Chem PPQ got wrong
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms


Give a chemical explanation for why a carton of milk expands on freezing
The hydrogen bonds in ice hold H2O molecules further apart (than in water)
Give a chemical explanation for why potassium is placed immediately after argon in the periodic table
Potassium atoms have 1 more proton than argon
Give a chemical explanation for why the reaction of ethane with chlorine under UV radiation is a poor method for preparing a high yield of chloroethane
Further substitution occurs
Give a chemical explanation for the concentration of water being 56moldm-3
1dm3 water has a mass of 1000g
n(H2O) in 1dm3 = 1000/18 approx 56mol
Give a chemical explanation why the C-C bonds in benzene are all the same length
The pi bonds in benzene are delocalised
Give a chemical explanation for why the rate of hydrolysis of 1-bromobutane is faster than that of 1-chloro-butane
The C-Br bond is weaker (than the C-Cl)
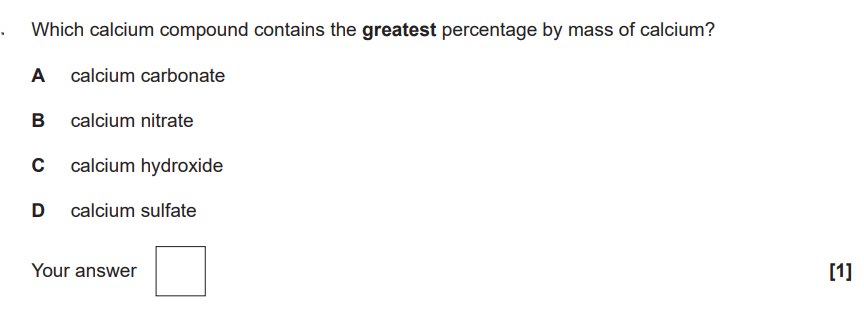
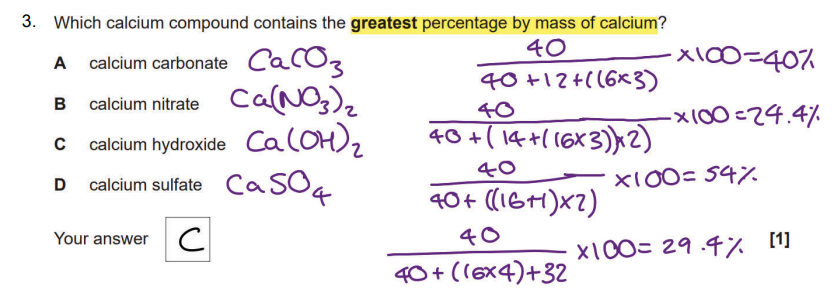

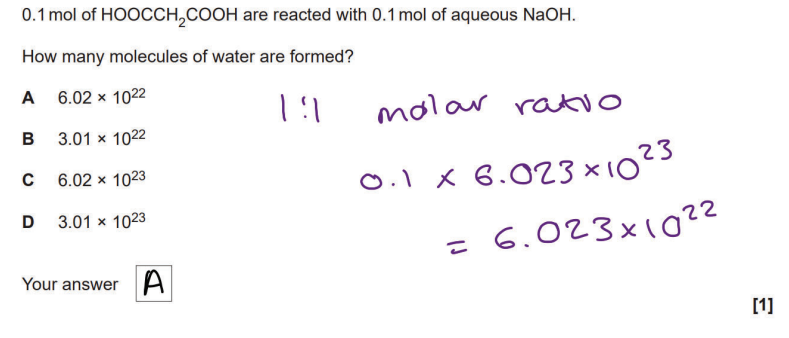
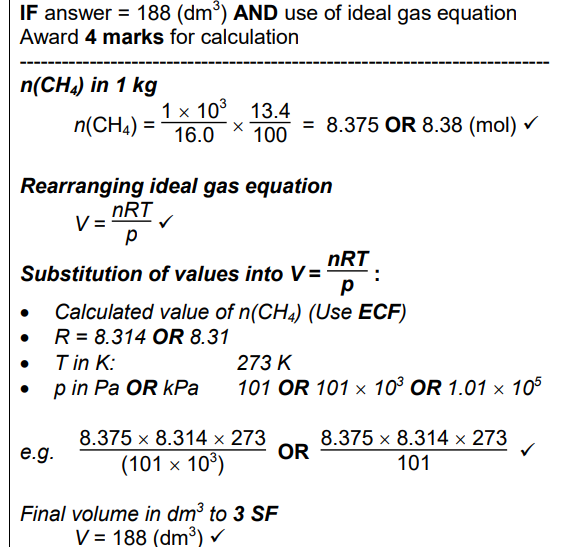
Within the permafrost in Arctic regions of the Earth, large amounts of methane are trapped within ice as ‘methane hydrate’, CH4•xH2O. Methane makes up about 13.4% of the mass of ‘methane hydrate’. Scientists are concerned that global warming will melt the permafrost, releasing large quantities of methane into the atmosphere. (a) The H–O–H bond angle in ice is about 109° but about 105° in gaseous H2O. Explain why there is this difference. (3)
Ice has hydrogen bonds/bonding
H2O(g) has 2 bonded pairs and 2 lone pairs
lone pairs repel more than bonded pairs
Within the permafrost in Arctic regions of the Earth, large amounts of methane are trapped within ice as ‘methane hydrate’, CH4•xH2O. Methane makes up about 13.4% of the mass of ‘methane hydrate’. Scientists are concerned that global warming will melt the permafrost, releasing large quantities of methane into the atmosphere.Determine the formula of ‘methane hydrate’, CH4•xH2O. In the formula, show the value of x to two decimal places

Within the permafrost in Arctic regions of the Earth, large amounts of methane are trapped within ice as ‘methane hydrate’, CH4•xH2O. Methane makes up about 13.4% of the mass of ‘methane hydrate’. Scientists are concerned that global warming will melt the permafrost, releasing large quantities of methane into the atmosphere.
Calculate the volume of methane, in dm3, that would be released from the melting of each 1.00 kg of ‘methane hydrate’ at 101 kPa and 0 °C. Give your answer to three significant figures. (4)





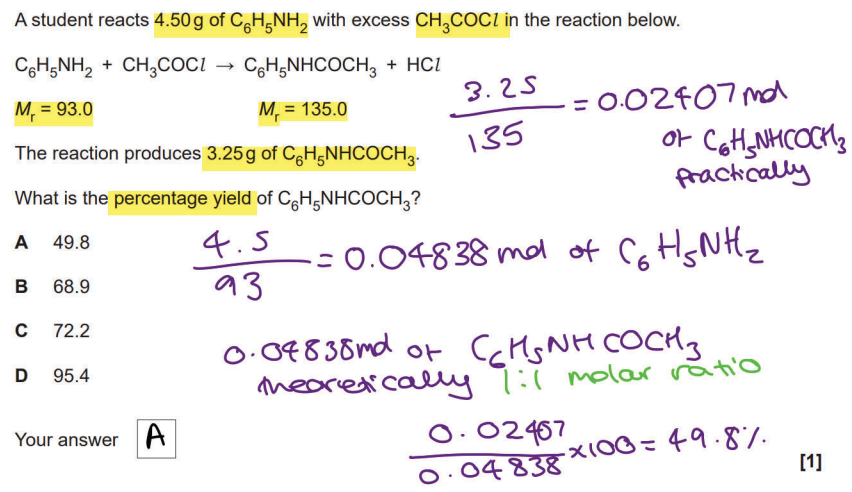
Explain why a CF4 molecule has polar bonds but does not have an overall dipole.
F atom is more electronegative than C atom OR F is very/the most electronegative
No overall dipole - CF4 is symmetrical OR tetrahedral OR dipoles cancel OR dipoles act in opposite directions
Explain why a small proportion of molecules in water have a relative molecular mass of 20.

What mass of carbon dioxide (in g) is formed by the complete combustion of 42.0 m3 (measured at RTP) of propane?

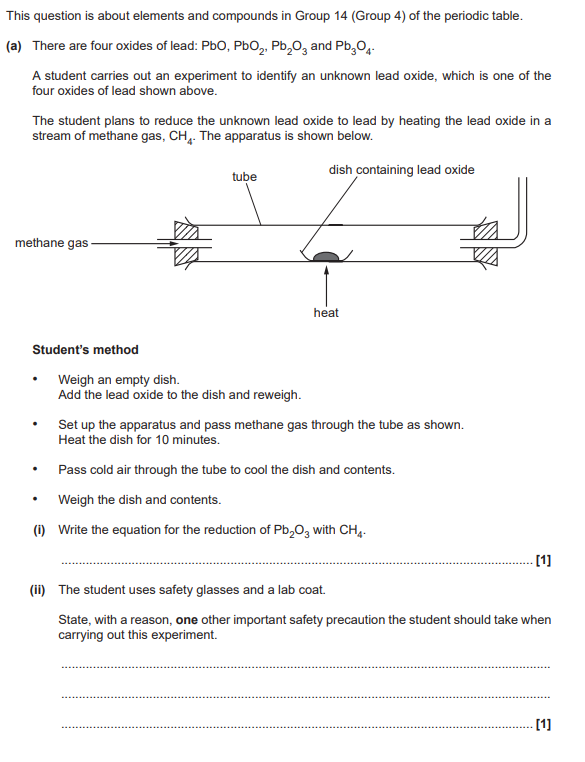


Ignore (i) and (ii)
The student was not sure that all the oxygen had been removed from the lead oxide.
Suggest two modifications that the student could make to their method to be confident
that all the oxygen had been removed. Explain your reasoning.


State 2 limitations of using radical substitution in organic synthesis
further substitutions
produces different termination products
more than one termination step
mixture of products are formed
substitution at different positions along the chain
D


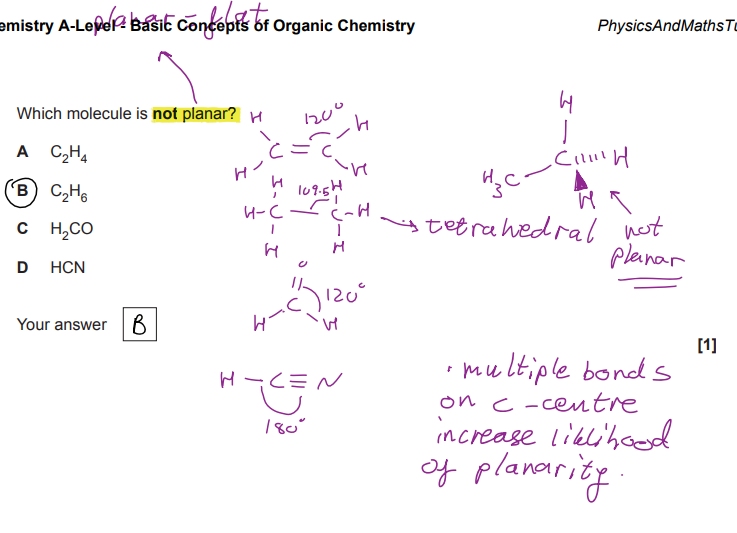
What does the curly arrows show in a reaction mechnism?
The movement of an electron pair
What is meant by heterolytic fission?
heterolytics
one bonded atom receives both/2 electrons.
fision
breaking of a covalent bond

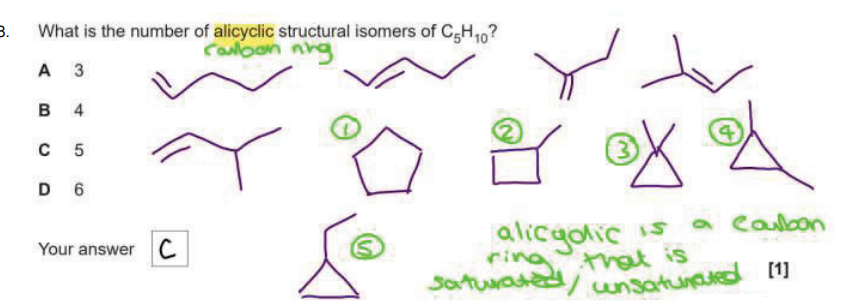



What is meant by structural isomers?
Compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural formula
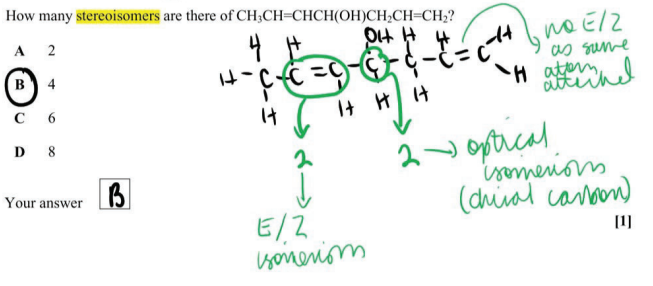
just b (4)
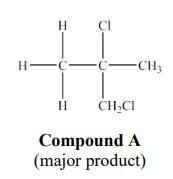
Why is this a minor product?
Because the intermediate/carbocation in the formation of compound B is less stable than the intermediate in the formation of compound A
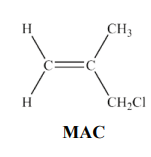
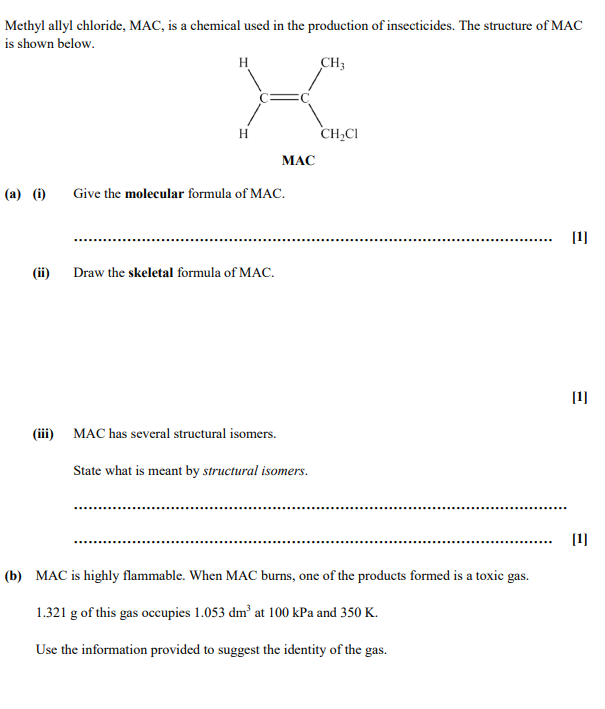
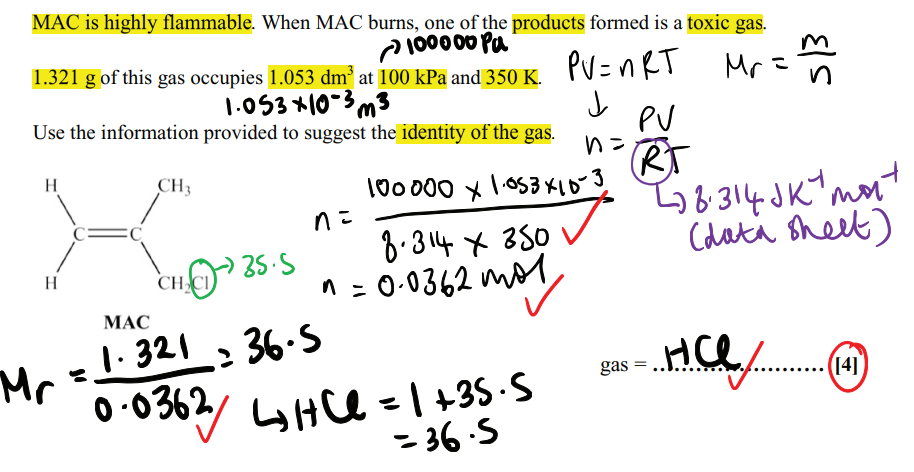
MAC reacts with water in the presence of AgNO3(aq) and ethanol. Draw the structure of the organic product of this reaction. State what you would observe in this reaction and identify the compound responsible for the observation.
Formation of white precipitate/solid/suspension and precipitate is silver chloride AgCl

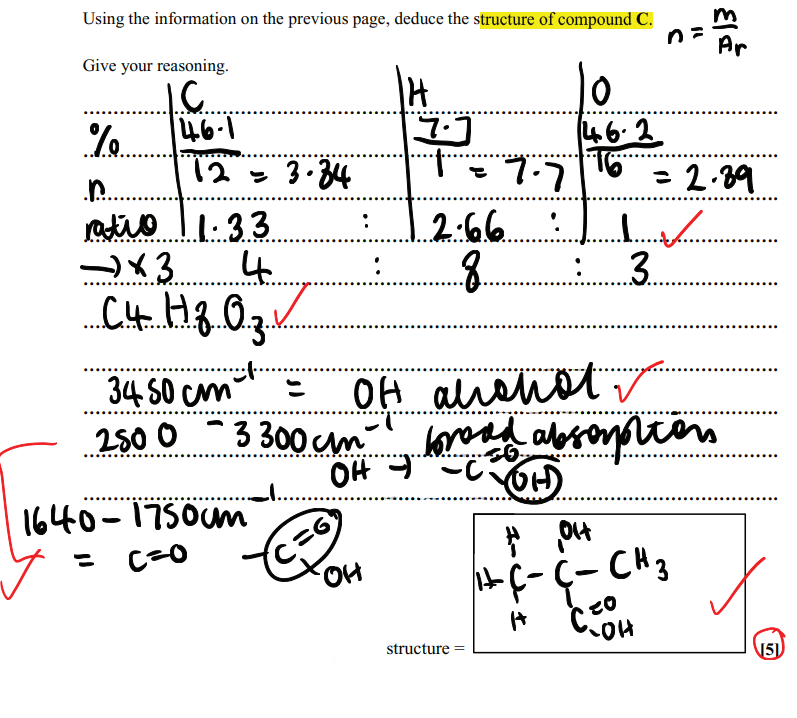
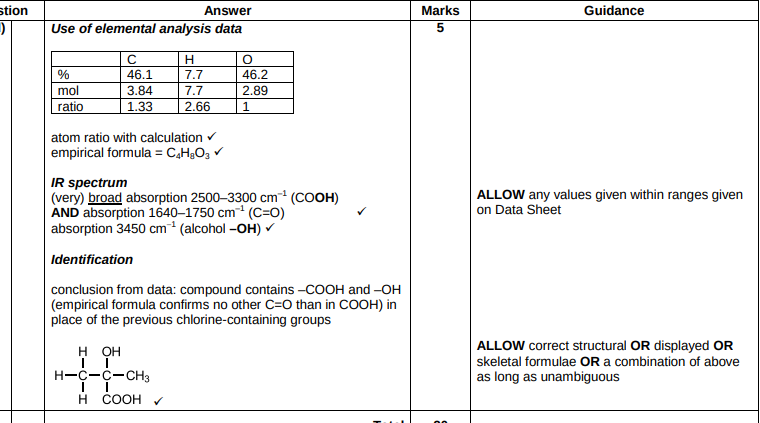
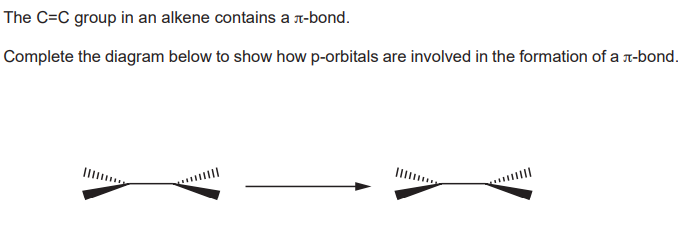
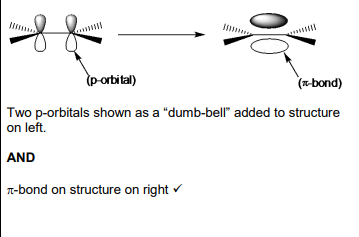
Suggest how HBr molecule can act as an electrophile
(The H atom of HBr) accepts a pair of electrons
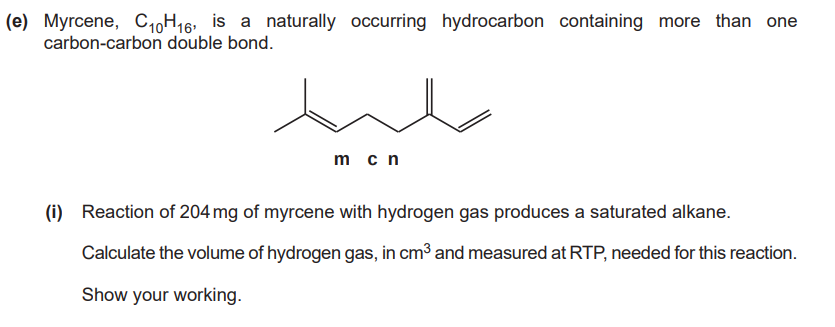


(4)
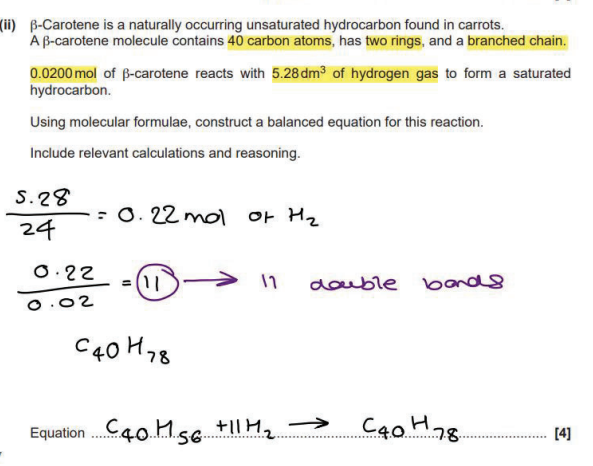
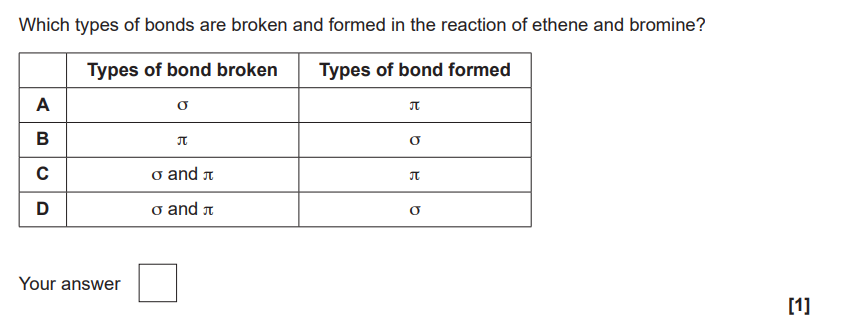
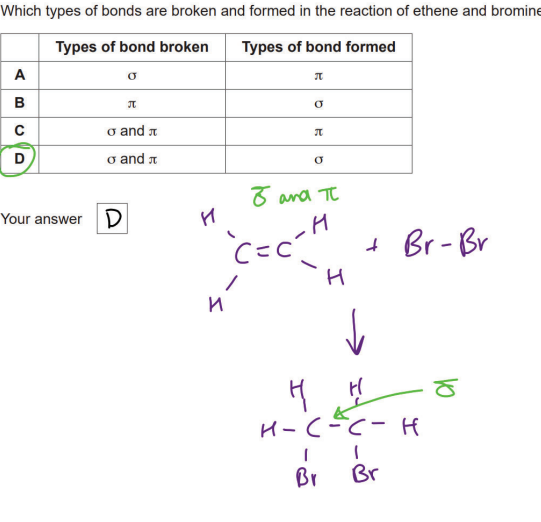
Why are silicon, carbon, oxygen and chlorine all classified as p-block elements?
Their highest energy electrons are in a p-orbital/p sub’shell
How could a student who has reacted magnesium with phosphoric acid obtain a sample of magnesium phosphate (hint: looking for how to get pure sample not how to get product)
Separation of solid
filter to obtain solid/precipitate
requires realisation that solid is filtered off
solid may be stated within ‘removal of water’
Removal of water
dry (solid)
OR evaporate (water/solution/liquid)
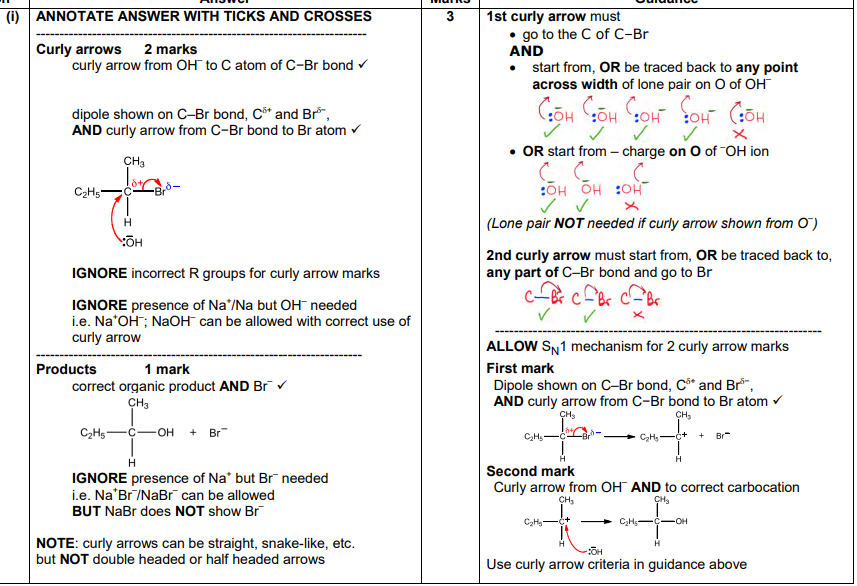
An alcohol can be prepared by hydrolysing the haloalkane C2H5CHBrCH3 with aq sodium hydroxide
outline the mechanism for this reaction
show curly arrows and relevant dipoles

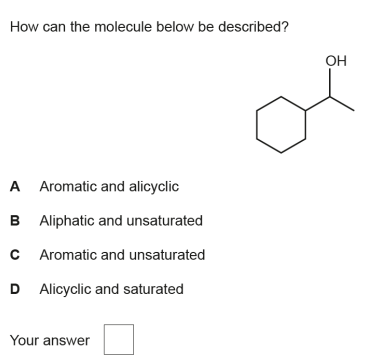
C
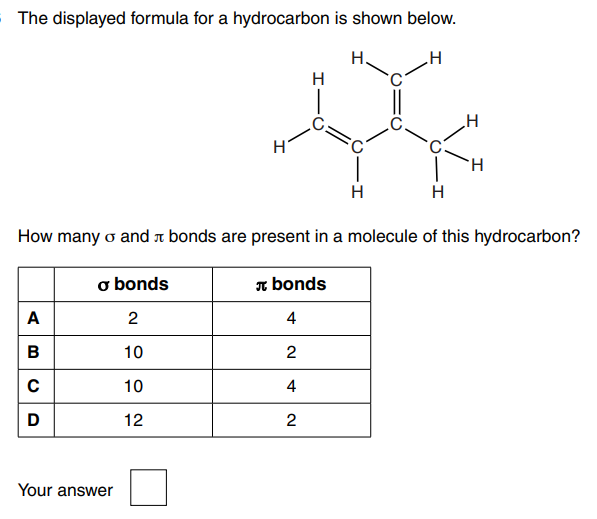
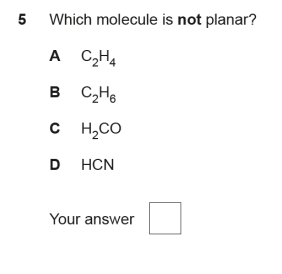
D
State the similarities and differences between the atomic structure of isotopes of the same element
Similarities: same number of protons AND electrons
Differences: Different number of neutrons
How can you decrease % uncertainty when using a mass balance?
Use balance weighing to 3/more decimal places
use a larger mass/amount
What is meant by the term alkali (1)
releases OH- ions in aqueous solution
What is meant by the term standard solution? (1)
A solution of a known concentration
What is an acid
releases H+ ions
What is a base (1)
A substance which readily accepts H+ ions