Microbiology Lab Final Study Guide (With pictures of slides)
1/165
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
166 Terms
aspergillus
fungi
sporangium
spores
hyphae
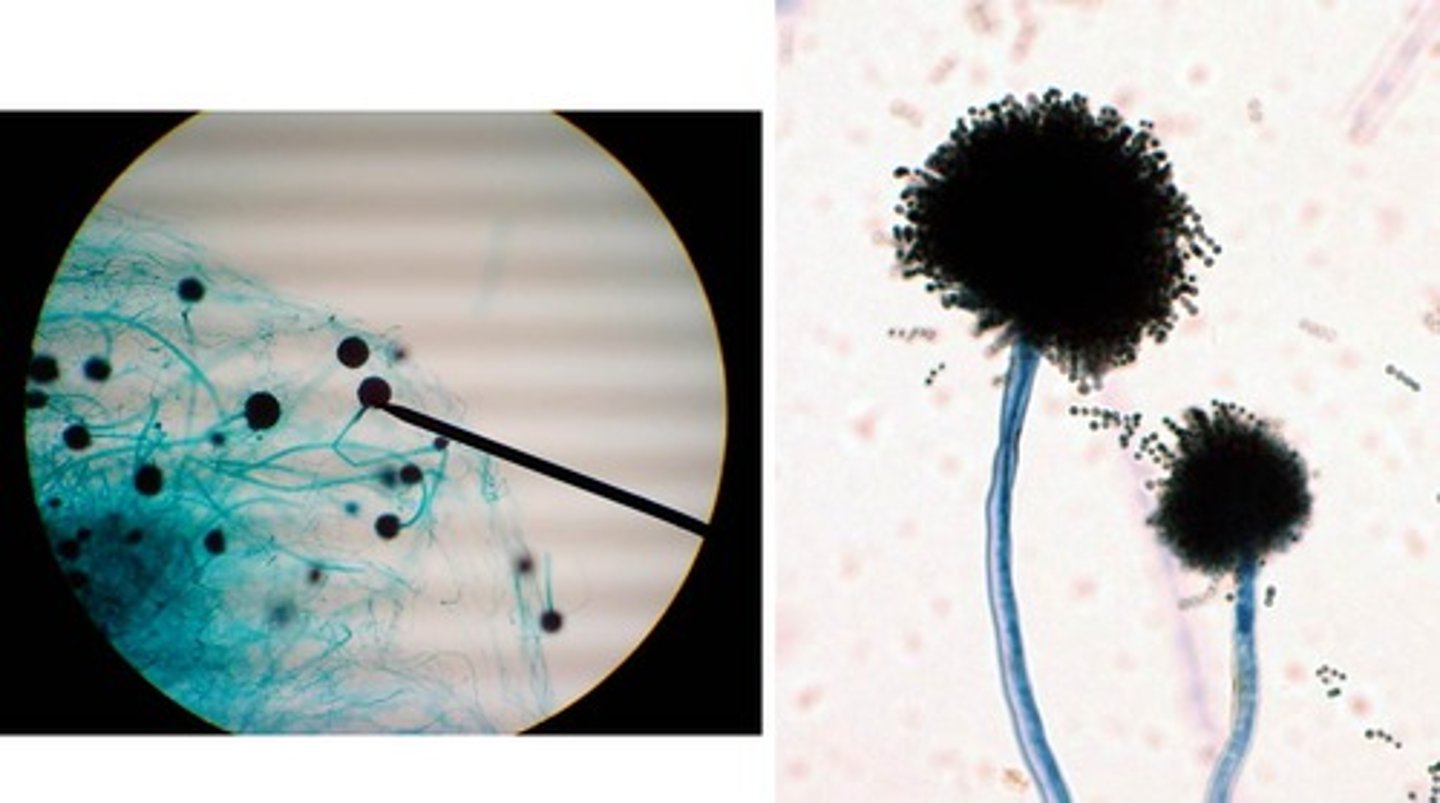
penicillium
fungi
phialides
conida
conidiophore

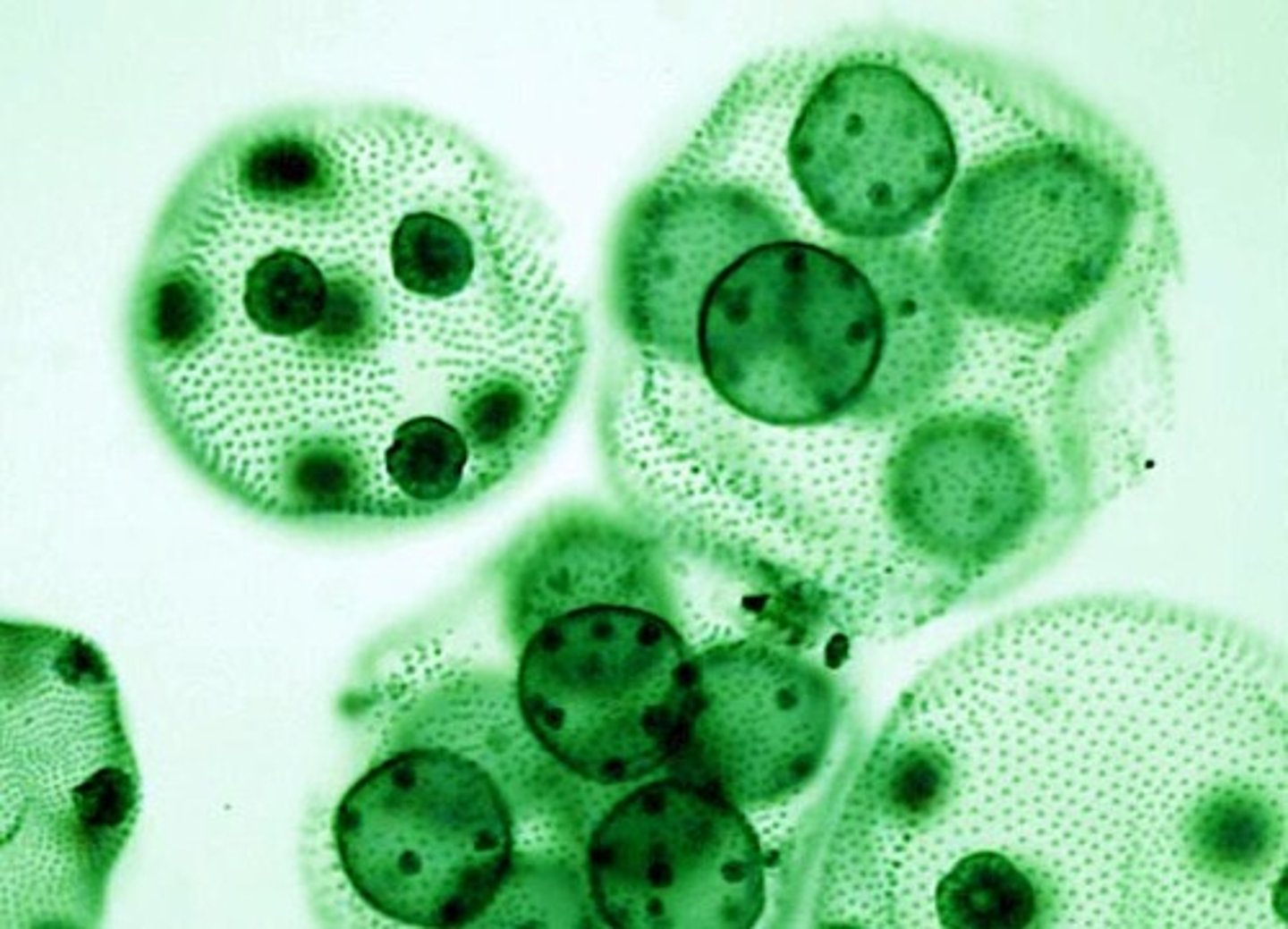
volvox
protist/algae
algal cells
daughter cells
colony
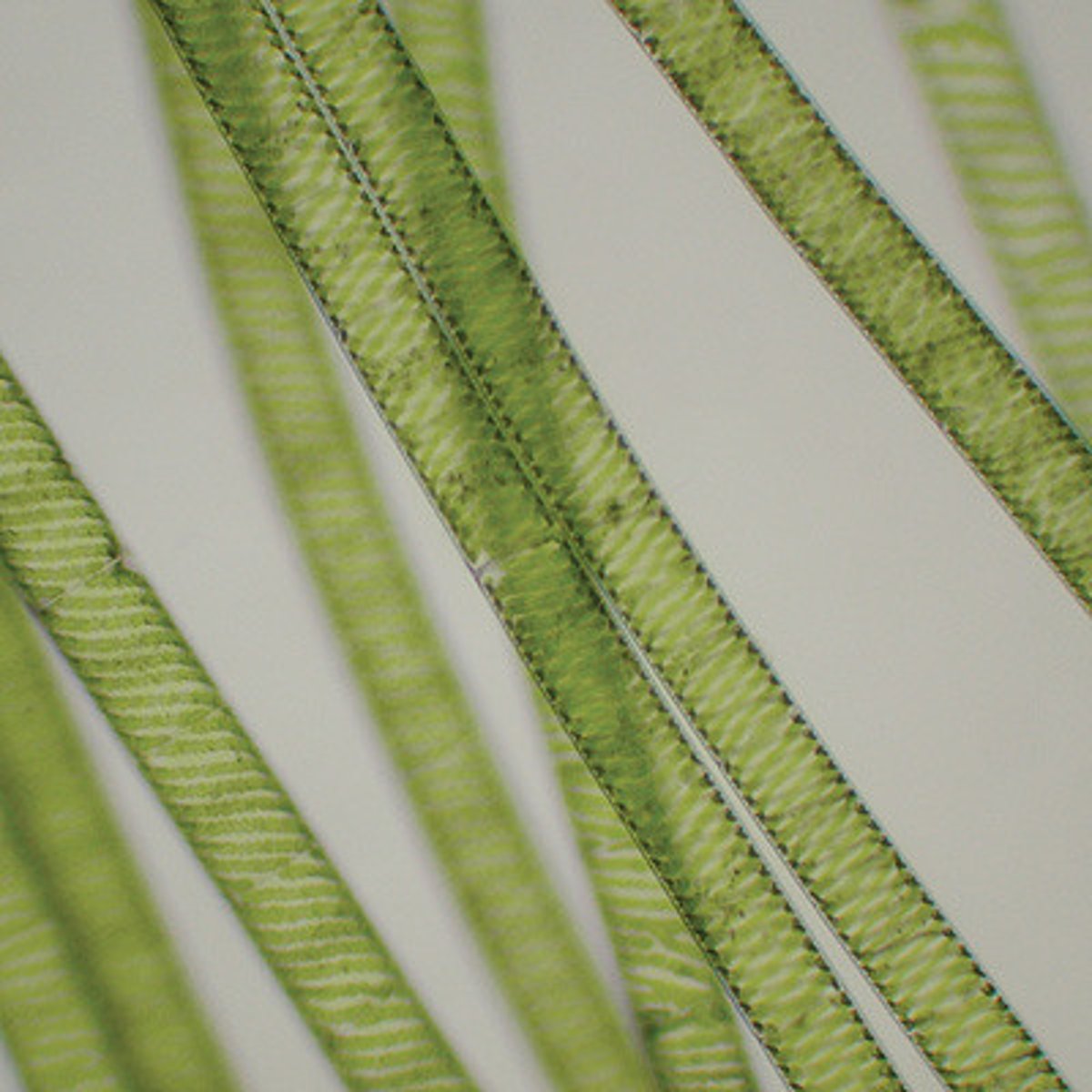
spirogyra
protist/algae
chloroplast
filamentous cell

amoeba
protist
pseudopod
nucleus
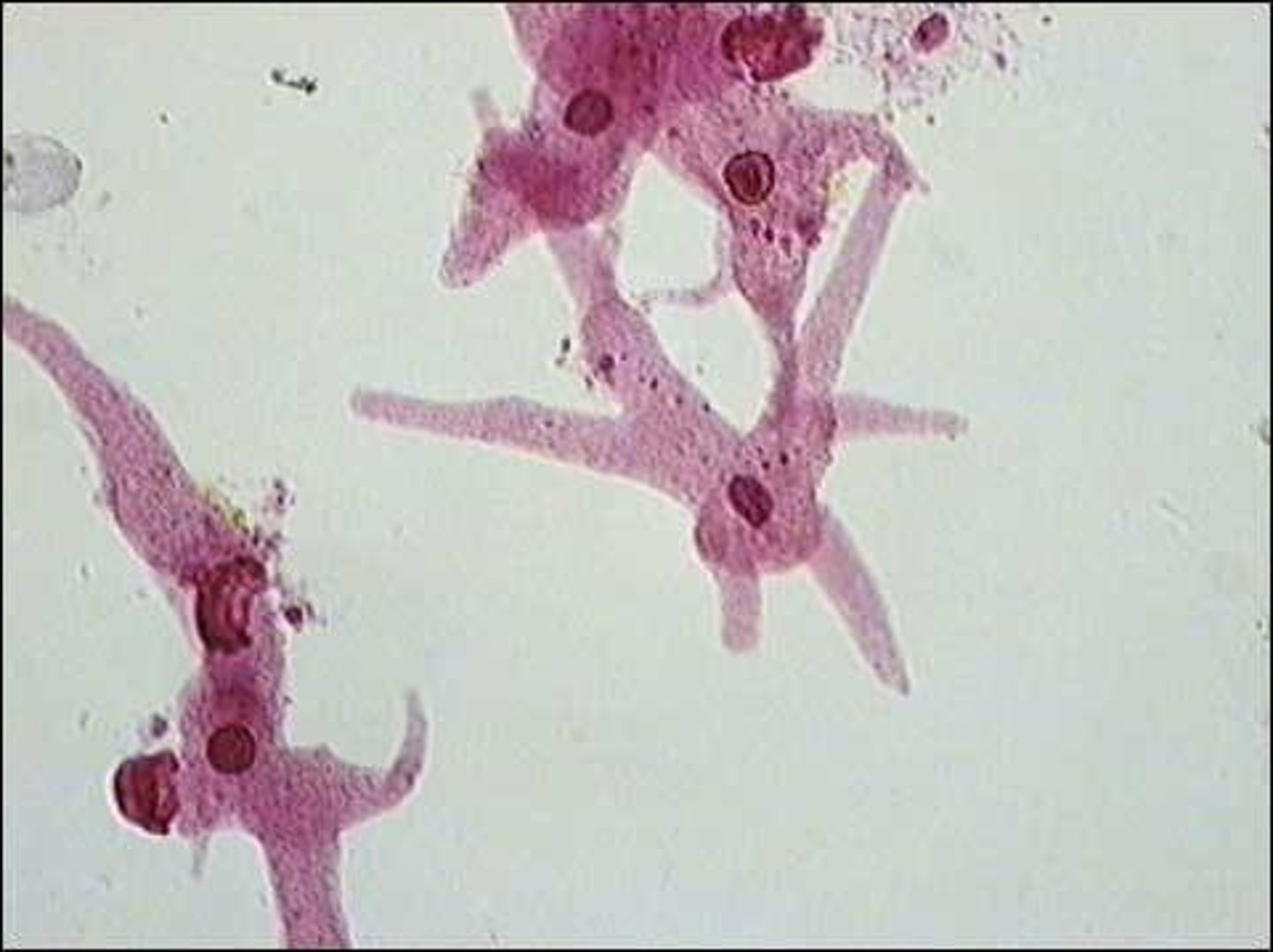
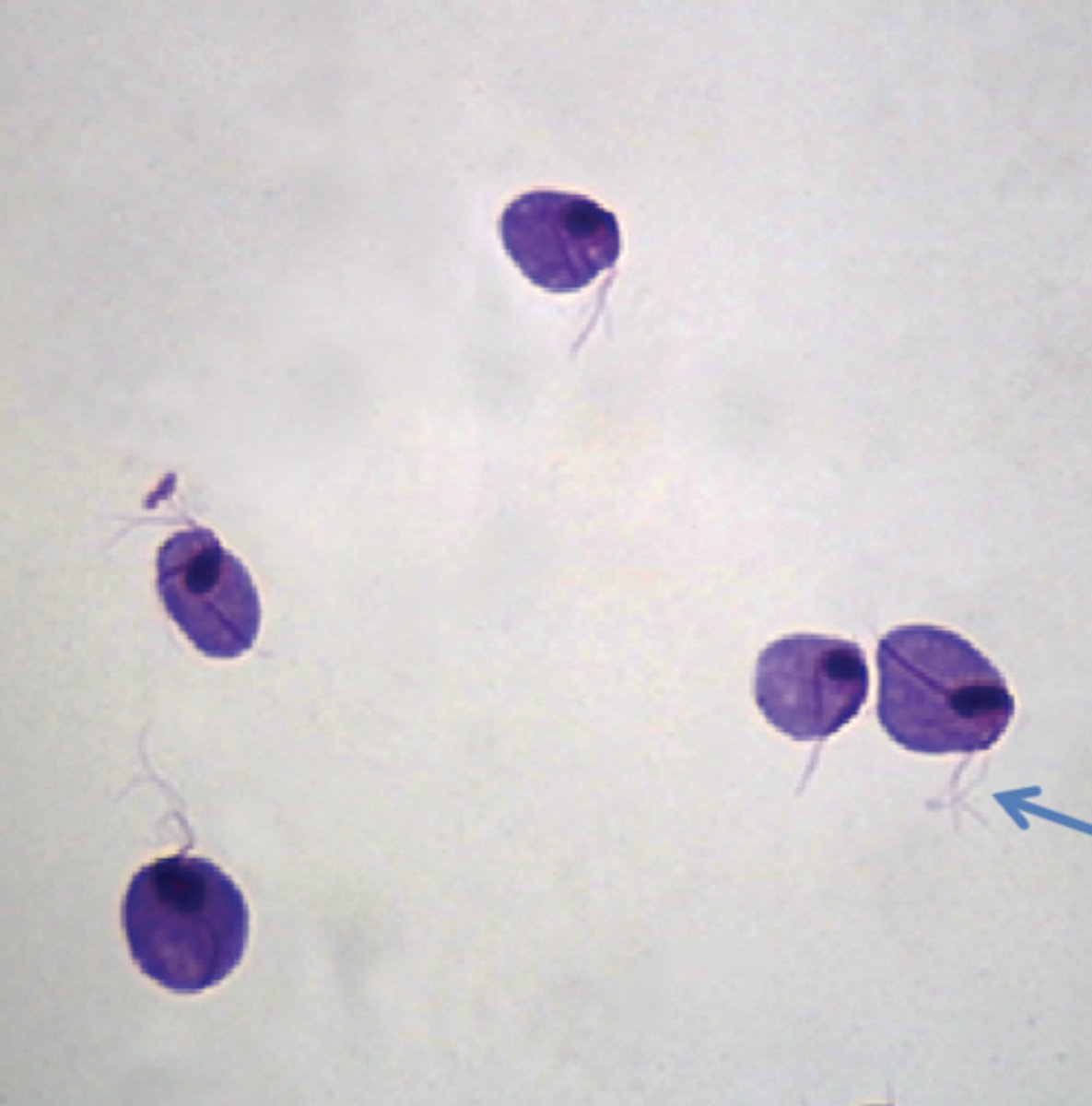
trichomonas vaginalis
protozoan parasite
flagella
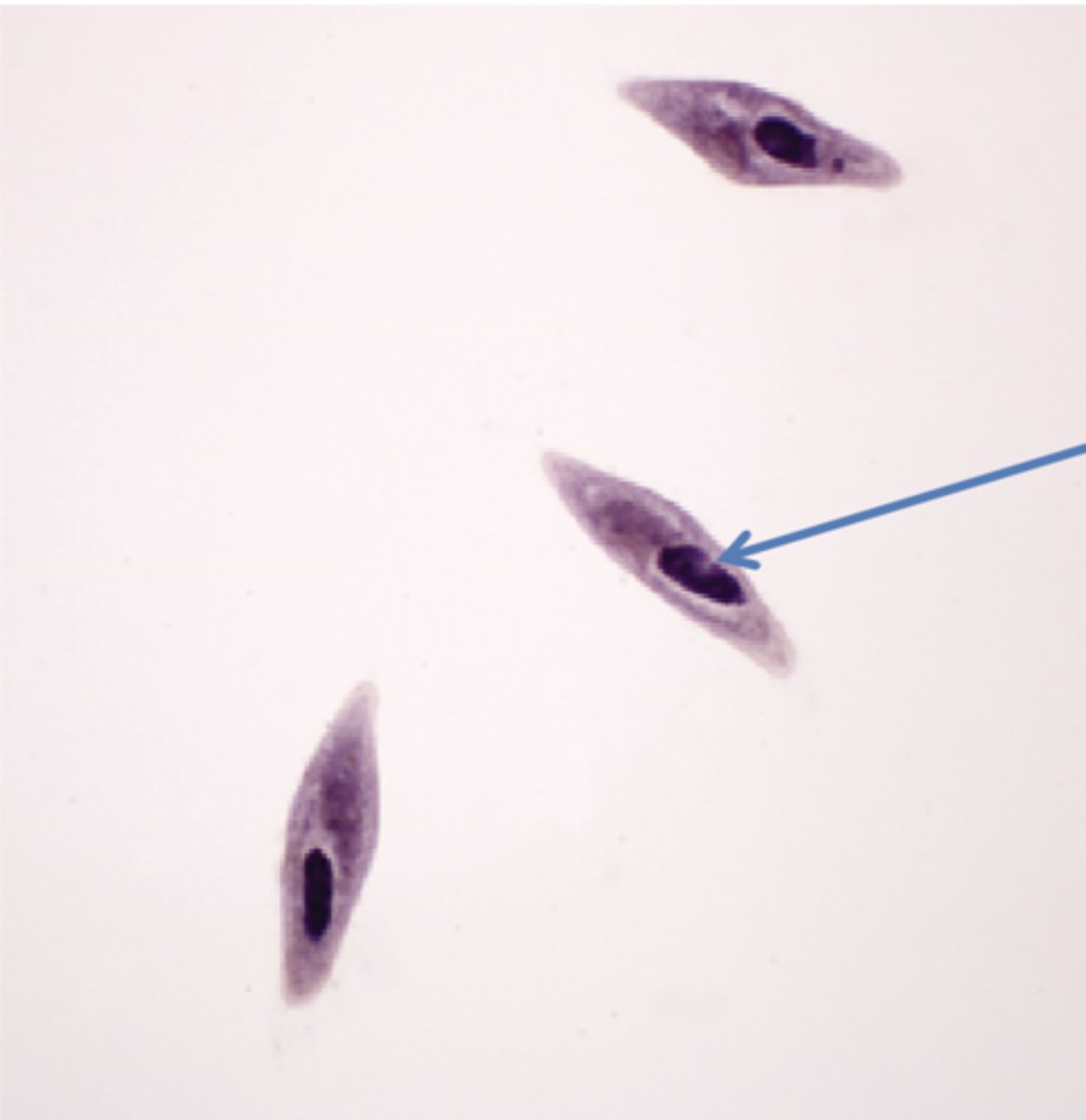
paramecium
protist
cilia not visible
macronucleus
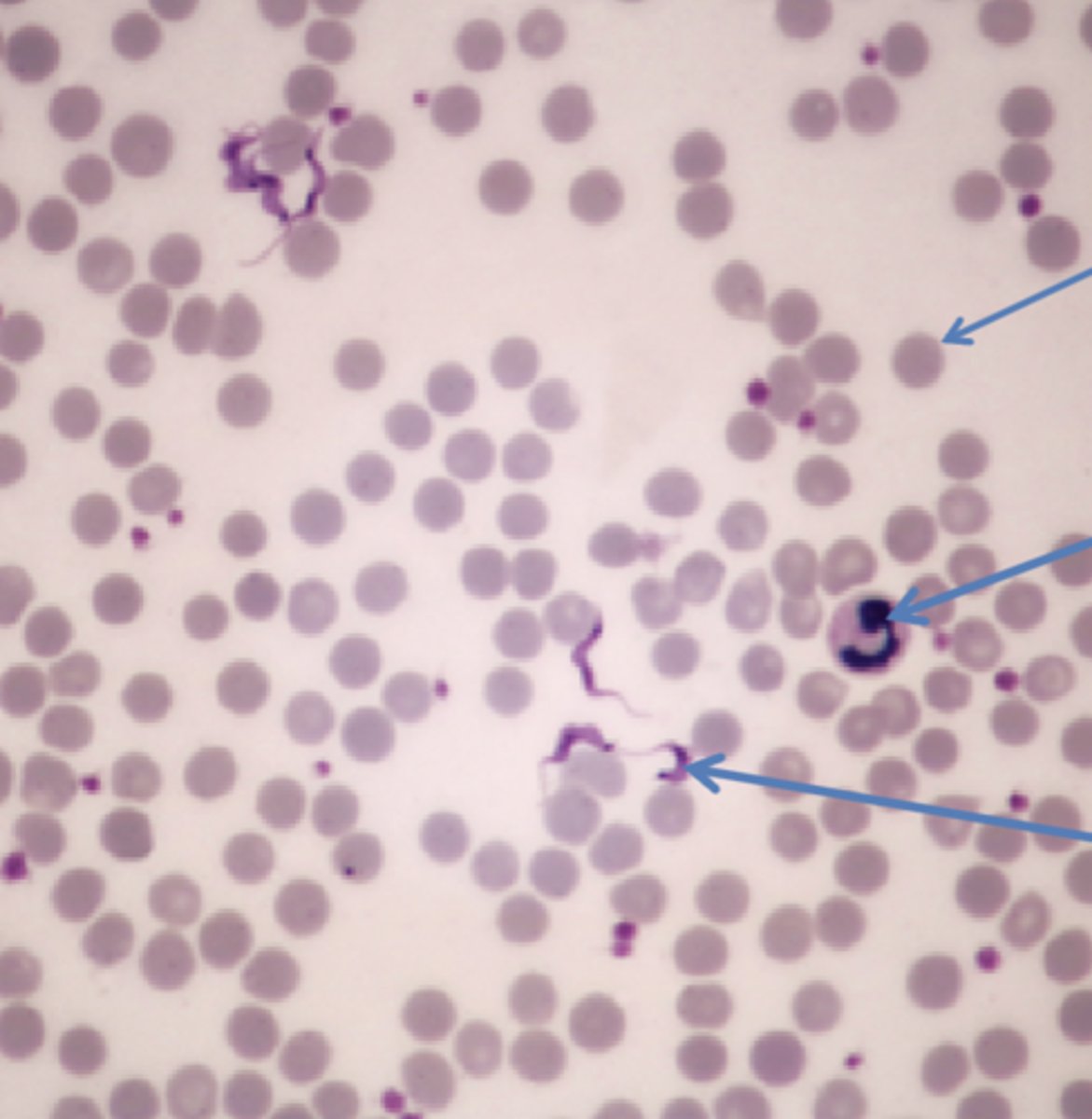
trypanosoma cruzi
protist
red blood cell
white blood cell
flagellated parasite
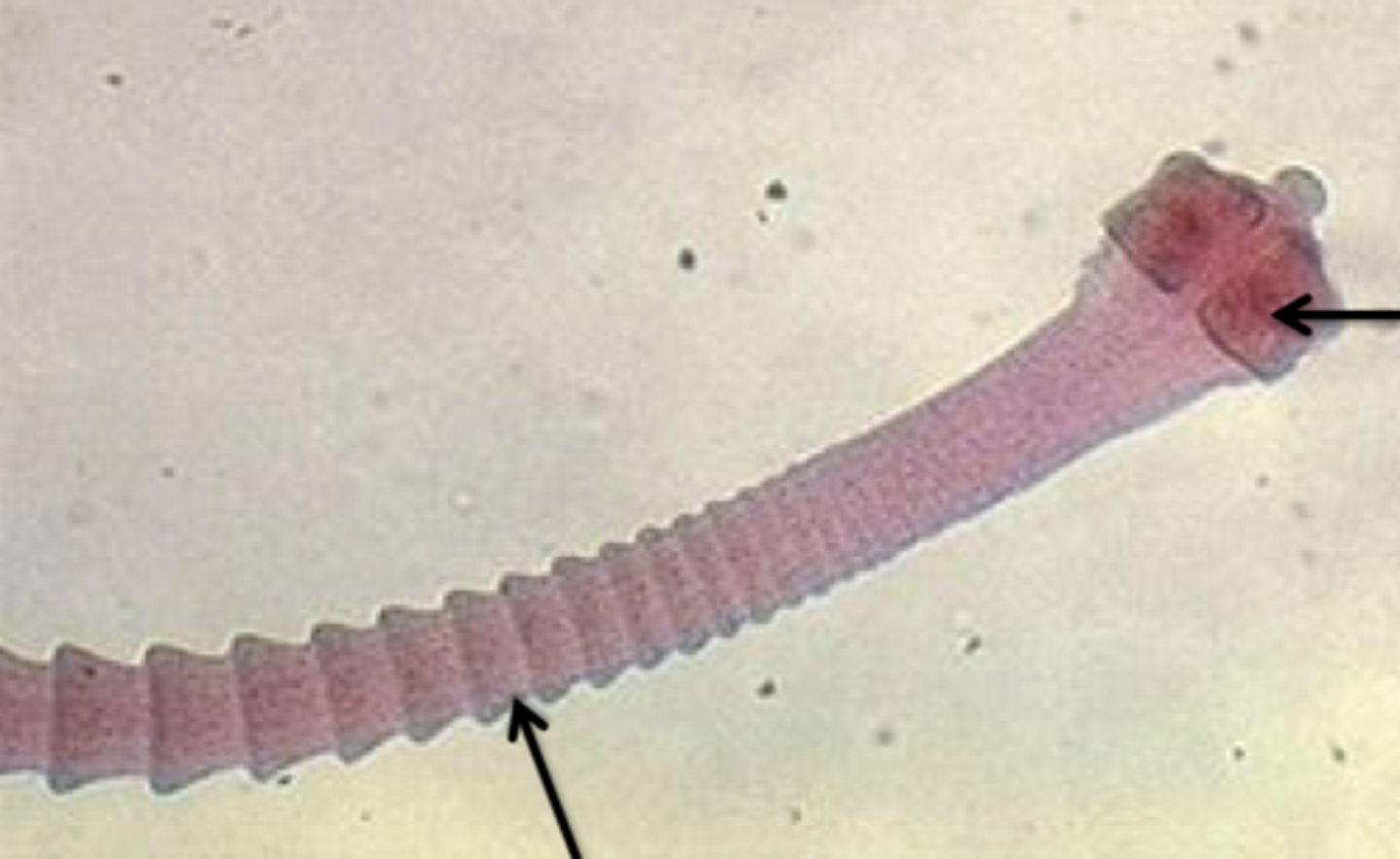
dipylidium caninum
parasite
scolex (face)
proglottid
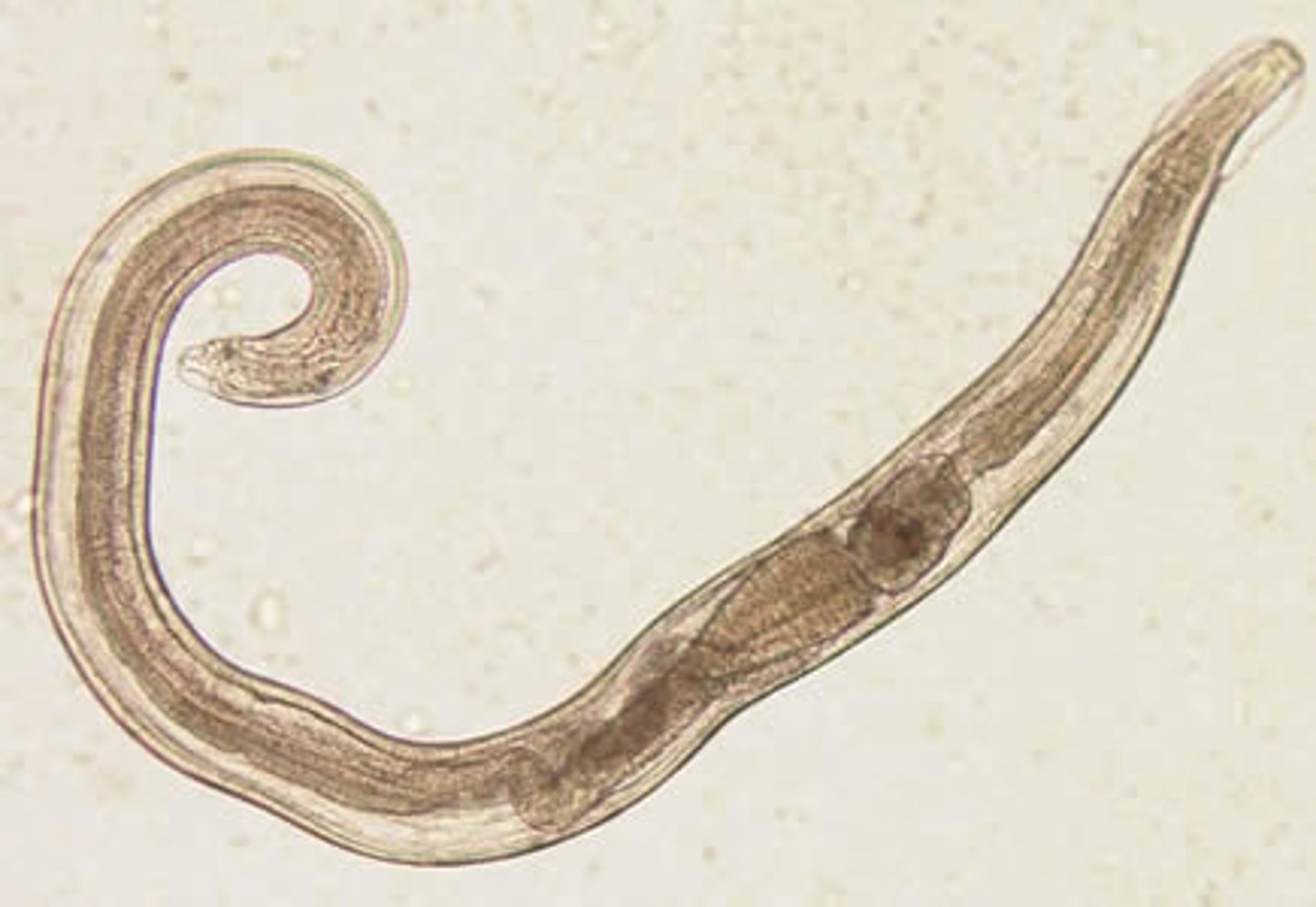
parasite
enterobius vermicularis
distance between lenses
interpupilary distance
objective lens
shortest, scanning, 4x
low power objective lens
initial focusing, 10x
high power objective lens
40x
oil immersion lens
requires oil, highest mag, 100x
iris diaphragm lever
The amount of light reaching the specimen can be controlled by manipulating what?
Contrast
Difference in color or light intensity between forms.
Iris Diaphragm
Adjusts light intensity in microscopy.
Working Distance
Distance from objective lens to specimen surface.
Microbial Smear
Preparation of bacterial cells on a slide.
Heat Fixing
Attaches cells to slide by killing them.
Culture Media
Nutrient solutions for growing microorganisms.
Enriched Media
Basic media with added nutrients like blood.
Indicators
Substances that change color based on metabolism.
Antibiotics in Media
Used to inhibit growth of unwanted organisms.
Cell Morphology
Study of cell shape and structure.
CHNOPS
Carbon, Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorus, Sulfur
flagella, cilia, pseudopods
Describe some of the different modes of motility among protozoa
lens wipe
What should be used to clean the lenses of a microscope?
hyphae,sporangium
What is the filamentous cell of a mold called? What is the reproductive structure of a mold called?
it exists as a spherical colony composed of numerous individual algal cells that are connected together, allowing them to function as a coordinated unit, with each cell contributing to the colony's movement and behavior
Why is Volvox referred to as a colonial alga?
The feces of insects called triatomine, or “kissing” bugs, transmits the parasite to humans. These bugs feed on the blood of animals and humans at night, and then they defecate. Infection can occur if you unknowingly wipe the feces into your eyes, nose, mouth, or a sore. Result in flu-like symptoms
Trypanosoma cruzi causes Chagas disease in humans. How is the disease spread, and what are the symptoms?
working distance decreases as magnification increases. Working distance is the distance between the specimen and the objective lens. As magnification increases, the depth of field also decreases
How does magnification affect working distance?
sterile technique
maintains purity of culture
inoculating loop
used to spread the cells across sections of theplate using a standard streaking pattern
condenser lens
focuses light on specimen
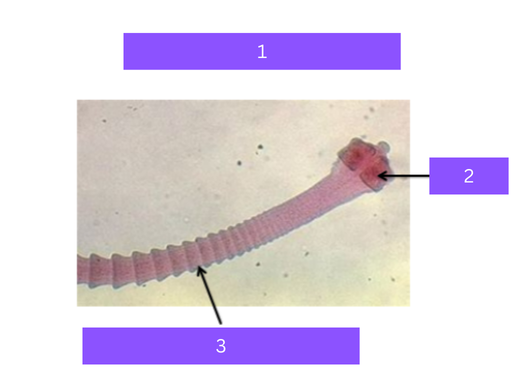
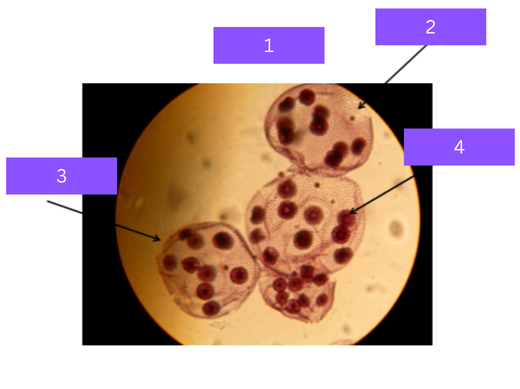
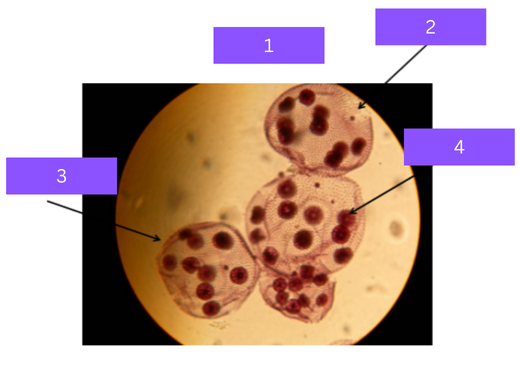
dipylidium caninum
What is 1
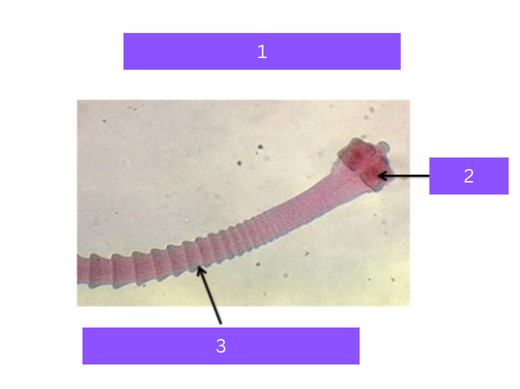
scolex
what is 2
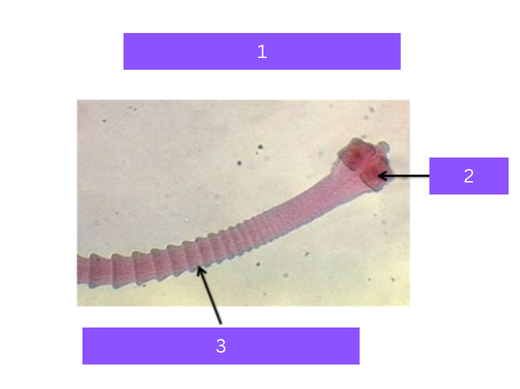
proglottid
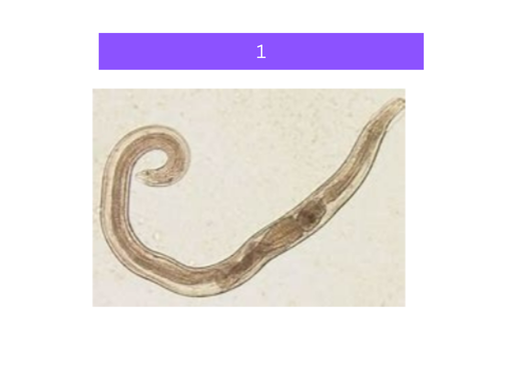
what is 3
enterobius vermicularis
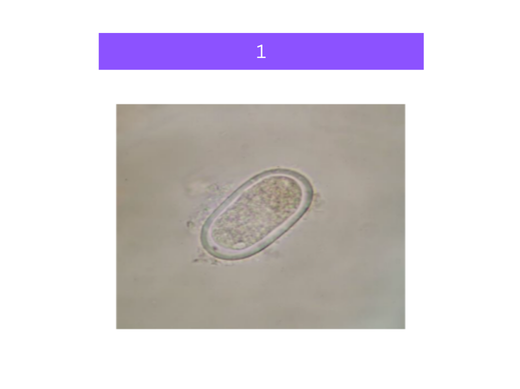
what is 1
enterobius eggs
what is 1
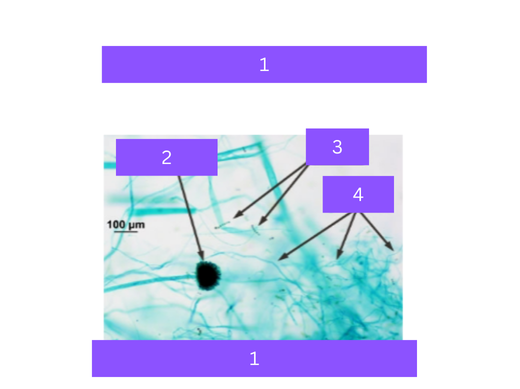
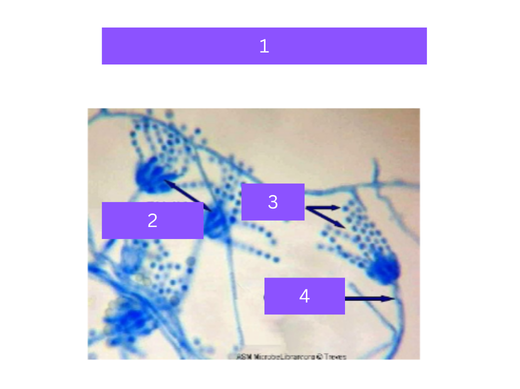
aspergillus
what is 1
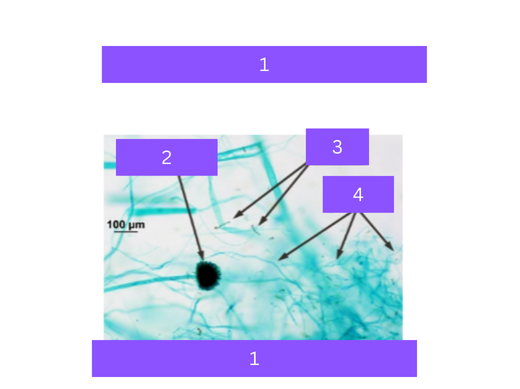
sporangium
what is 2
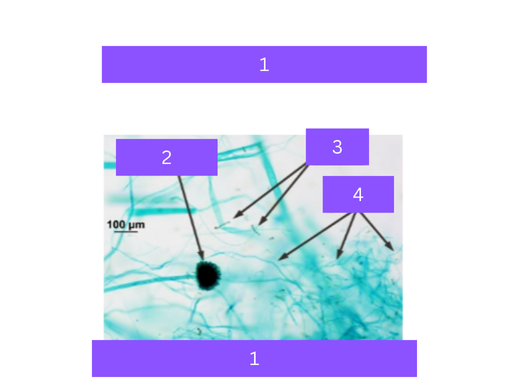
spores
what is 3
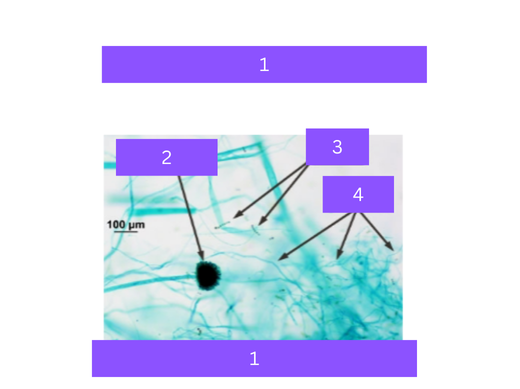
hyphae
what is 4
penicillium
what is 1
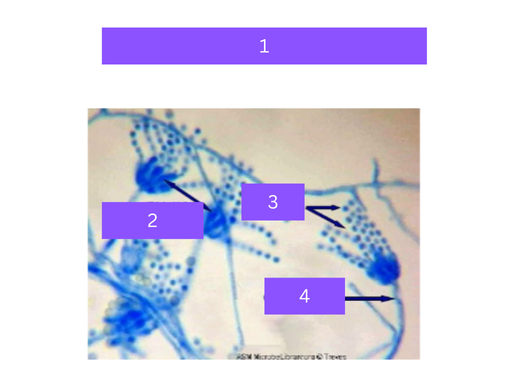
phialides
what is 2
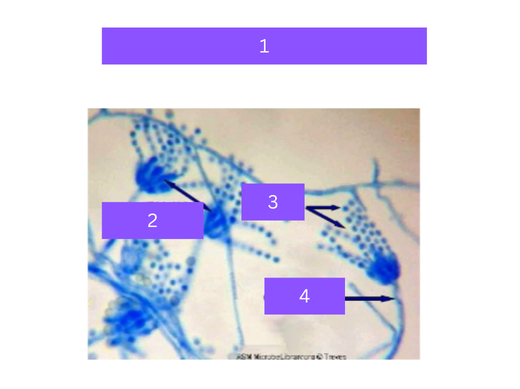
conidia
what is 3
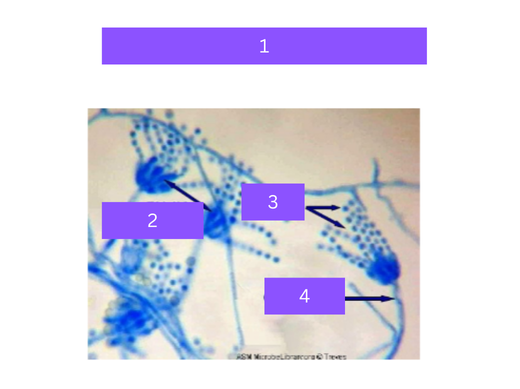
conidiophore
what is 4
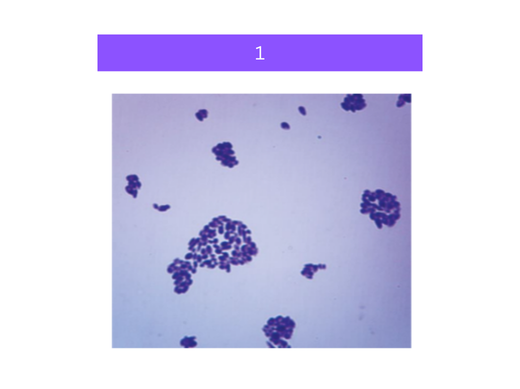
saccharomyces
what is 1
diatoms
what is 1

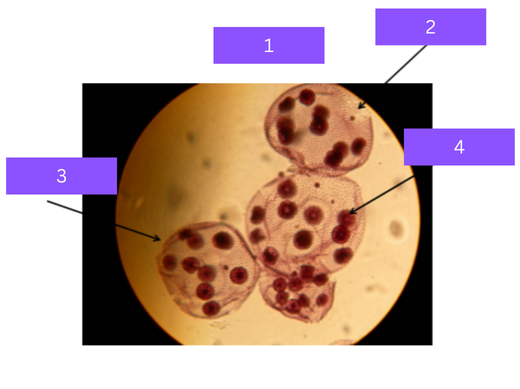
volvox
what is 1
algal cells
what is 2
colony
what is 3
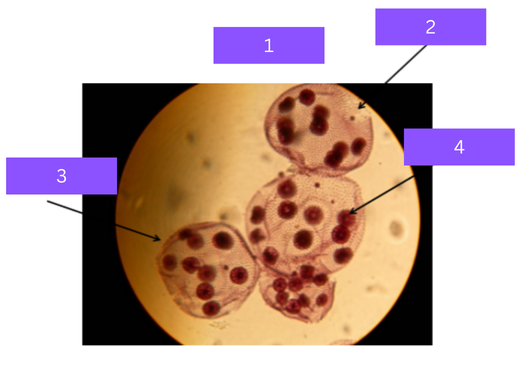
daughter cells
what is 4
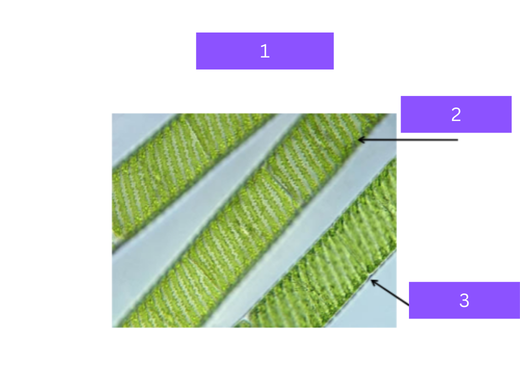
spirogyra
what is 1
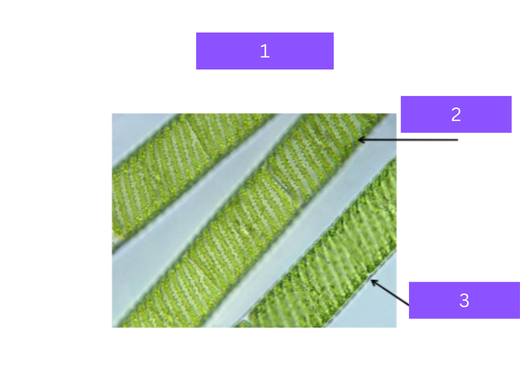
chloroplast
what is 2
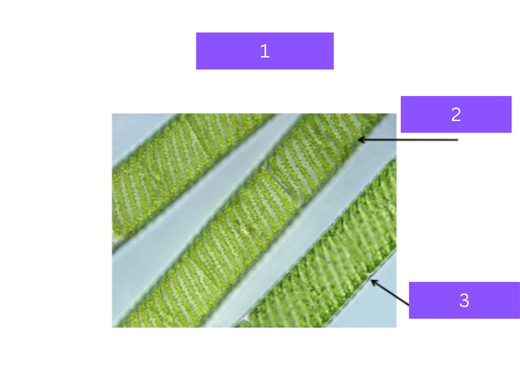
filamentous cell
what is 3
amoeba
what is 1
nucleus
what is 2
pseudopod
what is 3
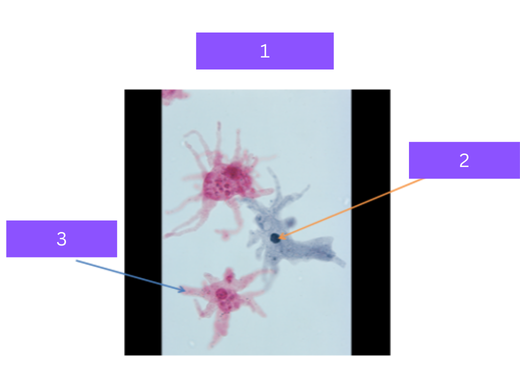
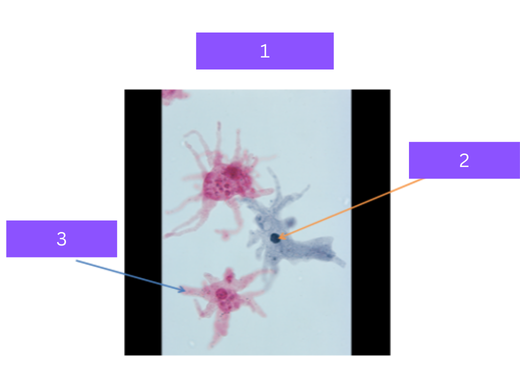
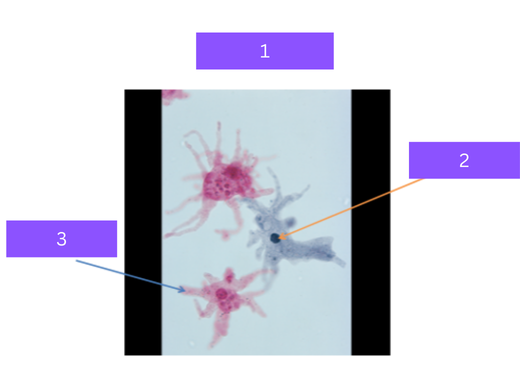
trichomonas vaginalis
what is 1
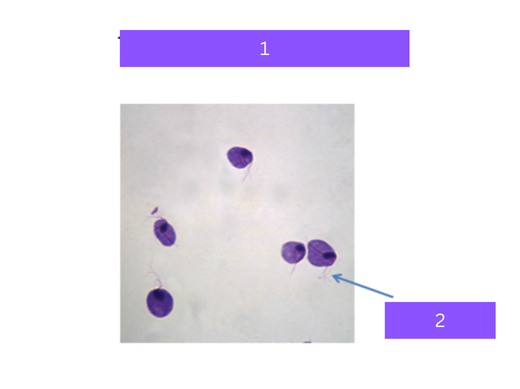
flagella
what is 2
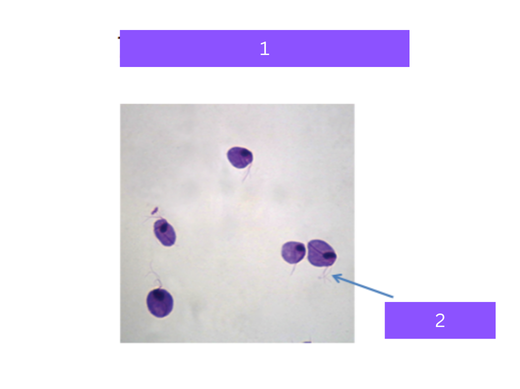
paramecium
what is 1

macronucleus
what is 2

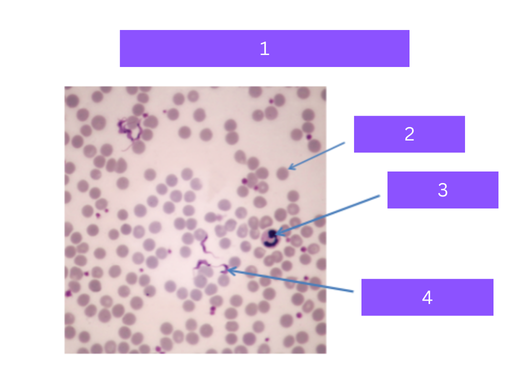
trypanosoma cruzi
what is 1
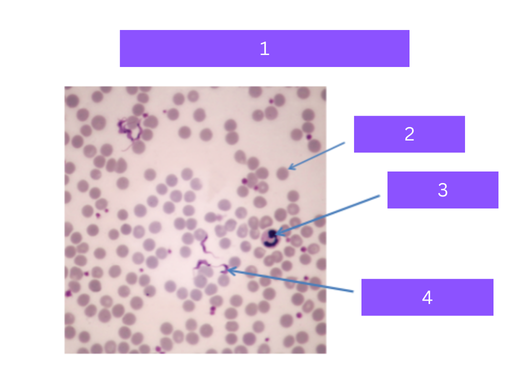
red blood cell
what is 2
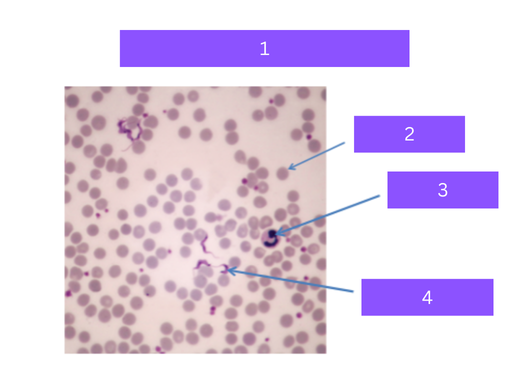
white blood cell
what is 3
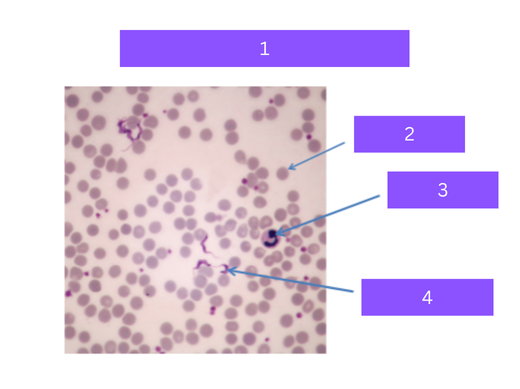
flagellated parasite
what is 4
Kingdom Fungi
- mushrooms, filamentous fungi (molds) and yeasts
- yeasts are unicellular and oval in shape
Hyphae
Filaments of fungi
- vegetative and reproductive
Mycelium
Several hyphae form a tangled mat
Vegetative hyphae
obtain food for the mold
Reproductive hyphae (aerial hyphae)
Involved in reproduction, ends contain reproductive spore sacs
Fungi examples
Aspergillus and Penicillium
Kingdom Protists
- include algae and protozoa
- some multicellular, some unicellular
- some parasitic
Protozoan motility
cilia, flagella, pseudopods
Algae examples
Volvox
Spirogyra
Volvox
Colonial algae
Spirogyra
Filamentous alga with a spiral-shaped chloroplast
Protozoa examples
Trichomonas vaginalis
Typanosoma cruzi
Paramecium caudatum
Amoeba proteus
Trypanosoma cruzi
Protozoa that causes Chagas' disease,
Amoeba proteus
Non-pathogenic Protozoa, uses pseudopod
Paramecium caudatum
Nonpathogenic Protozoa, uses cilia
Trichomonas vaginalis
Sexually transmitted protozoa, uses flagella
Kingdom Animalia
- flatworms and roundworms
- multicellular
- heterotrophic
- mostly nonparasitic
Animalia examples
Dipylidium canium
Enterobius vermicularis
Dipylidium canium
- flatworm called tapeworm
- parasitic
- scolex and proglottids
- gets longer over time
Enterobius vermicularis
- small roundworm
- human parasite, especially children
- acquired from bad hygiene practices
- found in soil and infected feces
Scolex
Head of tapeworm
Proglottid
Body segments of tapeworm
Cocci
- greatest arrangement
- single
- pairs (diplococci)
- tetrads
- irregular clusters (staphylococci and micrococci)
- chains
- cubical packet, always multiple of 8 (sarcina)
Bacillus
- not much variety
- single
- pairs (diplobacilli)
- chain (streptobacilli)
- row of cells oriented side by side (pallisades)
Spirilla
- least varied
- single cells
- occasionally found in short chains
Broth
Liquid media used for propagation
of large numbers of organisms and for various experiments and diagnostic tests
Slant
Solid media that gives the bacteria a greater surface area on which to grow in a tube.
- useful in maintaining bacterial cultures
Plate
Solid media particularly helpful in isolating a specific species of bacteria, which is not possible in a liquid medium
Synthetic medium
the chemical composition of the medium is known
Non-synthetic medium
Culture medium in which their exact composition is not known, most culture media
slaughterhouse waste/plant products and peptides, sugars, vitamins, minerals
How is non-synthetic medium typically made?