UNIT 2 AP PSYCH - Biological Basis of Behaviour
1/64
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
Hemispheres
Halves of brain
Right is left and left is right
They always coordinate with each other
The corpus callosum communicates
Corpus callosum
Bundle of nerves that communicate between the two hemispheres
LEFT and RIGHT hemisphere
LEFT
language, speech, handwriting, rhythm
Analytical side of the brain
control the right side of the body
RIGHT
widespread perception, visuals, patterns, facial recognition
processing and creativity
Controls the left side of the body
Lobes
Areas of the cerebral cortex with a SPECIFIC FUNCTION
Frontal Lobes
Reasoning, motor skills, cognition, expressive language
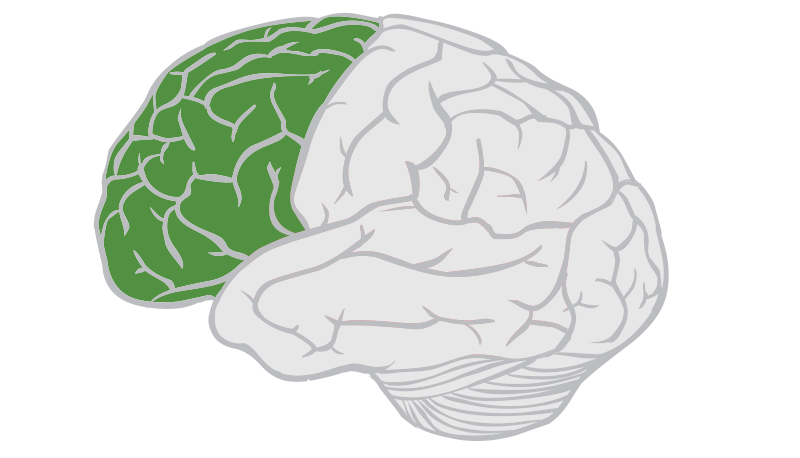
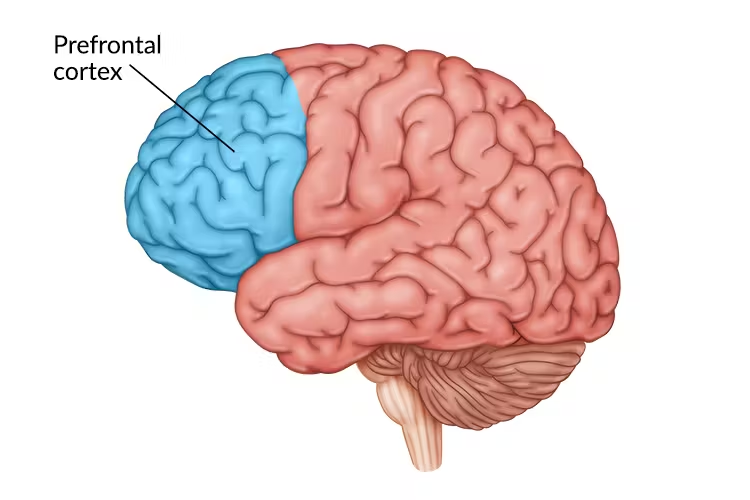
Prefrontal Cortex
complex cognitive behaviour, personality, decision-making, social behaviour
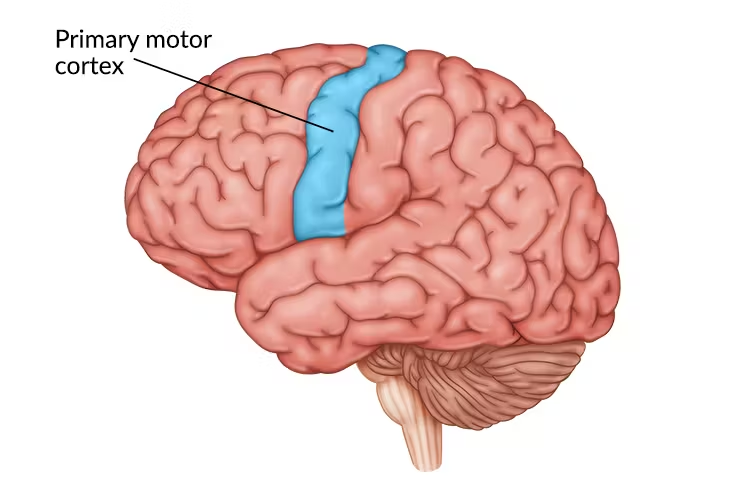
Motor Cortex
Receives information from various from various lobes of the brain and carries out body movement
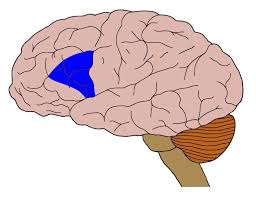
Broca’s Area
Speech production and language comprehension (speech muscle movements)
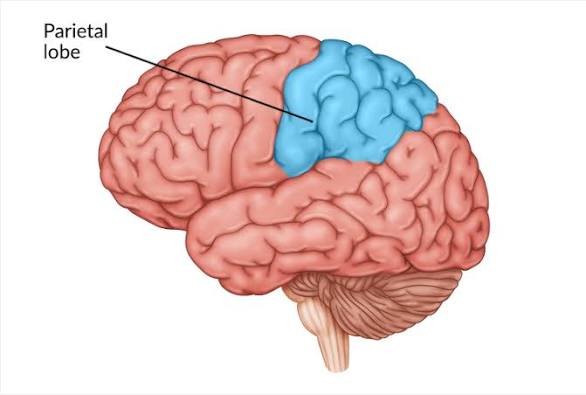
Parietal Lobes
Process sensory signals
Touch, pressure, sensitivity, pain
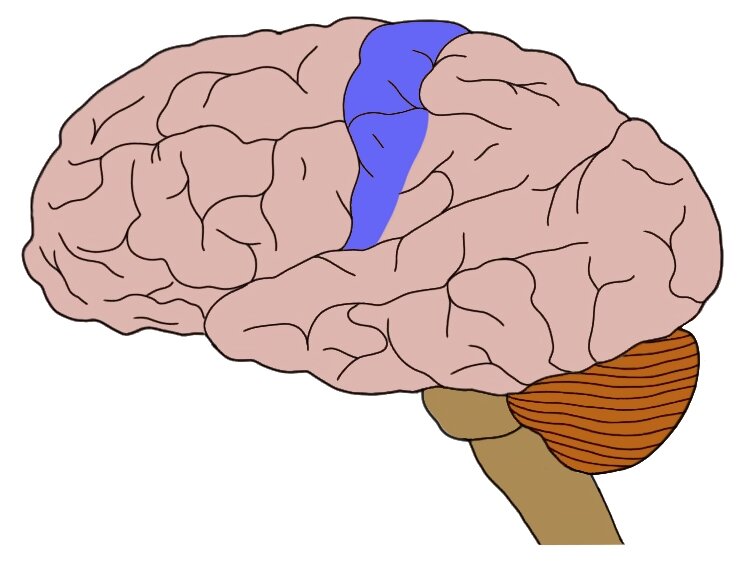
Somatosensory cortex
Receives and processes sensory information from the whole body
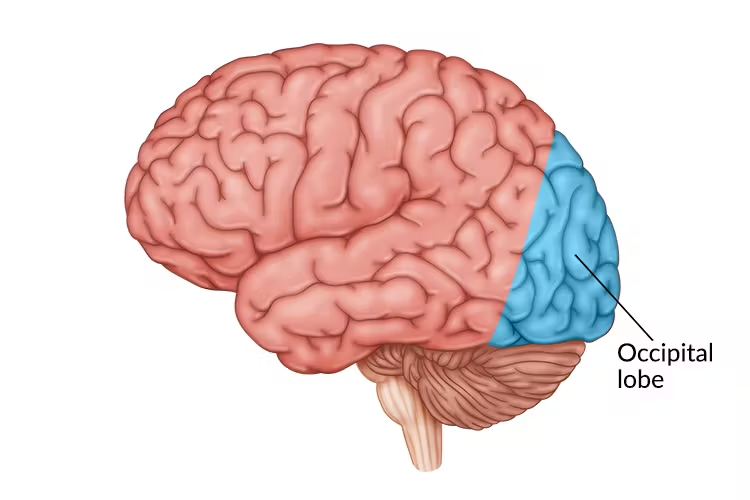
Occipital Lobes
Contains visual centers of the brain
Visual Association Cortex
Recognizes lines, angles, shapes, shadows, and movement
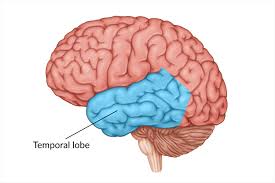
Temporal lobe
Neurons that help with sensible learning and meaningful speech
Wernicke’s area
Responsible for speech comprehension
Plans movements for Broca’s
Brainstem
Most primitive part of the brain
base connected to spinal cord
Controls message flow from brain —> body
Breathing, swallowing, ❤ rate, blood pressure, conciousness, sleepiness
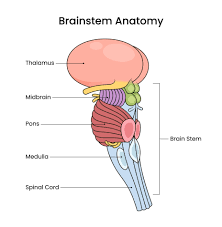
Pons
Bridges MEDULLA and CEREBELLUM, breathing and sleep cycle control
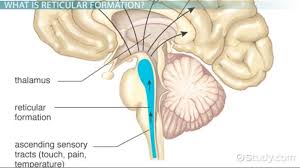
The Reticular Formation
Integrated Nervous system
Nerve network carrying messages from brainstem
pain intensity and body part regulation
filters unnecessary stimulus
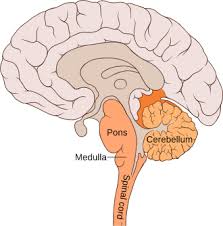
Cerebellum
Little brain
posture, balance, coordination of voluntary movements
Allows muscles to act together and produce fluid movement
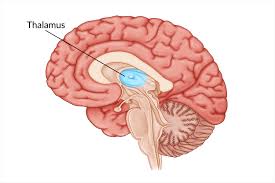
Thalamus
Processes and transmits movement and sensory information
Relay station to the cerebral cortex
Receives all sensory input
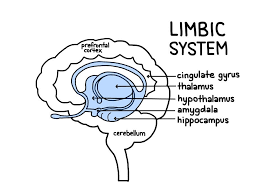
Limbic system
Emotions
Hunger and sex drive
Episodic memory formation
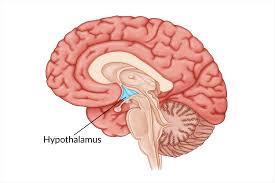
Hypothalamus
Connects with other regions
Hunger, thirst, emotions, body temp, circadian rhythms
Controls pituitary by secreting hormones
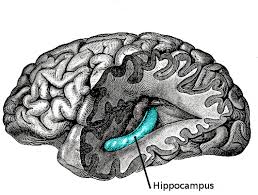
Hippocampus
Formation, organization, and storage of certain memories, connects certain sensations and emotions to memory
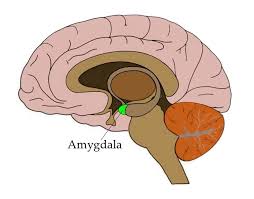
Amygdala
“Fear center” of the brain
processes emotion and survival responses '
Activated during potentially harmful situations
Aggression and fear
Neuroscience
Study of the brain, brain science
Works together with other disciplines
Looks at the brain and models the brain using multiple tools
Brain Autopsy
Examination of the brain tissue after death
Currently the only way to diagnose specific degenerative disorders
Remaining family members can often be cured after autopsy
Lesioning Studies
Humans with brain lesions can help us understand what specific parts of the brain do
Can also be done on LAB RATS
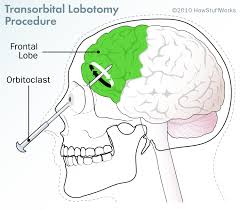
Prefrontal Lobotomy
Removes part of the brain (prefrontal cortex) to change and control behaviour
Unattaches cortex from the rest of the brain
Hemispherectomy
Removes half of the brain to control seizures
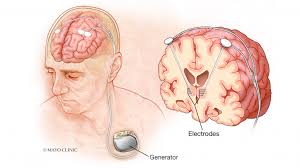
Deep brain stimulations
A newer way to change and assess psychological issues
Less invasive
Electrodes placed on specific parts of the brain to stimulate it
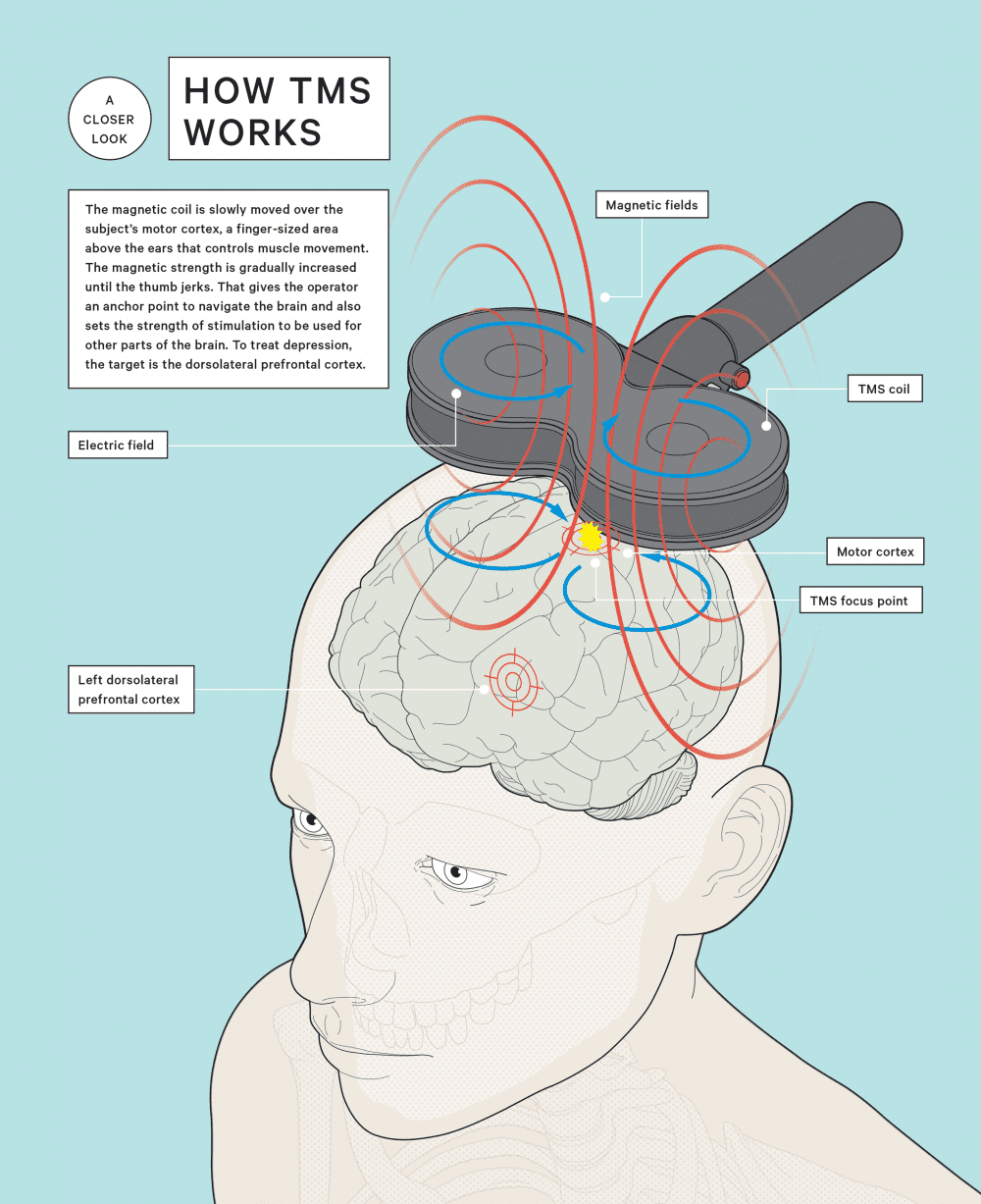
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS)
Uses magnetic want to alter brain’s electric fields
Helps change moods and cures depression
Brain Scanning
Provides information about brain structure and anatomy
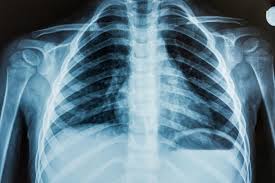
X-Rays
Shows hard structures
Bones and cartilage
Helps find fractures
NOT a complete evaluation
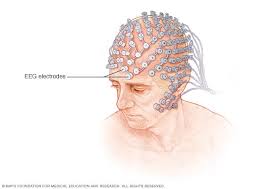
Electroencephalograph
Measures brain activity through electrical wave pulses
Electrodes placed on scalp
Electric output forms waves that indicate sleep, seizures, etc.
Used in laboratories usually to measure experimental patient brain activities
Records patterns on the brain’s SURFACE
What areas are active when
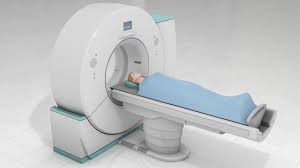
Computer tomography
2D x-ray photos that are identified from all kinds of angles to put together a 3D photograph of the organ, tissue, or area
Clots, Muscles, Etc.
Large scale brain features
Used in ERs to quickly identify issues
Functioning MRS (MRI)
Detects changes in blood oxygenation which responds
More oxygens more activity
Activity and high resolution images
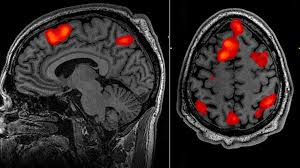
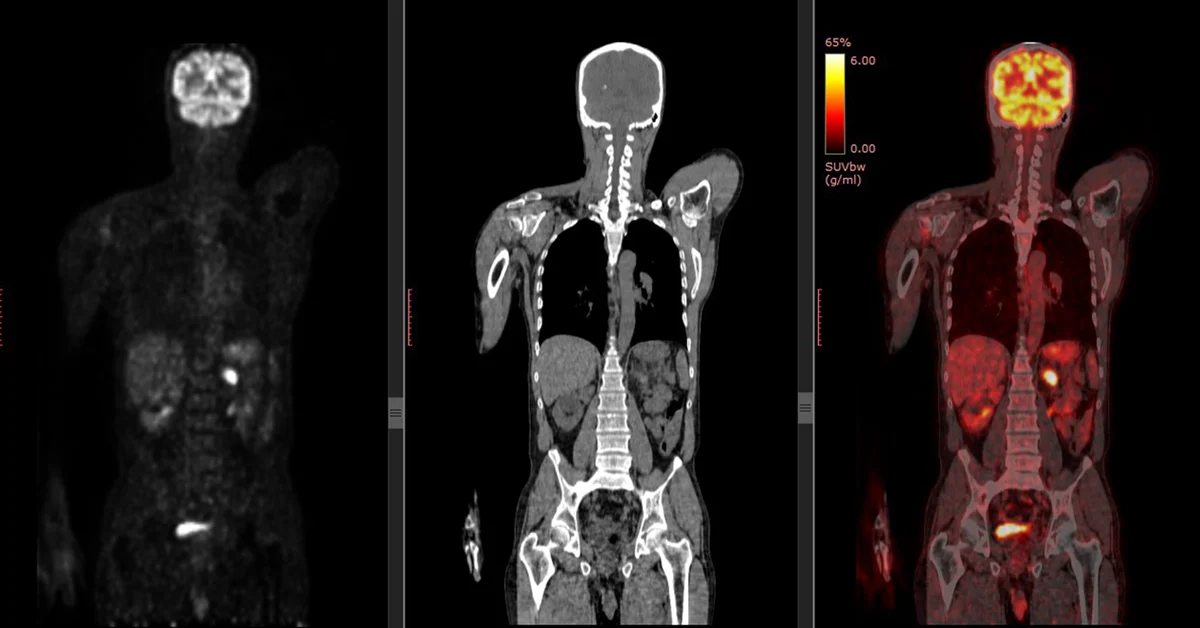
Positron Emission Tomography
Glucose is on energy source, decay emits positrons
Measures brain activity
Positron picked up by the detectors
Neuroplasticity
Brain can be damage resistant
The ability to structure and function of cells in the brain as a trauma response
This lessens as you age
Functional Plasticity
Brain moves functions from a damaged part of the brain to undamaged
Structural plasticity
Brain physically changes structure when learning new things
Split Brain
Corpus callosum in insufficient in communication between right and left hemispheres of the brain
The Nervous System
Body’s communication network that consists of all nerve cells
The body’s electrical wiring
Allows organisms to sense, organize, and react to environmental information
Central Nervous system
Coordinates the actions and interactions of the BRAIN and SPINAL CORD
Body’s main control center
Largest part of the nervous system
Spinal chord is an informational highway connecting the PNS to the brain
Peripheral nervous system
includes the sensory nerves outside the brain and spinal chord that connect the central nervous system (CNS) to the rest of the body
PNS connects the CNS to organs, limbs, and skin
Motor Pathway
Part of the PNS
Signals from brain to muscles/glands
Sensory pathway
part of the PNS
signals from sensory receptors to the brain
Somatic nervous system
part of a motor pathway
The nerves that transmit signals from your brain to skeletal muscles to allow voluntary movement
responsible for carrying sensory and motor information to and from the CNS
Sensory neurons (afferent neurons)
Carry information from nerves to the CNS
These sensory neurons allow us to take in sensory information and send it to the brain and spinal cord
Motor neurons (efferent neurons)
Carry information from brain and spinal cord to muscle fibers throughout the body
These motor neurons allow us to ttake physical action in response to stimuli in the environment
Interneurons
Neurons within the brain and the spinal cord that communicate internally and intervene between sensory inputs and motor outputs
Reflex Arc
Takes place ONLY IN THE SPINAL CORD (reflexes don’t move to the brain, stay only in the spinal cord)
signals sent from sensory organ to the spinal cord which processes information instead of passing onto the brain
Autonomic nervous system
regulated involuntary and unconscious actions
breathing, blood pumping through veins, digestion, heartbeat, work of internal organs
Done UNCONSCIOUSLY
Sympathetic nervous system
Part of your autonomic nervous system
Emergency response system if something alarms, alerts, or enrages you
Fight, fight, or freeze response
Accelerates your heartbeat, raises your blood pressure, slows your digestion, cools you with perspiration, makes you alert and ready for action
parasympathetic nervous system
functions to cal the person
rest and digest
reduces body arousal, energy, decreases blood sugar, increases blood flow to the digestive organs, decreased heart rate
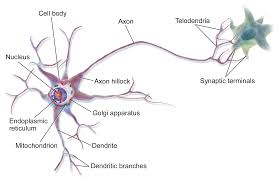
Neurons
A specialized cell in the nervous system that receives and sends messages with electrochemical signals
Chemicals stimulate the neuron
The neuron creates electricity
The neuron releases chemicals
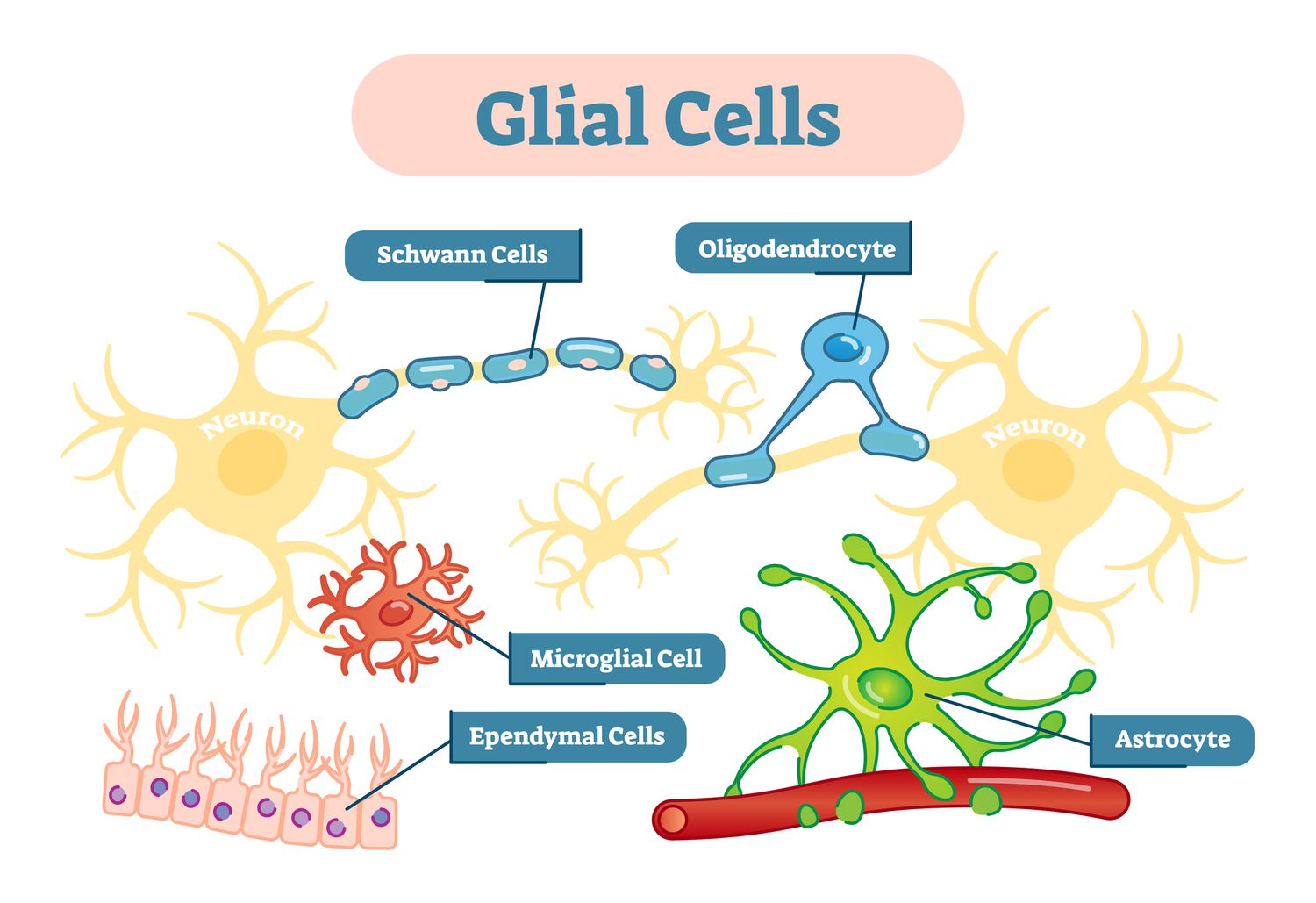
Glial cells
Cells that provide physical support for neurons to grow
make up around 90% of he brain (50;1)
surround and transfer nutrients to neurons, clean up neuron remains, and provide insulation
Dendrites (antenna)
part of the neuron
Branch like extension that receives electrical messages from other cells
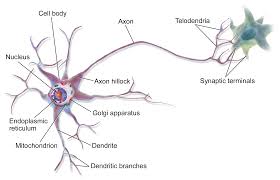
Soma (life support)
cell body of the neuron responsible for maintaining the cell and keeping the neuron, including the nucleus, functional
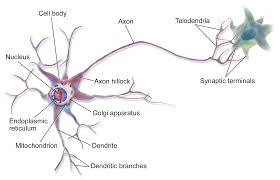
Axon (talker)
fibers that extend from the cell body to the terminal endings, help carry messages to other cells
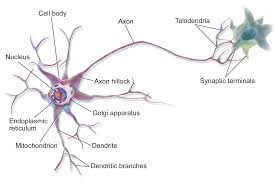
Myelin sheath
fatty substance produced by glial cells that wrap around axons to protect the nerve fiber from damage
insulates the cell and speeds up neural messaging
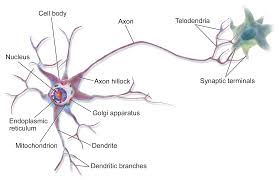
Axon terminals
tips at the end of the axon
send signals to other neurons
AKA terminal buttons OR synaptic knobs
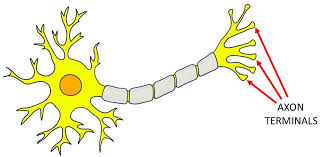
synapse
gap between the terminal button and the next neuron
where axons connect
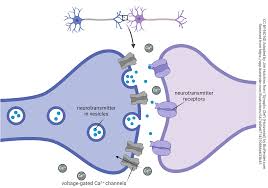
Synaptic vesicles
store neurotransmitting chemicals that are released at the synapse
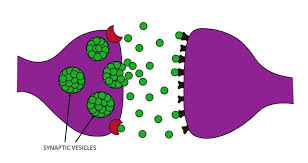
synaptic cleft or gap
Under a MILLIONTH of an inch wide
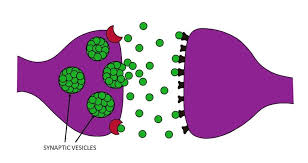
recept sites
receive signals
the “lock” that neurotransmitting molecules fit into