Lecture 2 Lifestyle Modifications
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Discuss the importance of proper nutrition for the prevention of chronic diseases Describe the 6 classes of nutrients for overall health Summarize the healthy eating recommendations in the American Heart Association Dietary Guidance Counsel a patient on the appropriate use of Alli (orlistat) Describe the Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans recommendation
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
The health behavior change fundamental concepts (4) are…
Self efficacy
Patient is the center of _____ _____ process
Effective communication, intervention, AND ______
Evaluate and discuss concepts w/ patient when designing a disease ____ program
behavior change
follow-up
prevention
What are calories? (Units)
Amount of energy it takes to raise 1 g of water 1oC
Units: kilocalories, kcal, cal
1 g carbohydrate = ? kcal
1 g protein = ? kcal
a. 4 kcal
b. 7 kcal
c. 9 kcal
a. 4 kcal
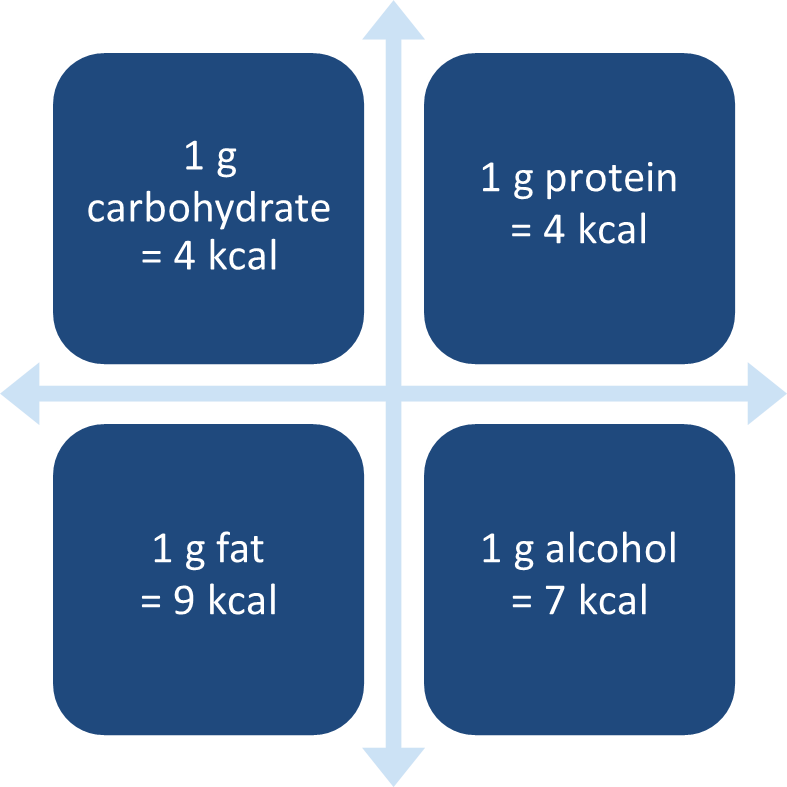
1 g alcohol = ? kcal
a. 4 kcal
b. 7 kcal
c. 9 kcal
b. 7 kcal
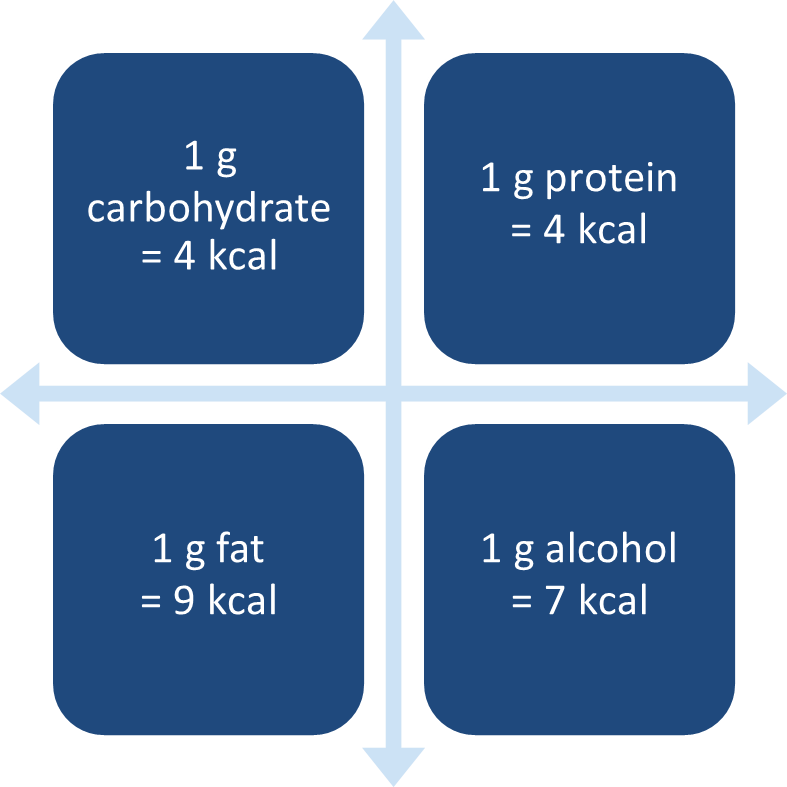
1 g fat = ? kcal
a. 4 kcal
b. 7 kcal
c. 9 kcal
c. 9 kcal
True or false: Metabolic rate is the sum total of all energy expended each day.
True!
Metabolic Rate is dependent on (select all that apply 3 total) …
a. Genetics
b. Basal metabolic rate
c. Sleep
d. Thermic effect on food
e. Physical activity
b. Basal metabolic rate
d. Thermic effect on food
e. Physical activity
What are the 6 classes of nutrients for overall health?
Hint: Macronutrients class (3) & Micronutrient class (3)
Macronutrients class
Carbohydrates
Fats
Protein
Micronutrients class
Vitamins
Minerals
Water
Which of the following nutrients for overall health composes of 45-65% of daily calories and is our major energy source?
a. Carbohydrates
b. Fats
c. Proteins
d. Vitamins
e. Minerals
f. Water
a. Carbohydrates
Which of the following nutrients for overall health composes 20-35% of daily calories and is a carrier for absorption of fat-soluble vitamins?
a. Carbohydrates
b. Fats
c. Proteins
d. Vitamins
e. Minerals
f. Water
b. Fats
Which of the following nutrients for overall health composes 10-35% of daily calories and is another source of energy?
It is also converted to carbs during starvation.
a. Carbohydrates
b. Fats
c. Proteins
d. Vitamins
e. Minerals
f. Water
c. Proteins
Which of the following nutrients for overall health has no caloric value and is not a source of energy but maintains physiologic and energy processes?
a. Carbohydrates
b. Fats
c. Proteins
d. Vitamins
e. Minerals
f. Water
d. Vitamins
Which of the following nutrients for overall health has no caloric value but is used to build tissue and regulate metabolism?
a. Carbohydrates
b. Fats
c. Proteins
d. Vitamins
e. Minerals
f. Water
e. Minerals
Which of the following nutrients for overall health is the most essential nutrient?
Hint: it influences food digestion, metabolism, regulates body temp, and is a carrier for all electrolytes
a. Carbohydrates
b. Fats
c. Proteins
d. Vitamins
e. Minerals
f. Water
f. Water
True or false: Simple sugars (mono/di/tri) have calories with sufficient nutrients to our diet and supplies energy as glucose!
False!
Simple sugars → little to no nutrients in diet
Example: table sugar, brown sugar, dextrose, honey, milk
COMPLEX CARBS (Starches/Poly) supplies energy as GLUCOSE
Example: flour, bread, rice, corn, oats
Dietary fiber is a ____ ______ carb from plant food not digested by enzymes in the small intestine. Recommended intake is 14 g/1000 cal
non-starch
decrease risk of coronary ❤ disease and lowers diabetes
Examples: navy beans, lentils, oats, citrus fruits, strawberries, barley, carrots
Which kind of fatty acid is is liquid in room temp, is healthier (↓ amount of newly formed cholesterol and help lower blood cholesterol lvls) and should represent 10-20% of total daily caloric intake?
a. unsaturated (mono/poly)
b. saturated
c. cis/trans
d. cholesterol
a. unsaturated (mono/poly)
Examples: canola, olive, peanut oils, avocados, sunflower, sesame, soybeans, nuts, seeds
Which kind of fatty acid is solid in room temp and ↑ in total and LDL cholesterol? It should represents <10% of total calories
a. unsaturated (mono/poly)
b. saturated
c. cis/trans
d. cholesterol
b. saturated
Examples: beef, lamb, pork, poultry fat, butter, cream, milk, coconut oil, cocoa butter
What kind of fatty acid ↑ risk for coronary <3 disease?
a. unsaturated (mono/poly)
b. saturated
c. cis/trans
d. cholesterol
b. saturated
c. cis/trans
Example for cis/trans: shortenings, butter, animal fat, cakes, cookies, salty snacks, cake frostings, sweets
d. cholesterol
What kind of fatty acid is not an essential nutrient and should be <300mg/day? It is a fat-like substance found in animals
a. unsaturated (mono/poly)
b. saturated
c. cis/trans
d. cholesterol
d. cholesterol
Examples: Meat (especially organ meats), poultry, seafood, dairy products, egg yolks
True or false: Proteins not only provide essential AAs and are structural bases for tissues, but they also regulate metabolism!
True!
Examples: peanuts, soybeans, milk, yogurt, cheese, eggs, beef, chicken, turkey, salmon, veal, lamb, wheat bread
What are examples of antioxidants?
a. 8 B-Complex vitamins and Vitamin C (ascorbic acid)
b. Vitamins A, D, E, K
c. Vitamins E, C, beta carotene
c. Vitamins E, C, beta carotene
What are examples of fat soluble vitamins?
a. 8 B-Complex vitamins and Vitamin C (ascorbic acid)
b. Vitamins A, D, E, K
c. Vitamins E, C, beta carotene
b. Vitamins A, D, E, K
What are examples of water-soluble vitamins?
a. 8 B-Complex vitamins and Vitamin C (ascorbic acid)
b. Vitamins A, D, E, K
c. Vitamins E, C, beta carotene
a. 8 B-Complex vitamins and Vitamin C (ascorbic acid)
True or False: The recommended intake for water intake for males > 19 yo: 2.7 L/day
females > 19 yo: 3.7L/day
False!
Males (>19 yo) → 3.7L/day
Females (>19 yo) → 2.7 L/day
Before exercise (2hrs) → 17 fl oz
Healthy Eating Recommendations in the American Heart Association Dietary Guidance
Adjust ____intake & expenditure to achieve & maintain a healthy ______
energy, body weight
Healthy Eating Recommendations in the American Heart Association Dietary Guidance
Eat plenty of fruits & veggies, choose a wide variety
Whole fruits/veggies have more _____
True or False: Lighter colored fruits/veggies are more nutrient dense than darker.
dietary fiber
False → darker color are more nutrient dense
Healthy Eating Recommendations in the American Heart Association Dietary Guidance
Choose foods mostly made w/ ____ grains (rather than ____ )
Whole grain products = have at least 51% whole grains
whole, refined
Healthy Eating Recommendations in the American Heart Association Dietary Guidance
Choose healthy sources of protein
Mostly protein from ____ (legumes & nuts)
fish, seafood
Meat/poultry → lean cut, avoid processed
low-fat/fat-free
plants
Healthy Eating Recommendations in the American Heart Association Dietary Guidance
Use liquid ____ oils rather than _____ oils (coconut, palm, palm kernel)
liquid, tropical
Healthy Eating Recommendations in the American Heart Association Dietary Guidance
Choose minimally ______ foods
Unprocessed or processed?
Processed
Greater risk of DM2, incident CVD, all-cause mortality
Healthy Eating Recommendations in the American Heart Association Dietary Guidance
Minimize intake of beverages & foods w/ ____ sugars
Examples: glucose, dextrose, sucrose, corn syrup, honey, maple syrup
added sugars
any sugar added to food/beverage during preparation
Healthy Eating Recommendations in the American Heart Association Dietary Guidance
Choose and prepare foods w/ little or no salt
True or False: There is a direct (+) relationship between salt (NaCl) intake & blood pressure
True!
Leading salt of dietary sodium → processed foods, outside-prepared foods, packaged foods
Healthy Eating Recommendations in the American Heart Association Dietary Guidance
If you dont drink alcohol → do not start
If you choose to drink → limit intake
Women drink up to ___ drink/day; Men drink up to 2 drinks/day
1 drink/day
Drink
12 oz beer
5 oz wine
1.5 oz hard liquor
Healthy Eating Recommendations in the American Heart Association Dietary Guidance
10. True or False: Adhere to guidance regardless of where food is prepared or consumed
True!
Food-based dietary guidance applies to all foods and beverages, regardless of where prepared, procured, and consumed
What is the active ingredient in Alli?
Orlistat
What is the indication for Alli? What should you remember when taking the medication? (Hint: diet)
Weight-loss in overweight adults
Used along with a reduced-calorie and low-fat diet
What is the efficacy of Alli?
Inhibits dietary fat absorption by approx. 30%
What is the mechanism of action for Alli?
It is a reversible inhibitor of intestinal lipases
True or False: The dosing for Alli (OTC) is 60 mg PO 3x/day during or within 1 hr of a non-fat containing meal.
FALSE! Must be a fat-containing meal!
What are the important precautions to know before taking Alli? (2 precautions)
Decreases absorption of …
cyclosporine
counseling pt: separate administration >2hrs & cyclosporine lvl monitoring
fat-soluble vitamins (ADEK) & beta-carotene absorption
counseling pt: separate administration >2hrs
Match the key recommendation to the correct age group.
Should be physically active throughout the day to enhance growth & development
a. Preschool-Aged (3-5 yrs)
b. Children & Adolescents (6-17yrs)
c. Adults
d. Older Adults
a. Preschool-Aged (3-5 yrs)
Match the key recommendation to the correct age group.
60 minutes (1hr) or more moderate-to-vigorous physical activity daily
a. Preschool-Aged (3-5 yrs)
b. Children & Adolescents (6-17yrs)
c. Adults
d. Older Adults
b. Children & Adolescents (6-17yrs)
Match the key recommendation to the correct age group.
AVOID INACTIVITY
Aerobic Physical Activity
150-300 min (2 hr & 30 min - 5 hrs) a week; moderate-intensity
i.e. brisk walking
75-100 min (1 hr 15 min to 2 hr & 30 min) week of vigorous-intensity
i.e. jogging or running
a. Preschool-Aged (3-5 yrs)
b. Children & Adolescents (6-17yrs)
c. Adults
d. Older Adults
c. Adults
Match the key recommendation to the correct age group.
do multicomponent physical activity that includes balance training as well as aerobic and muscle-strengthening activities
cannot do 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity a week because of chronic conditions, they should be as physically active as their abilities and conditions allow
a. Preschool-Aged (3-5 yrs)
b. Children & Adolescents (6-17yrs)
c. Adults
d. Older Adults
d. Older Adults
Which of the following is not a component of physical activity?
a. Warm-up
b. Cool-down
c. Aerobic conditioning
d. Resistance training
e. Stretching
f. None of the above
f. None of the above
What are the tips when stretching joints?
Slow movements for 10-30secs
No pain, mild discomfort
4 repetitions per muscle group for 2-3days/week
Stretch smoothly & NEVER BOUNCE!
True or False: Drinking the most preventable cause of death.
False! Smoking!
Match the key recommendation to the correct age group.
Aerobic: most of the 60 min+/day should be moderate/vigorous intensity at least 3 days/week
Muscle-strengthening: at least 3 days a week
Bone-strengthening: at least 3 days a week
a. Preschool-Aged (3-5 yrs)
b. Children & Adolescents (6-17yrs)
c. Adults
d. Older Adults
b. Children & Adolescents (6-17yrs)
Match the key recommendation to the correct age group.
= combo of moderate & vigorous intensity aerobic activity
Spread aerobic activity throughout the week
Add. health benefits if aerobic physical activity >300 min (5 hrs) of mod. Physical activity/week
a. Preschool-Aged (3-5 yrs)
b. Children & Adolescents (6-17yrs)
c. Adults
d. Older Adults
c. Adults
What is considered being Active?
a. Not getting physical activity beyond basic movement form daily life activities
b. Doing some mod- or vigorous-intensity physical activity but <150 minutes of mod-intensity/week or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity physical activity
c. Doing the equivalent of 150 minutes to 300 minutes of moderate-intensity physical activity a week
d. Doing the equivalent of more than 300 minutes of moderate-intensity physical activity a week
c. Doing the equivalent of 150 minutes to 300 minutes of moderate-intensity physical activity a week
What is considered being Inactive?
a. Not getting physical activity beyond basic movement form daily life activities
b. Doing some mod- or vigorous-intensity physical activity but <150 minutes of mod-intensity/week or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity physical activity
c. Doing the equivalent of 150 minutes to 300 minutes of moderate-intensity physical activity a week
d. Doing the equivalent of more than 300 minutes of moderate-intensity physical activity a week
a. Not getting physical activity beyond basic movement form daily life activities
What is considered being Insufficiently Active?
a. Not getting physical activity beyond basic movement form daily life activities
b. Doing some mod- or vigorous-intensity physical activity but <150 minutes of mod-intensity/week or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity physical activity
c. Doing the equivalent of 150 minutes to 300 minutes of moderate-intensity physical activity a week
d. Doing the equivalent of more than 300 minutes of moderate-intensity physical activity a week
b. Doing some mod- or vigorous-intensity physical activity but <150 minutes of mod-intensity/week or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity physical activity
What is considered being Highly Active?
a. Not getting physical activity beyond basic movement form daily life activities
b. Doing some mod- or vigorous-intensity physical activity but <150 minutes of mod-intensity/week or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity physical activity
c. Doing the equivalent of 150 minutes to 300 minutes of moderate-intensity physical activity a week
d. Doing the equivalent of more than 300 minutes of moderate-intensity physical activity a week
d. Doing the equivalent of more than 300 minutes of moderate-intensity physical activity a week