Amplifiers, Op-Amps, and Transistors Overview
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
The feedback resistor determines the stability of an op-amp circuit. (T/F)
True
The power efficiency of an amplifier is unaffected by the power supply voltage. (T/F)
False
Which quantity is used to express amplifier gain in decibels?
20log(Vout/Vin)
Transconductance amplifiers produce an output voltage proportional to input current. (T/F)
False
Which of the following describes transresistance?
Vout/Iin
A lower output resistance in amplifiers leads to better power transfer to the load. (T/F)
True
What is the primary purpose of transfer characteristics in amplifiers?
Determine input/output relationship
Amplifiers with higher voltage gain always have better power efficiency. (T/F)
False
The significance of input resistance in amplifiers is that it determines loading effects.
Determine loading effects
Power amplifiers typically have the lowest input resistance among amplifier classes. (T/F)
True
Which amplifier type converts input voltage into output current?
Transconductance amplifier
An inverting op-amp configuration has a positive voltage gain. (T/F)
False
In a summing amplifier, the output voltage is proportional to:
The sum of all input voltages
Which op-amp circuit is designed to integrate an input signal?
Integrator
Input bias current in op-amps can lead to small output errors. (T/F)
True
Unity gain bandwidth is defined as:
The frequency where the open-loop gain equals 1
DC imperfections in op-amps only occur at high temperatures. (T/F)
False
What is the primary role of the feedback network in an op-amp?
Stabilize gain
Practical op-amps have infinite input impedance. (T/F)
False
What is the typical voltage gain of a non-inverting op-amp?
1+(Rf/Rin B)
Doping a semiconductor introduces free charge carriers. (T/F)
True
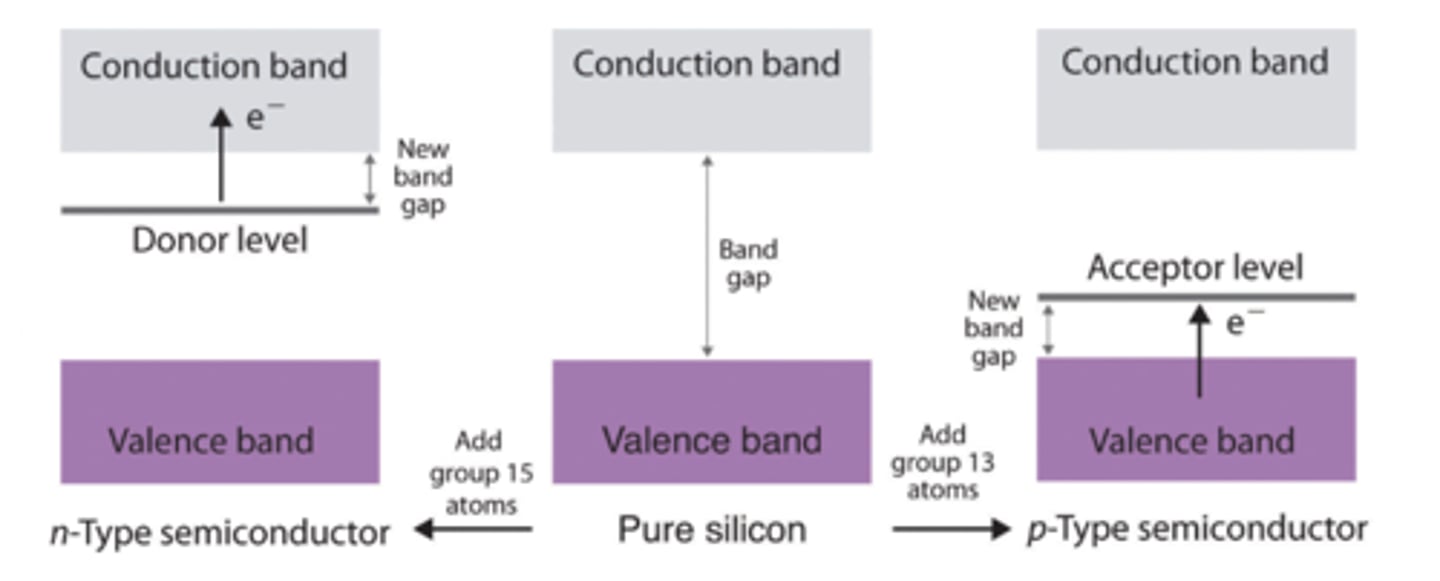
What current flow mechanism dominates in intrinsic semiconductors?
Diffusion Current
Forward bias in a pn junction widens the depletion region. (T/F)
False
IN a pn junction diode, reverse bias results in:
Widened depletion region
Intrinsic semiconductors have equal concentrations of holes and electrons. (T/F)
True
What is the primary function of a Zener diode?
Limit Voltage
A full-wave rectifier is more efficient than a half-wave rectifier. (T/F)
True
Which diode model best approzimates real behavior at voltages?
Constant voltage drop model
Diodes exhibit negative resistance in their forward bias region. (T/F)
False
How does load resistance affect a full-wave rectifier circuit?
Affects ripple voltage
MOSFETs operate with no gate current in DC analysis. (T/F)
True
What region of a MOSFET defined by VDS>(VGS−VT)?
Saturation
Transconductance measures how efficiently a MOSFET converts gate voltage to drain current. (T/F)
True
What is the primary parameter controlling BJT operation?
Base-emitter voltage
A BJT in saturation allows maximum current flow. (T/F)
True
What happens to a BJT in the cutoff region?
Both junctions are reverse-biased
The small-signal model for transistors is used for analyzing AC behavior. (T/F)
True
In the small-signal model, input resistance represents:
The resistance between base and emitter
MOSFETs require significant input power for operation. (T/F)
False
What parameter determines the threshold voltage of a MOSFET?
Gate oxide thickness