Cell organelles functions
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Plasmalemma
comp: Lipid bilayer with phospholipids, steroids, proteins, microvilli (sa increasing projections found in cells that absorb materials), carbohydrates
fxn: 1. Protects 2. Structural support 3. Sensitivity (some membrane proteins act as receptors) 4. Regulation of exchange/ controls on the entrance and exit of materials
Diffusion
passive-movement of gases, ions, and molecules from high to low concentration
Osmosis
passive-diffusion of fluid from high to low concentration
facilitated diffusion
passive-glucose and amino acids pass with a carrier protein
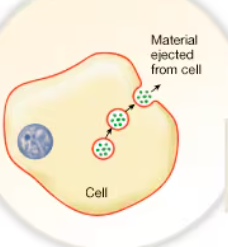
Exocytosis
The release of fluids and or solids from cells when intracellular vesicles fuse with the plasmalemma
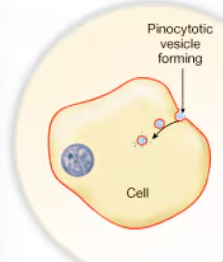
Pinocytosis
Vesicles form at the plasmalemma and bring extracellular fluid and small molecules into the cell “cell drinking”
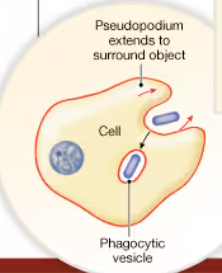
Phagocytosis
Vesicles form at the plasmalemma to bring solid particles into the cell “cell eating”
pseudopodium (cytoplasmic extensions) engulf the large particle
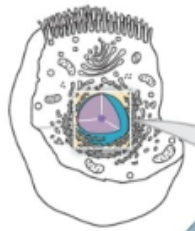
membranous Nucleus
control center. contains chromosomes (the cell’s DNA wrapped around histones, nucleosomes, and chromatin). regulates cell function and protein synthesis
membranous Mitochondria
produce atp. double membrane, cristae are folds of the inner one. The inner fluid is the matrix
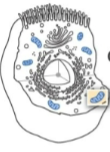
membranous Golgi apparatus
storage, renewal and modification of plasmalemma, synthesis, and packaging of secretions.
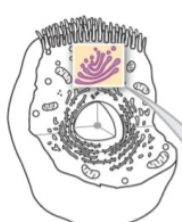
membranous Lysosomes
vesicles contain enzymes to digest unwanted substances in a cell and perform autolysis (the destruction of cells or tissues by their own enzymes)
membranous Peroxisomes
vesicles contain enzymes to remove peroxides from the body. abundant in the liver.
contains enzymes formed by free ribosomes
membranous Endoplasmic Reticulum
Synthesis, storage, and transport of macromolecules, and detoxification/ neutralization. Some contain ribosomes.
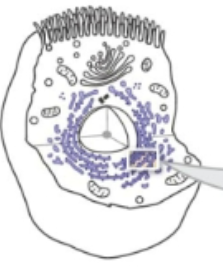
non membranous Ribosomes
60% RNA 40% protein. Protein synthesis
non membranous Cytoskeleton
A network of proteins that provides flexibility, strength, support, and structure. consists of Microfilaments, Intermediate filaments, Thick filaments, Microtubules
non membranous Centrioles
Groups of microtubule triplets form a cylindrical shape. Organize in the spindle to move chromosomes apart during cell division
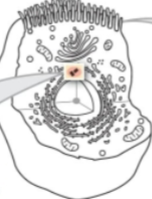
non membranous Cilia
tail-like projections that sweep fluids or secretions across the cell surface
non membranous Flagella
One or two long tails that propel the cell
receptor- mediated endocytosis
most selective
target molecules bind to specific receptor proteins
gap juntions
Two cells held together by two interlocking transmembrane proteins called connexons. connection between cells that permits electrical coupling and free diffusion of ions and small molecules
Tight junctions
liquid portions of two plasma membranes bound by interlocking membrane proteins
desosome
CAMs and proteoglycans link opposing plasma membranes. these resist stretching /twisting.
Intercalated Disc
regions where adjacent cardiocytes interlock and where gap junctions permit electrical coupling between cells
endocytosis
packaging of extracellular materials into a vesicle for importation into the cell
spot desmosome
small discs connected to bands of intermediate filaments that stabilize cell shape
hemidesmosomes
resemble half a spot desmosome; they attach cell to the extracellular filaments in the basement membrane. subject to abrasion and shearing forces