CBL- Cells: The Building Blocks of Life
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
cells
the smallest unit of life
cell membrane
the outer protective covering of the cell; selectively permeable; uses osmosis, protein channels, and active transport to let materials in and out of the cell; receptor proteins receive and transmit messages into a cell
centrosome
the centriole containing the region of clear cytoplasm adjacent to nucleus; plays a vital role in the cell cycle because it is responsible for distribution of chromosomes to newly forming cells
chomatin
a complex of a nucleic acid with basic proteins (as histone) in eukaryotic cells that is usually dispersed in the interphase nucleus and condensed into chromosomes in mitosis and meiosis
cytoplasm
the material or protoplasm within a living cell, excluding nucleus
cytokinesis
the division of the cytoplasm of a plant or animal cell into two
endoplasmic reticulum
network of interconnected structures that function especially in the transport of materials within the cell
genes
structures that carry inherited characteristics
genome
a total set of chromosomes with the genes they contain, consisting of strings of DNA nucleotides
golgi apparatus
a cytoplasmic organelle that consists of a stack of smooth membranous saccules and associated vesicles and that is active in the modification and transport of proteins; shipping & storage warehouse of the cell; responsible for carbohydrate synthesis
glycolysis
the breakdown of glucose inside a cells
lysosomes
a sac-like cellular organelle that contains various hydrolytic (digestive) enzymes; clean up/garbage disposal of the cell
meiosis
form of cellular reproduction specific to sex cells in all sexually reproducing single-celled and multicelled eukaryotes
mitochondria
the “powerhouse of the cell” found outside the nucleus; responsible for producing energy for the cell through the breakdown of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats via chemical rxns
mitosis
form of cellular reproduction that occurs in the nucleus of a dividing cell resulting in the formation of two new nuclei each having the same number of chromosomes as the parent nucleus
nucleolus
located inside the nucleus; responsible for the reproduction of ribosomes
nucleus
a mass located in the cytoplasm of a cell, separated from the cytoplasm by a nuclear membrane, considered the control center of the cell
organ
a differentiated structure (as a heart or kidney) consisting of cells and tissues and performing some specific function in an organism
organelles
a specialized cellular part (as a mitochondrion or ribosomes) that is analogous to an organ
pinocytic vesssels
pocket-like folds located in the cell membrane allowing the entrance and storage of large molecules such as proteins and fats
tissues
an aggregate of cells usually of a particular kind together with their intercellular substance that form one of the structural materials of a plant or animal and that in animals include connective tissue, epithelium, muscle tissue, and nerve tissue
protoplasm
the basic substance of all life; forms the cell
stem cells
an unspecialized cell that gives rise to differentiated cells
system
a group of body organs or structures that together perform one or more vital functions
vacuoles
pouch-like storage structures located throughout the cytoplasm
hypertrophy
when cells enlarge caused by an increase of proteins in the cell membrane and cell structures, not an increase in the cells fluid
hyperplasia
the number of cells increases; there is an increased rate of cell division
dysplasia
the size, shape, or organization of mature cells becomes abnormal; also called atypical hyperplasia
neoplasia
the formation of tumors, either cancerous (malignant) or noncancerous (benign)
cell cycle
the series of events including the growth, replication, and division of a eukaryotic cell
vesicle
small structure consisting of fluid enclosed by a lipid bilayer membrane
ribosomes
spherical structures made of RNA & proteins where protein synthesis occurs
rough endoplasmic reticulum
surrounds the nucleus; decorated w/ ribosomes
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
located near rough ER; controls fat transport and sex hormone synthesis
cytosol
crowded solution of different types of molecules that fills much of the volume of the cells
cilia & flagella
motility extensions of certain cells; cilia- hairlike protrusions that move materials across cell surfaces; flagellum- one tail like structure that propels a cell through a medium
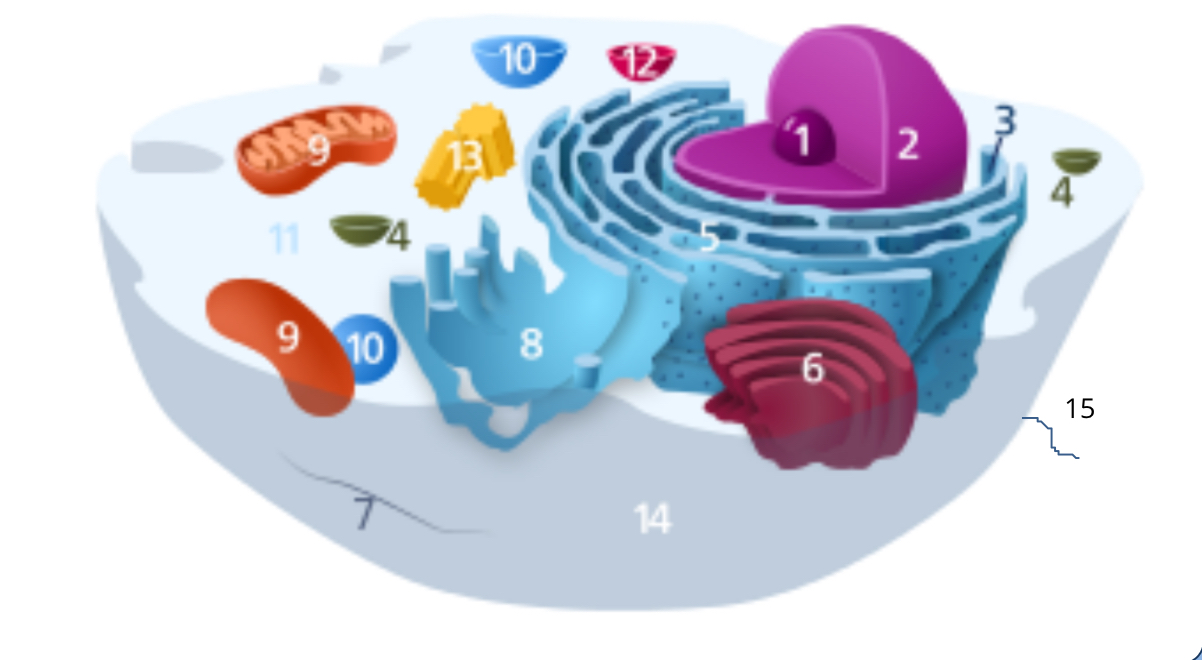
#1
nucleolus
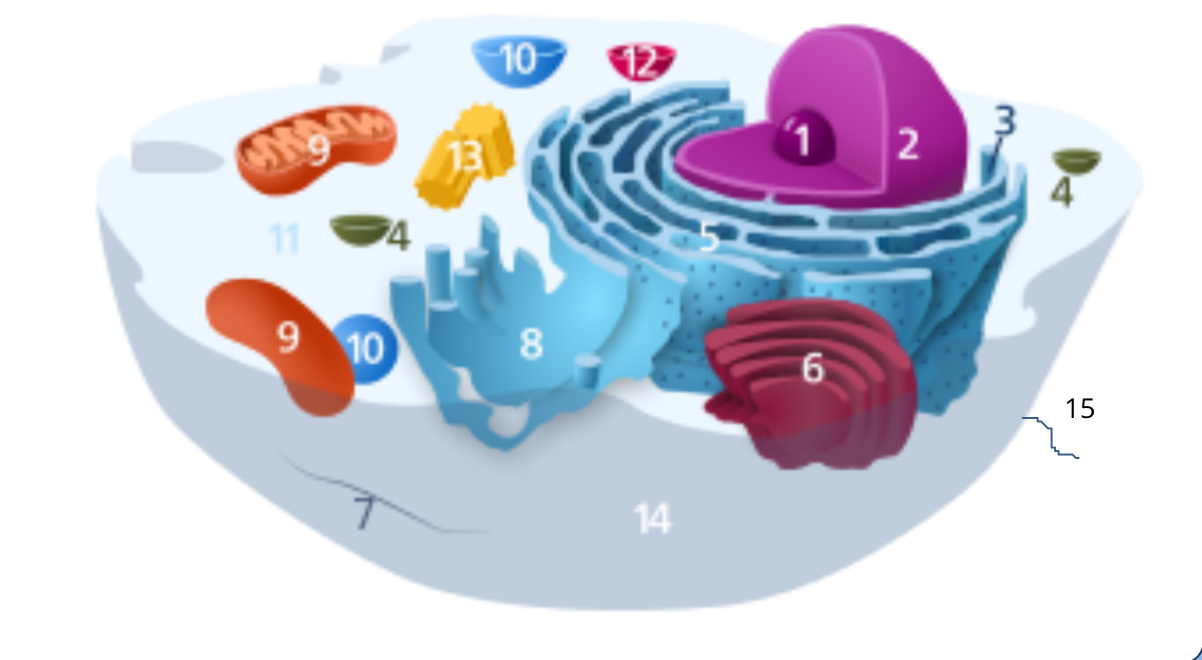
#2
nucleus
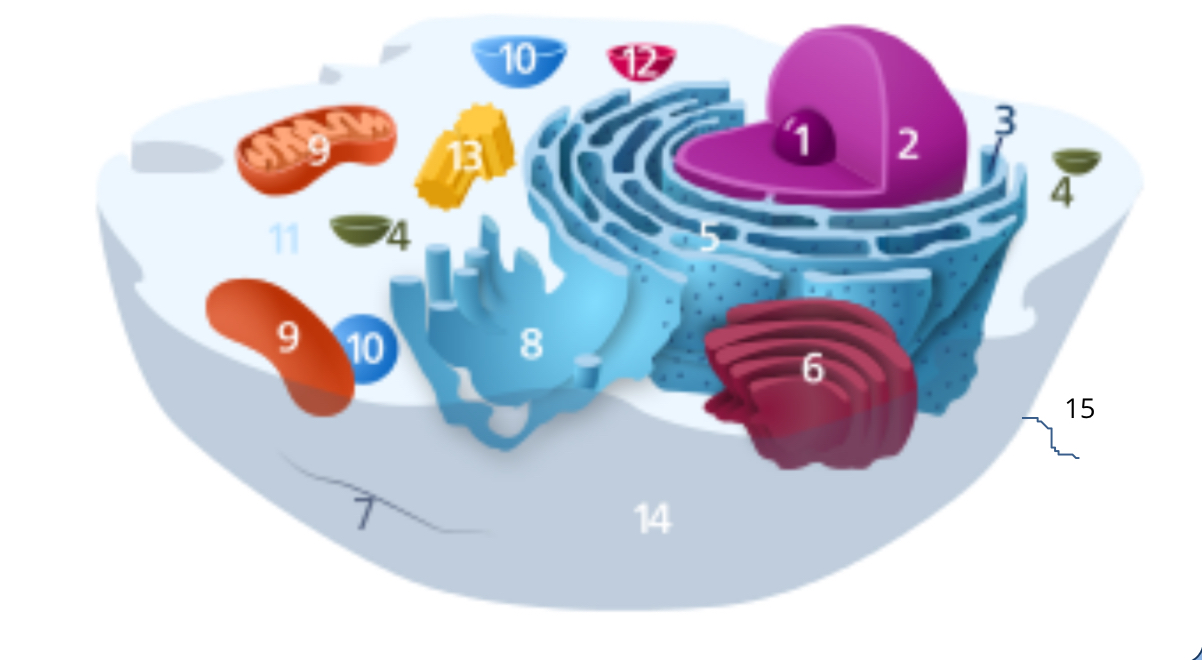
#3
ribosomes
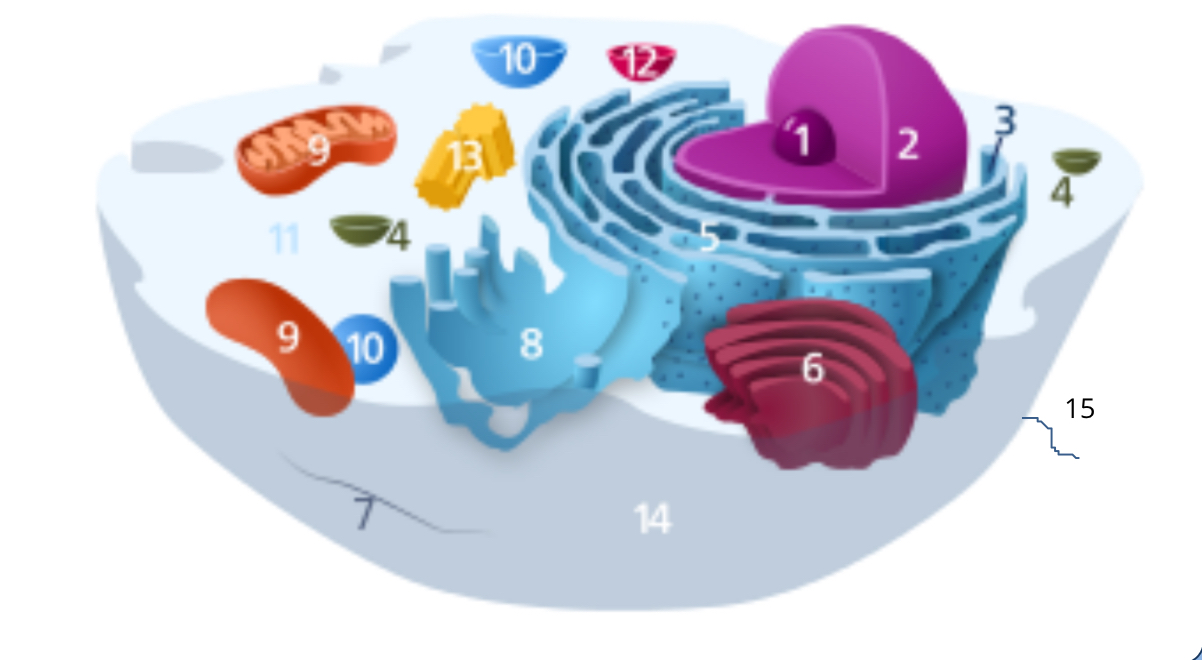
#4
vesicle
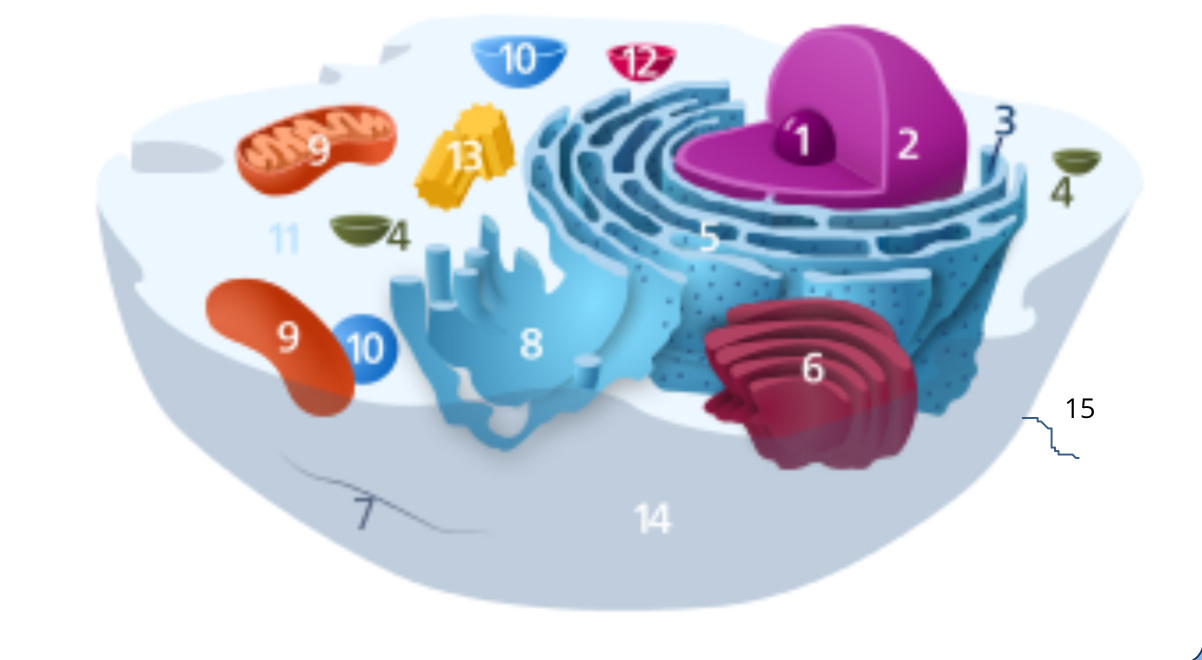
#5
rough endoplasmic reticulum
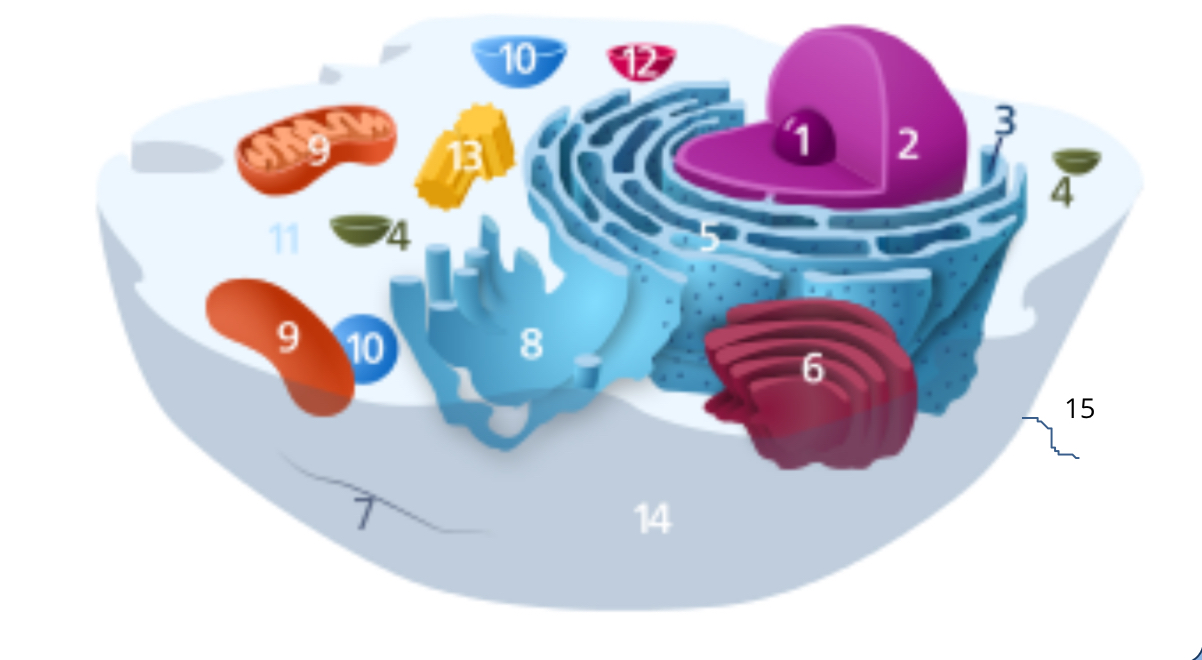
#6
golgi apparatus
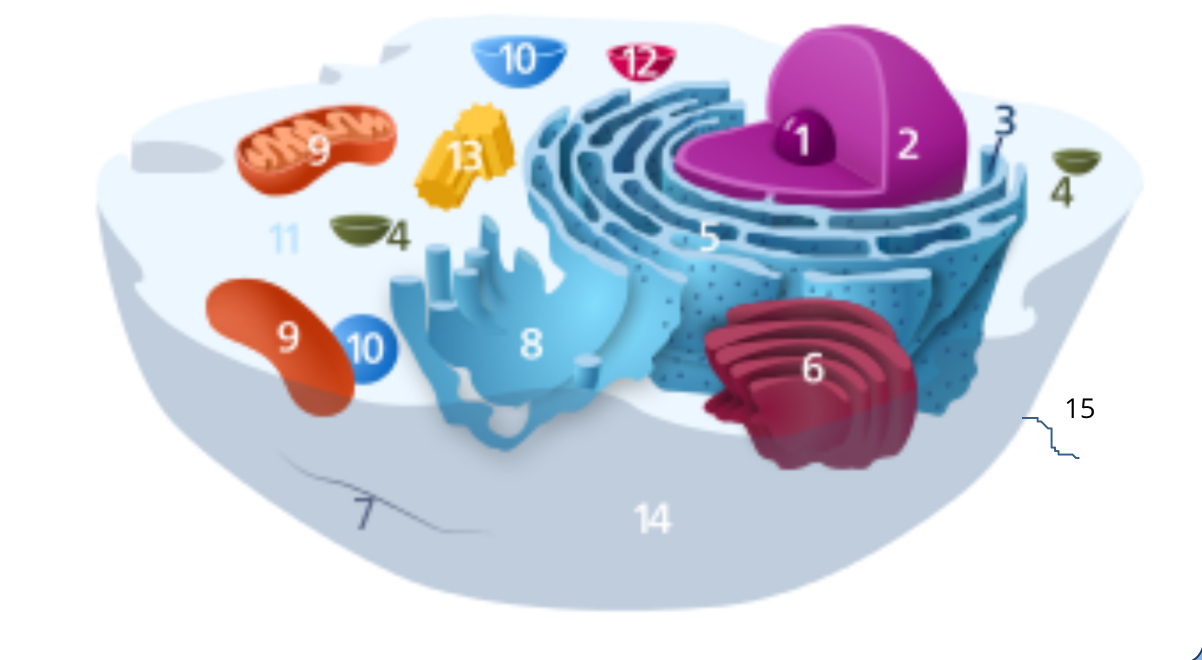
#7
cytoplasm
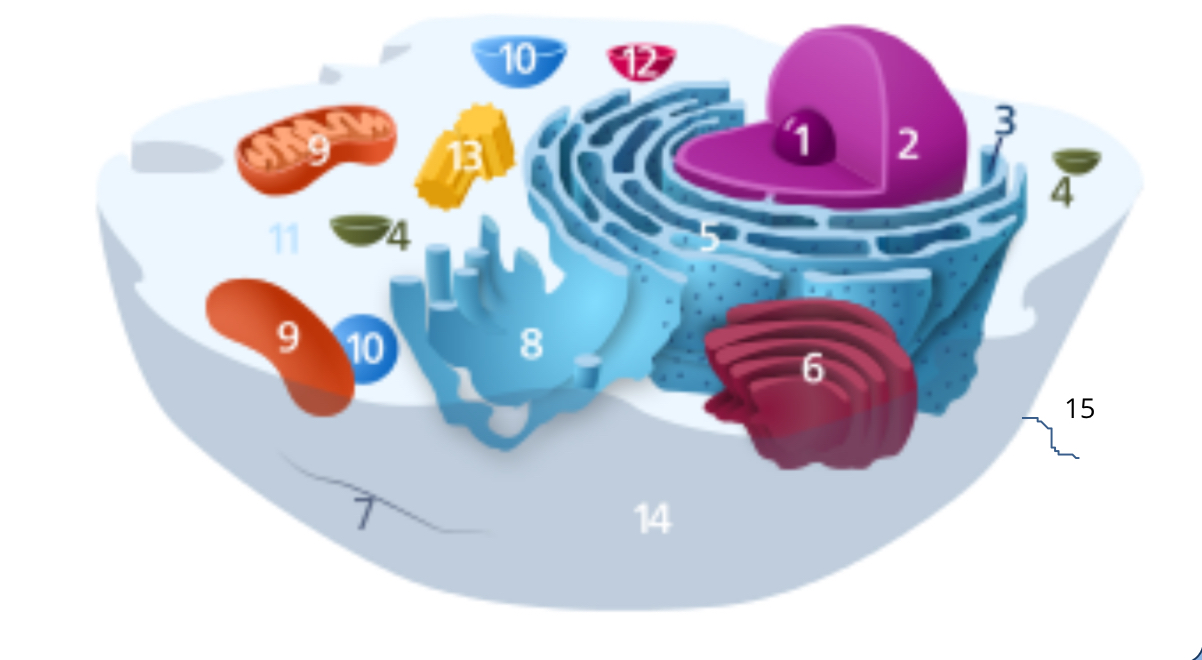
#8
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
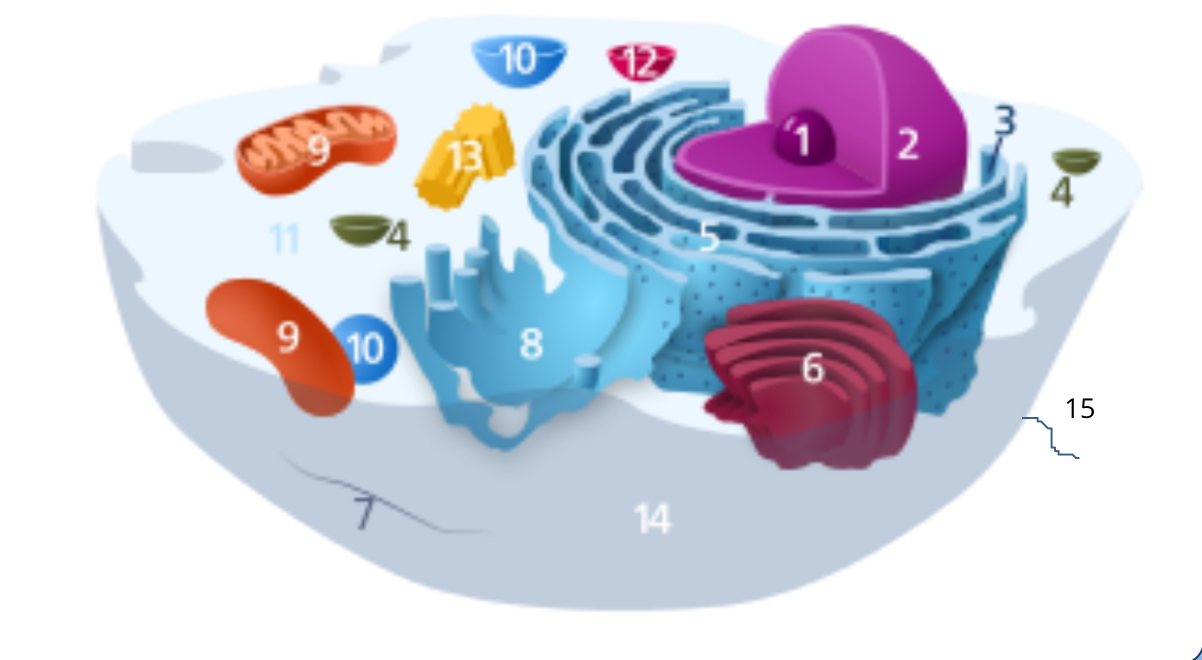
#9
mitochondria
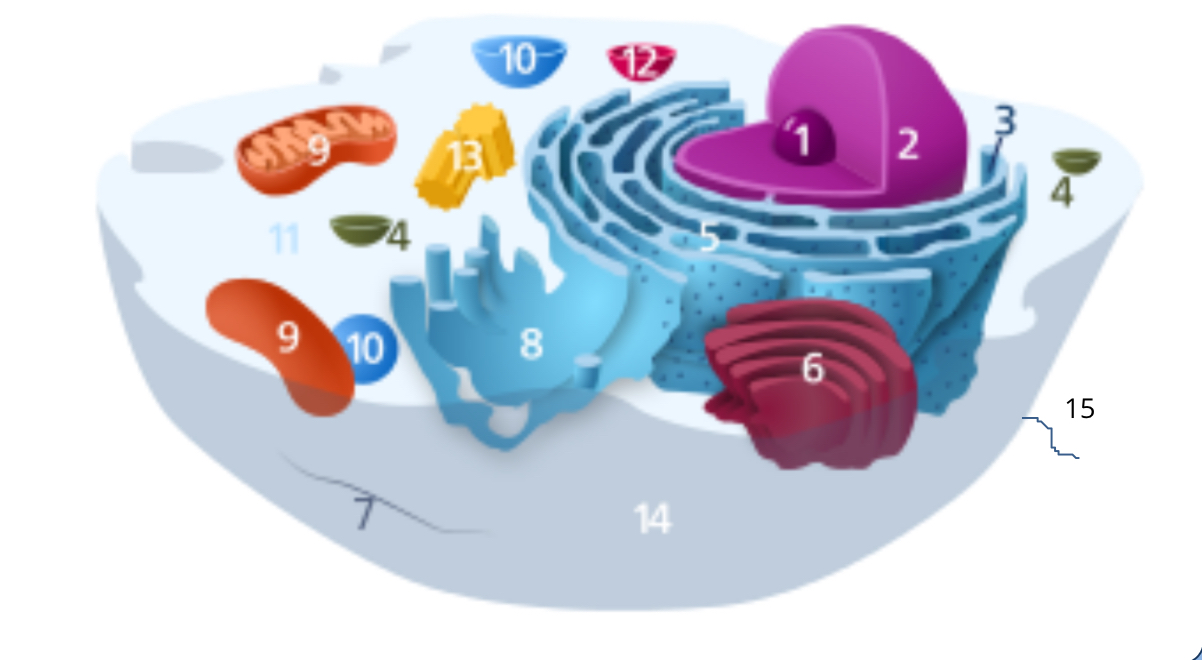
#10
vacuole
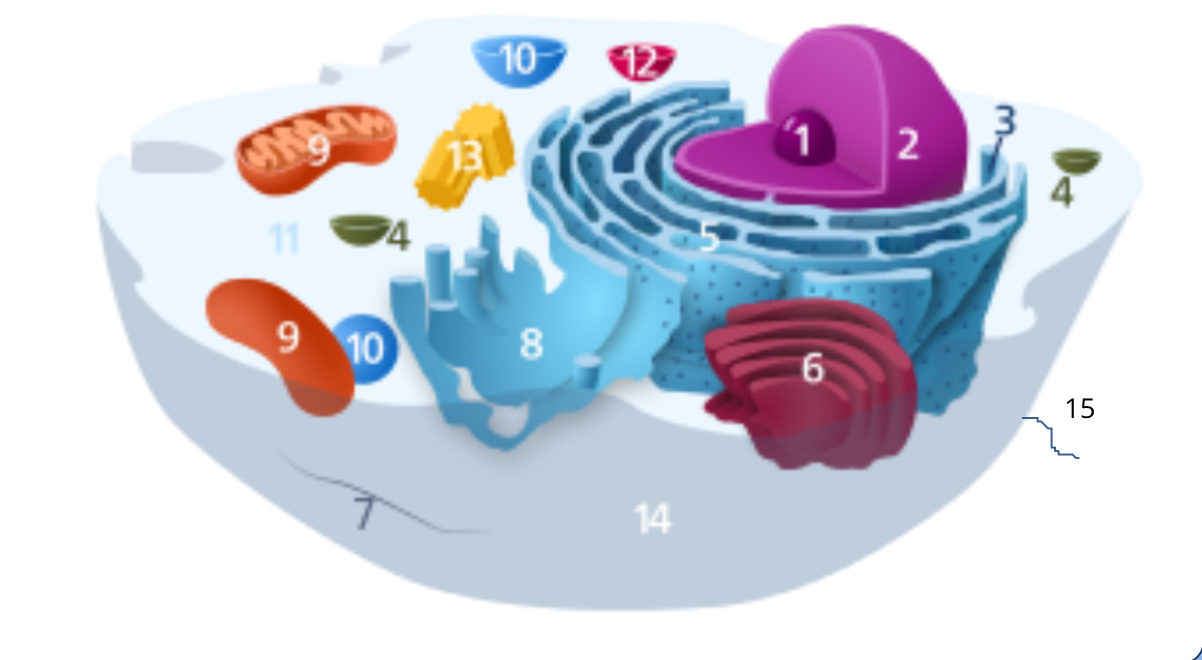
#11
cytosol
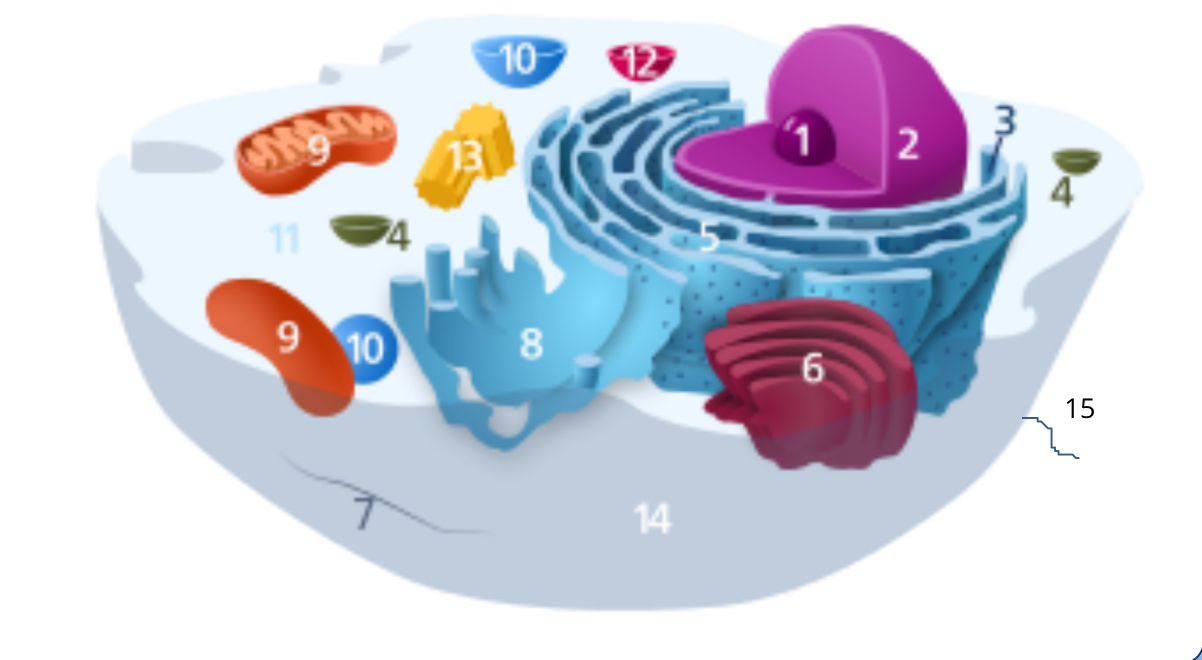
#12
lysosome
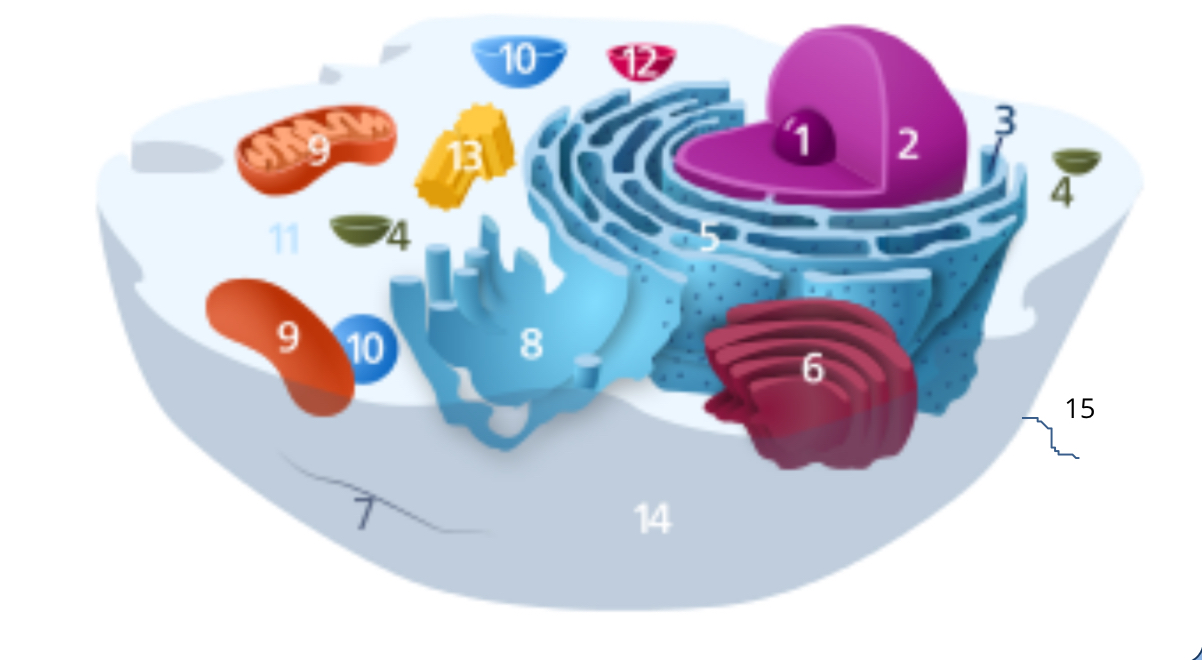
#13
centrosome
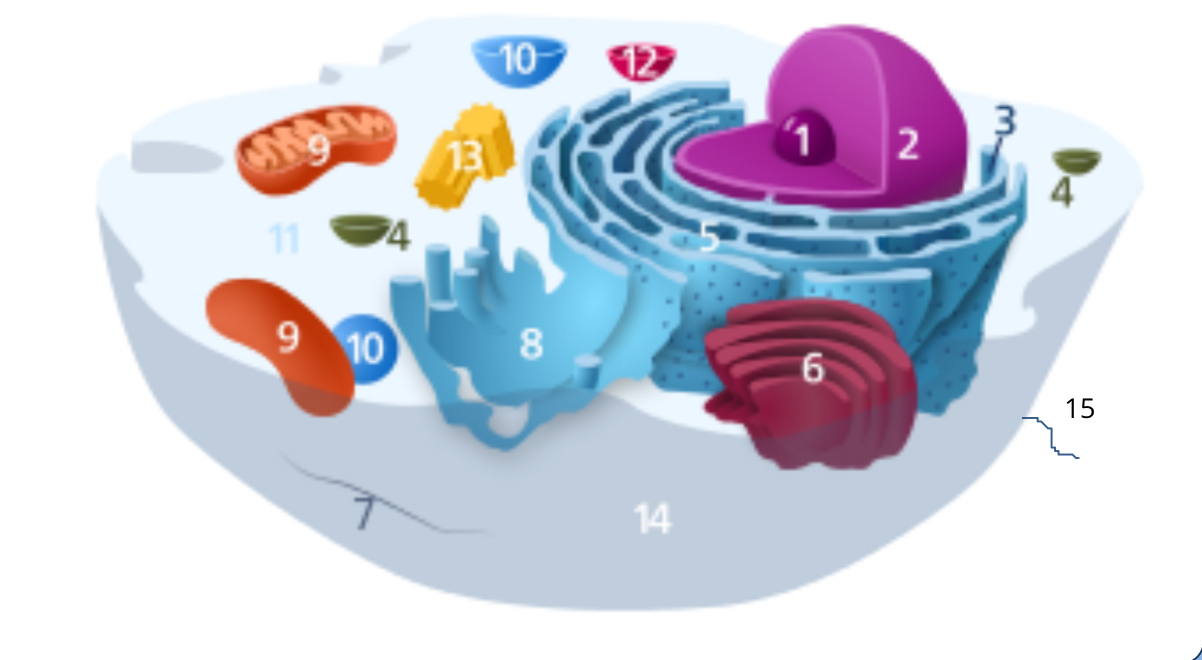
#14
cell membrane
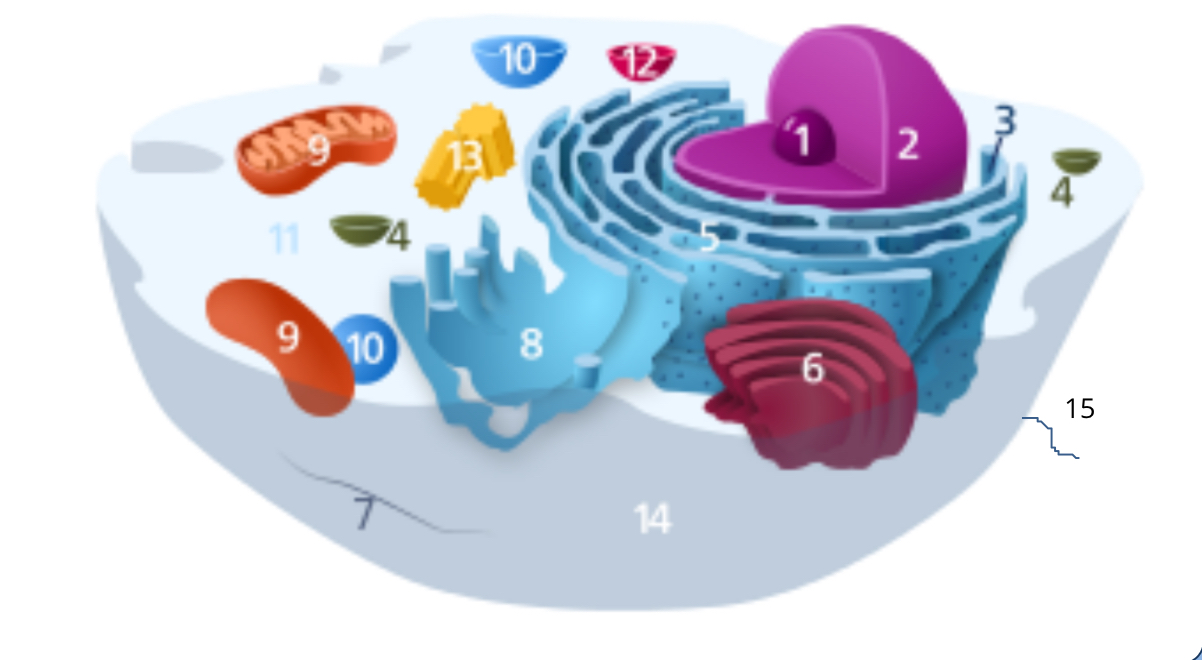
#15
cilia & flagella