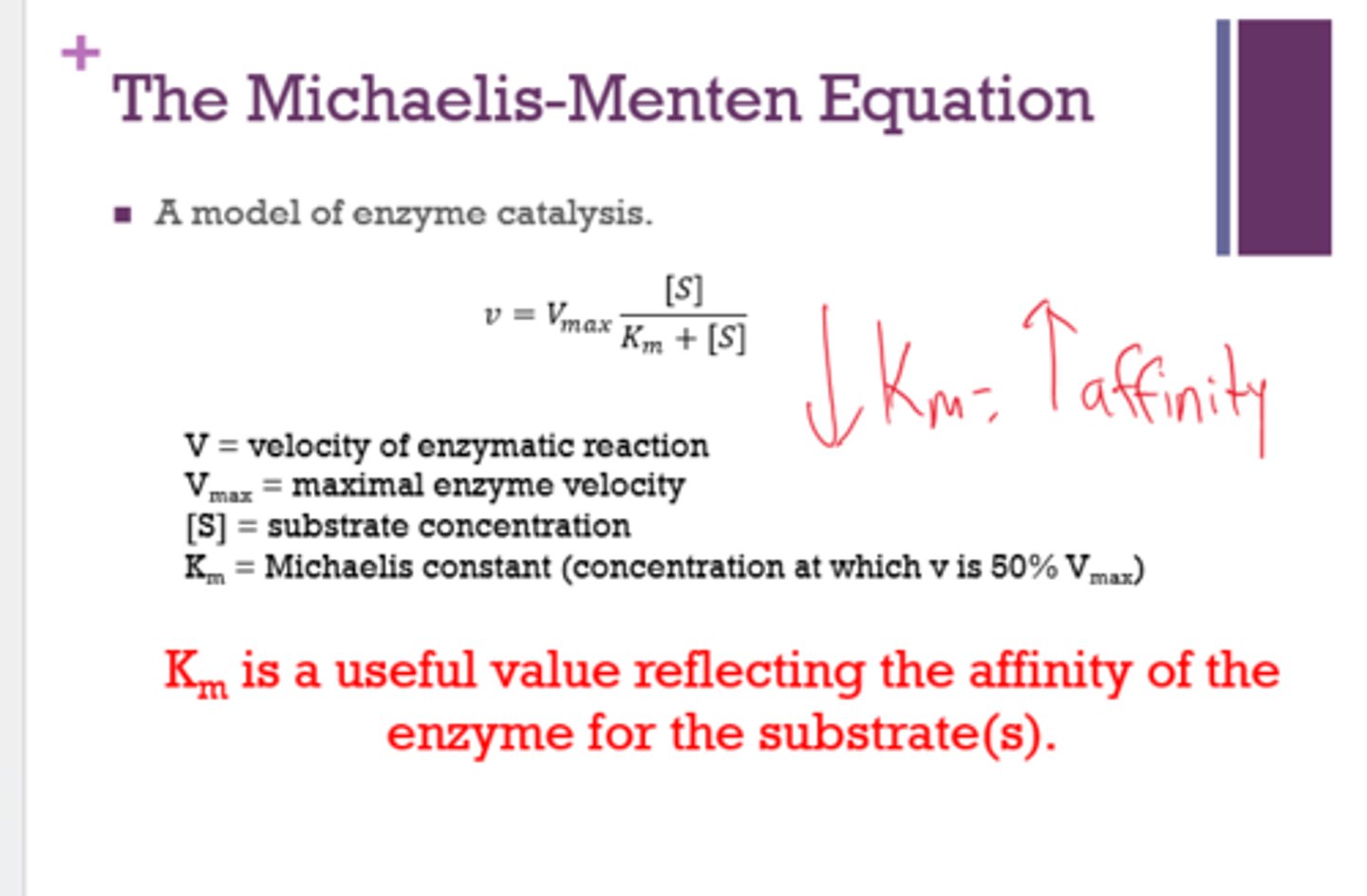
Km is a useful value reflecting the ______ of the enzyme for the ______.
A low Km indicates a _____ affinity.
affinity
substrate
high
Competitive inhibitors:
1. How does it affect Vmax and Km?
2. What are two examples?
1. Vmax stays the same, increases Km
2. sulfonamides and methotrexate
Noncompetitive inhibition:
1. How does it affect Vmax and Km?
2. What are two examples?
1. Vmax is reduced, Km stays the same
2. heavy metals, CN

Uncompetitive inhibition:
1. How does it affect Vmax and Km?
2. What are 3 examples?
1. Vmax and Km are reduced in same proportion
2. leucine, phenylalanine, inhibit alk phosphatase

Allosteric inhibition:
1. How does it affect Vmax and Km?
2. What are 2 examples?
1. both are reduced
2. aspartate carbomylase, hemoglobin cooperativity