Light and the Electromagnetic Spectrum
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
What is refraction?
When waves pass from one medium to another it changes speed and wavelength.
How does refraction of a wave affect its speed?
Refraction can decrease a wave's speed if it enters a denser medium, or increase it if it enters a less dense medium
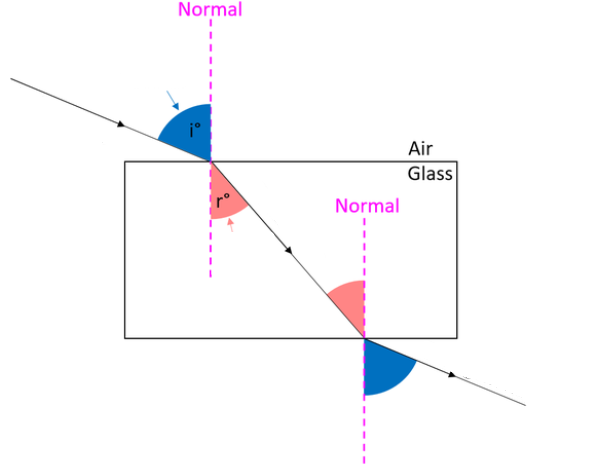
Which is the angle of incidence, angle of refraction and normal?
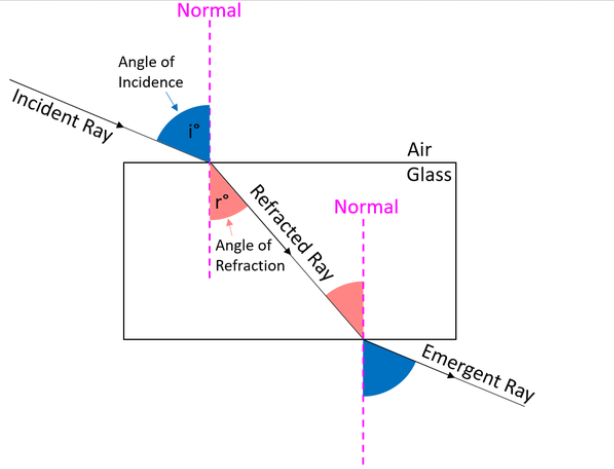
What is the angle of incidence?
The angle between the normal and the ray of light
What is the angle of refraction?
The angle between the normal and the refracted ray
What is the normal?
A line drawn at a 90-degree angle to a surface
How can we determine the angles of incidence and refraction of light?
In an experiment, a protractor is used to measure the angle between the incident ray and the normal (angle of incidence), and between the refracted ray and the normal (angle of refraction).
What does a light ray look like travelling from a thinner medium to a thicker medium and out the other side.
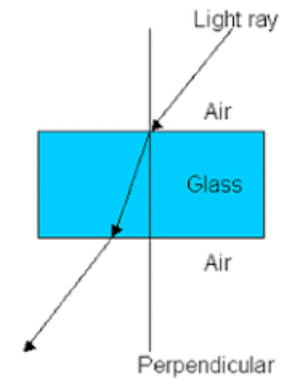
Everyday applications of refraction?
Eyeglasses
Cameras
Telescopes
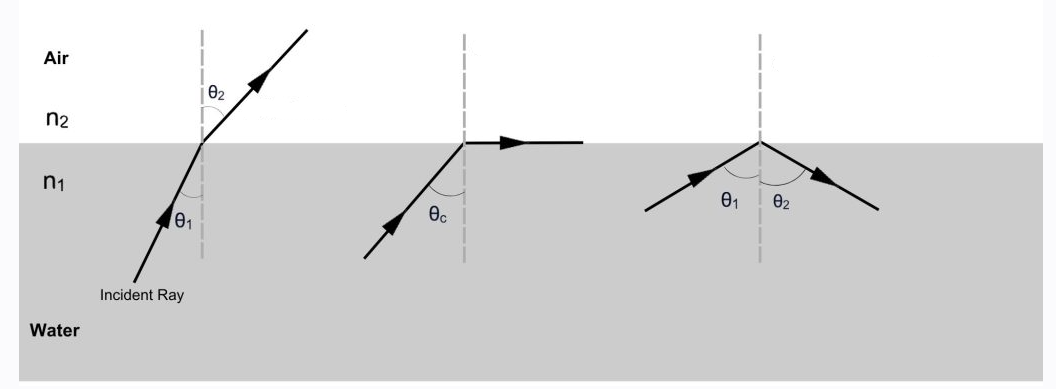
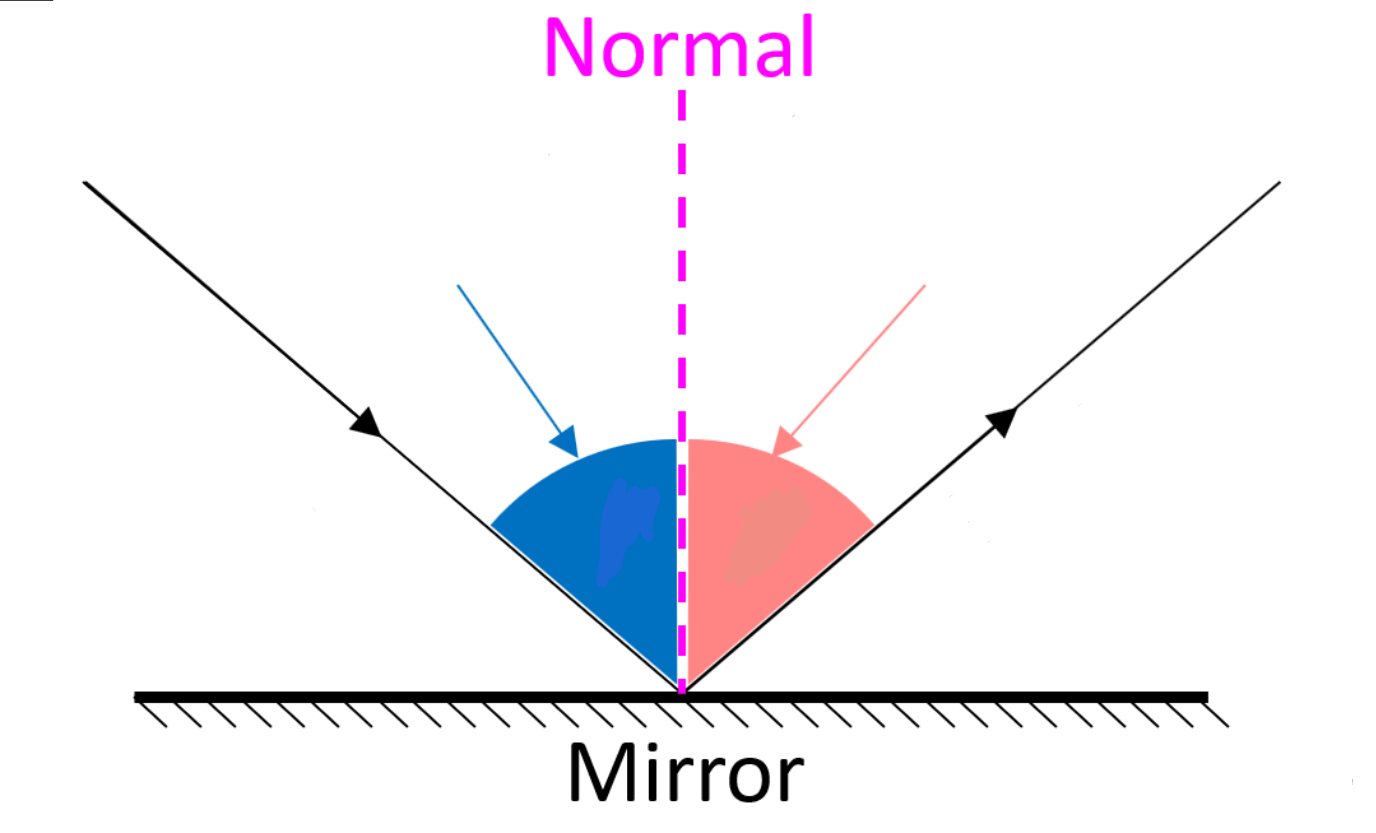
Label which kinds of angles are these?
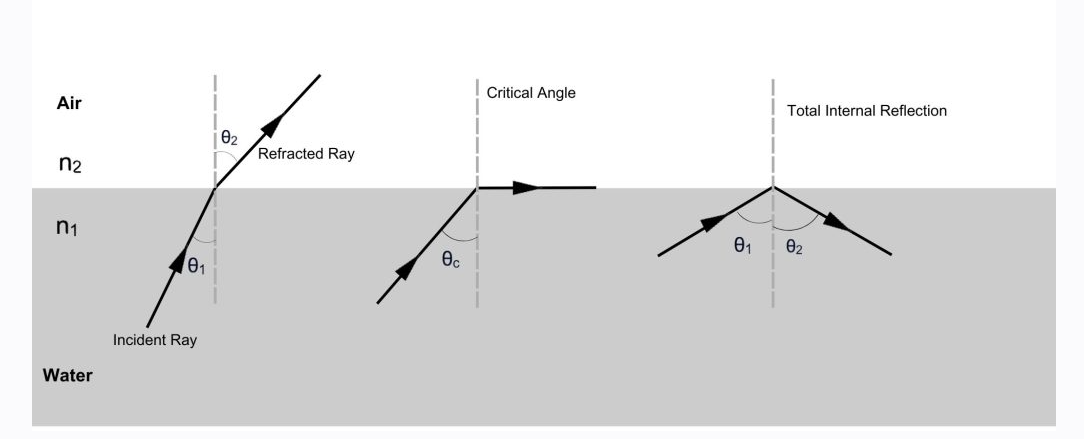
How do you measure the critical angle of light through a different medium

What does long sight (hyperopia) mean?
Naturally, the image focuses behind on the retina, the convex lens closes the rays so that it focuses on the retina
What does short sight (myopia) mean?
Naturally, the image focuses on the front of the retina. The concave lens spaces out the rays so it focuses better on the retina.
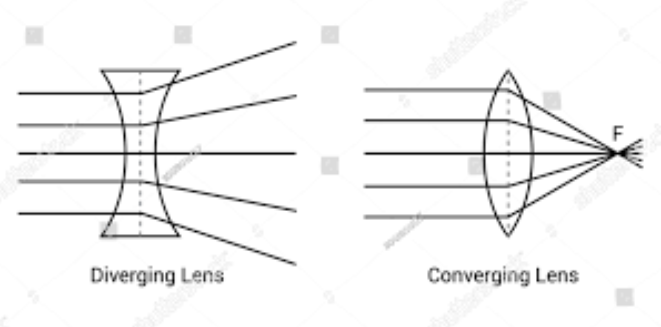
A diagram that shows the effects of converging and diverging lens
What speed do all radiations of the electromagnetic spectrum?
3×10^8m/s
What is a convex lens, what does it do and what is its focal length?
Converges light (brings the rays together). Positive
What is a concave lens, what does it do and what is its focal length?
Diverges the light (spreads the rays) negative
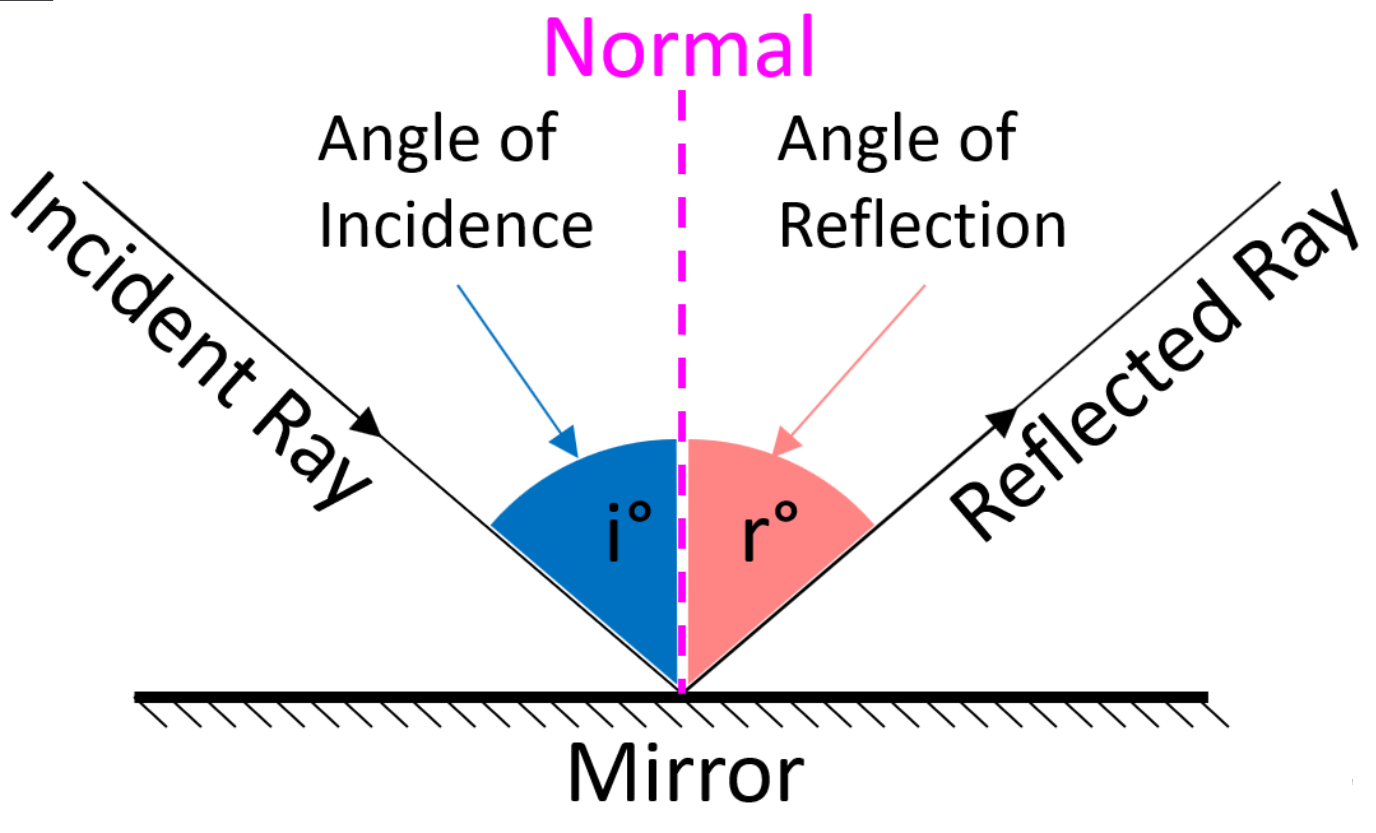
What is this diagram and example of and label the missing parts.
Notice how the angle of incidence and angle of refraction are equal?
Explain why refraction in a prism looks the way it does.
Refraction in a prism occurs when light bends as it enters and exits the prism, causing white light to split into a spectrum of colors (dispersion). This happens because each color (wavelength) of light bends at a slightly different angle, with shorter wavelengths like violet bending the most and longer wavelengths like red bending the least.
Based of the prism example, which color refracts the most?
Violet light
Based of the prism example, which color refracts the least?
Red light