Fungi
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
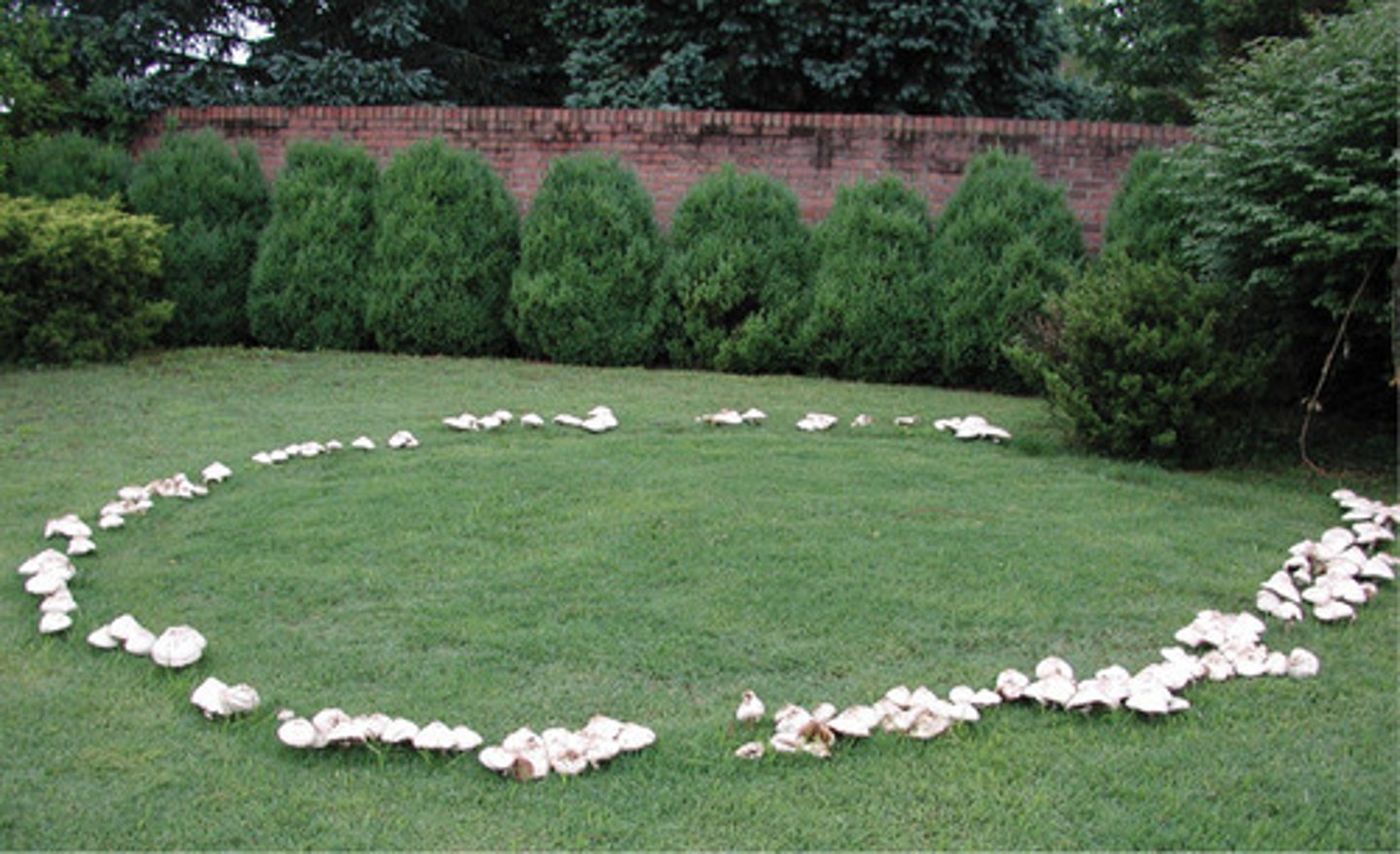
fairy ring
a ring of mushrooms that grows in circles. They are a natural phenomenon. Mystical qualities include:
If you step into them, misfortune can fall on you
That's where Faries would dance, and if a human steps in, they will dance until they die
If a cow steps into them, it's milk will be curdled

fungi
Eukaryotes
Heterotrophs - have to get their energy from other things. Includes saprophytes - getting their energy from dead organic matter and Parasites
Cell wall made of chitin
Multinucleated cells
Lacking chloroplasts
plants
Eukaryotes
Autotrophs - able to create their own energy
cell wall made of cellulose
single-celled nuclei
containing chloroplasts
General characteristics of fungi
Devoid of leaves, stems, or roots
Lacking chlorophyll:
Require an external carbon source (heterotrophic)
Carbon derived as saprophytes by adhering to decomposing nonliving organic matter
Carbon derived as parasites by invading living plants and animals (including humans)
Eukaryotic - Possess nucleus, nuclear membrane, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and mitochondria
Possess a rigid cell wall composed of chitin: Cell wall constituents absorb several dyes. Aid in identification
yeasts, molds, and spores
Fungi can be in several different forms:
yeasts
single celled fungi forms
molds
Multiple cells forming a filamentous mycelium
Spores
Fungi reproduce by spores - Sexually or asexually
Morphology, arrangement, and mode of derivation of spores serve as criteria for genus and species identification
spore, germ tube, hypha, and mycelium
molds - Multiple cells forming a filamentous mycelium steps:
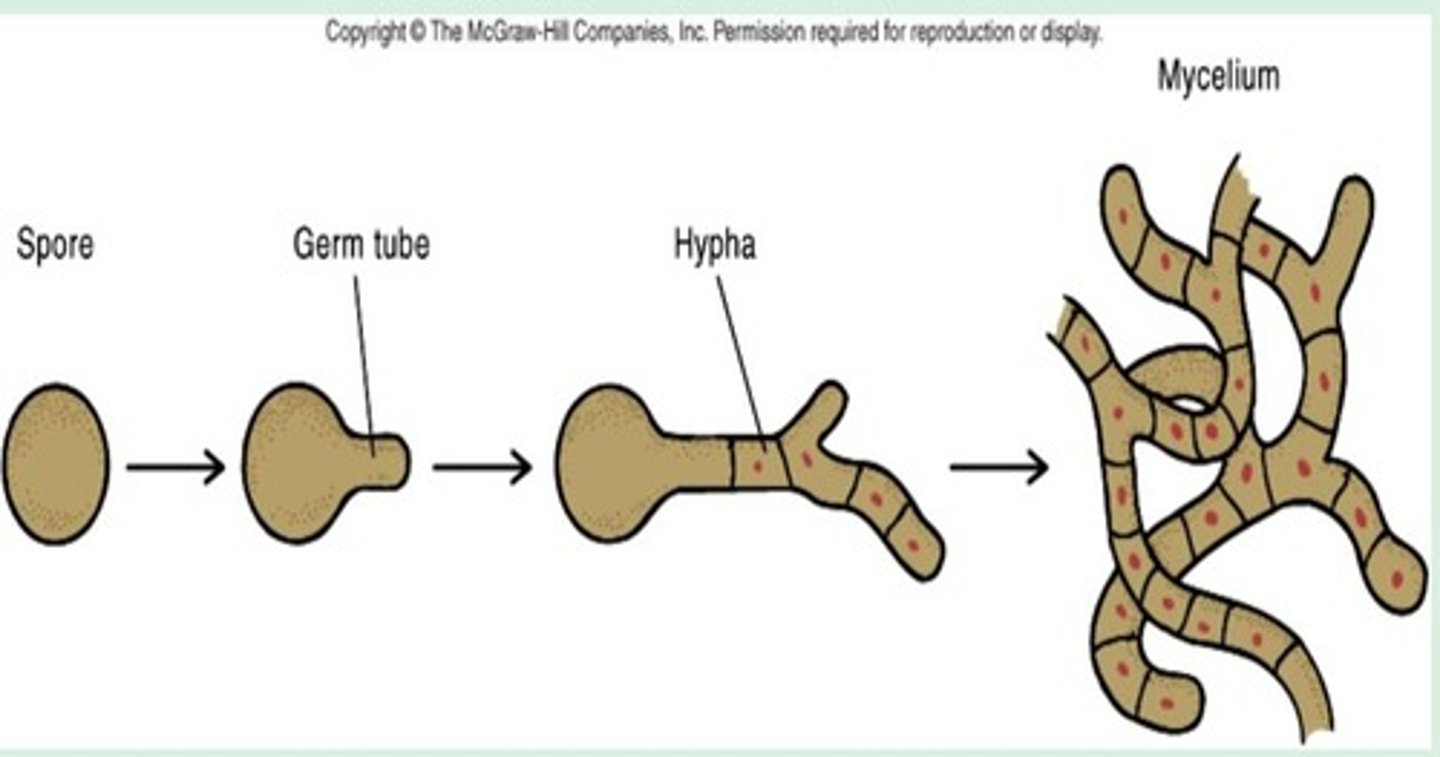
fungi habitat
Fungi are found in nearly every habitat on earth where organic materials exist
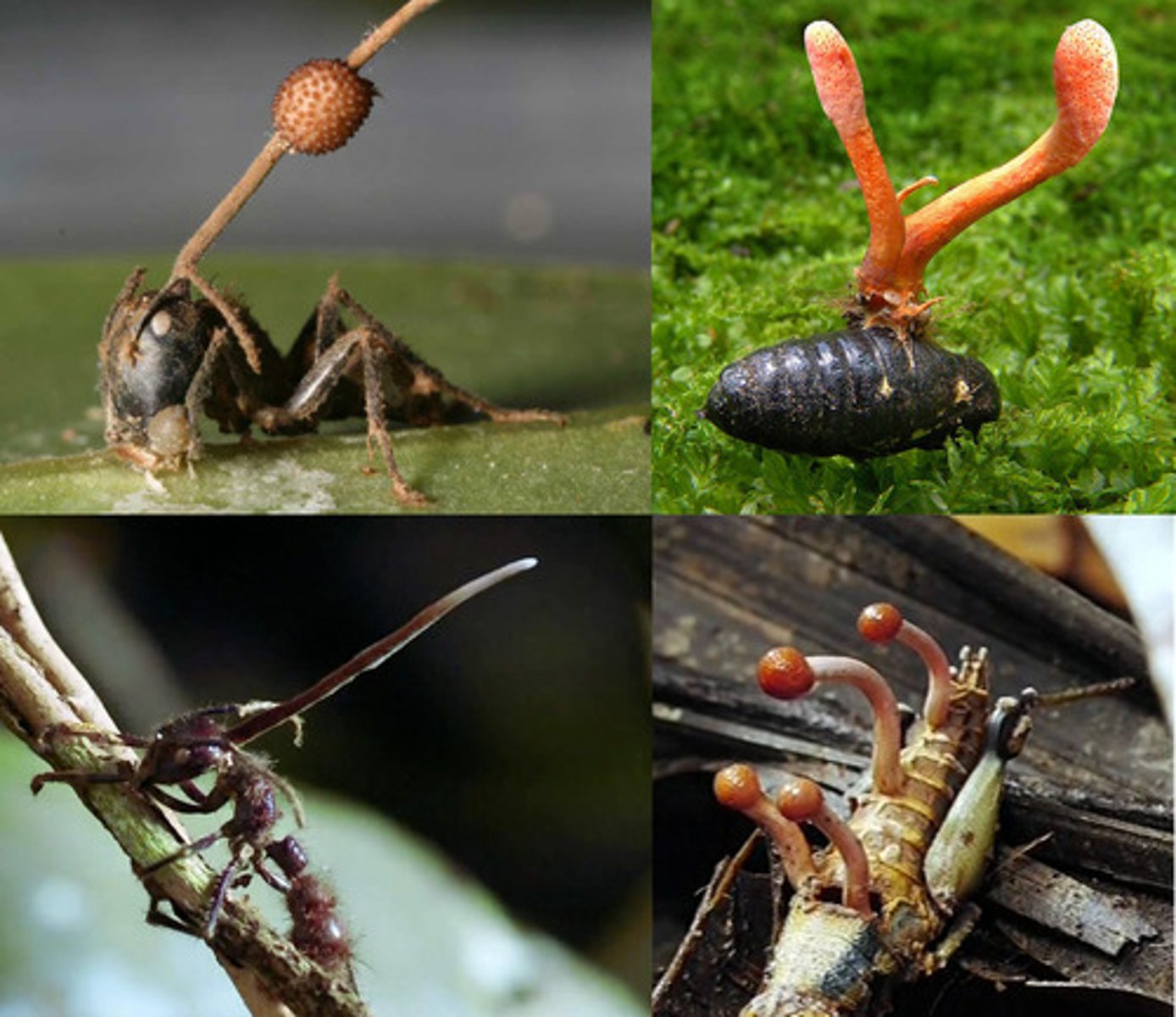
Cordyceps fungus
Cordyceps fungus
infects different insects, fish, or wood

allergic reaction, reaction to toxin, Fungi that destroy the human food supply, and Colonization of the human body by fungi (mycoses)
Fungi can cause harm or disease to humans in one of four ways:
Allergic reaction
Exposure causes a person to become sensitized (immediate hypersensitivities)
If you have a mold allergy, your immune system overreacts when you breathe in mold spores. A mold allergy can cause coughing, itchy eyes, and other symptoms. In some people, a mold allergy is linked to asthma, and exposure causes restricted breathing and other airway symptoms.
Reaction to toxin
Hallucinogenic properties of some mushrooms
Poisonous effects of ergot fungus (rye smut)
Carcinogenic toxins of Aspergillus (aflatoxins)
Ergotism
ERGOT FUNGI causes:
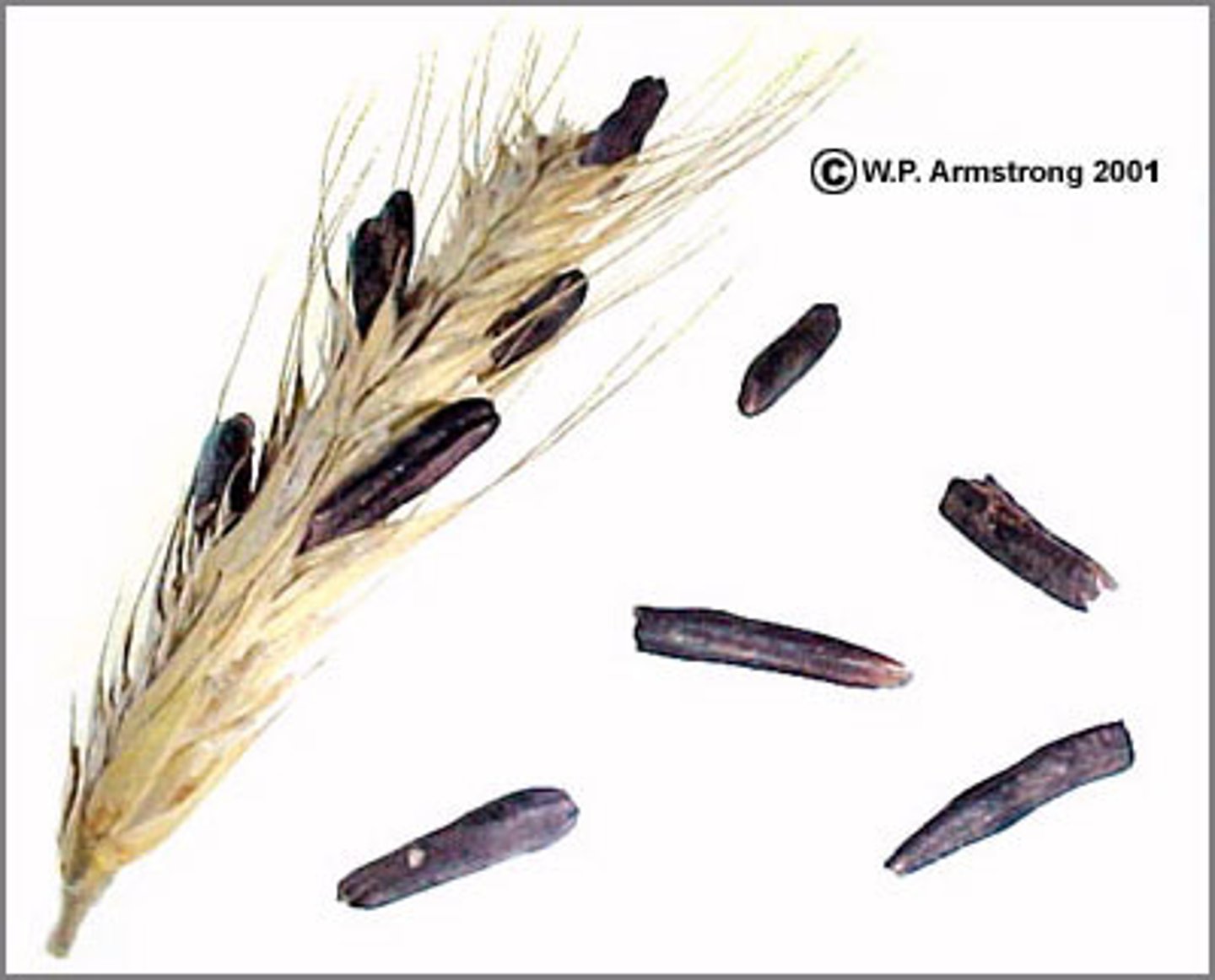

Ergotism
Is the name for sometimes severe pathological syndromes affecting humans or other animals that have ingested plant material containing ergot alkaloid, such as ergot-contaminated grains.
Causes severe vasoconstriction, leading to gangrene due to loss of blood circulation
The neurotropic activities of the ergot alkaloids may also cause hallucinations and attendant irrational behaviour, convulsions, and even death.
Ergometrine (from Ergot) is used to induce uterine contractions and to control bleeding after childbirth
can impact food crops and food supplies. Can damage corn
ASPERGILLUS causes Aspergillosis
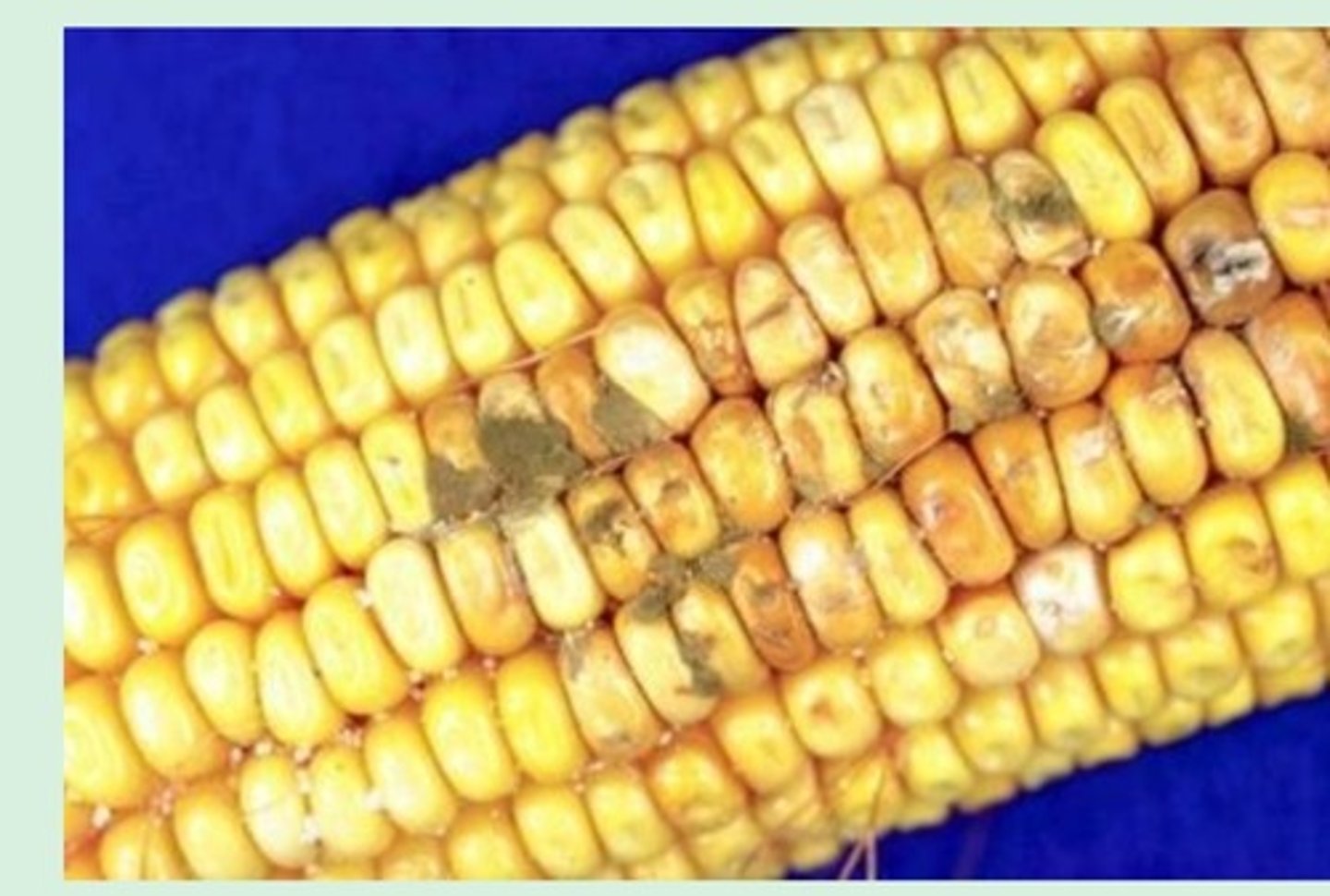

Fungi that destroy the human food supply
Wheat rust: Puccinia graminis
Potato blight: Phytophthora infestans
So, when infected by the blight, it wiped out the whole crop of potatoes. This destroyed Ireland's economy at the time.
The Irish Potato Famine occurred in Ireland during the 1800s. The potato blight infected their potatoes. Potatoes are clones, and they have a weakness of no resistance to potato blight.
Colonization of the human body by fungi (mycoses)
Superficial mycoses - on the surface level of our bodies
Intermediate mycoses - Specific tissue not yet disseminated
Systemic mycoses
mycoses
is a disease caused by fungi
superficial mycoses
Candidiasis (thrush, vaginal)
Dermatophytes (athletes' foot, Tinea capitis, Jock itch, nails, etc.)
Sporotrichosis (gardener's hazard)
Blastomycosis (skin)
Candidiasis is caused by Candida albicans (Yeast)
Candidiasis that develops in the mouth or throat is called thrush or oropharyngeal candidiasis
Candidiasis in the vagina is commonly referred to as a Yeast infection
Athlete's foot, known medically as tinea pedis
a common skin infection of the webs of the toes and soles of the feet
may spread to the palms, groin, and body
signs and symptoms often include itching, scaling, and redness
in severe cases, the skin may blister
It is caused by Fungi: Trichophyton, Epidermophyton, and Microsporum
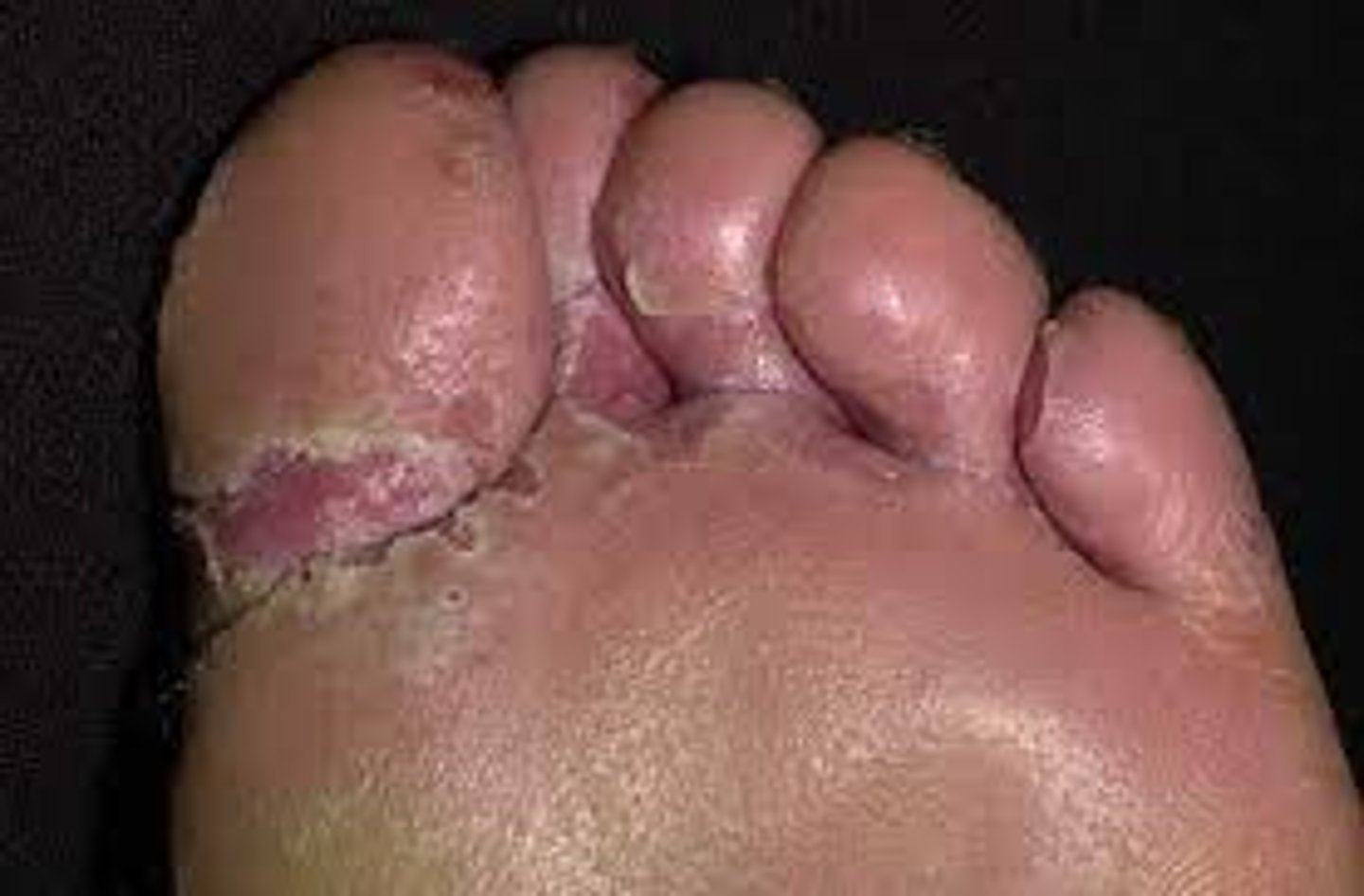
toenail fungus
the nail will become weak and yellowed and usually bigger than it was before the fungus started growing underneath the nail
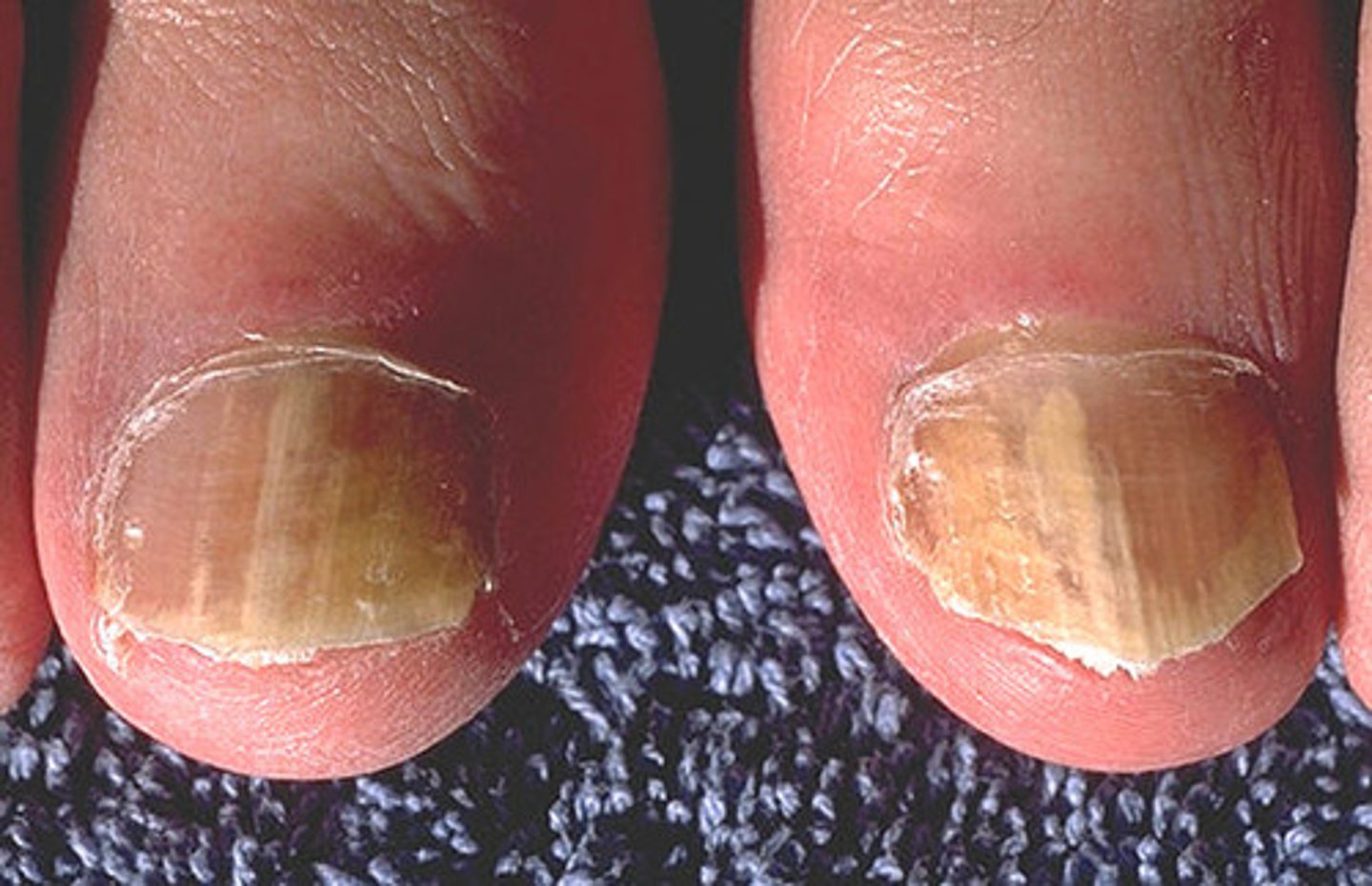
Sporotrichosis (gardener's hazard)
Someone working in the garden gets scratched by some of the plants, and there may be spores from the fungus that will start growing on the person's body. It used the abrasion or damage to the skin as a portal of entry
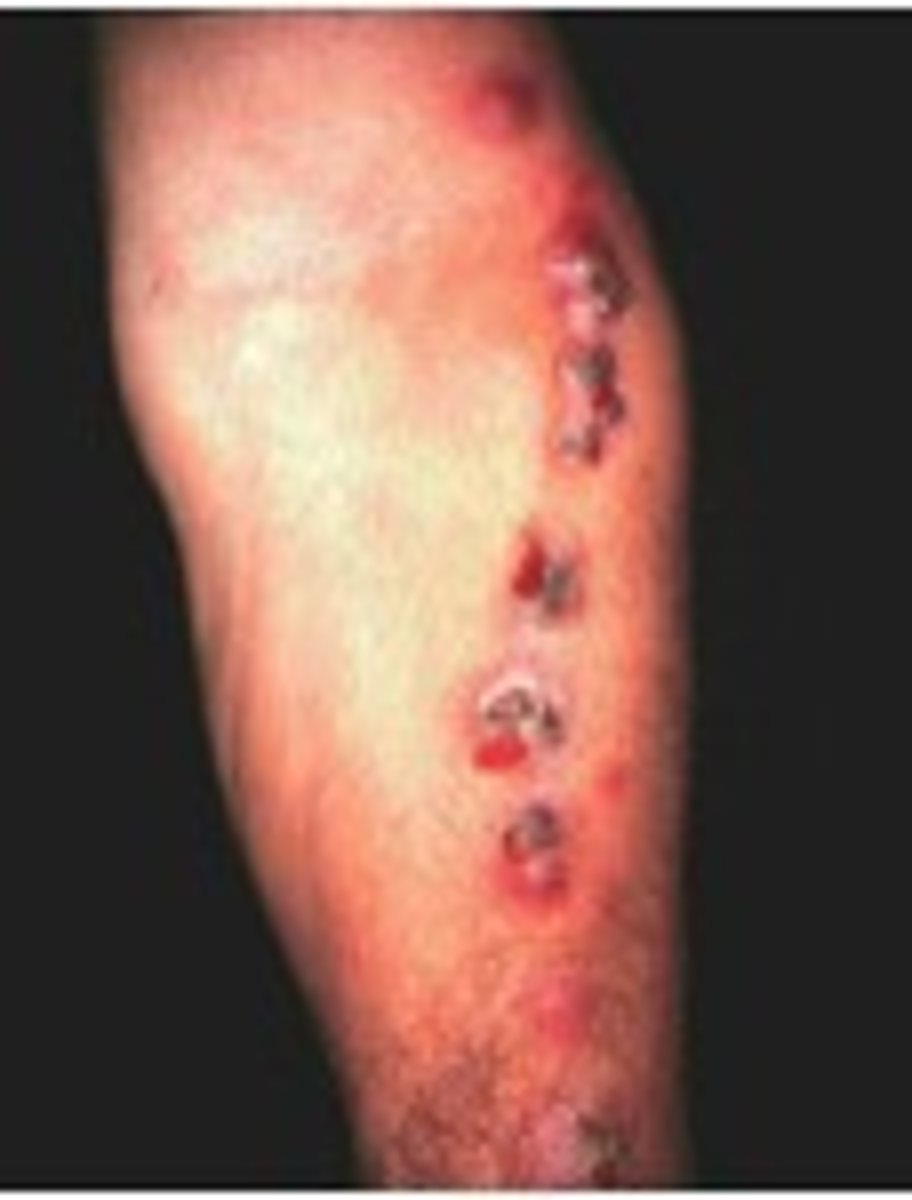
blastomycosis
a deeper skin infection that certain fungi can cause
Intermediate mycoses
Aspergillus: lungs, gut-ingested spores, fungal ball
Candidiasis: children and immunocompromised
Cryptococcus: pulmonary, cerebral
Dimorphic: can be a yeast or a mold depending on the temperature. It can affect any organ in our body. Mold-like at room temperature, they release their spores. Warmer body temperature, they become a yeast with a capsule formed around them
Mucormycosis: rhino cerebral (nasal passages and brain), pulmonary, GI, fungal ball
Aspergillosis
is the name given to a wide variety of diseases caused by infection by fungi of the genus Aspergillus. The majority of cases occur in people with underlying illnesses such as tuberculosis or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), but with otherwise healthy immune systems
People with deficient immune systems, such as patients undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, chemotherapy for leukemia, or AIDS, are at risk of more disseminated disease
A fungus ball in the lungs may cause no symptoms and may be discovered only with a chest X-ray, or it may cause repeated coughing up of blood, chest pain, and occasionally severe, even fatal, bleeding
Poorly controlled aspergillosis can disseminate through the bloodstream to cause widespread organ damage.
Systemic mycoses
Mucormycosis: necrotizing, rapid, fulminating
Aspergillosis
Candidiasis
Cryptococcus
Dimorphic
Dimorphics
Mycotic organisms that possess different morphological forms under different temperature conditions
Includes Histoplasmosis, Blastomycosis, Coccidiomycosis
Histoplasmosis
fungal infection of the lungs
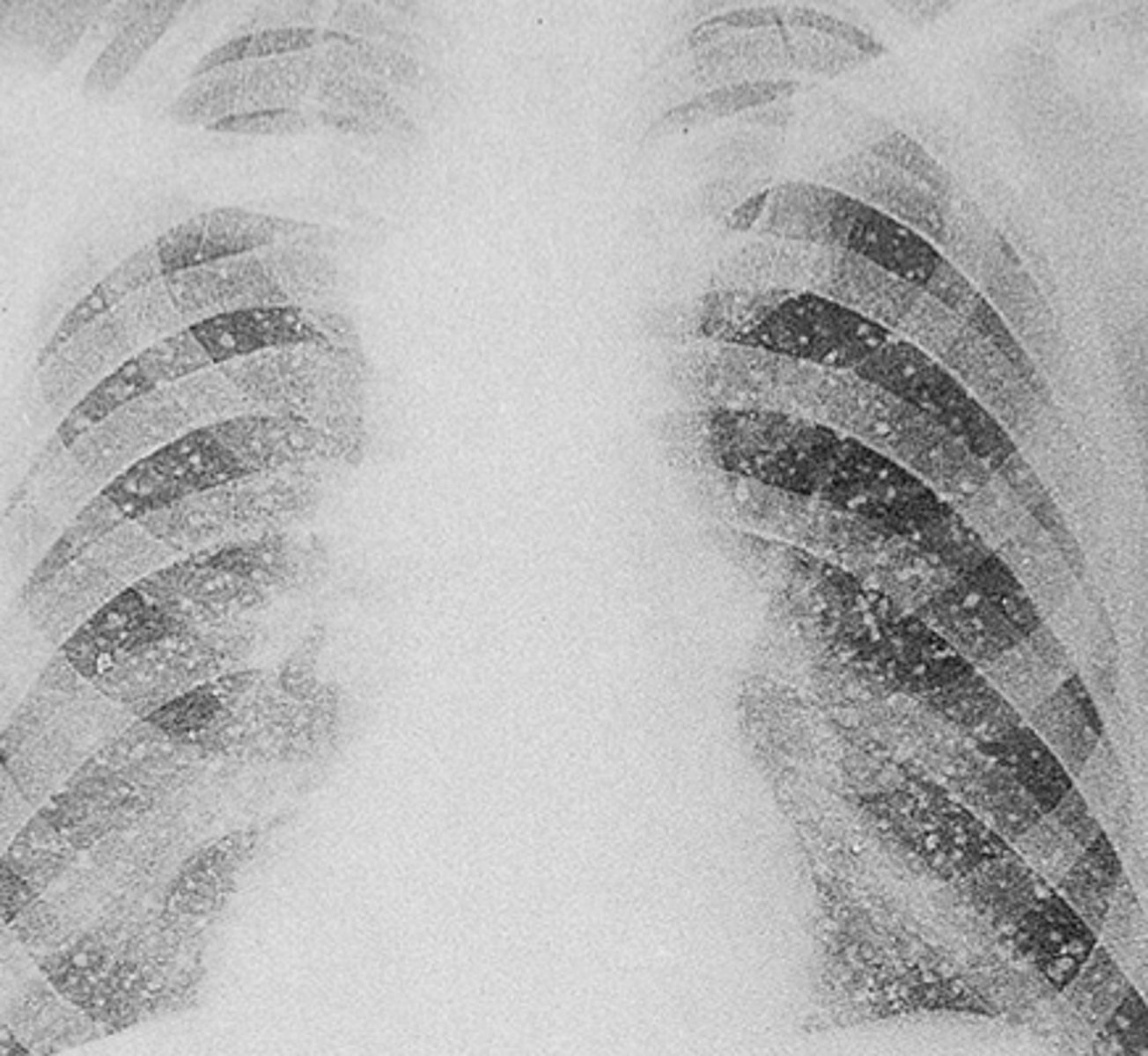
mucormycosis
is a serious but rare fungal infection caused by a group of molds called mucormycetes. These molds live throughout the environment. Mucormycosis mainly affects people with weakened immune systems and can occur in nearly any part of the body. It most commonly affects the sinuses or the lungs after inhaling fungal spores from the air, or the skin after the fungus enters the skin through a cut, scrape, burn, or other type of skin trauma.
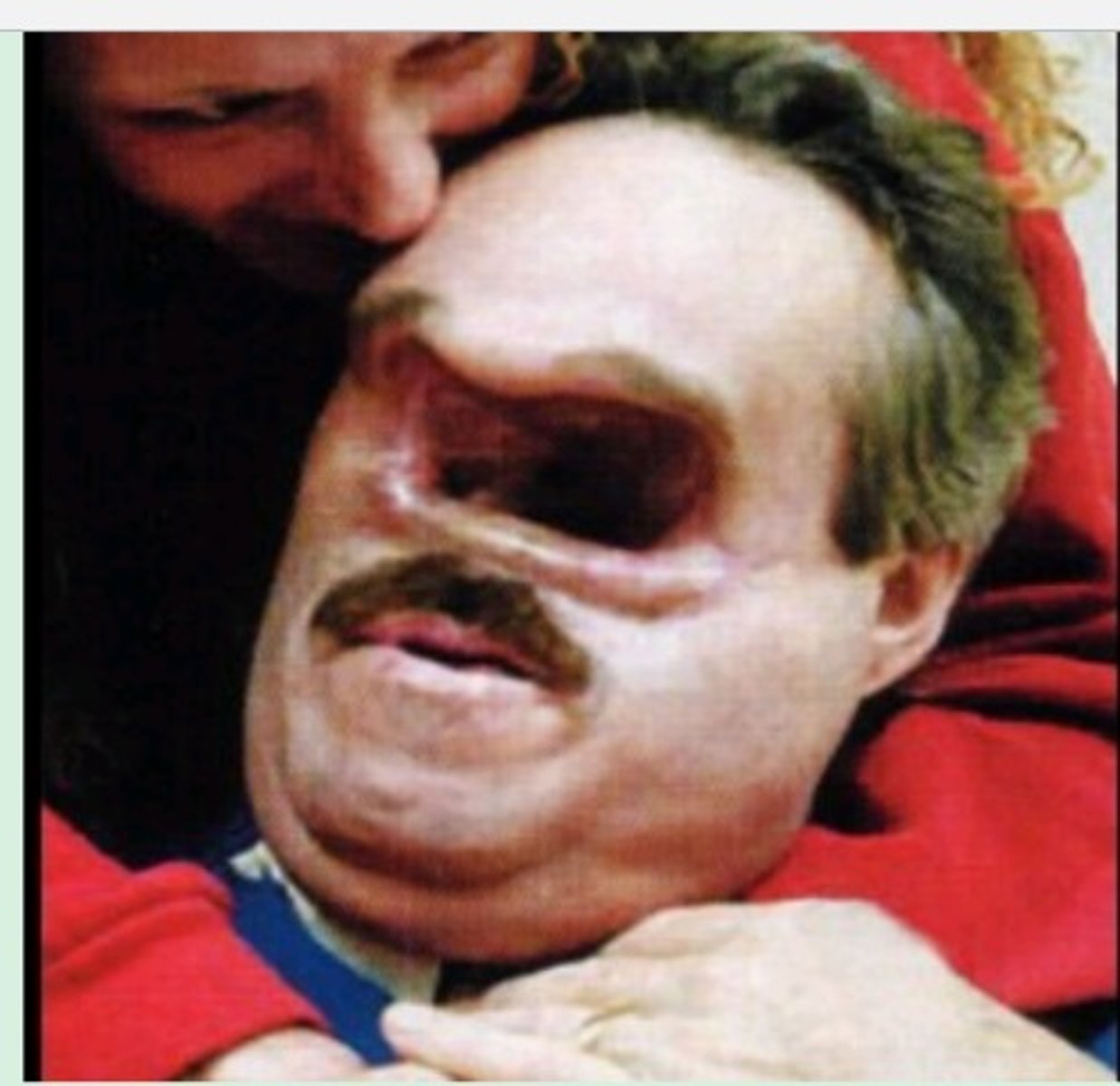
Cryptococcus
Cryptococcus neoformans is a fungus that lives in the environment throughout the world. People can become infected with C. neoformans after breathing in the microscopic fungus, although most people who are exposed to the fungus never get sick from it. C. neoformans infections are extremely rare in people who are otherwise healthy; most cases occur in people who have weakened immune systems, particularly those who have advanced HIV/AIDS.
Fungi as useful tools for genetic and biochemical studies
Neurospora crassa (common mold) has been used for the genetic and biochemical studies
Human insulin, Growth hormone, Somatostatin, and Vaccine against viral hepatitis
Yeasts have been genetically engineered to produce:
Fungi as food
Mushrooms
Yeast in alcoholic beverages, breads
Fungi in symbiosis
Lichens - are a combination of a fungus and a single-celled algae. The fungus gives the lichen protection, and the algae gives the lichen food. It has chloroplasts and it can do photosynthesis.
Lichen is used as food by animals including reindeer

Laboratory Diagnosis of Fungal Infections direct observation
Skin scrapings, hair, and nail clippings
Tissue imprints or sections - Special stains
culture media of fungal infections
Non-selective - Sabouraud's dextrose
Selective - Mycobiotic, Sabouraud's with antibiotics (PCN, Streptomycin, Gentamicin, and Chloramphenicol. Cyclohexamide: prevents overgrowth by mold contaminants
Enriched - Brain Heart Infusion with blood and potato dextrose agar: sporulation
Identification or Preliminary isolate observations of fungi
Yeast-like (creamy, pasty to mucoid)
Mold (cottony to wooly)
Rate of growth
Colony pigmentation
Growth on media containing antifungal agents
Dimorphic growth
creamy, pasty to mucoid
Yeast-like:
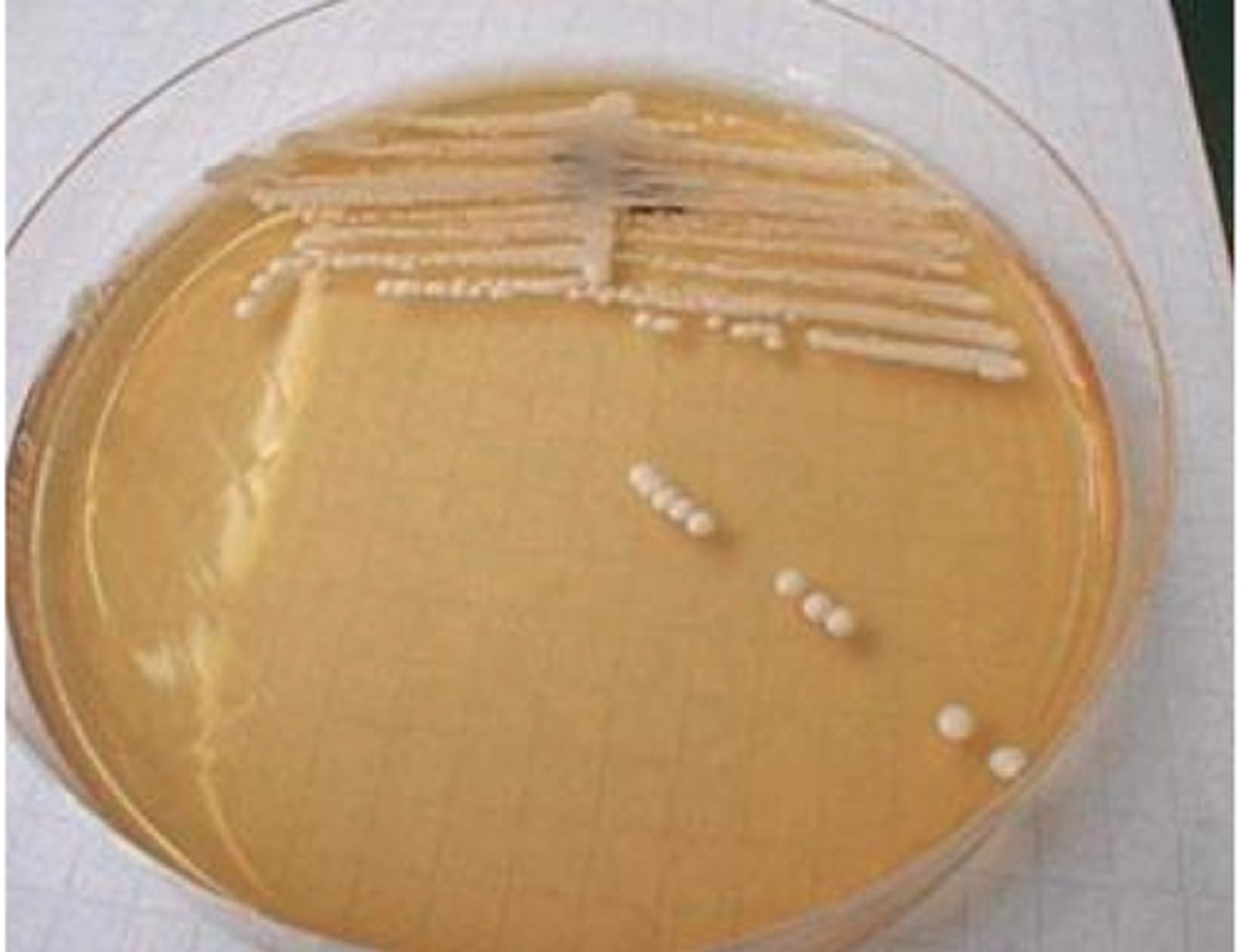
cottony to wooly
Mold:

Mount preparations (molds)
Tease mount - lactophenol aniline blue
Scotch tape mount - lactophenol aniline blue -
Tease mount
For microscopic examination, a fragment of fungal culture is teased out using two teasing needles and placed on a glass slide in a drop of LCB stain
To study the morphology of hyphae, spores, and other structures, tease mounts are prepared in lactophenol cotton blue (LCB), which contains lactic acid, phenol, glycerol, and cotton blue
Microscopic characteristics that should be observed are the following:
Septate versus sparsely septate hyphae
Spores or conidia
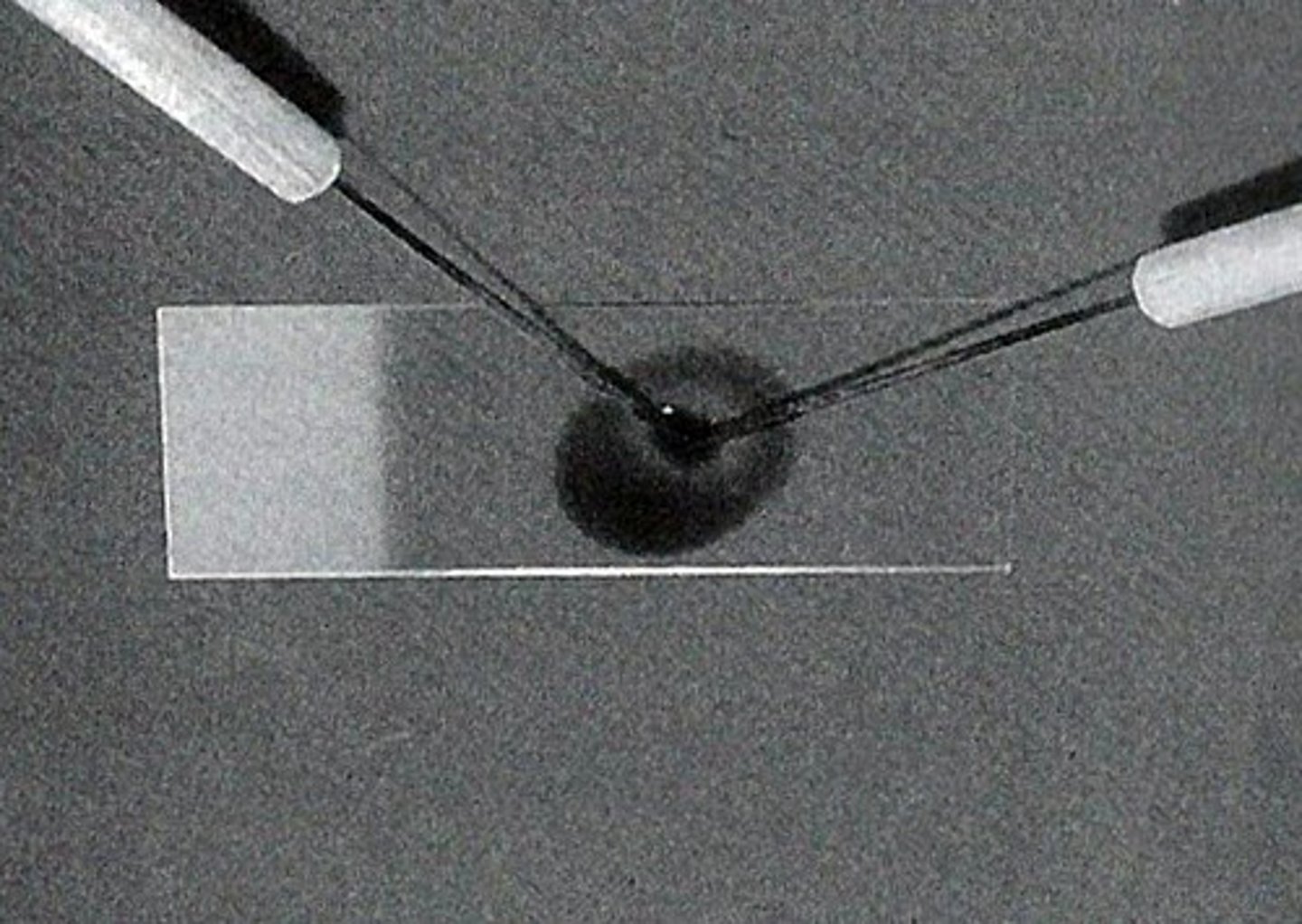
Scotch tape mount
On a clean glass slide, place one drop of LPCB.
Touch the adhesive side of the tape of transparent scotch tapes on the surface of the colony at a point intermediate between its centre and periphery.
Fix the adhesive side of the tape over an area on the glass slide containing the LPCB.
Examine the preparation under 10x and 40x of a light microscope.

Subculture, Biochemical, and DNA techniques to aid in identification
Identification of fungi can be done by:
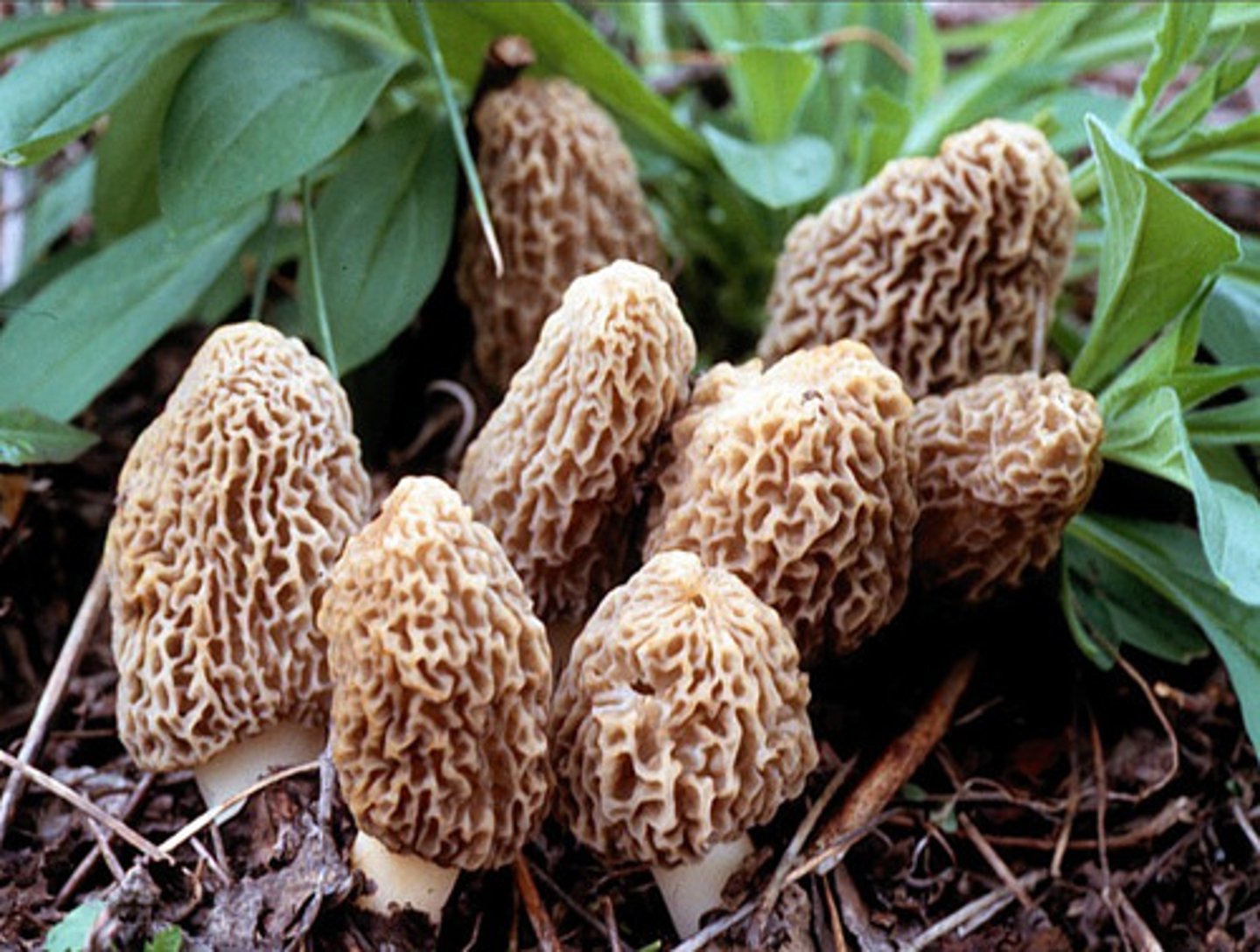
Morels
The Best Fungus of them all is:
