MCAT General Chemistry
1/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Atoms
smallest unit of any element - has protons, neutrons, and electrons
p = +1, mass = 1amu
e = -1, mass = 0amu
n = 0, mass = 1amu
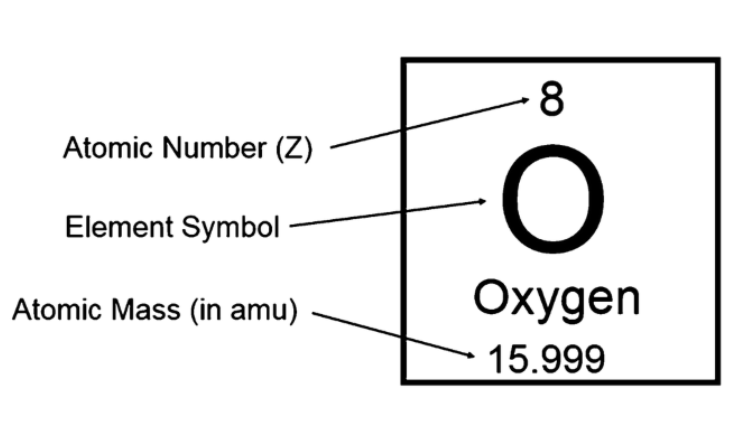
Atomic Number
Z, the number of protons(p+)
Mass number
= P*+n
The charge on atoms
= p-e
Cations and anions are ions
C>0 = cation → +
C<0 = anion → -
C=0 = atom level
Isotopes
two atoms of the same element that differ in their number of neutrons - determined by mass number
Bohr model of the atom
Electrons orbit at a fixed distance from the nucleus - the orbit decreases with distance from the nucleus - as we move away, the ends come closer and energy increases with distance from the nucleus
Electrons absorb only specific allowed E(due to fixed quantities of E)
Current orbit = ground state
Higher E orbit = excited state
Ephoton = Ef-Ei
e- in an excited state can come to a lower level to emit a photon - when dropped, the e- becomes relaxed
Hydrogen Absorption and Emission spectrum
Absorption = dark bands on a bright background(absorb, so black line)
Emission = bright bands on a dark background(emit, so bright lines)
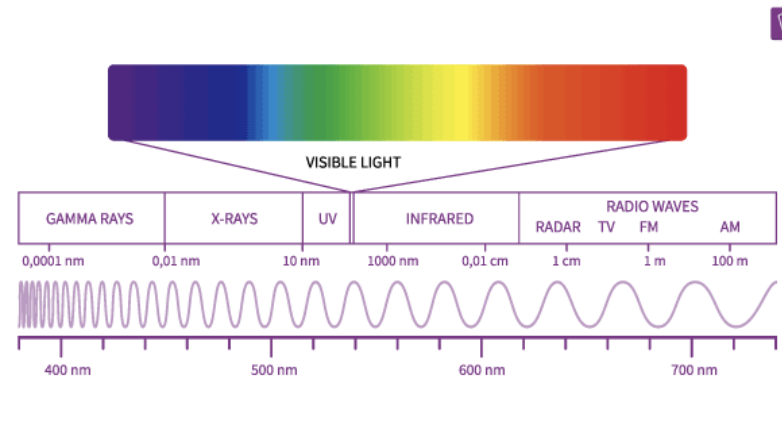
The Energy of a photon is related to…
its wavelength(λ lambda) and frequency(f)
E = hf = hc/λ → Wavelength and frequency are inversely related - when f is high, λ is low, E is high; when f is low, λ is high, E is low
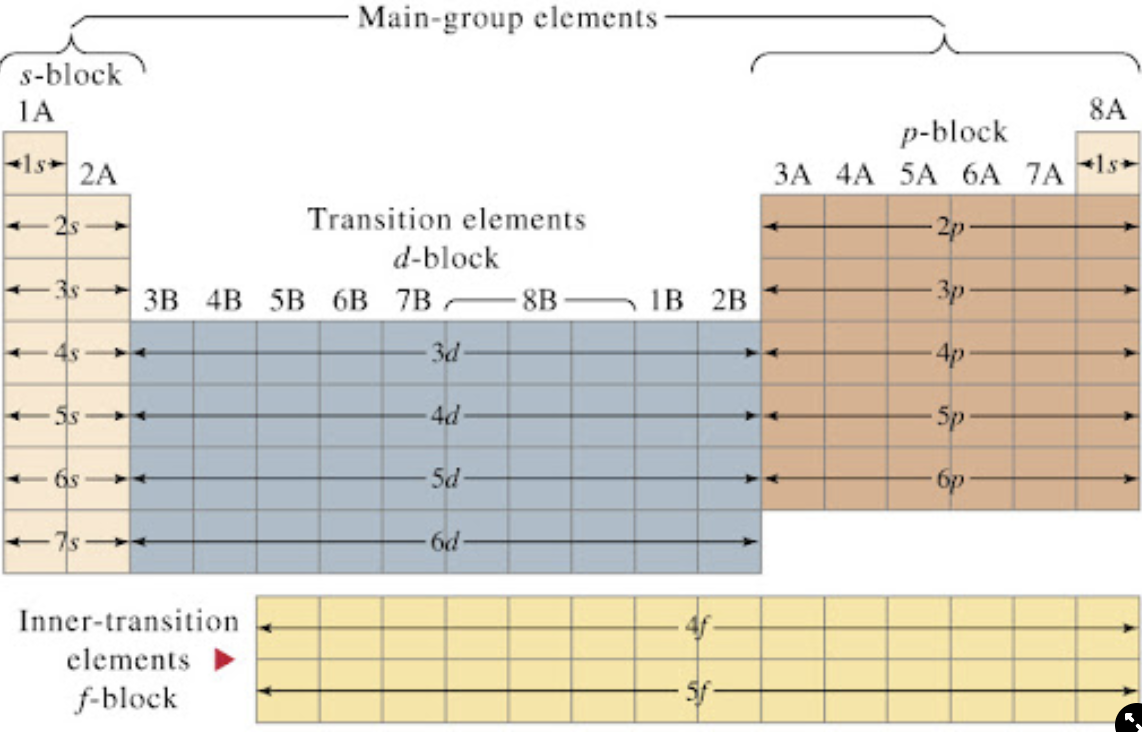
E- exists in 3D orbitals and 4 quantum number describe their structures
orbitals are the areas around the nucleus where an e- is most likely to be found)
s, p, d, f → s being lowest in E and F in highest E
ex. boron= 1s2 2s2 2p1 → goes by block and row of the periodic table
3 basic rules for Electron filling:
Pauli principle: there can be no more than 2 e- in any given orbital(spin up and down)
e- cannot be the same, hence, different spins
Aufbau principle: E- occupies the lowest orbitals first and is filled in increasing E
exception is 3d and 4s → 4s are removed before 3d
Hund’s Rule: E- first occupy an orbital singly then pair up(no orbital left empty)
Anomalous electron configurations
when some elements prefer to be half-filled or filled by taking an e from 4s and putting it into 3d ex. Cr and Cu
Paramagnetic
at least one unpaired e-
Diamagnetic
all e- are paired ex. noble gases
Ground state e-configuration
the ground state is the lowest e configuration → correct amount of e as the element has
Excited state e-configuration
the element has jumped an orbital but it has not changed the amount of electrons as it originally had
A half-filled shell is…
more stable than one that isn’t; filled one is the most stable ex. noble gases
Valence shell configurations
determine the chemical reactivity of the elements → Elements in the same group show similar characteristics ex. noble gases as calm due to their octet shells, while halogens are reactive gases with 1 e-missing
Valence shell electrons experience electrostatic attraction due
to the nucleus → shielding effect
force of electrostatic attraction is proportional to Zeff + C/r²
Atomic radius increases…
going down right to left
Ionization E increase…
going up from left to right
Electron affinity(negativity) increases…
going up from left to right
Electronegativity increases going…
up from left to right
FON=ClBrISC=H