CHEM 108: Extra - Electrochemistry and Nuclear Chemistry
1/76
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
electrochemistry
the branch of chemistry that examines the transformations between chemical and electrical energy
redox reactions
reactions in which a substance gains or loses electrons
oxidation
occurs when an atom’s oxidation state increases during a reaction (gain electrons)
reduction
occurs when an atom’s oxidation state decreases during a reaction (lose electrons)
reducing agent
reactant that reduces an element, contains the element that is oxidized
oxidizing agent
reactant that oxidizes an element, contains the element that is reduced ele
electrochemical cell
apparatus that converts chemical energy into electrical work or electrical work into chemical energy
cell diagram
symbols that show how the components of an electrochemical cell are connected
electrodes
surfaces for exchange of electrons
anode
electrode at which an oxidation occurs
cathode
electrode at which a reduction occurs
current
the number of electrons that flow through the system per second
unit for current
ampere
1 A
6.242e18 electrons per second
electrode surface area dictates
the number of electrons that can flow
larger batteries produce
larger currents
potential difference
difference in potential energy between reactants and products
electromotive force
amount of force pushing the electrons through the wire
cell potential
the difference in potential energy between the anode and the cathode in a voltaic cell
cell potential depends on
relative ease of reduction and oxidation
standard reduction potential
potential of a reduction in half-reaction in which all reactants/products are in standard states
standard cell potential
measure of how forcefully an electrochemical cell can pump electrons through an external circuit
electrical work
charge x potential difference
voltaic cell
electrochemical cell in which chemical energy is transformed into electrical energy by a spontaneous redox reaction
Ecell
cathode - anode
Standard Hydrogen Electrode (SHE)
given value of 0V, all half cell potentials are measured relative to SHE
positive cell voltages give
negative delta G values, spontaneous redox reactions
strongest oxidizing agents
largest E cell values
strongest reducing agent
most negative E cell value
free energy and Ecell formula
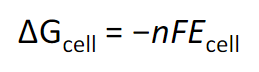
Faraday’s constant
96500 C
what kind of variable is Ecell?
intensive variable
what kind of variable is delta G?
extensive variable
concentration cells
it is possible to get a spontaneous reaction when the oxidation and reduction reactions are the same, as long as the electrolyte concentrations are different
direction of electrons flow in an electrode
less concentrated solution to a more concentrated solution
less concentrated solution
has the anode
more concentrated solution
has the anode
nernst equation
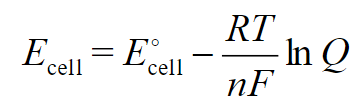
electrolysis
process in which electrical energy drives a nonspontaneous chemical reaction
electrolytic cell
device in which an external source of electrical energy does work on a chemical system, turning reactants into higher-energy products
nucleon
protons, neutrons
nuclide
any particular nucleus
atomic number (Z)
number of protons, nuclear charge
atomic mass (A)
number of protons and number of neutrons
isotopes
atoms whose nuclei have the same Z but different A
nuclear chemistry
the study of reactions that involve changes in the nuclei of atoms
radioactive decay
the spontaneous disintegration of unstable particles accompanied by the release of radiation
nuclear reaction
involves nuclei - mass number and atomic number must be balanced
alpha rays
positively charged
beta rays
negatively charged
gamma rays
neutral
antimatter
particles that are charge opposites of normal subatomic particles
annihilation
result of a collision of matter/antimatter particles
alpha emission
emission of helium nucleus - decrease atomic number by 2, decrease mass number by 4
gamma emission
emission of photon from nucleus
beta emission
emission of electron from the nucleus - increase atomic number by 1
positron emission
emission of positively-charged electron from a nucleus - decrease atomic number by 1
electron capture
reaction of proton and electron - atomic number decreases by 1
radioactive decay formula
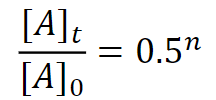
magic numbers
numbers of nuclear particles in a completed shell of protons or neutrons
magic numbers for protons
2, 8, 20, 28, 50, and 82
magic numbers for neutrons
2, 8, 20, 28, 50, 82, and 126
belt of stability
region on a graph of the number of neutrons vs. number of protons that includes all stable nuclei
neutron rich
undergo beta decay
neutron poor
undergo positron decay or electron capture
lighter elements
fusion
heavier elements
fissionn
nuclear fusion
nuclear reaction in which sub-atomic particles or atomic nuclei collide and fuse together, forming more massive nuclei and releasing energy
energy released from the formation of a single helium nucleus
-3.955e-12 J
mass defect formula
mass of products - mass of reactants
binding energy
the energy release when nucleons combine to form a nucleus
EINSTEIN’S EQUATION
fus
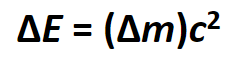
fusion reactors
high-temperature reactions between deuterium and tritium
tokamak
high-temperature reactions produce an incandescent plasma which is contained by strong magnetic fields
nuclear fission
nuclear reaction in which a heavy nucleus splits into two lighter nuclei, accompanied by the release of one or more neutrons
chain reactions
a self-sustaining series of fission reactions in which neutrons released when nuclei split apart initiate additional fission events
critical mass
the minimum amount of fissionable material needed to sustain a chain reaction