Supplemental O2
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Goals and indications for O2 tx
-increased survival
-decreased dyspnea
-eliminated exercise induced hypoxia
-improved QOL
-decrease R heart strain
Indications for medicare coverage
-PaO2
Normal PaO2
-80-100mmHg
PaO2 60-80
-tachycardia
-dyspnea
PaO2 50-60
-malaise
-central cyanosis
-lightheadedness
-vertigo
-incoordination
-poor judgement
PaO2 35-50
-resp. distress
-arrhythmia
-confusion
PaO2 25-35
-acidosis
-LOC
PaO2 <25
-apnea
-shock
-cardiac arrest
O2 systems have 2 components
-storage
-delivery
O2 storage for hospital
-piped storage from wall
-portable cylinders
pts on long term O2 tx often use
-portable units with
-O2 conserving devices
O2 conserving devices
-control flow of O2 releasing gas from the source only when the pt initiates inspiration
-increase duration of O2 delivery and allow pts to be away from fixed O2 source for longer pd of time
types of O2 conserving devices
-fixed pulse unit
-demand pulse unit
-nasal cannula with reservoir (ex: oximizer)
nasal cannula
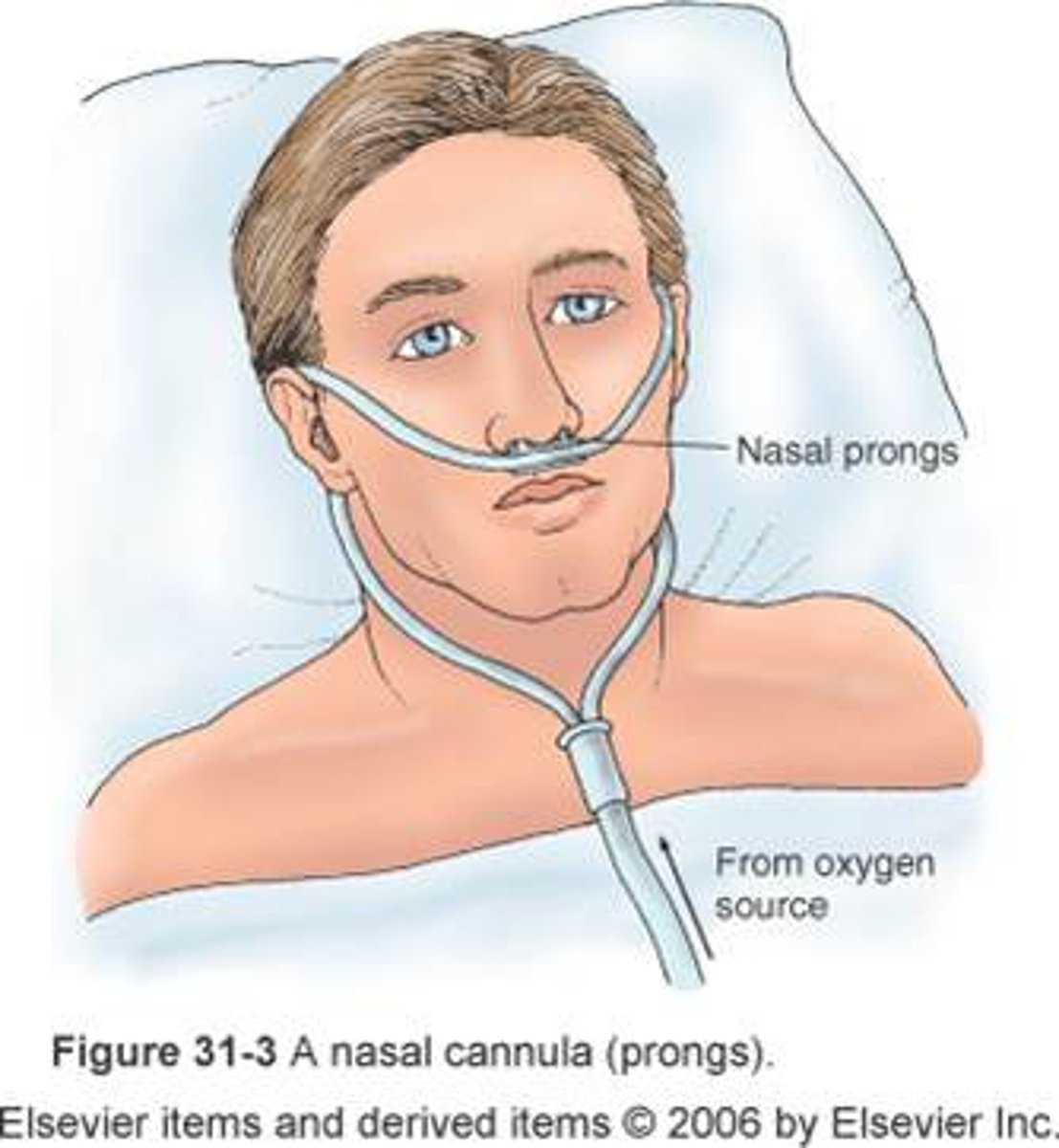
FiO2 formula
-for every liter you add .04
high flow nasal cannula
-uses mechanical aerosol system
-delivers meds and warmth
-provides small amt of positive pressure which allows higher Fio2 delivery
-not portable
-larger bore tubing
-flow up to 50-60L/min
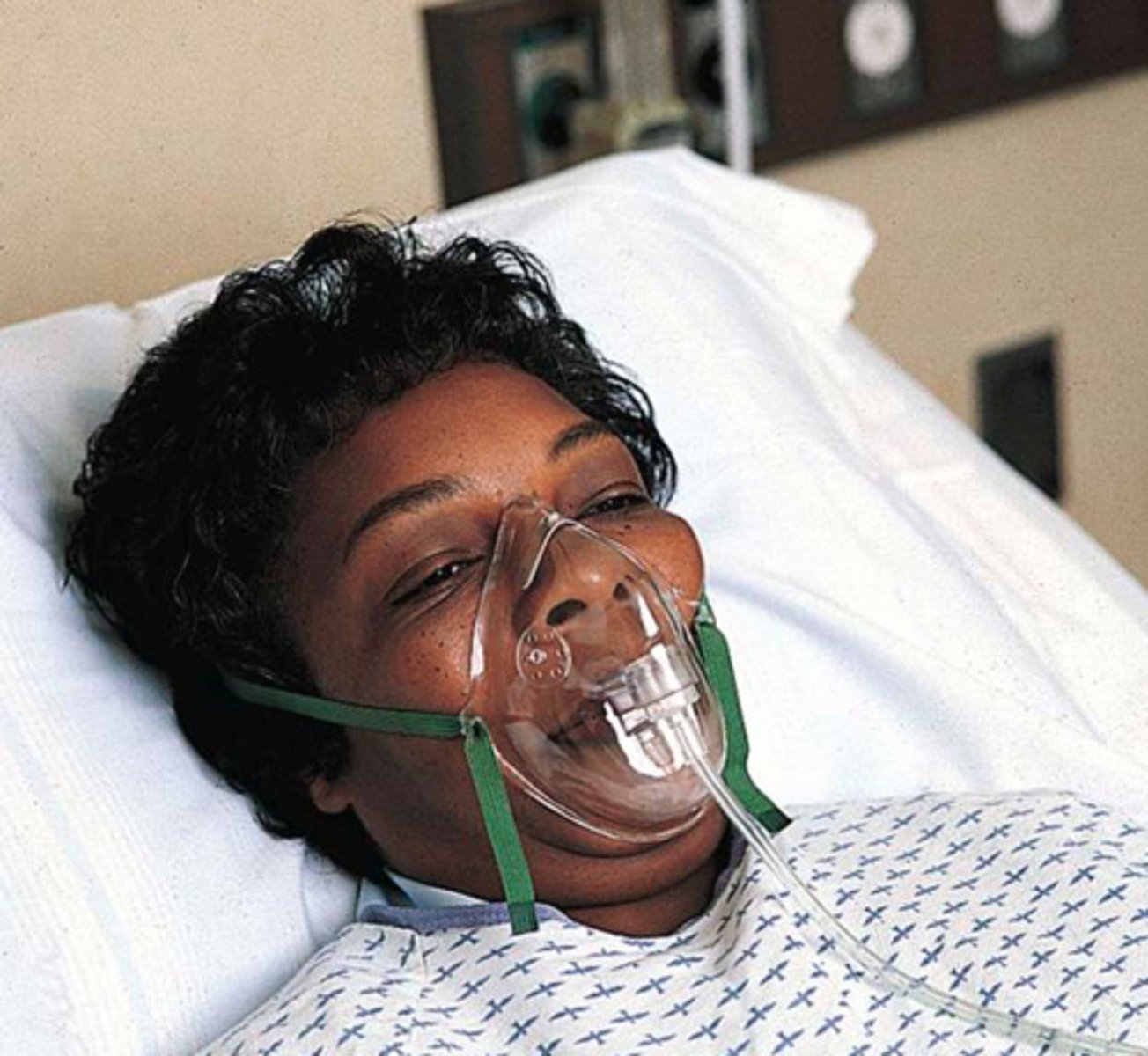
simple mask
-Delivered FiO2: 0.35-0.55
-Flow: 5-10 L/min
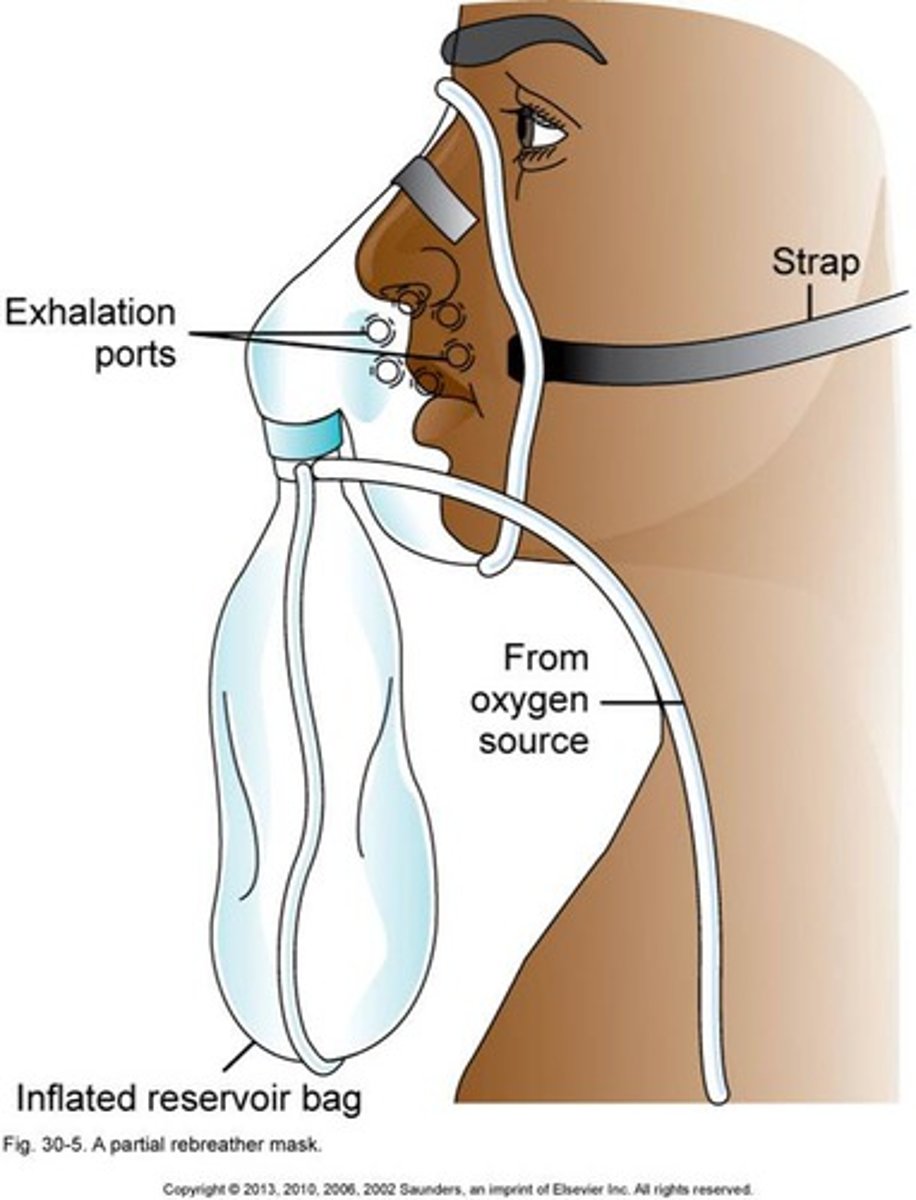
reservoir mask non-rebreather
-Fio2 60-80%
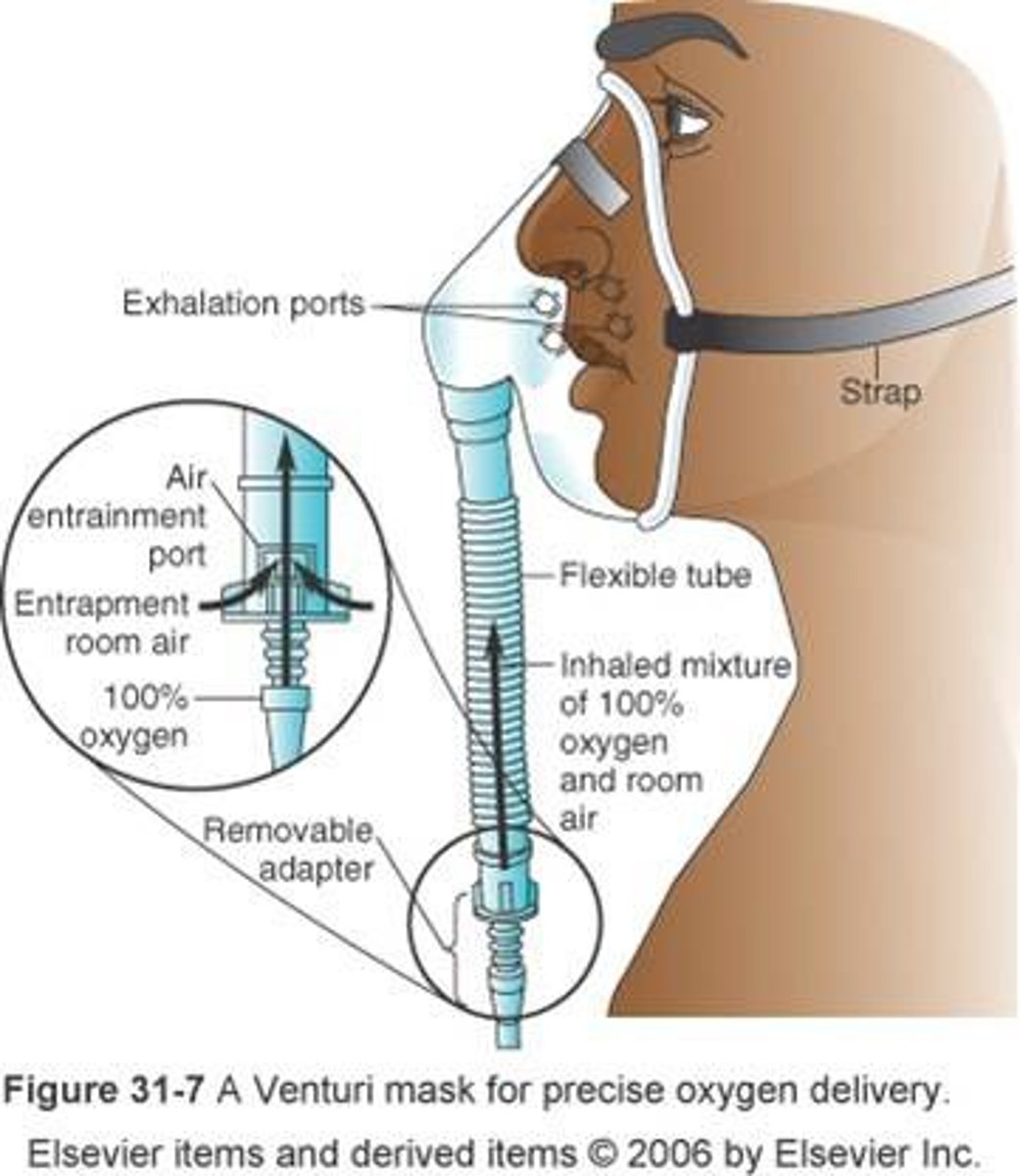
venturi mask
-flow: 4-10L/min
-Fio2: 0.24-0.50
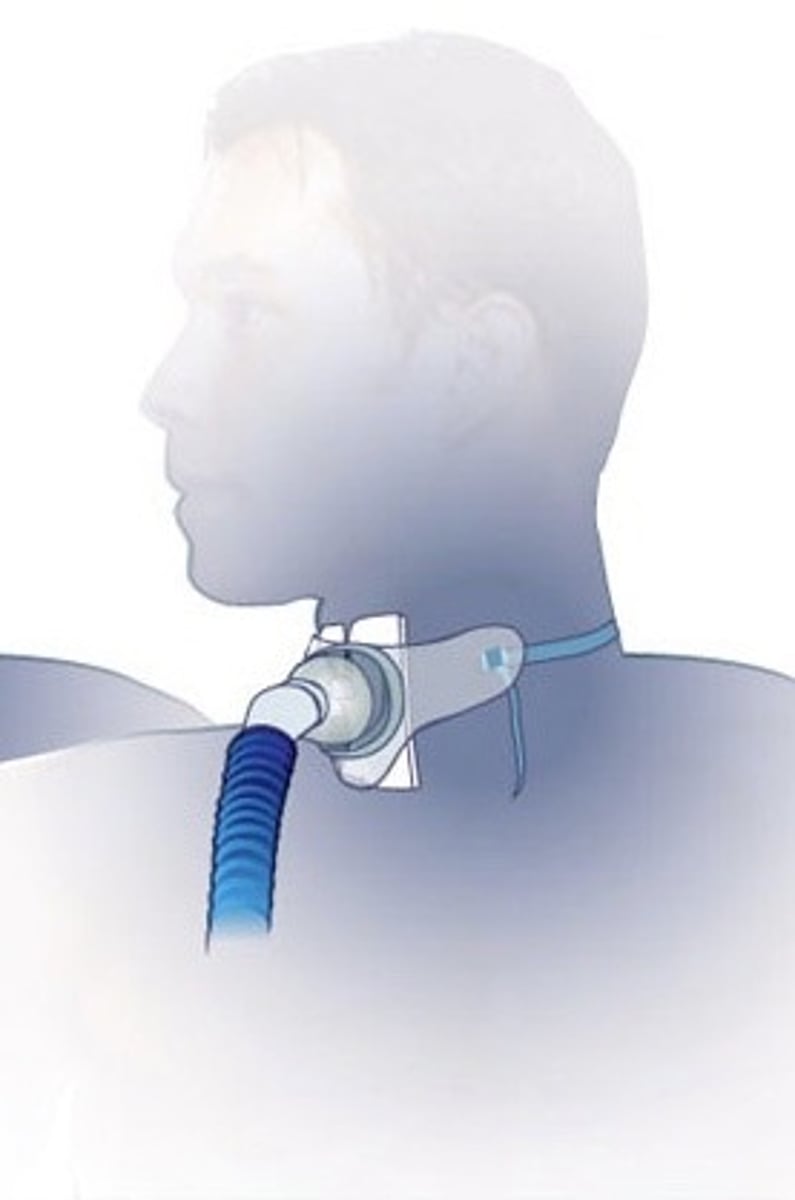
tracheostomy collar
Precautions
-prescription: 2L/min vs maintain SpO2 >88%
-O2 toxicity
-cellular injury to parenchymal tissue
-retinopathy
-atelectasis
-Irritation to mucosa
-epistaxis (bloody nose), drying
-Safe use
-burns
-potential user or equip failure