Other food preservation and processing methods and assessment of risks
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
What is the water activity in food?
Proportion of available water in food for micro organisms needs
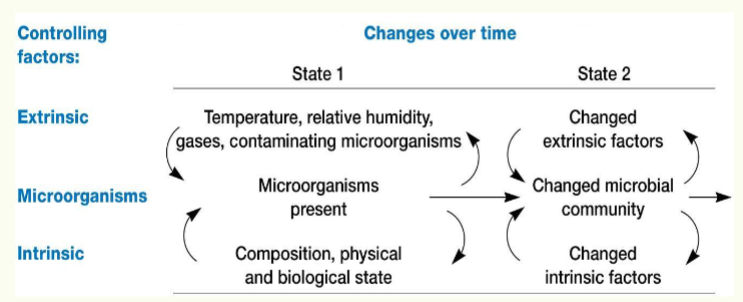
What factors affect microbial growth in food?
How does adding salt affect microbial growth and survival in food?
Reduces water activity in food
What is the name for organisms that can grow in dry food?
Xerophilic
What is salt and curing and how does it work?
Add 2-6% salt, Nitrite <150ppm max
Salt reduced the water activity
Gives red/pink colour when cooked
List examples of food additives
Polyphosphates ( increase the ability of meat proteins to bind water. Enable incorporation of additional water, up to 30%)
Antioxidants (Ascorbic acid)
Food colours
Preservatives
Sweeteners (saccharin, acesulfame K, aspartame)
Flavour enhancers (Na glutamate)
Emulsifiers
What do polyphosphates do?
Increase the ability of meat proteins to bind water
What are the different types of curing?
Dry curing
Curing by injection
Define fermentation
Phase of intensive growth and metabolism of lactic acid bacteria accompanied with rapid fall of pH
or
Any partial breakdown of carbohydrates taking place in the absence of oxygen
What is the difference between natural fermentation and fermentation with starter cultures
Natural fermentation : gram negative flora replaced by gram positive
Fermentation with starter cultures: course essentially same but faster- add a culture
What factors lead to fermentation?
Salt and drying: decrease aw
pH
Antagonism
Possibly pasteurised afterwards
What is smoking?
A result of aerobic or anaerobic pyrolysis of woods, their polysaccharides: cellulose, hemi-cellulose and lignin
Intensive exothermic nature
Can be cold (30), warm (40-60) and hot (70-80)
What are the different ways of smoking?
Can be hardwood smoke or liquid (injected)
What is the maximum temperature of smoking and why?
Not higher than 300°C
High temperatures can lead to inc. in carcinogens (Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs))
What are the methods of drying?
Keeping product suspended in air
Lyphophilization (freeze drying)- frozen then low pressure and temp then removes ice by sublimation
What are the three groups of drying?
Based on final aw values:
High moisture products: 0.9-1.0
Intermediate moisture products: 0.6-0.9 can be stored without refrigeration
Low moisture products: <0.6 that are self stable
What are the heat treatments available?
Pasteurisation in water or steam at temps <100°C
Various sausages, canned hams, hot-smoked meats
Boiling in water at 100°C, product centre reaches 80-90°
Liver paté, black pudding, sausage etc.
Commercial sterilisation at >100°C in pressurised steam autclaves
Canned mats sealed, botulinum treated can be stored for years
Example of an acid tolerant food borne pathogen
E. coli O157
What are the different divisions of the descriptive risk assesment in meat products?
Uncooked
Fermented sausages
Dry, raw meats
Cooked
Cooked, uncured meats
Cooked, cured meats
Which food borne pathogen produces spores?
Clostridium perfingens
Bacillus
What are the potential hazards associated with fermented (dry, raw) sausages?
From raw meat and/or contaminated equipment during batter preparation
Foodborne bacteria (Listeria monocytogenes, Staphylococcus aureus)
Toxins (enterotoxin S. aureus, aflatoxins on the surface)
Parasites (Trichinella)
Biogenic amines (tyramine)
What are the potential hazards associated with dry, raw meats?
Growth and toxin production of botulinum due to low-quality raw meat, insufficient curing at higher temps.
What hazards are associated with undercooked uncured meats?
E. coli O157, Listeria monocytogenes, Salmonella and parasites (Trichinella)
The risks greater with burgers, pathogens distributed throughout the product due to mincing (survival)
What temperature is required for inactivation of most aerobic mesophilic bacteria?
72°C for 2 minutes
What hazards are associated with lightly cooked (pasteurized) uncured meats?
Clostridium perfingens, vegetative bacteria killes, but spores survive and germinate during refrigeration
Heat stable S. aureus wont be inactivated
Salmonella and L. monocytogenes post cooking cross- contamination
Meat should be consumed shortly after cooking, stored at >63°C or rapidly cooled <4°C
What are the hazards associated with self-stable uncured sterilised cans?
Botulinum cooked cans
Contamination with bacterial spores due to insufficient heat treatments
Main hazard clostridium botulinum
Faulty cans- cooling water can be sucked through
What are the main hazards associated with pasteurised cured meats?
Listeria monocytogenes and S. aureus (halotolerant), % of salt and nitrites insufficient to prevent growth
L. monocytogenes – psychrotroph, growth during refrigeration
S. aureus – for growth and enterotoxin production higher temperature and the presence of oxygen required
Possible recontamination – all other foodborne pathogens
Gammon usually not cooked, so naturally present microbiota
What are the hazards with pasteurised cured sausages?
Listeria monocytogenes – halotolerant, % of salt and nitrites insufficient to preventgrowth
Possible recontamination during slicing and packing (S. aureus too)
What is mechanically separated meat?
Paste-like meat product produced by forcing pureed or ground pork, turkey or chickenn under high pressure thorugh a sieve to separate bone from edible meat tissue
MSM from all ruminants banned for human consumption