LAL 4) Memory Systems and Amnesia Lecture
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This set of flashcards covers key concepts related to memory systems, types of amnesia, cognitive neuropsychology, and implications of memory on learning.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms

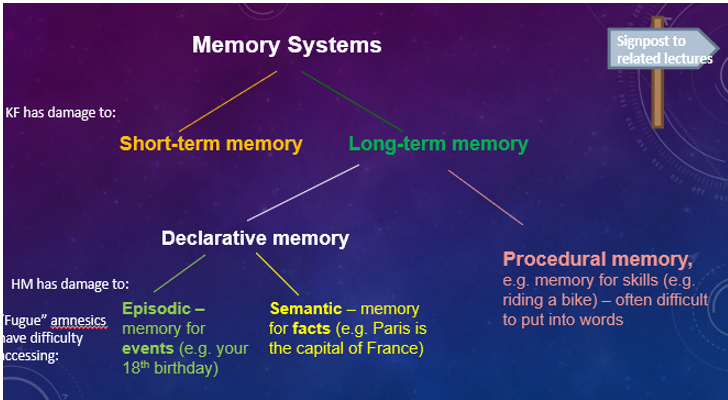
Memory Systems
Different kinds of memory that may be stored differently in the brain, each with unique methods of storage, recall, and forgetting.
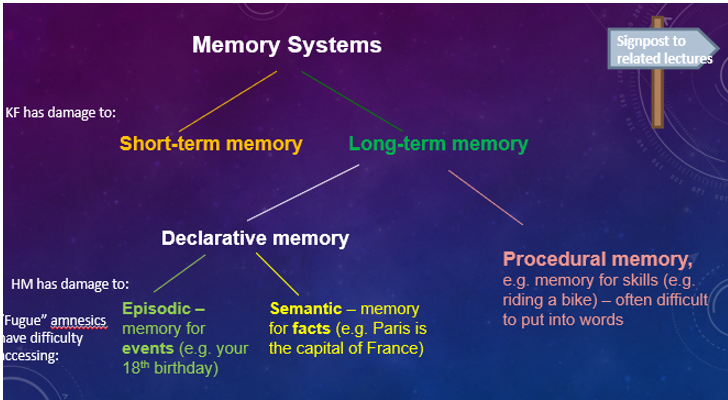
Short-Term Memory
The capacity to hold a small amount of information for a brief duration, typically seconds to minutes.

Long-Term Memory
Memory that is not forgotten as quickly, and is more resistant to distractions compared to short-term memory.
Working Memory
A form of short-term memory used for executing plans, allowing for quick access to information while tasks are being performed.
Amnesia
A condition characterized by the loss of memories, such as facts, experiences, or skills.
Episodic Memory
A type of long-term memory that involves recollection of specific events and experiences.
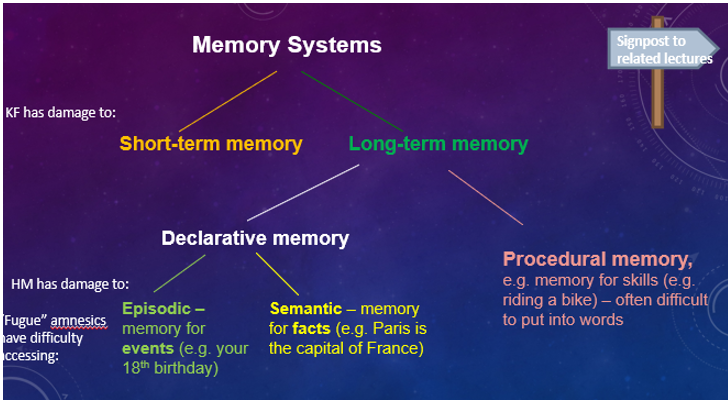
Semantic Memory
A type of long-term memory that involves the storage of factual information and knowledge.
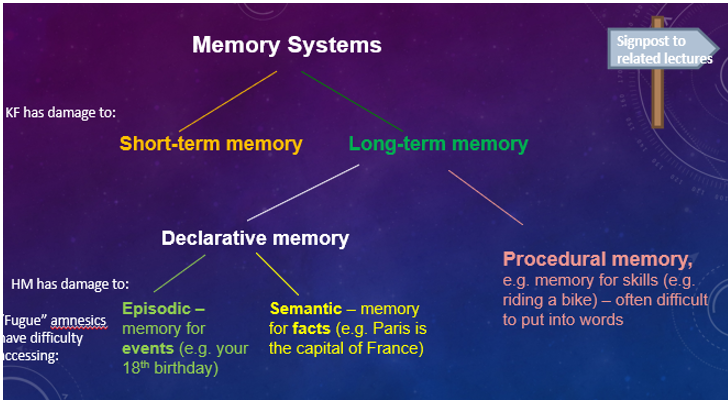
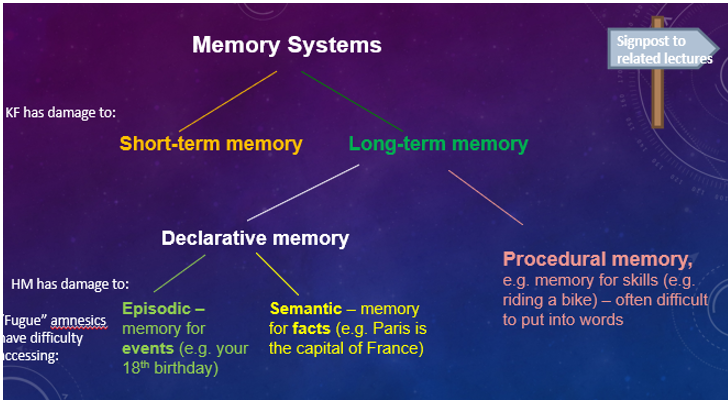
Procedural Memory
A type of long-term memory related to knowing how to perform tasks, often difficult to verbalize.
Anterograde Amnesia
A form of amnesia where new memories cannot be formed after the onset of amnesia.
Retrograde Amnesia
A form of amnesia where memories from before the onset of amnesia are lost.
Cognitive Neuropsychology
A field that studies the effects of brain damage on cognitive functions and memory.
Fugue Amnesia
A type of amnesia characterised by sudden, unplanned travel away from home and inability to recall one's past.
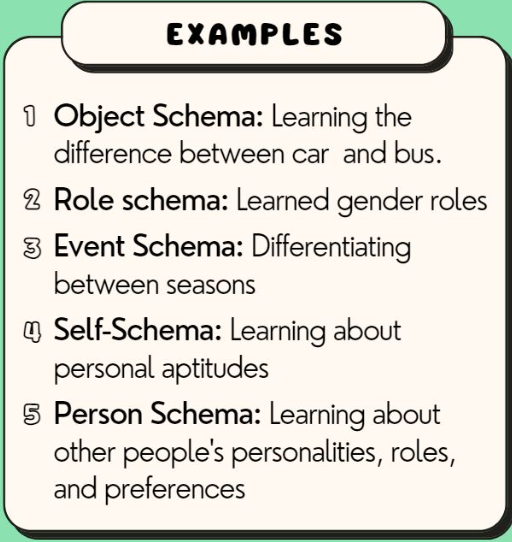
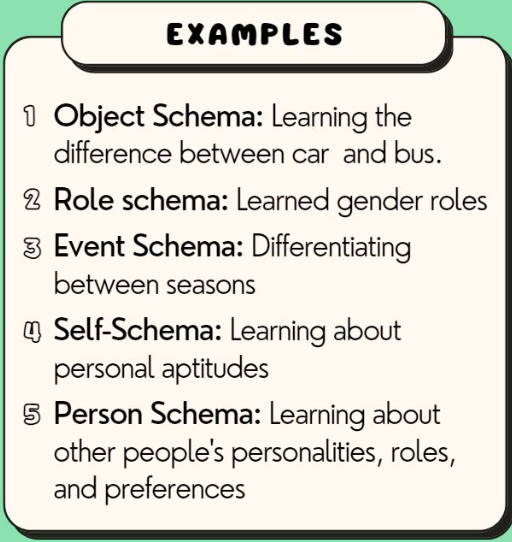
Schema
A conceptual framework that helps organise and interpret information based on past experiences.
Flashbulb Memory
A highly detailed, exceptionally vivid memory of the moment and circumstances in which a surprising or emotionally arousing event was learned.
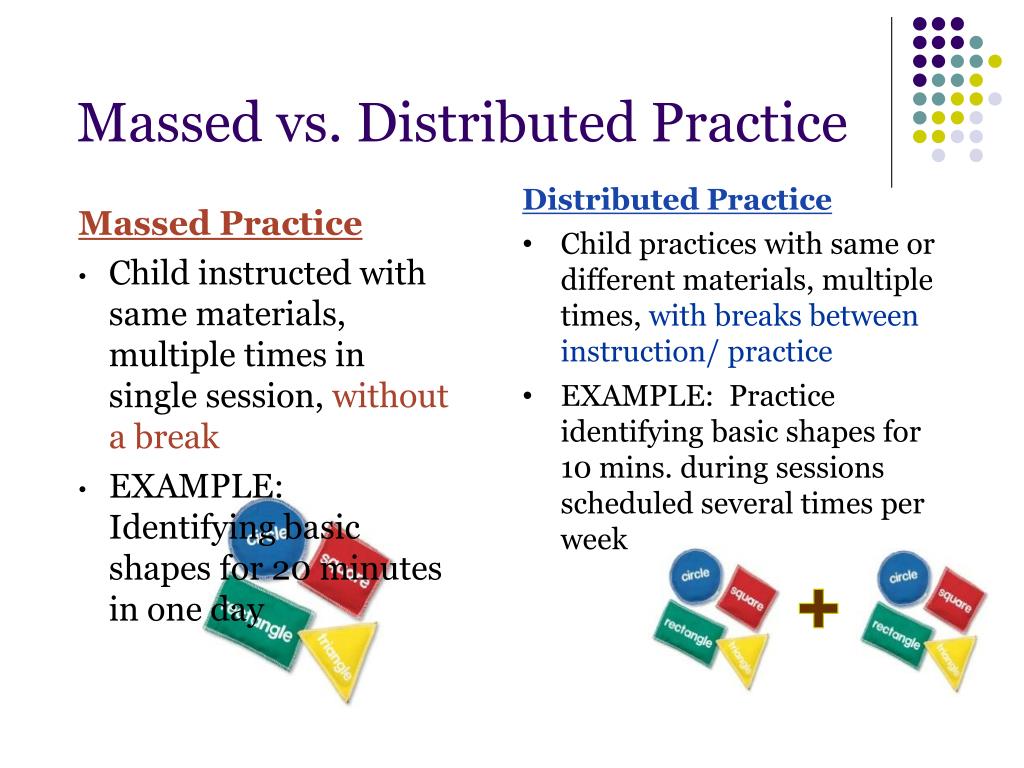
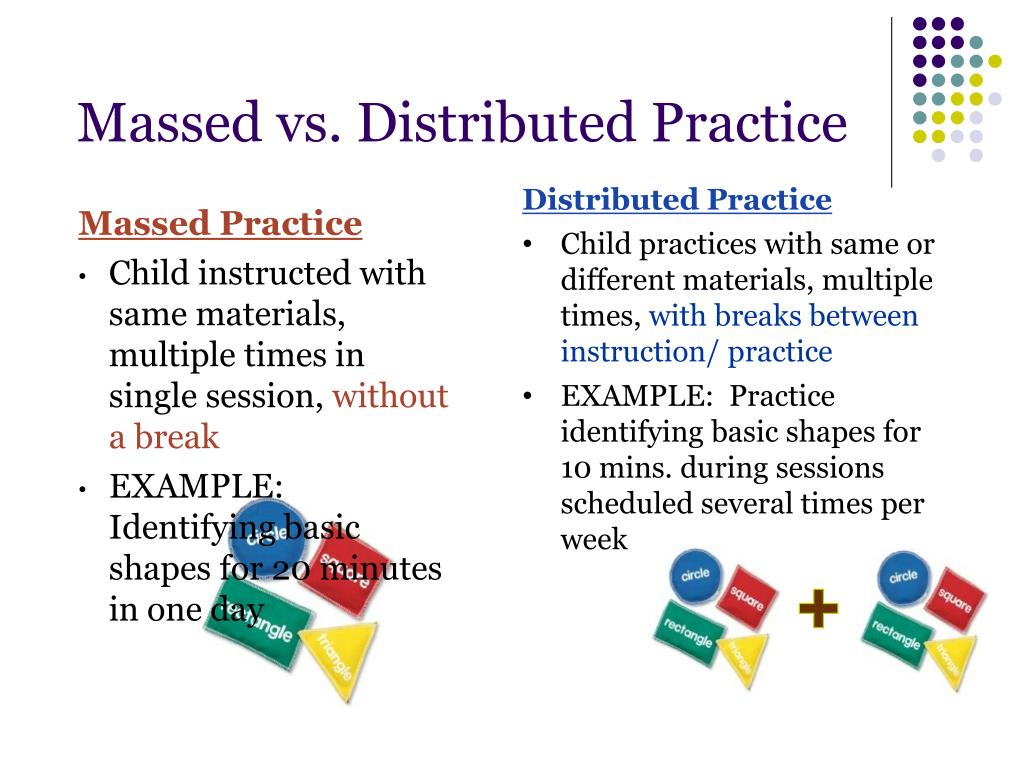
Massed Practice
A learning method where the learner studies material in a single session; often contrasted with distributed practice.
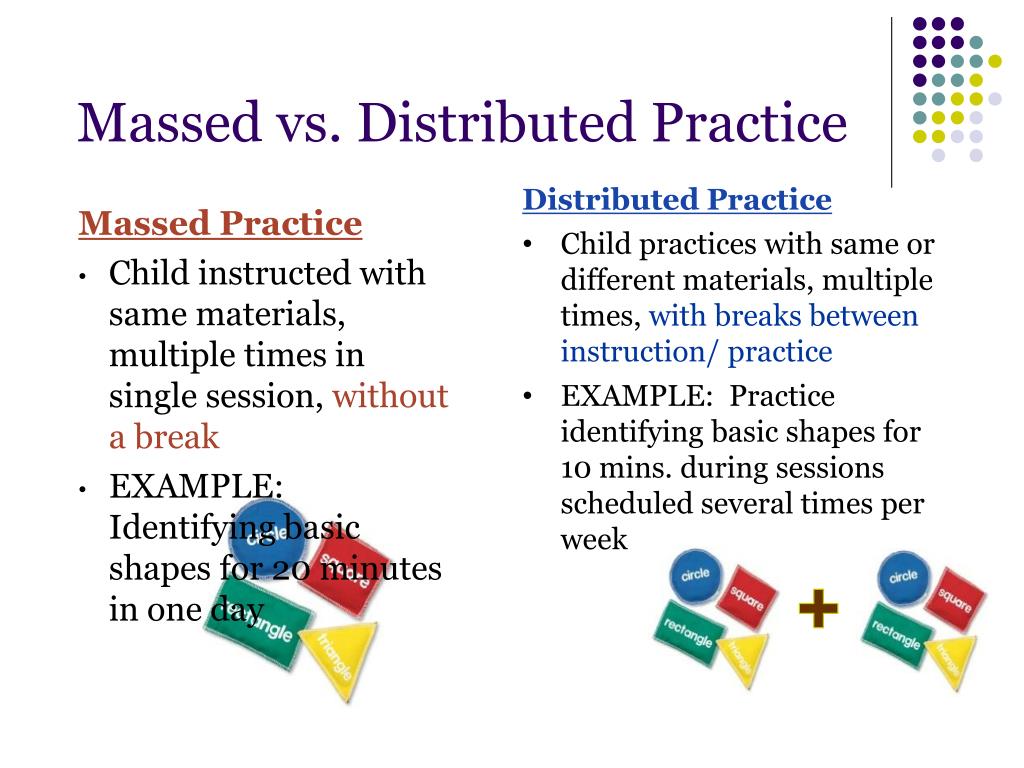
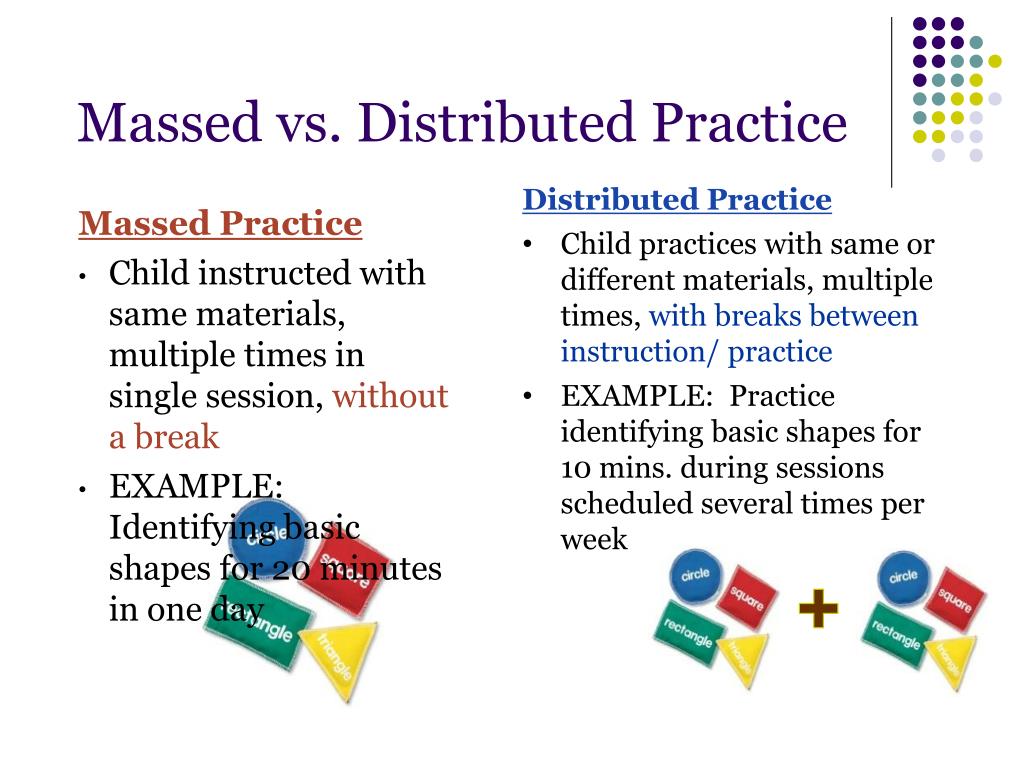
Distributed Practice
A learning method where study sessions are spaced out over time; known to enhance long-term retention.
Recollection
The retrieval of memories, especially those associated with clear context, emotions, or sensory details.
Cognitive Load
The total amount of mental effort being used in the working memory.
Digit-Span Task
A psychological test that assesses short-term memory capacity by having subjects repeat a sequence of numbers.
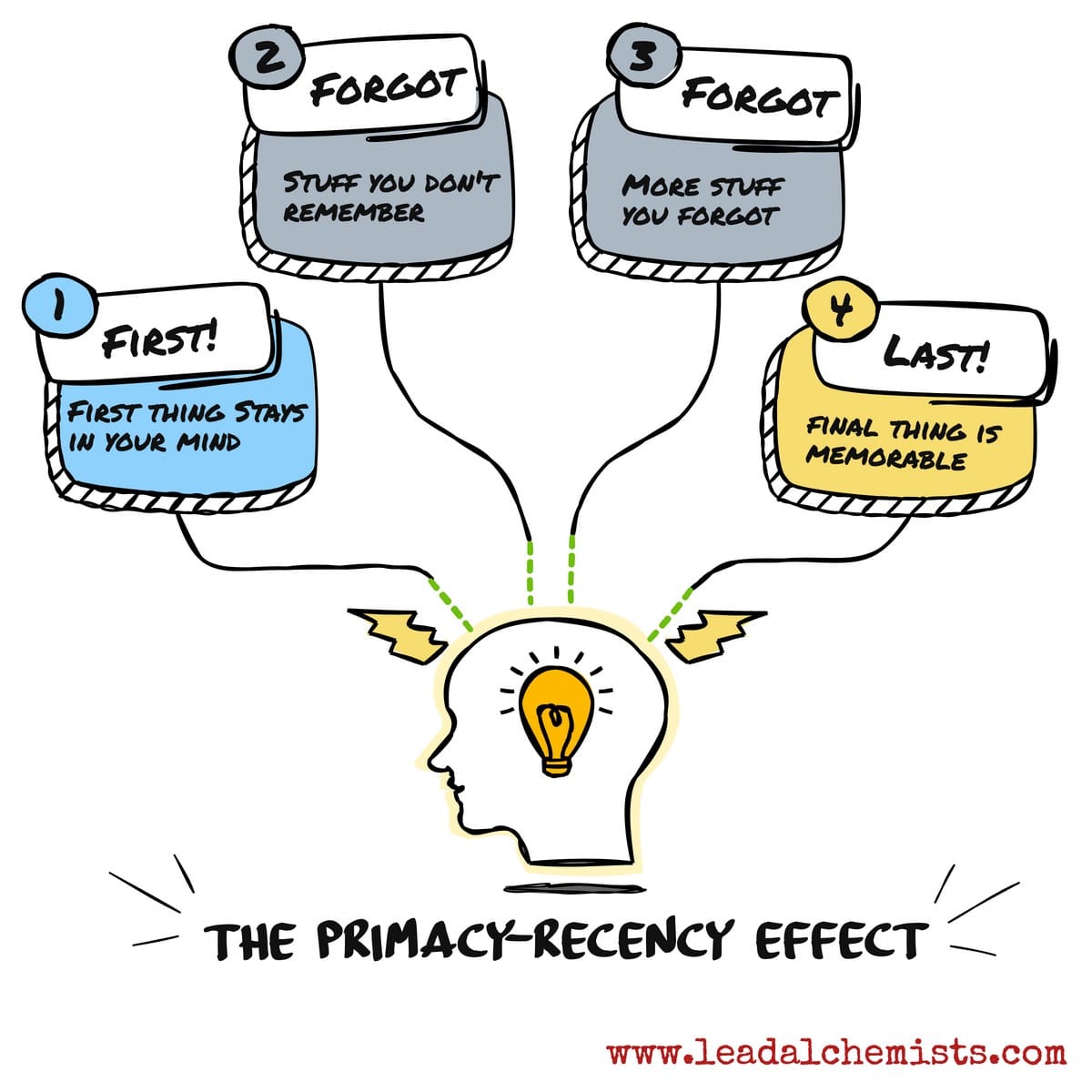
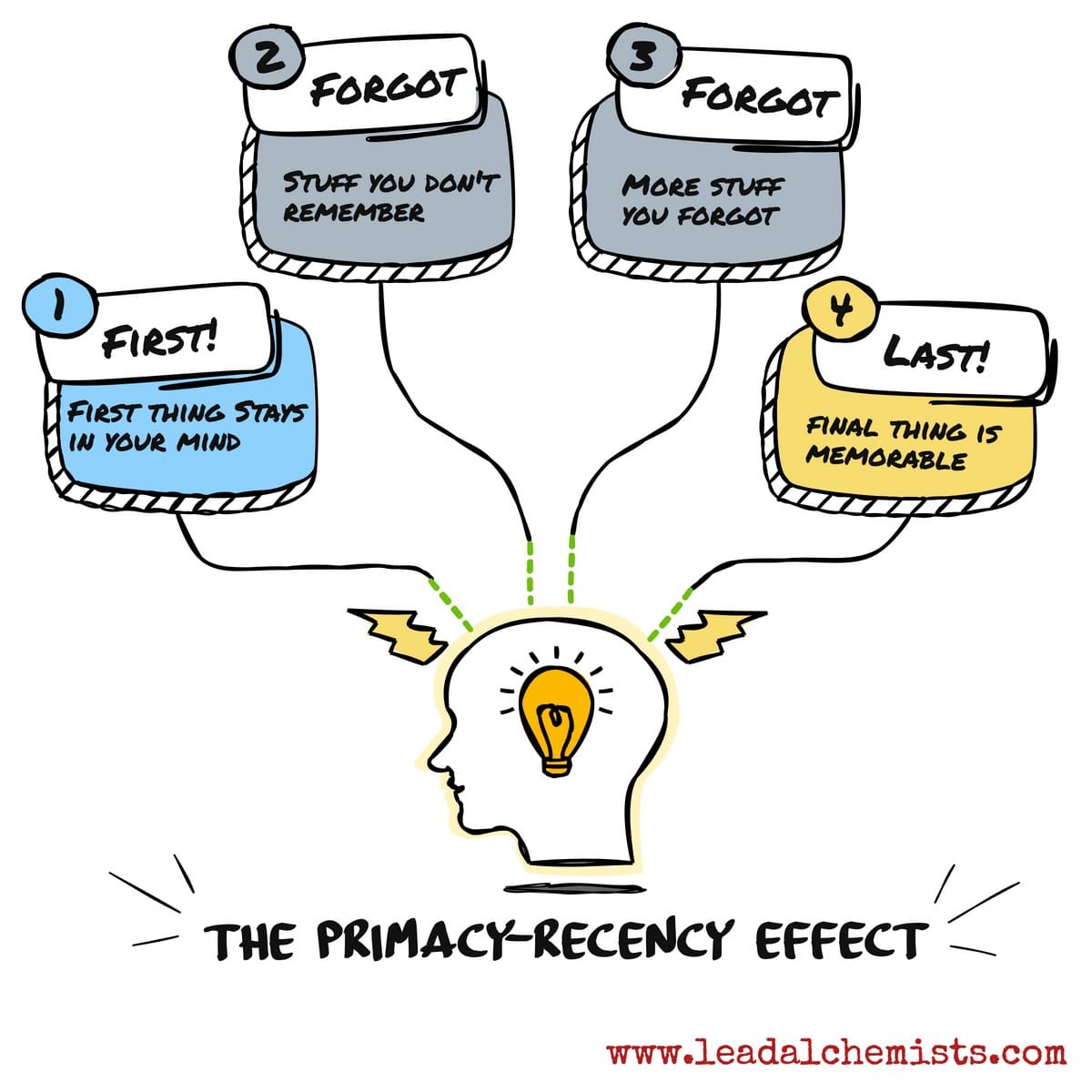
The Recency Effect
A phenomenon where later items in a list are easier to recall than items in the middle.
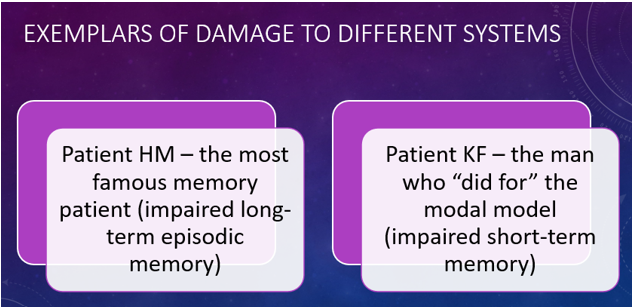
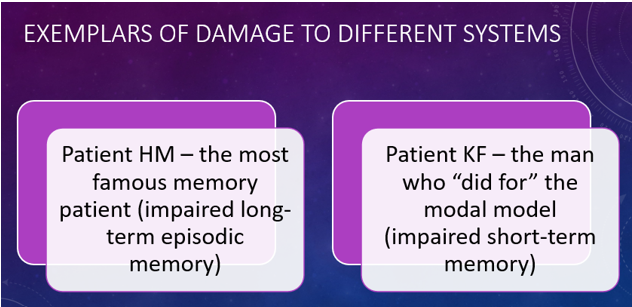
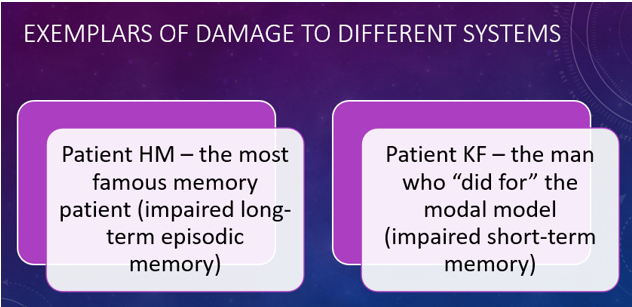
Patient HM (Henry Molaison)
A famous patient who suffered from anterograde amnesia after having surgery on his hippocampus to treat epilepsy. He learns that memory is a distinct cerebral function, separable from other cognitive abilities, and identified the medial aspect of the temporal lobe as important for memory.
Conditioning in Amnesiacs
The ability of amnesic patients to learn through conditioning despite their memory deficits.
Cognitive Development
The progression of learning and memory capabilities as one ages.
Age-Related Memory Decline
The general trend that older adults tend to have more difficulties with memory tasks than younger individuals.
Non-word Repetition Task
A task used to assess phonological memory based on a person's ability to repeat nonsense words.
Expertise Acquisition
The process of becoming highly skilled in a certain domain, often requiring extensive practice.
Neuroconstructivism
A theory positing that cognitive abilities develop through interaction with the environment and experience.

Prosopagnosia
Face blindness; a condition where individuals cannot recognize familiar faces, potentially due to brain damage in specific areas.

Contextual Memory
Memory that is enhanced or influenced by the context in which the information was learned.
Dual N-Back Task
A working memory task that involves remembering the positions of items presented in sequence over time.
Feedback in Learning
Information returned to the learner about their performance, important for correcting errors and improving skills.
Dissociation of Function
A principle that certain types of cognitive functions can be selectively impaired while others remain intact.
Cognitive Routines
Well-practiced strategies or methods employed to process information and solve problems.
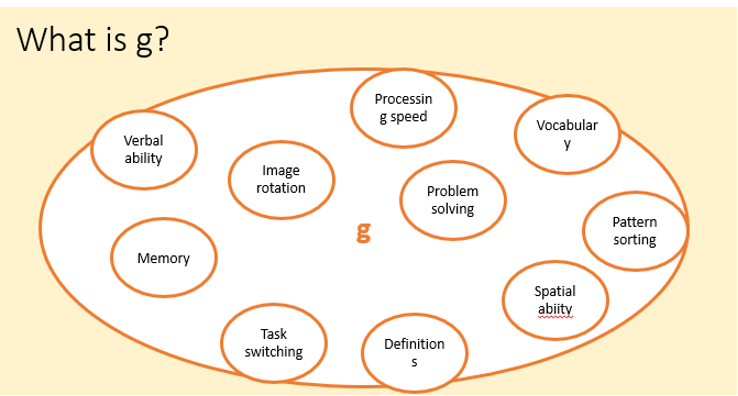
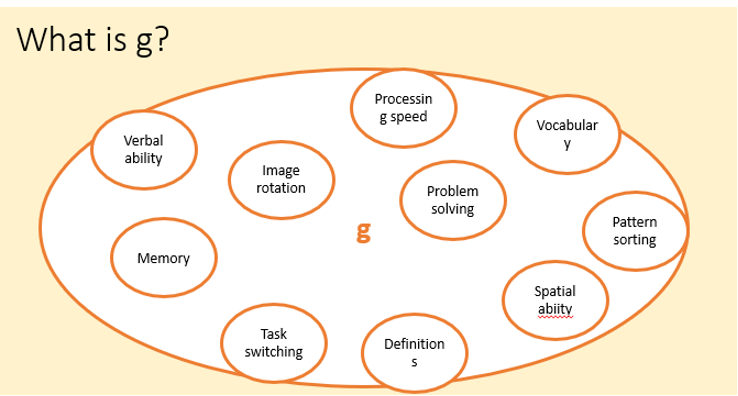
General Intelligence (g)
A measure of an individual's overall cognitive ability, often linked to performance on various mental tasks.
Repressed Memories
Memories that have been unconsciously blocked due to the traumatic nature of the event.
Temporal Order
The sequence in which events occur, critical for accurate memory retention and recall.
Vicarious Learning
Learning that occurs through observing the experiences of others.
Retention Interval
The duration of time between learning information and being tested on it, which can influence recall.
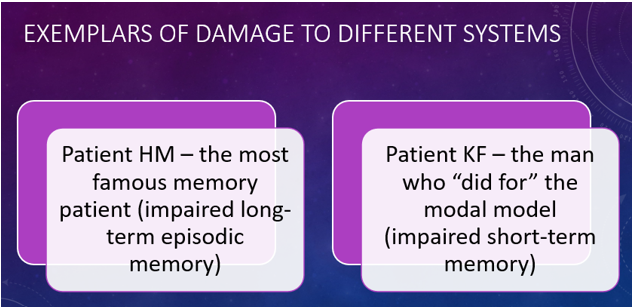
Patient KF
A famous case study for memory research, who suffered brain damage in a motorcycle accident, resulting in severely impaired verbal STM but intact visual STM and LTM, providing key evidence for the Working Memory Model by demonstrating that STM has separate components.
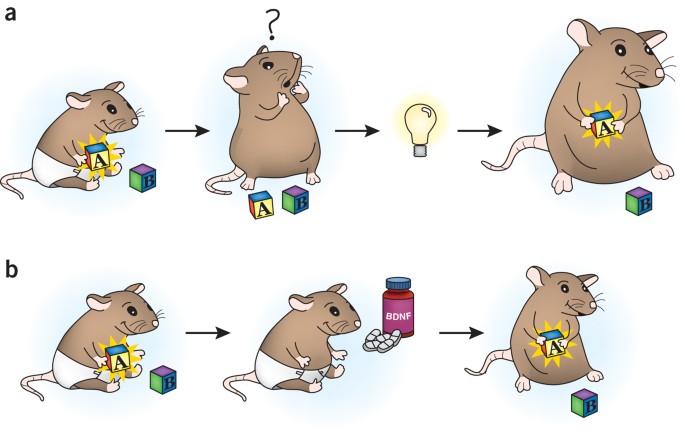
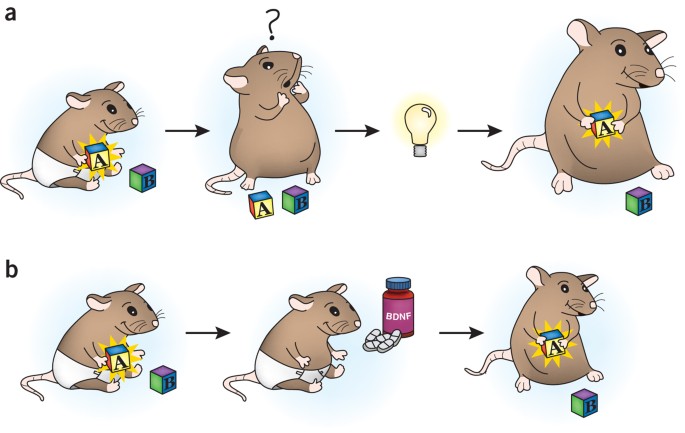
Travaglia et al (2016)
Demonstrated evidence of infantile amnesia in rats, highlighting hippocampal maturation's role in episodic memory acquisition. They noted that while memories are formed, they might not be easily accessible without contextual reminders.
Patient PV Case study
Excelled at learning word-word pairs but struggled with word-nonword pairs.
Patient SR Case study
a high-achieving individual with a digit span of 4, encountered difficulties in repeating back multi-syllabic nonwords, despite normal ST and LT visual memory.

Mitchell et al. (2003)
Participants were shown a video of a burglary and asked misleading questions afterward. older adults as more susceptible to misleading information during eyewitness events.
