Sequential Bayesian Interference
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
What is an estimator?
A computed value used to estimate a population parameter.
Example: Sample mean estimates true average salary
Variance
Variability of estimator around its expectation (remember spread on each side of a mean)
Robustness
Resistance to outliers and bad data.
Sequential Bayesian inference
Use posterior from one update as the prior for the next.
Example: Weather apps updating forecast as new sensor data arrives.
Conjugate priors
Posterior has same form as prior
Why conjugates are useful
Enables fast/analytical Bayesian updates.
Example: Quality control line updating defect rate in real time.
Markov property
Next state depends only on current, not full history.
Analogy: Chess knight moves - only board position matters, not how it got there.
Transition matrix
Probability from state i → j
Web surfing model: probability of clicking links between pages.
Under what condition are two events, A and B, said to be 'conditionally independent' given a third event, C?
They are conditionally independent if P(A∣B∩C)=P(A∣C).
What is the practical advantage of using a conjugate prior in Bayesian calculations?
They are very useful for simplifying Bayesian calculations, as the form of the posterior distribution is known in advance.
What defines the 'stationary distribution' of a Markov chain?
It is a probability distribution that remains unchanged when the transition matrix is applied to it.
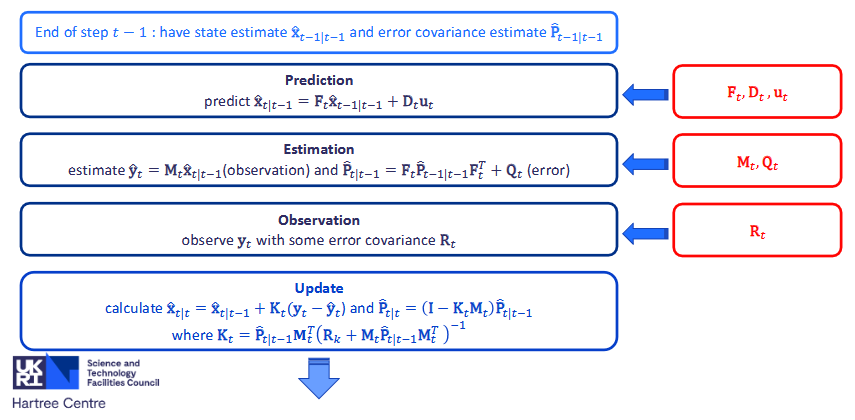
Key Process for Kalman Filter
Prediction - Estimation - Observation - Update