6th grade Science Midterm Review Questions [2026 version]
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
watershed
The area of land, including water, that drains into a larger body of water is called a ___________.
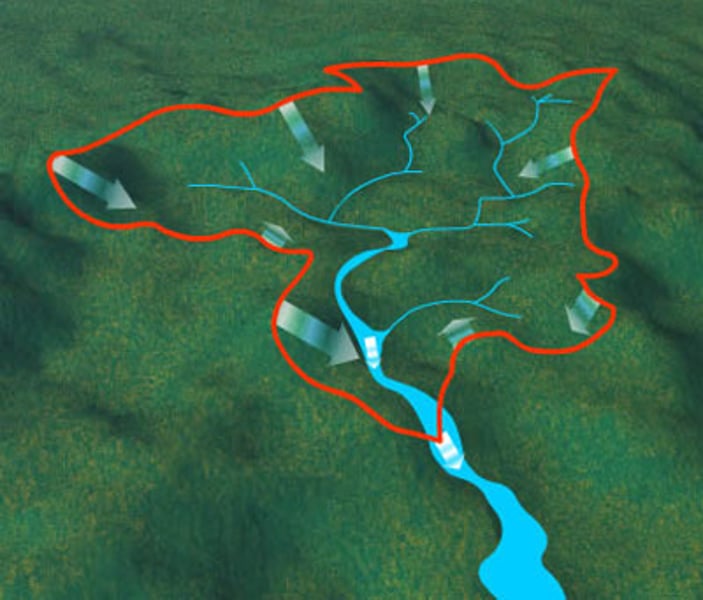
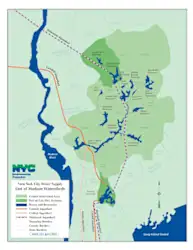
Croton
Yorktown is part of the ___________ Watershed.
riffle
An area of the stream where water bubbles over rocks is called a _______.
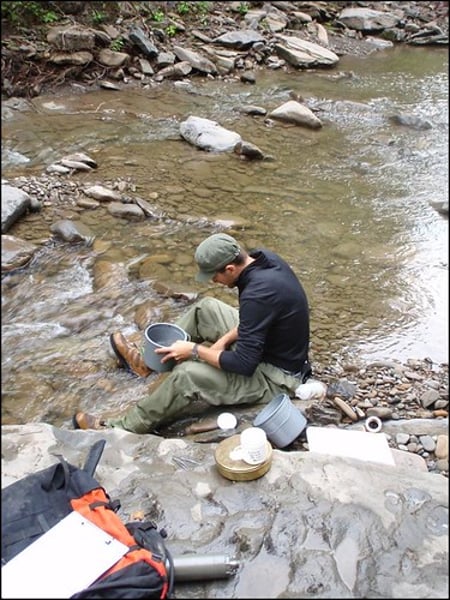
biomonitoring
Studying living organisms to determine the quality or health of a stream or ecosystem is __________.

True
True or False: Macroinvertebrates live in riffles because they provide shelter, food, and oxygen.
Macroinvertebrates
Animals that are used to determine water quality are called ___________.

taxa 2
Organisms that are somewhat pollution tolerant and found in fair quality water belong in _________.
taxa 1
Pollution sensitive organisms found in good quality water belong in _________.
taxa 3
Pollution tolerant organisms and can live in poor quality water belong in __________.
biodiversity
Different forms of life living in an ecosystem is referred to as _____________.
pH
The level of acidity or alkalinity (basic) found in the stream (substance) is the ________.

False
True or False: Pesticides are not harmful to stream.
cohesion
When molecules of the same substance (ex. water) combine, this is the property of ___________.

water cycle
The process(es) of evaporation, precipitation, and condensation are involved with the _____________.
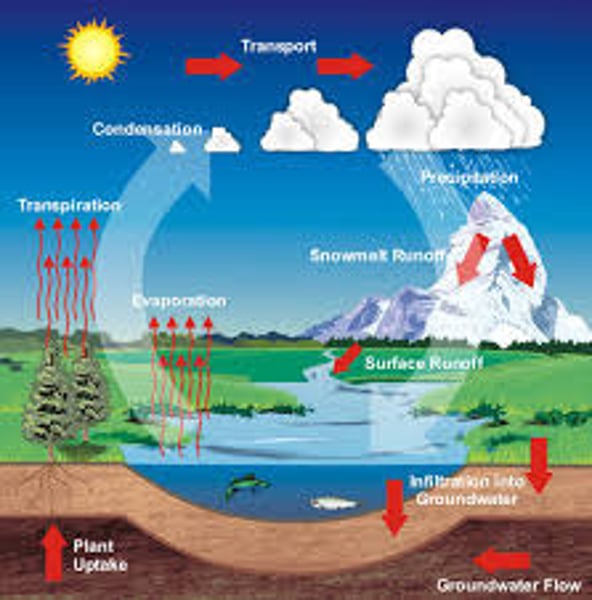
adhesion
The process in which a water molecule "adheres" or sticks to another object is known as ___________.
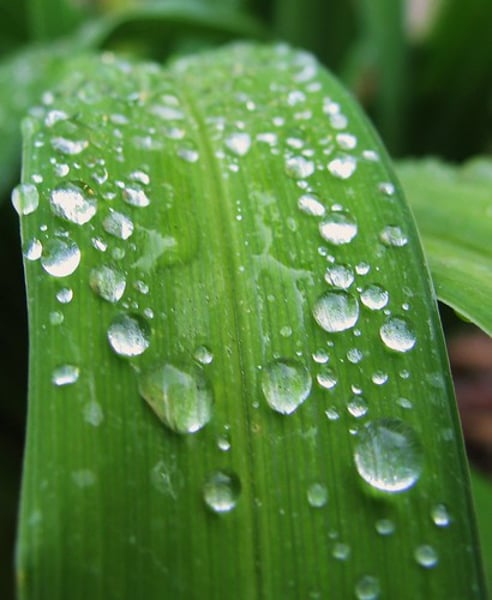

surface tension
The "skin-like" layer across the surface of water created by polor molecules linking together is called _______________.
specific heat
The amount of heat it takes to raise the temperature of a substance by one degree Celsius is called _____________.

dissolve
___________ means when a substance is absorbed by another substance.
Example: Water dissolves Alka-Seltzer.
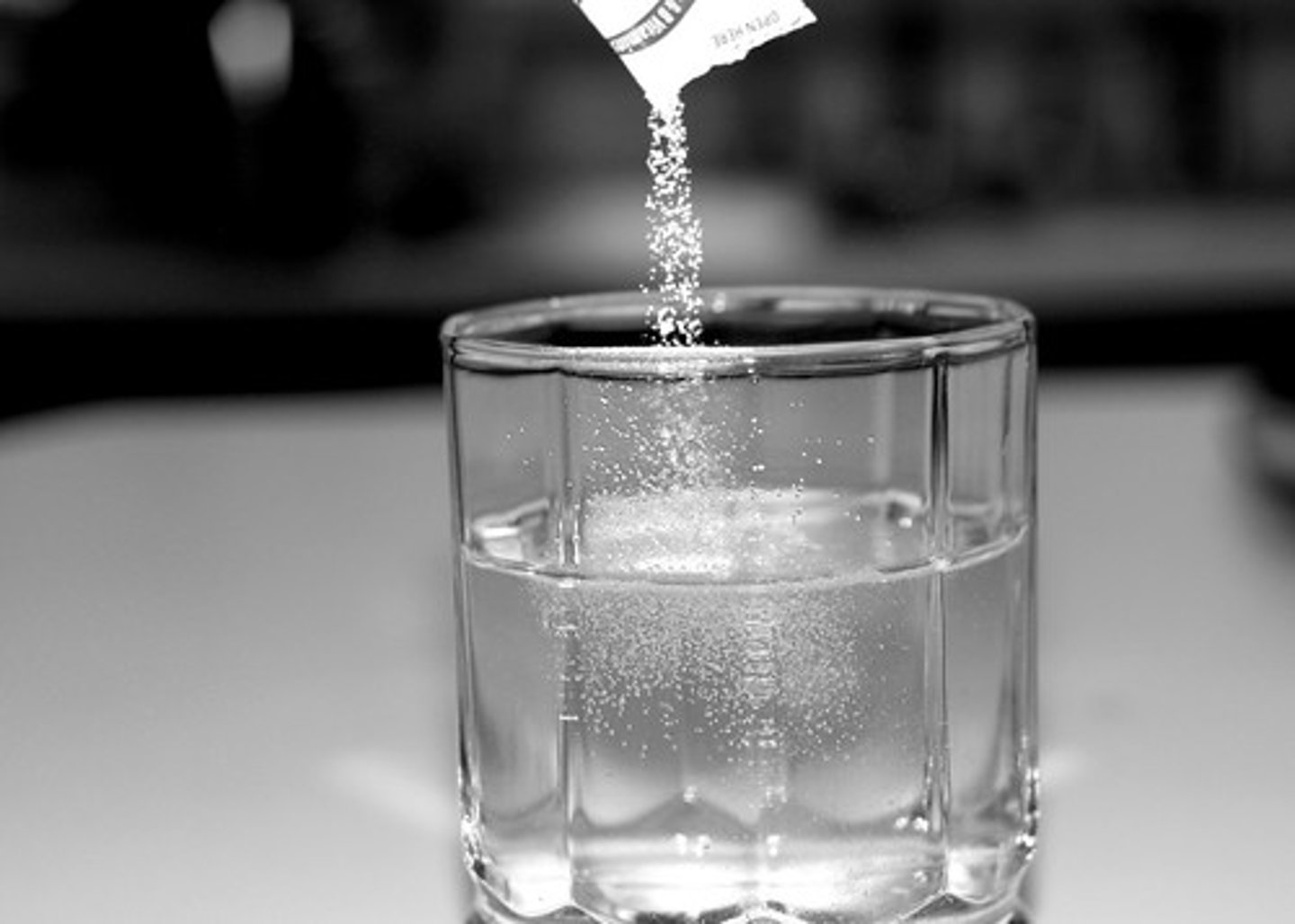

condensation
The change in state from a gas to a liquid is known as ______________. The temperature at which this occurs is known as the "Dew Point."
evaporation
The change of a liquid to a gas is known as ____________.
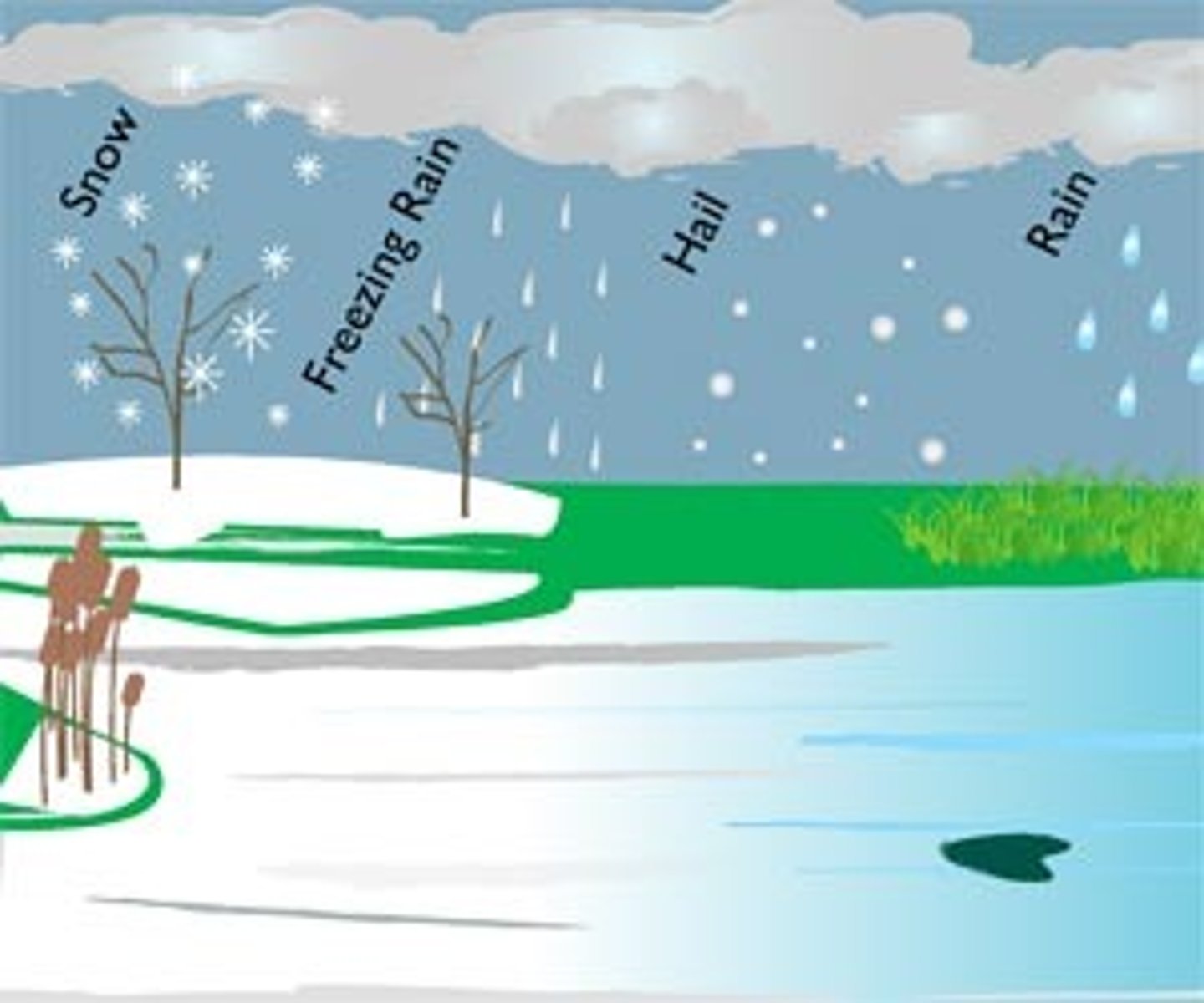
precipitation
Any form of water (hail, snow, sleet, or rain) that falls from clouds and reaches Earth's surface is referred to as __________.
0 [zero]
Water changes from a liquid to solid at ________ degrees Celsius.
100
Water changes from a liquid to a gas at _______ degrees Celsius.
water vapor
Water, in the form of a gas, is called _______.
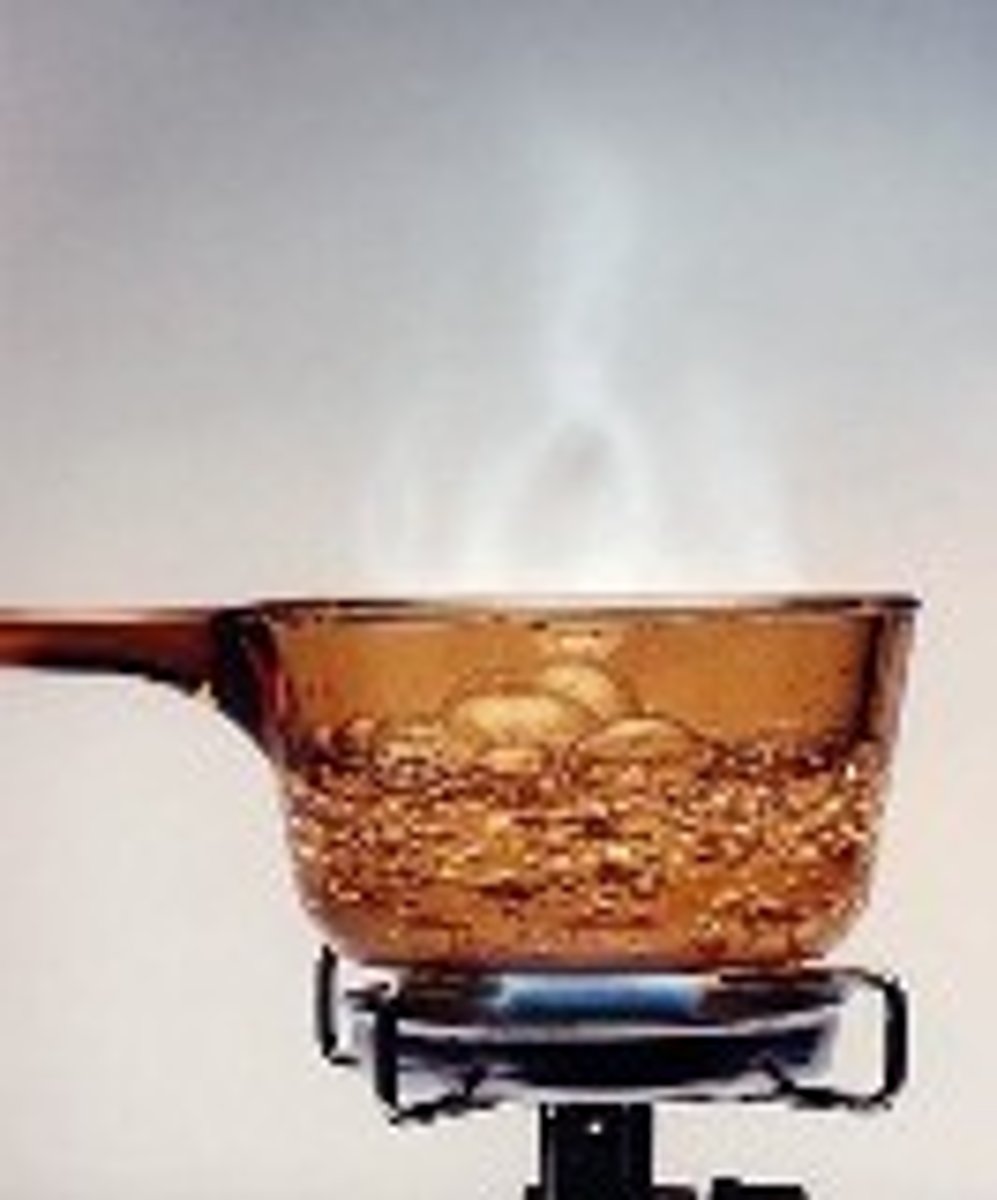

volume
____________ is the amount of space a 3-dimensional object or substance has or takes up.

density
__________ is the amount of matter within a 3-dimensional space. The formula is mass/volume.
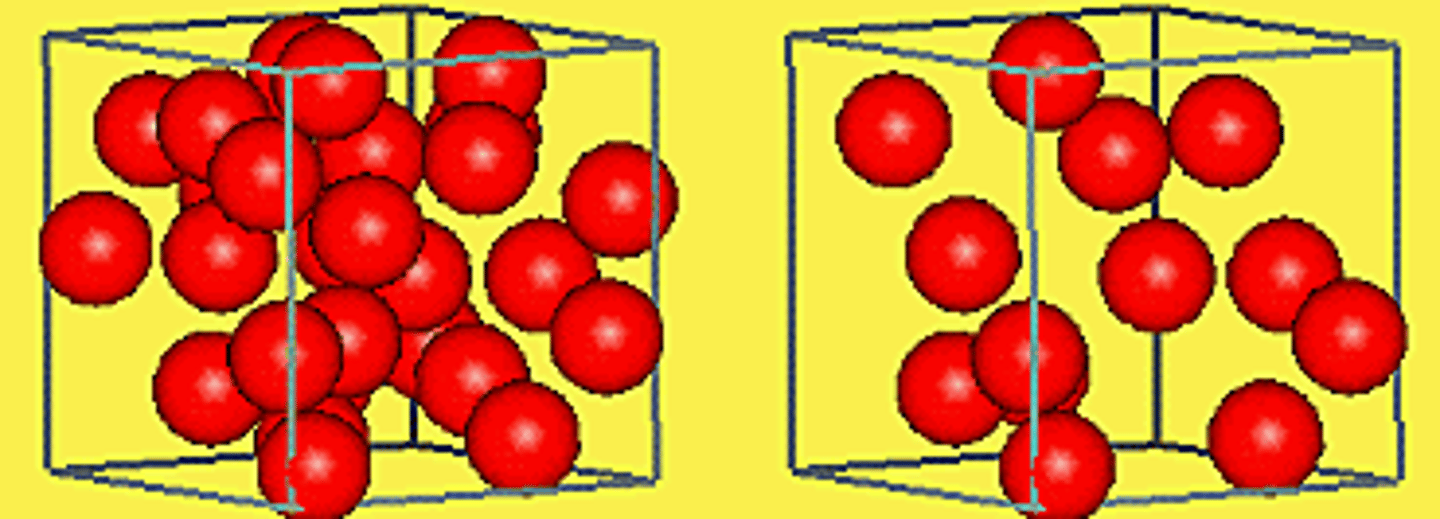
mass
The amount of matter [stuff] there is in an object is its __________.
![<p><span><span>The amount of matter [stuff] there is in an object is its __________.</span></span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/fc387d1c-10d2-4dc7-bbd1-791a0f431a2f.image/jpeg)
triple beam balance
Which tool is used to determine the mass of an object?

liquid capacity
The amount of liquid a container can hold is referred to as __________. The metric units are L or mL.

graduated cylinder
Which tool is used to determine the volume of liquids?

linear measurement
Measuring distance or length of lines is known as ______. The units used are mm, cm, m, or km.

gravity
The force of ____________ pulls the moon and Earth toward each other. Factors that control gravitational force include mass and distance.
24
It takes Earth ____ hours to rotate on its axis (at a 23.5 degrees tilted angle) for one full rotation
365
It takes Earth _____ days to revolve around the Sun.
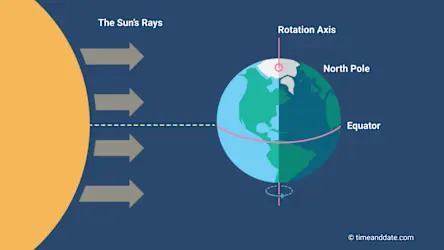
equinox
During a(n) __________ there are equal hours of daylight and darkness all over the Earth. (ex. spring or fall).
neap
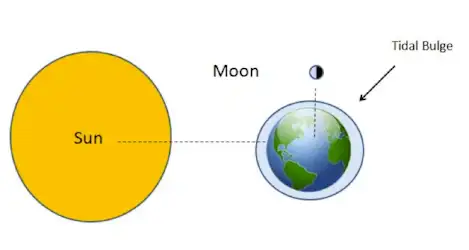
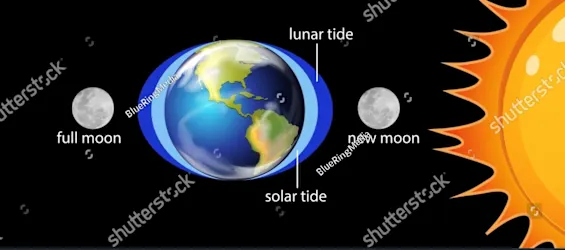
A ________ tide occurs when the sun is at right angles to the line between Earth and the moon (moon phases: first quarter & last quarter) .
spring
A ______ tide occurs when the sun, moon, and Earth line up. (The highest and the lowest tides ~ full moon and new moon)
solstice
The shortest day of the year is during the summer ______ and the longest day of the year is during the winter _______.
rotation
The spinning of Earth on its axis is called __________.
revolution
The movement of an object around another object is called __________. Example ~ The Earth moving around the Sun.
True
True or False: During the summer or winter solstice, the sun is farthest north or south of the equator.
False
True or False: We have seasons because the Earth revolves around the moon tilted on its axis.
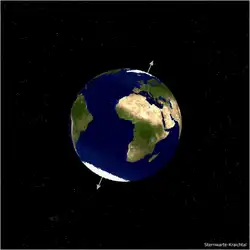
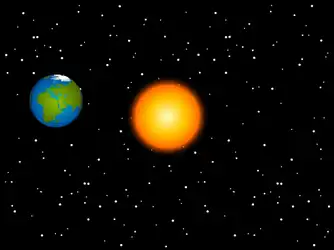
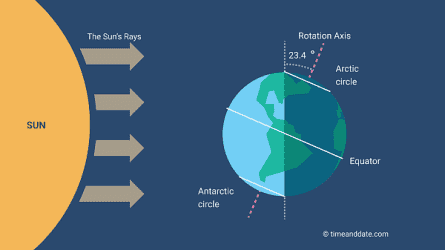
Winter
Which season is being represented in the model (picture)?
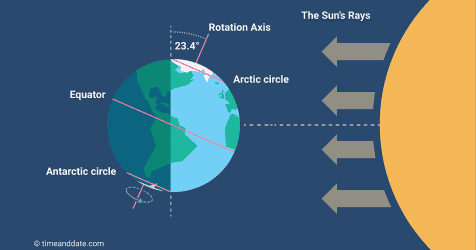
Summer
Which season is being represented in the model (picture)?
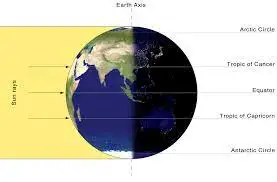
Spring and Fall
Which seasons are being represented in the model (picture) below?
claim
A _______________ is an assertion or statement believed to be true.
evidence
Scientific data used to support the claim is called _____________.
Reasoning
_____________ is a statement or statements that connect the evidence to the claim.
hypothesis
The ______________ is the expected outcome of an experiment that is used as a starting point for further investigation. It is written as an if-then statement.
independent variable
The _____________ is a factor that scientist changes during a controlled study.
dependent variable
The ____________ is a factor that is measured by the scientist and depends on the independent variable.
Qualitative data
_______________ is data that is not measurable. It is collected using the senses [touch, smell, taste, hearing, and sight].
Quantitative data
________________ is measurable data that is collected with instruments [examples: temperature, height, mass, and volume].
type of fertilizer
A student wanted to see if the type of fertilizer made sunflowers grow larger. What is the independent variable?
accuracy
A student wants to see if their stance affects their accuracy. What is the dependent variable?
dependent variable
A student wonders if the length of a rubber band affects how far it can travel. The distance it can travel is the ________.
independent variable
A student wonders if the length of a rubber band affects how far it can travel. The length of the rubber band is the _________.
controlled variables
The _________ are the factors that remain the same in order to create a valid experiment.
Ecosystem
__________ is an environment made up of living and nonliving things interacting together in the same habitat.
nonliving factors
Abiotic factors are the ________ in an ecosystem.
living factors
Biotic factors are the ___________ in an ecosystem.
Population
__________ is all of the individuals of the same species within an ecosystem.
Species
__________ are a group of living organisms that have similar features and can reproduce with one another.
orbit
The path Earth follows as it revolves around the sun is referred to as ________.
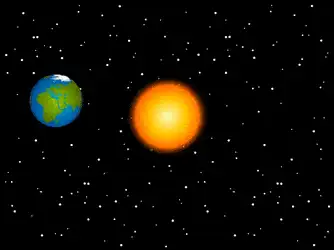
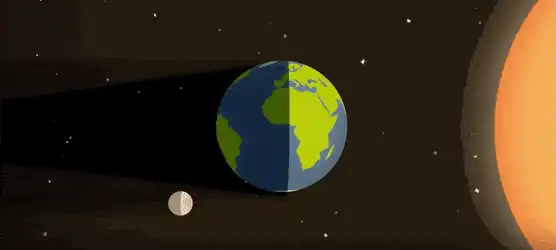
solar eclipse
When the sun is blocked by the moon, there is a ___________.

lunar eclipse
When the Earth is blocking the sun there is a ________.
greater
Objects with _________ mass have __________ gravitational pull.
more
The Sun has ________ gravitational pull than the Earth.
distance between them
The strength of the force of gravity between two objects depends on the two factors: the masses of the objects and the _________.
decreases
As the distance between objects ___________, gravitational pull decreases.
Water
____________ is the only substance on Earth that commonly exists in all of its different phases (solid, liquid, or gas).
sun
The energy for the water cycle originally comes from the ____________.
Matter
____________ can exist in different states such as solid, liquid, and gas.
solid
Which phase of matter holds its shape and has a fixed volume?
liquid
Which phase of matter has definite volume, but no definite shape?
A __________ will take the shape of a container.
gas
Which phase of matter has no definite volume and no definite shape?
A __________ will expand to fill any container and it can also be compressed.