ucla phleb session 3
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
What are the advantages of using the evacuated tube method or straight method? (3 reasons)
Double sided, can collect more than one tube, and faster
What does a double sided needle mean?
One side punctures the vein, the other side punctures the tube
What is the common gauge of the evacuated tube method or straight method?
21G
How many times must tubes be inverted and at what degree?
8-10 times at 180 degrees
ensures additives are properly mixed and to prevent clotting
How can you tell that you are in the vein when using the winged infusion set or butterfly method?
Flash
small amount of blood appears in tubing
What is a disadvantage of using the winged infusion set or butterfly method? (3 reasons)
Needlestick injuries, more expensive, slower
What population commonly requires the winged infusion set or butterfly method?
Pediatric and geriatric patients
What is the common gauge for the winged infusion set or butterfly method?
23G
What type of needle does the syringe method use?
Hypodermic needle
What is an advantage of the syringe method? (1 reason)
Controlled vacuum
What population commonly requires the syringe method?
Geriatric or patients who have fragile and weak veins that tend to collapse
What is the common gauge for the syringe method?
21G
What is the process of blood collection and transfer for the syringe method? (3 steps)
Blood enters the graduated barrel → Blood vacuumed by plunger → Blood transfer device transfer blood into tube from syringe
What antiseptic is used to clean the site before a routine venipuncture?
70% isopropyl alcohol
How are antiseptics applied to clean the site?
Scrub up and down and allow to air dry for 30 sec
What is the difference between a hub and a blood transfer device?
Blood transfer device already has a permanent needle and rubber sleeve
What area should be tried before the basilic vein and at what degree should the needle be inserted?
Dorsal hand at 10 degrees
What is the purpose of preservatives?
Slows down metabolic activity of cells and makes sample last longer
What is plasma?
Cell-free liquid part of blood that has been treated with anticoagulant
What makes up the buffy coat?
WBCs and platelets, makes up <1%
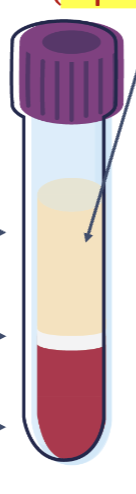
Name the portions of this plasma tube from top to bottom.
Plasma → Buffy coat → RBCs
What is serum?
Liquid part of blood after coagulation
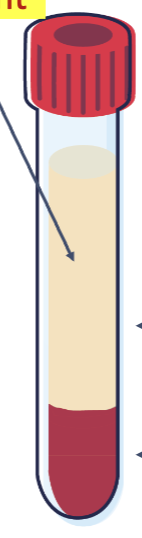
Name the portions of this serum tube from top to bottom.
Serum → Clot
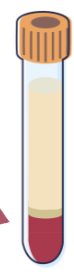
Name the portions of this serum tube from top to bottom.
Serum → Gel → Clot
What does supernatant mean?
Liquid
The supernate of a lavender top tube is what?
Plasma
The order of draw is determined by which organization?
CLSI
What is the order of draw?
Blood cultures (aerobic first) → Light blue → Serum (red, gold, tiger) → Light green → Dark green → Lavender → Gray
What department do blood cultures bottles go to?
Microbiology
Besides 2 bottles, what is another option for blood culture bottles?
SPS; sodium polyanethol sulfanate yellow tubes
What method should be used for blood culture bottles?
Butterfly method
What antiseptic is used for a blood culture sample?
Chlorhexidene (Chloraprep)
How many mL is required for each blood culture bottle?
10mL each
What anticoagulant is in the light blue tube?
Sodium citrate
What department does the light blue tube go to?
Coagulation
What tests are commonly requested for light blue tubes?
PT (prothrombin time), aPTT (activated partial thromboplastin time)
The blood to additive ratio of 9:1 is required for specimen collected in what tube?
Light blue
How many times must the light blue tube be inverted?
3-4 times
Which tube is the discard tube?
Red top

Is a discard tube needed?
No

Is a discard tube needed?
Yes
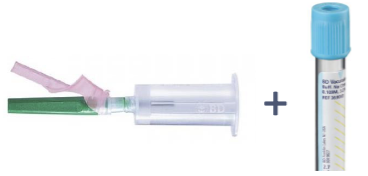
Is a discard tube needed?
No
Which tubes are SST (serum separator tube)?
Gold and Tiger
Which tubes are PST (plasma separator tube)?
Light and Dark Green
Which department do the green tubes go to?
Chemistry
What anticoagulant is in the light green tube and what does it test for?
Lithium heparin. Tests for sodium level/electrolytes
What anticoagulant is in the dark green tube and what does it test for?
Sodium heparin. Tests for lithium level/Vitamin B1
What anticoagulant is in the lavender tube?
EDTA
Which tube preserves blood cell morphology and platelet aggregation/clotting?
Lavender
What department does the lavender tube go to?
Hematology
What 3 commonly requested tests are ordered for lavender tube?
CBC (complete blood count), WSR (Westergren Sedimentation Rate), ESR (Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate)
Which tube should NOT be centrifuged?
Lavender
What anticoagulant is in the gray tube and what is its mode of action?
Potassium oxalate; binds to Calcium
What preservative is in the gray tube and what is its mode of action?
Sodium fluoride; inhibits glycolytic activity
What antiseptic is used to clean site for gray tube sample collection?
Povidone iodine
Which tests are performed for the gray tube and what department do they go to?
Glucose testing goes to Chemistry, EtOH goes to Toxicology
Why do we need to draw blood? (2 reasons)
Information about bodily functions, Blood analysis of information received
What should a blood draw always begin with?
Requisition
What does LIS stand for?
Laboratory Information System
What is the most important task does the phlebotomist perform?
Identification of patient
According to the Joint Commission, the patient must be identified using at least __ identifiers?
2
If the patient is unconscious how should you verify ID?
Verify ID with nurse/relative/physician
What form of identification do patients in the emergency department have?
Temporary ID bands
What should be done if the patient is out of the room?
Document and inform the nurse