Unit 9: Globalization
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
Big Bang theory
theory which suggests that at some moment all matter in the universe was contained in a single point, which is considered the beginning of the universe
cultural imperialism
the practice of promoting or imposing one's culture on another, usually between powerful societies and less-powerful ones
environmentalism
ideology which regards the environmental concerns

European Economic Community
EEC; also known as the Common Market; founded in 1957; originally consisted of Italy, France, West Germany, Belgium, the Netherlands, and Luxembourg; expanded membership to almost all of Europe, including former communist states; renamed the European Union in 1994

UN General Assembly
one of the six principal organs of the United Nations and the only one in which all member nations have equal representation; oversee the budget of the United Nations, appoint the non-permanent members to the Security Council, receive reports from other parts of the United Nations and make recommendations in the form of General Assembly Resolutions

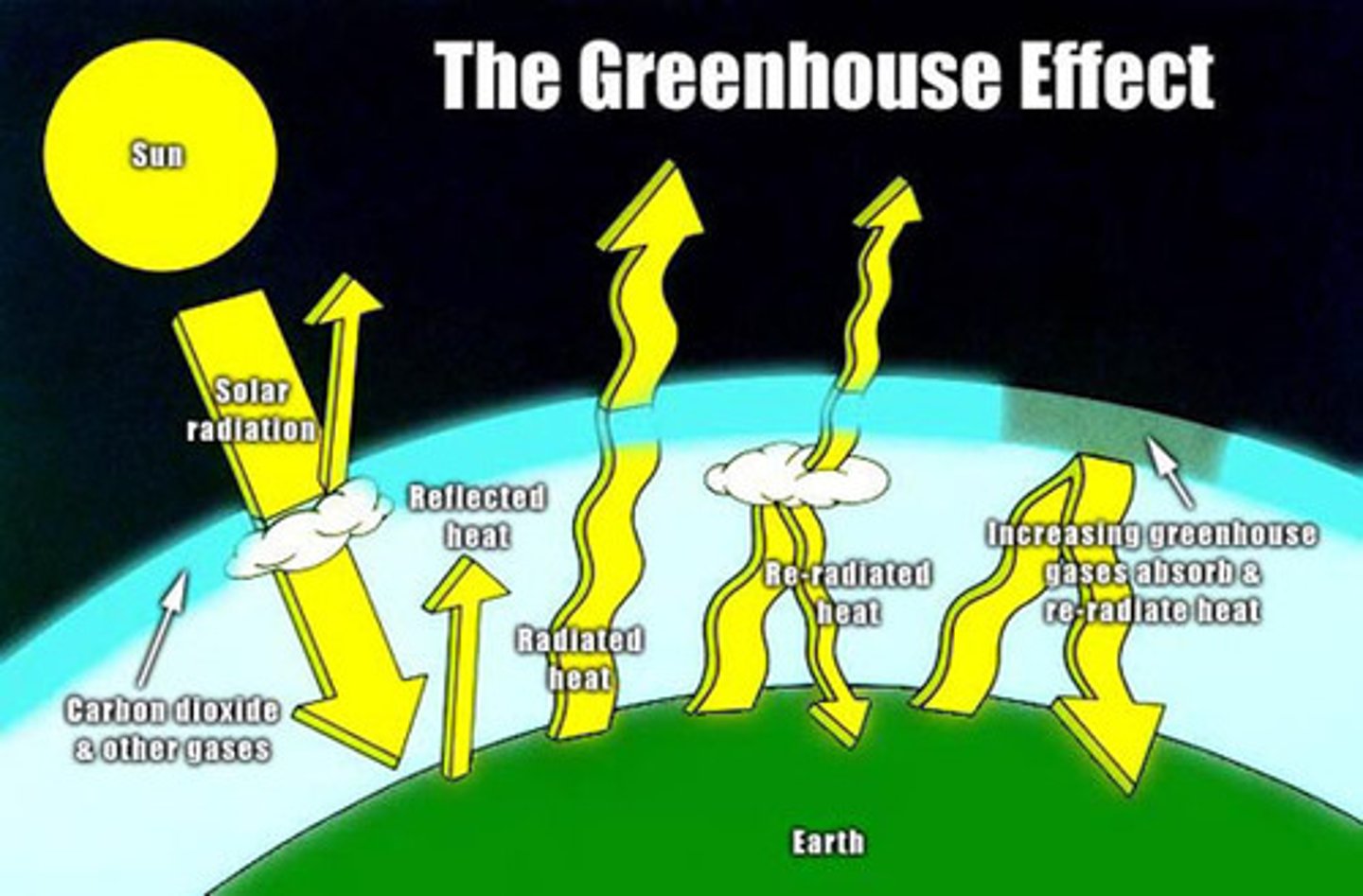
global warming
term which refers to the continuing rise in the average temperature of Earth's climate system; viewed as a result of human emissions of greenhouse gases

globalization of democracy
the spread of democracy throughout the world
Green Revolution
a series of research, and development, and technology transfer initiatives, occurring between the 1940s and the late 1960s, that increased agriculture production worldwide, particularly in the developing world

International Monetary Fund
IMF; established in 1944 by the Bretton Woods Conference in New Hampshire; sought to promote market economies, free trade, and high growth rates

Islamic renewal
also referred to as Islamic revival; refers to a renewing of the Islamic religion throughout the Islamic world, that began roughly sometime in 1970s; sought greater religious piety and a growing adoption of Islamic culture
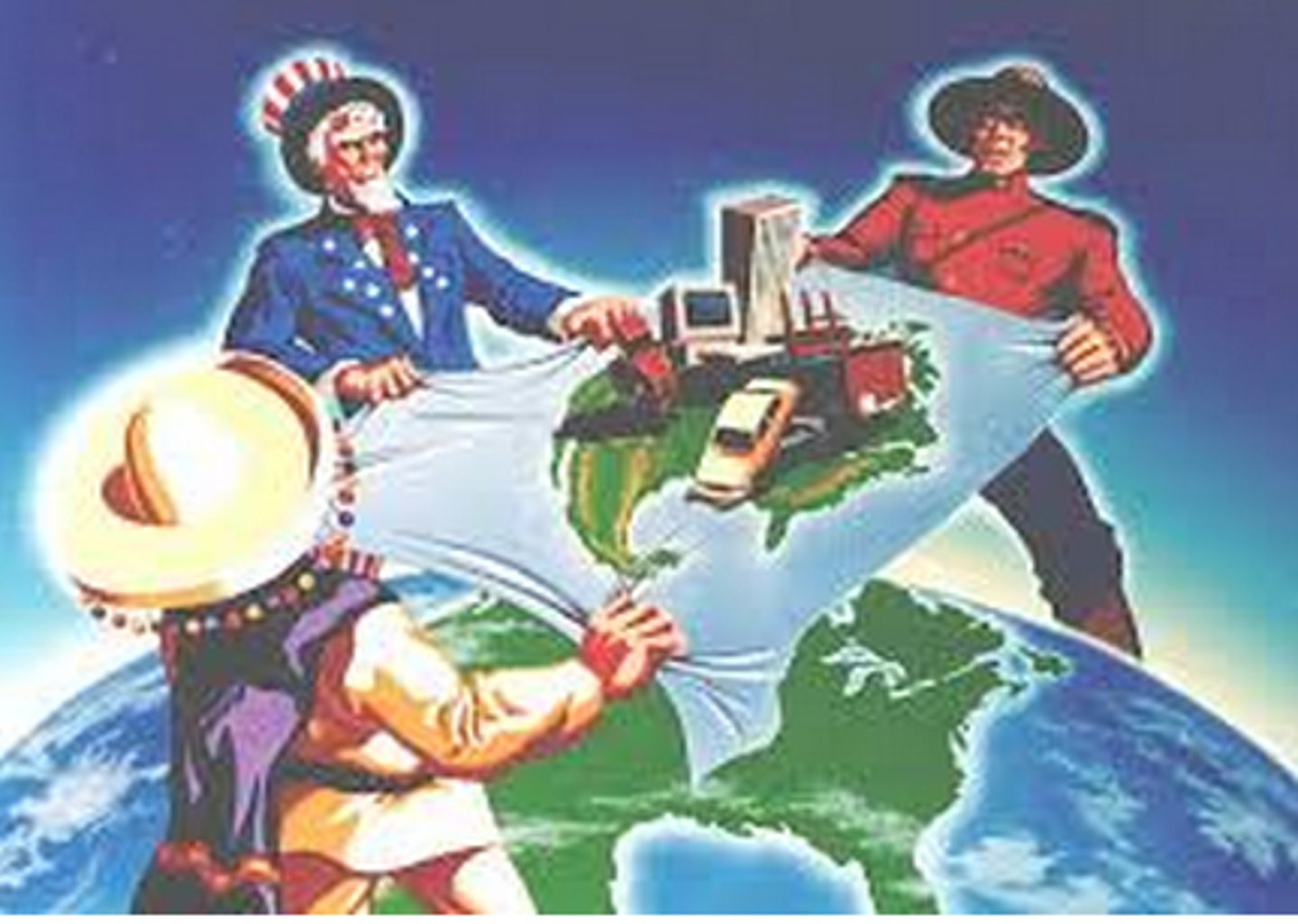
North American Free Trade Agreement
NAFTA; regional alliance founded in 1993 and consists of Canada, Mexico, and the United States; the world's second largest free-trade zone
North Atlantic Treaty Organization
NATO; a military alliance based on the North Atlantic Treaty which was signed in 1949; alliance in which its member states agree to mutual defense in response to an attack by any external party; consists of 28 member states across North America and Europe

non-governmental organization
NGO; an organization that is neither a part of a government nor a conventional for-profit business

HIV/AIDS epidemic
epidemic which was first discovered in 1981 among homosexual men and intravenous drug users in New York and San Francisco; eventually became widespread around the world, particularly sub-Saharan Africa; virus attacks and destroys the immune system, which causes a fatal disorder in the immune system; spread through sexual contact with an infected person, contact with contaminated blood, and transmission from mother to child
during pregnancy and breastfeeding
ebola epidemic
an epidemic caused by the Ebola virus; symptoms include fever, throat and muscle pains, headaches, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea, and decreased functioning of the liver and kidneys; an 2014 outbreak in West Africa has led to a reported 142 deaths
influenza epidemic
an epidemic caused by the H1N1 influenza virus; lasted from 1918 to 1920; resulted in 50 to 100 million deaths, ranking it one of the most deadliest natural disasters in human history
post-modernism
a late 20th Century movement in the arts, architecture, and criticism; includes skeptical interpretations of culture, literature, art, philosophy, history, economics, architecture, fiction, and literary criticism
second-wave feminism
a period of feminist activity that first began in the United States in the early 1960s and eventually spread throughout the Western world; later became a worldwide movement that was strong in Europe and parts of Asia, such as Turkey and Israel; focused on sexuality, family, the workplace, reproductive rights, and various legal and de facto inequalities

UN Security Council
one of the six principal organs of the United Nations; in charge of the maintenance of international peace and security; this body is able to establish peacekeeping operations, establish international sanctions, and authorize military action through resolutions; the only UN body with the authority to issue binding resolutions to member states

theory of relativity
theory which is composed of special relativity and general relativity; proposed by Albert Einstein; proposes that measurements of various quantities are relative to the velocities of observers, space and time should be considered together and in relation to each other (Spacetime), and the speed of light is constant
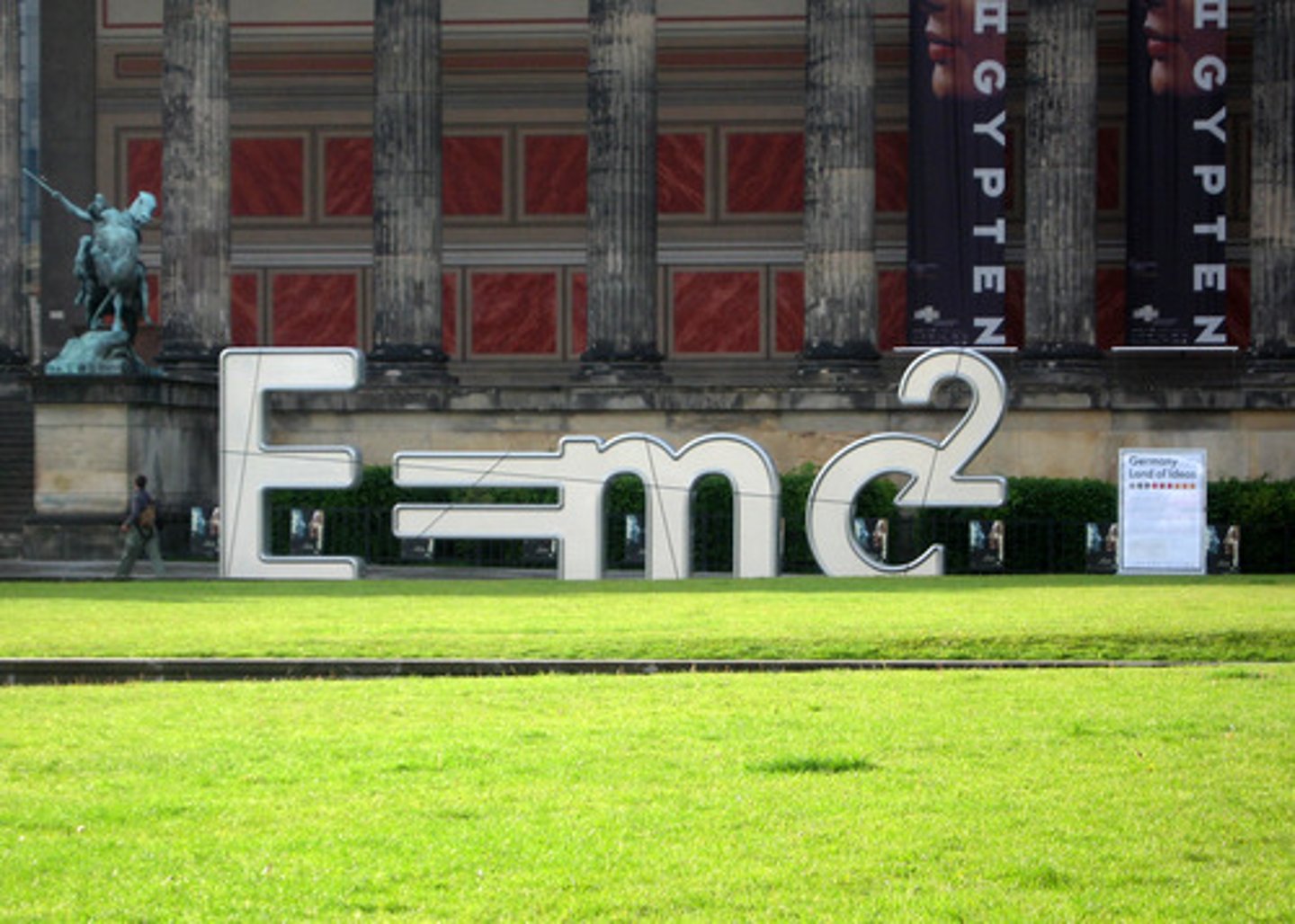
Third World
term which describes the countries that did not align with the Soviet Union or the United States
transnational corporations
a.k.a multi-national corporation; an organization that owns or controls production or services facilities in one or more countries other than its home country

United Nations
organization established in 1945 as a successor to the League of Nations; attempts to find solutions to global problems and deal with virtually any matter of concern to humanity

weapon of mass destruction
WMD; a weapon which has the capability to kill large numbers of people and decimate large swaths of land

World Bank
a United Nations international financial institution that provides loans to developing countries for capital programs; its primary goal is to reduce poverty

World Trade Organization
WTO; established in 1994 by the 123 members of GATT; took over GATT activities in 1995; developed into a forum for settling international trade disputes

nongovernmental organizations
Organizations that are not established or associated with any specific organizations. They may be recognized, however, they run on their own. Examples are Green Peace and Amnesty International.

NATO
An international organization created in 1949 by the North Atlantic Treaty for purposes of collective security.

Women's Rights and Fertility
more effective forms of birth control and greater control over fertility have led to declining rates of fertility in much of the world
Diseases associated with poverty
malaria, tuberculosis, cholera have had significant effects on populations around the world.
Debates about the environment
deforestation, desertification, decline in supply of fresh water have led to humans competing for resources more intensely than before
Greenhouse gases
Gases such as carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, water vapor, and ozone in the atmosphere which are involved in the greenhouse effect. These have caused climate change around teh world
Knowledge Economies
an economy in which growth is dependent on the quantity, quality, and accessibility of the information available, rather than the means of production.
examples) Japan, US, Finland

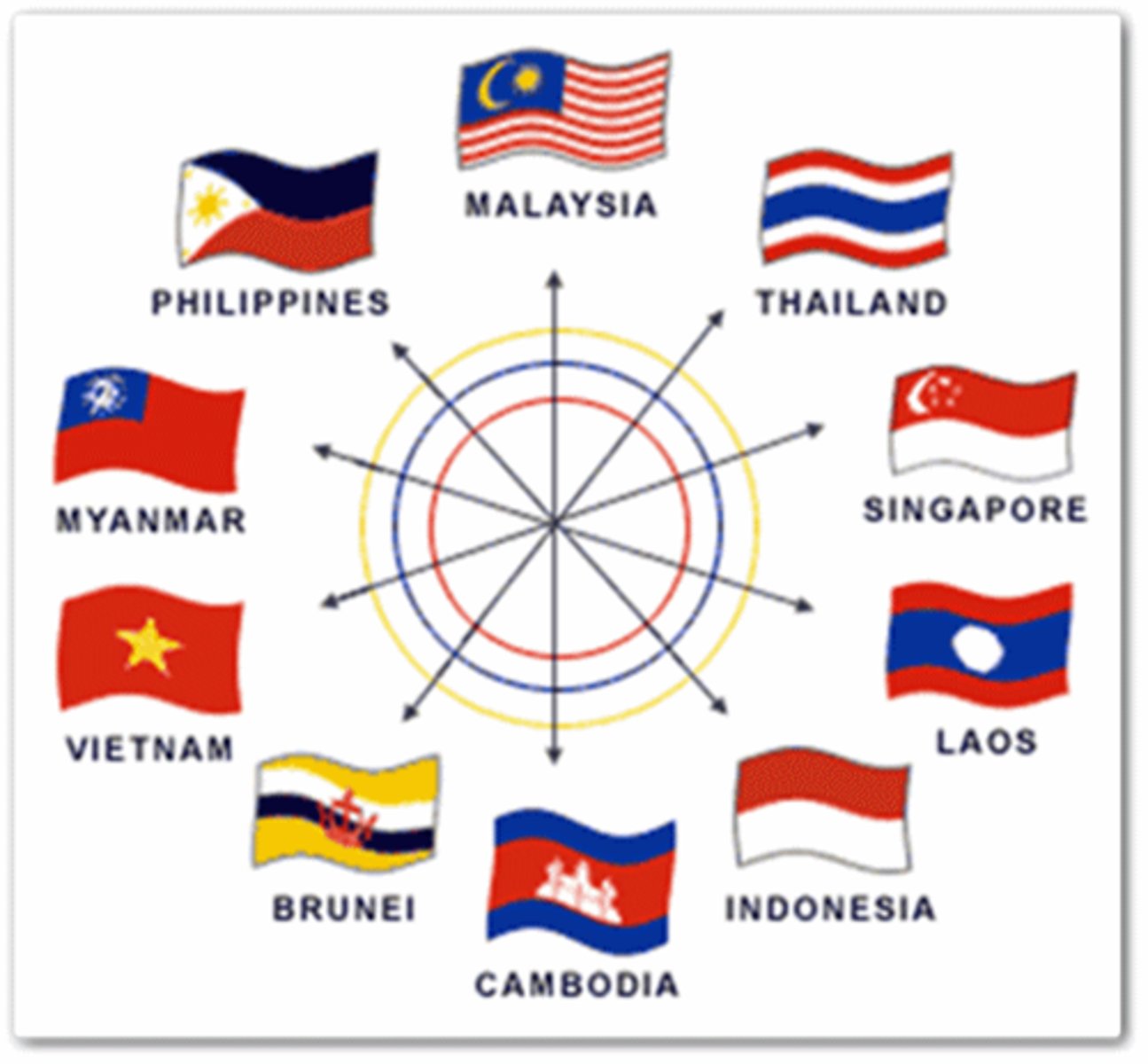
Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN)
a trade alliance that promotes trade and economic integration among member nations in Southeast Asia
Economic LIberalization
Changes consistent with liberalism that aim to limit the power of the state and increase the power of the market and private property in an economy
examples) US under Ronald Reagan
Britain under Margaret Thatcher
China under Deng Xiaoping
Chile under Augusto Pinochet

Manufacturing economies
increasingly industrial production has been moved in Asia and Latin America as other nations turn to knowledge based economies
Asia examples--Vietnam, Bangladesh
Latin America--Mexico, Honduras

UN Universal Declaration of Human Rights
• International declaration of human right. this declaration was the first basic document to outline "human rights".it was passed by the united nations in 1948 and announced " a common standard of achievement for all people and nations". sought to protect women, children, and refugees

Negritude Movement
movement in which writers and artists of African descent expressed pride in their African heritage
Liberation theology
a movement within the Catholic church to understand Christianity from the perspective of the poor and oppressed, with a focus on fighting injustice
Global Feminism
women living in low-income nations of the world experience gender inequality and a disadvantaged position in the global economic system
US Civil Rights Act of 1965
social movements in the U.S. where they want to end segregation and discrimination against blacks and it helps secure and protect the rights of citizens and citizenship within the laws

apartheid
Laws (no longer in effect) in South Africa that physically separated different races into different geographic areas.

Greenpeace
an international organization that works for environmental conservation and the preservation of endangered species

Greenbelt Movement
is an indigenous grassroots non-governmental organisation based in Nairobi, Kenya that takes a holistic approach to development by focusing on environmental conservation, community development and capacity building. created by Professor Wangari Maathai in Kenya

World Fair Trade Organization (WFTO)
is a global network of fair trade organizations and a resources for locating vendors and products- create opportunities for economically disadvantaged producers, develop producers independence, fair pricing, gender equity, safe working environments and practices
Global Culture
behavioral standards, symbols, values, and material objects that have become common across the globe
examples--Reggae, Bollywood, Facebook, Twitter, BBC, World Cup Soccer, The Olympics

Global Consumerism
Online Commerce---alibaba, ebay
global brands--Toyota, Coca-Cola
Chinese Twitter; regulated by government one response to globalization is local social media such as this site

Resistance to Globalization
Responses to rising cultural and economic globalization has led to anti-IMF and anti-World Bank Protests
Globalization
Actions or processes that involve the entire world and result in making something worldwide in scope.

Colonial Metropole
area of a nation where formerly colonized peoples move to as part of an immigration pattern
ex) Southeast Asian moving to Great Britain