1. The Multi Store Memory model
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Atkinson and Shiffrin (1968)
the multi store memory model
diagram
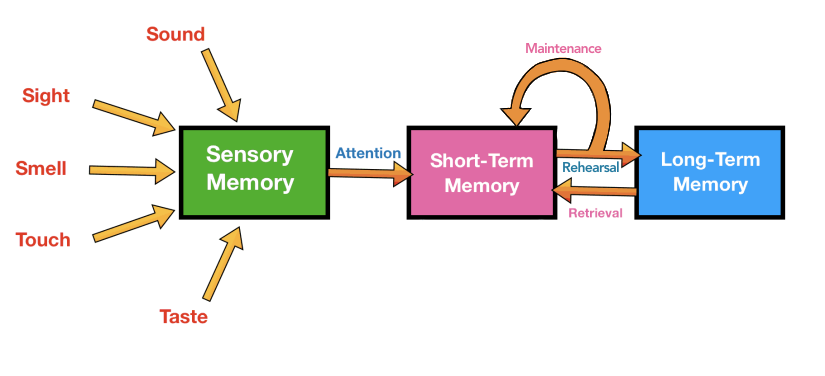
coding
the different information formats the brain uses to store memory
capacity
how much information can be held by a store
duration
how long information can be held in that store for before loss
coding of sensory register
modality specific
capacity of sensory register
unlimited
duration of sensory register
250ms
coding of STM
acoustic
capacity of STM
7 +- 2 items
duration of STM
18 seconds
coding of LTM
semantic
capacity of LTM
unlimited
duration of LTM
unlimited
Glanzer and Cunitz (1966)
asked pps to free recall word lists. found recall was stronger for words at the start and end of the lists.
suggests there are separate short and long term memory stores
primacy effect
words first heard enter LTM
recency effect
most recent words are held by STM
one strength is research to suggest that there are separate stores of memory which is the basis of the MSM
Glanzer and Cunitz (1966) observed that pps remember more from the start and end of a word list than the middle
this supports the MSM as the words at the start of the list had been rehearsed more and thus transferred to the LTM for retrieval. the words at the end of the list were still in the STM (maintenance rehearsal) but the middle words had decayed/ been displaced
this evidence points towards separate stores of memory (improves reliability)
one strength is supporting evidence by lab studies
Beardsley (1997) found that the prefrontal cortex is active during STM but not LTM
Squire et al (1992) used brain scanning and found that the hippocampus is active when the LTM is engaged
this provides strong support from the MSM
improves validity
one limitation is that it is oversimplified
the model suggests that both STM and LTM are unitary stores but research does not support this
the WMM suggests we have different stores for acoustic and visual memories (STM). for LTM it is suggested we have episodic, procedural, and semantic memories
therefore this suggests the MSM is too simplistic
one limitation is the experiments testing MSM are artificial
research supporting the MSM are lab experiments involving artIficial tasks (memorising word lists, trigrams) which do not reflect real life (lacking external validity)
there is low ecological validity and results collected in lab environments may not be generalisable to natural situations (lack of mundane realism)
therefore the MSM lacks ecological validity
state how information in STM is lost
displacement
decay
state how information in LTM is lost
interference
retrieval failure