UNIT EXAM
1/85
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
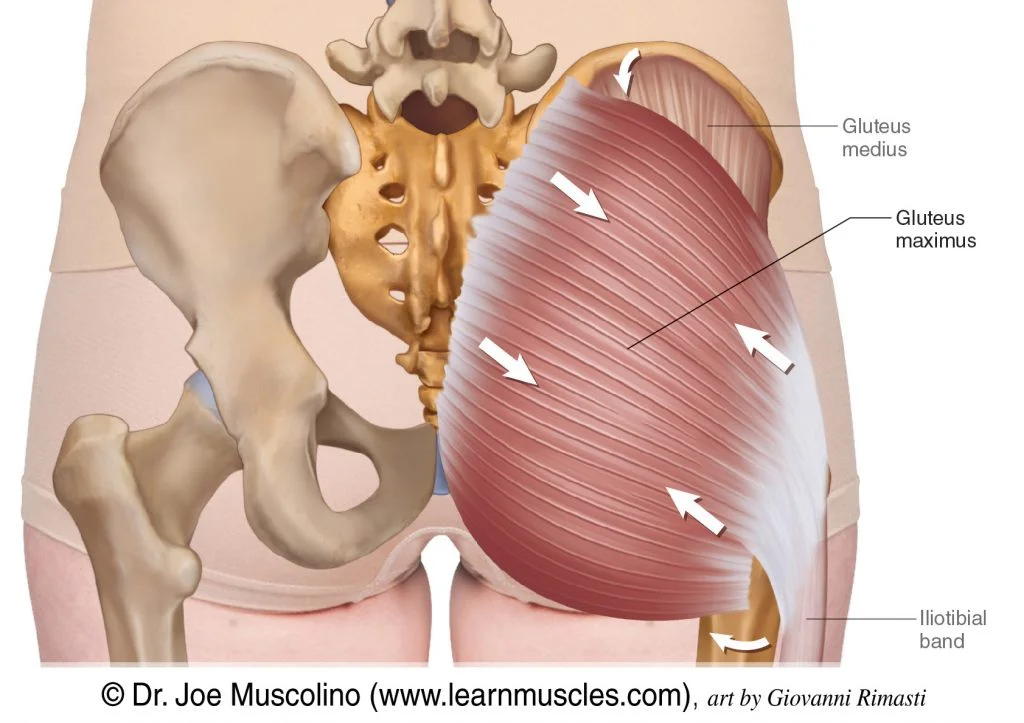
Gluteus maximus
Largest buttock muscle; extends and rotates the hip.
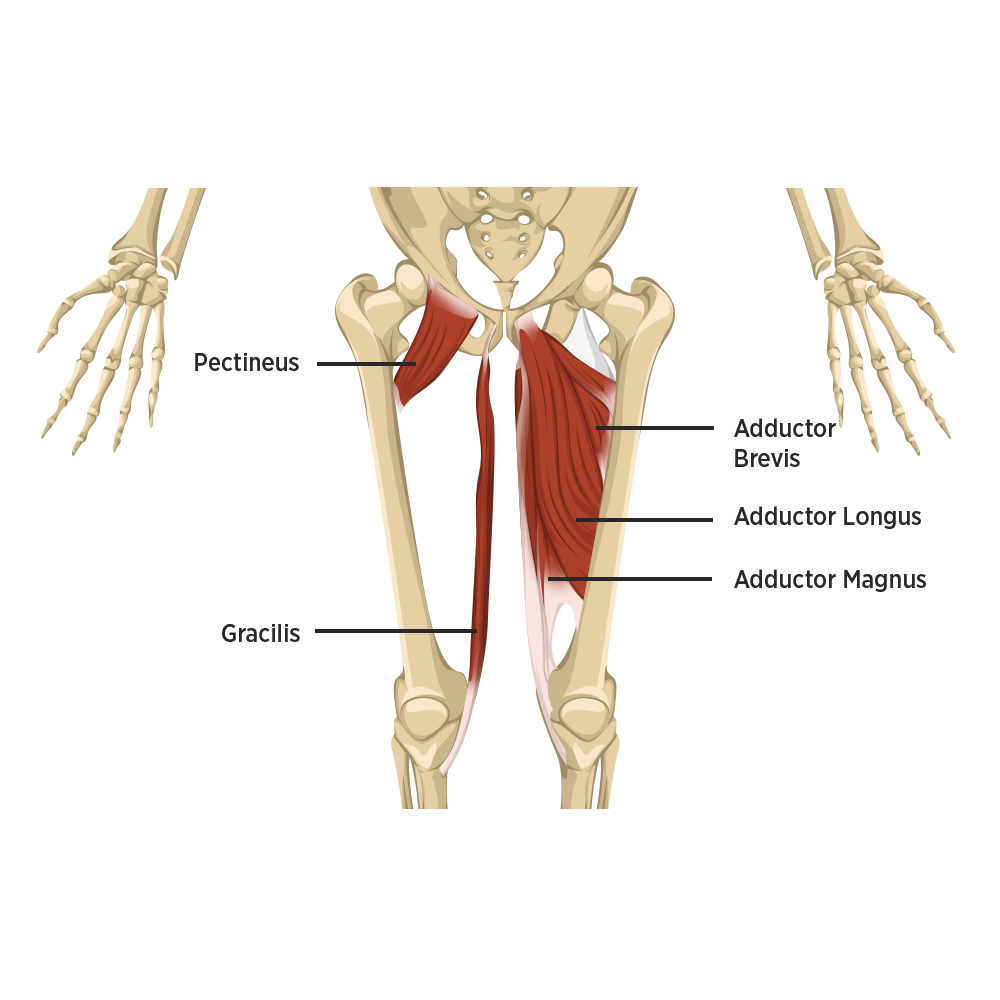
Adductor muscle
Group of muscles on the inner thigh that bring the legs together.
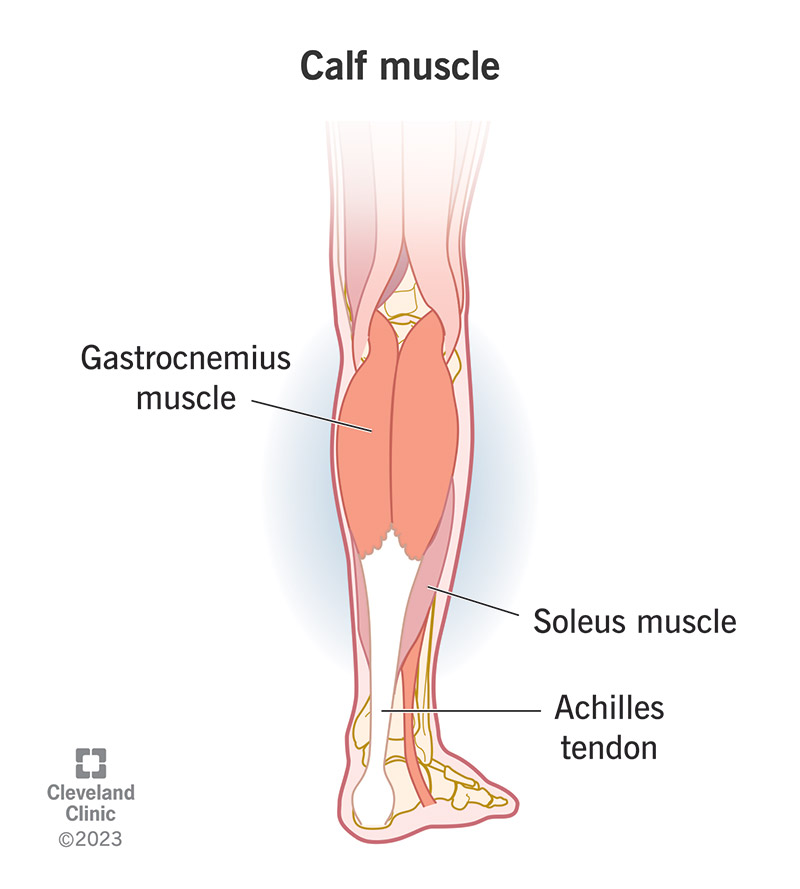
Gastrocnemius
Calf muscle; helps with walking, running, and jumping.
Latissimus dorsi
Large back muscle; aids in pulling and arm movement.
Semitedinosus
Part of the hamstrings; helps extend the hip and bend the knee.
Soleus
Lower calf muscle; works with the gastrocnemius to point the foot downward.
Biceps femoris
Another hamstring muscle; bends the knee and extends the hip.
Triceps brachii
Back of the upper arm; extends the elbow.
External oblique
Side abdominal muscle; twists and flexes the torso.
Gluteus medius
Buttock muscle; stabilizes the pelvis and moves the leg sideways.
Trapezius
Upper back and neck muscle; moves and stabilizes the shoulder blades.
Splenius capitus
Back of the neck muscle; rotates and extends the head.
Occipitalis
Muscle at the back of the skull; moves the scalp.
Rhombus
Muscles between shoulder blades; retract the scapula.
Infraspinastus
Shoulder blade muscle; rotates the arm outward.
Calcaneal tendon
Connects calf muscles to the heel; helps with walking and jumping.
Fascia
A sheet of connective tissue that surrounds muscles, blood vessels, and nerves, binding some structures together while allowing others to slide smoothly over each other.
Aponeurosis
A flat, broad tendon that connects muscles to each other or to bone.
Cardiac muscle
Found only in the heart; involuntary, striated, with intercalated discs.
Skeletal muscle
Voluntary, striated muscle attached to bones for movement
Smooth muscle
Involuntary, non-striated muscle found in walls of hollow organs.
Aponeuroses
Plural form of aponeurosis.
Epimysium
Connective tissue surrounding the entire muscle.
Perimysium
Connective tissue surrounding groups of muscle fibers (fascicles).
Fascicles
Bundles of muscle fibers within a muscle.
Endomysium
Connective tissue surrounding each individual muscle fiber.
Muscle fiber
A single muscle cell.
Myofiber
A single muscle cell.
Myofibril
Rod-like units within muscle fibers, made of repeating sarcomeres.
Actin
A thin filament protein involved in muscle contraction; works with myosin.
Myosin
A thick filament protein with "heads" that bind to actin to produce contraction.
Sarcolemma
The cell membrane of a muscle fiber.
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
A specialized endoplasmic reticulum that stores and releases calcium ions to trigger muscle contraction.
Troponin
A regulatory protein that binds to calcium and moves tropomyosin, exposing binding sites on actin.
Tropomyosin
A protein that blocks the binding sites on actin until moved by troponin.
Cross bridge
The connection formed when myosin heads bind to actin during muscle contraction.
Synapse
Junction between a neuron and another cell (e.g., muscle cell).
Neurotransmitter
Chemical that transmits a signal across the synapse.
ACh- acetylcholine
The neurotransmitter that stimulates skeletal muscle contraction.
Sarcoplasm
The cytoplasm of a muscle fiber.
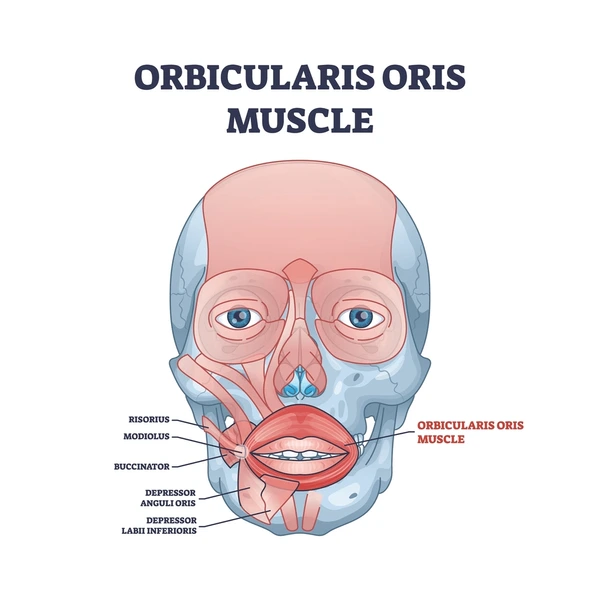
Orbicularis Oris
a complex muscle encircling the mouth, responsible for lip movements and facial expressions; it's sometimes called the "kissing muscle".
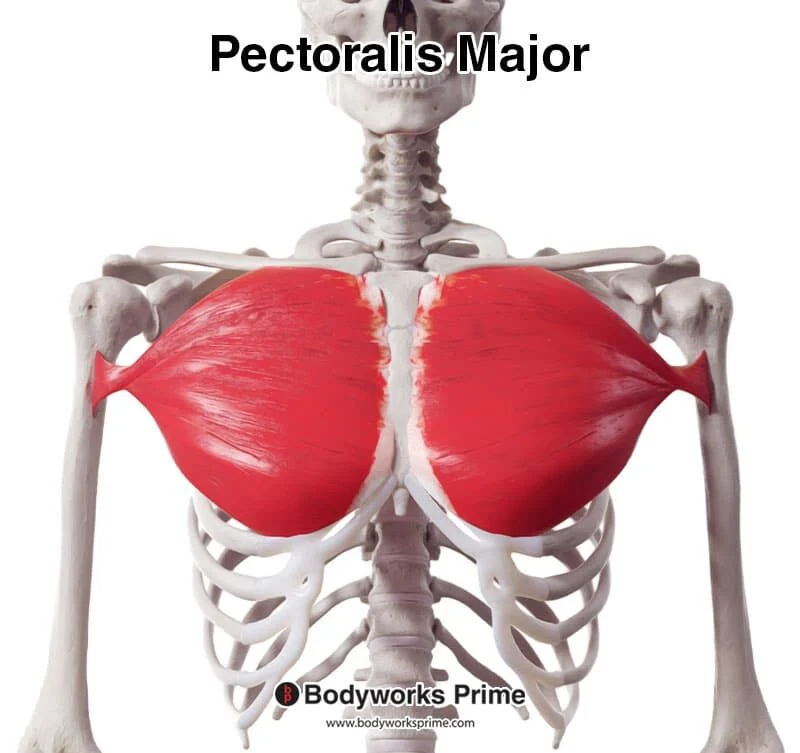
Pectoralis major
the largest muscle of the anterior chest wall, a thick, fan-shaped muscle that lies under the breast tissue and forms the anterior wall of the axilla (armpit), with attachments to the clavicle, sternum, and upper ribs, inserting onto the humerus.
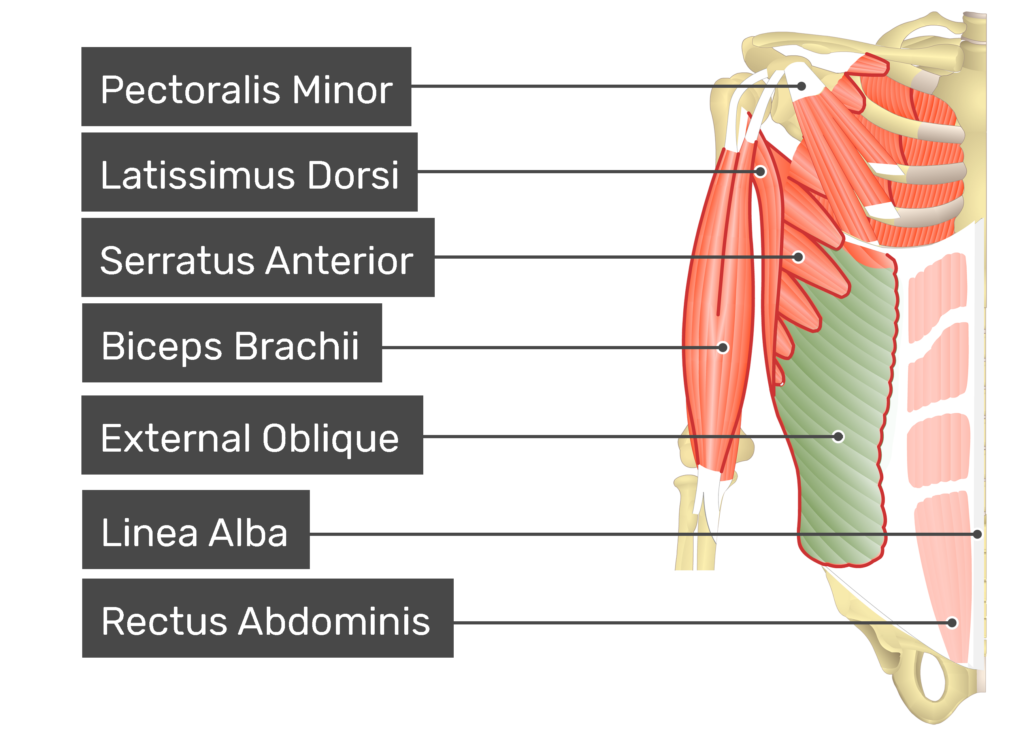
External oblique
a broad, thin, and superficial muscle of the anterior abdominal wall, originating from the lower eight ribs and inserting into the linea alba, pubic tubercle, and iliac crest, playing a crucial role in trunk flexion, rotation, and lateral flexion.
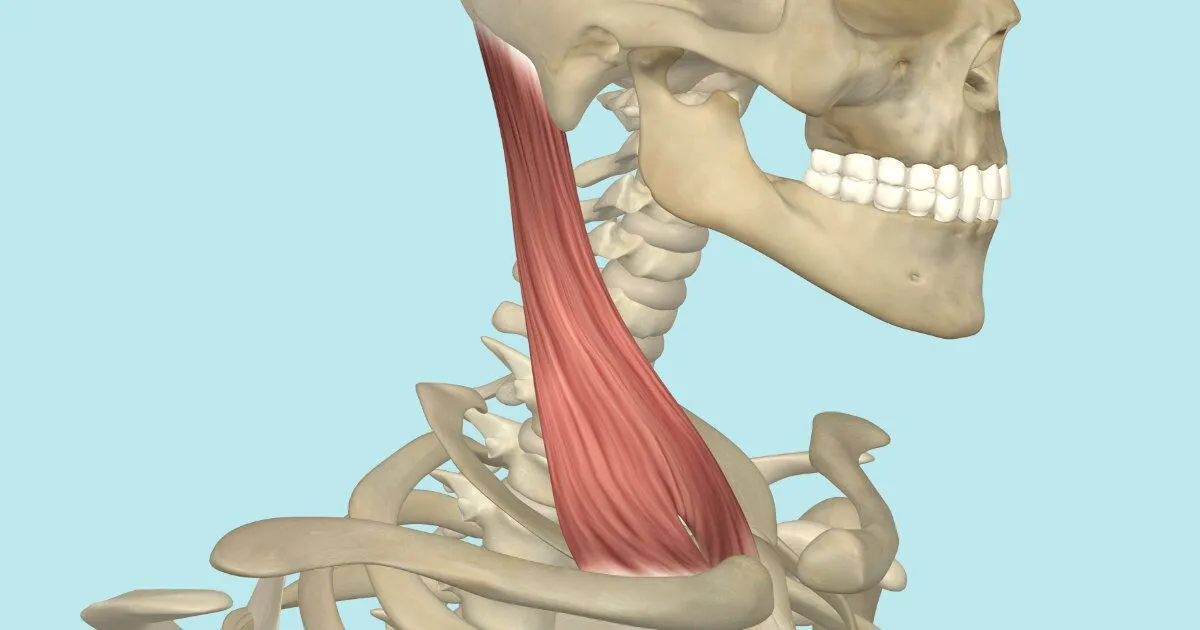
Sternocleidomastoid
a large, superficial muscle located in the anterior portion of the neck.
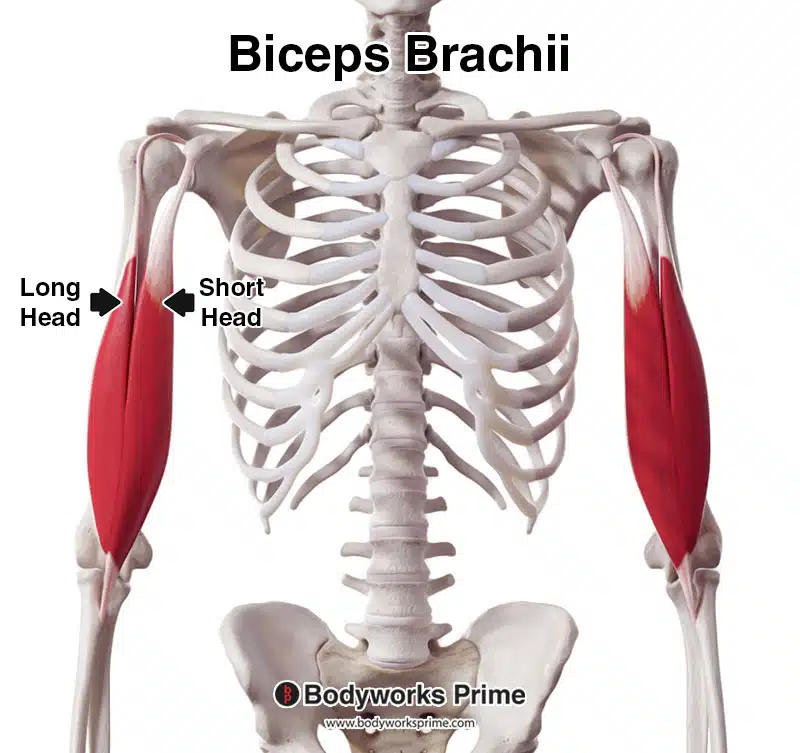
Biceps brachii
a large, two-headed muscle located on the front of the upper arm, responsible for flexing the elbow and supinating (rotating) the forearm.
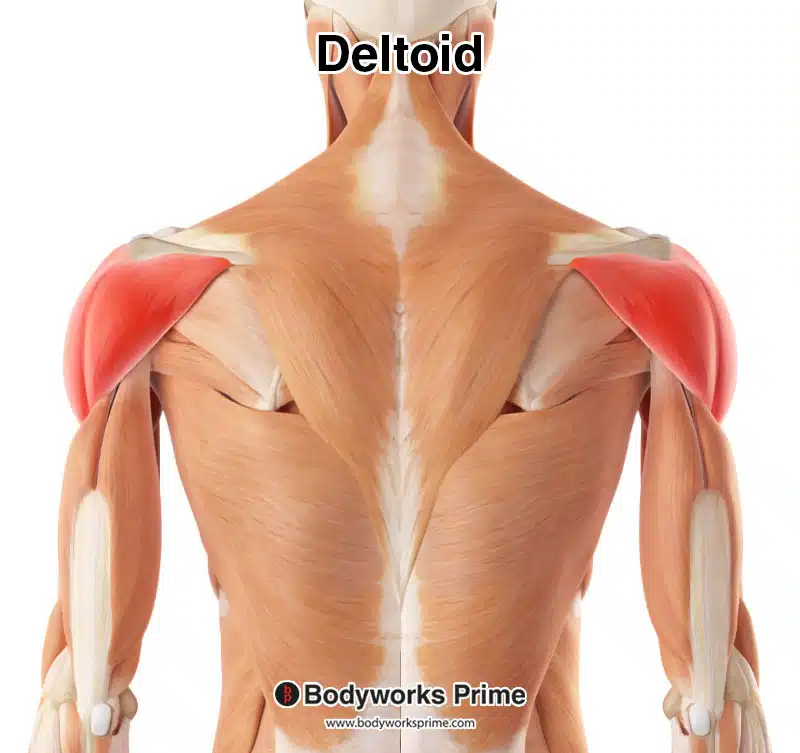
Deltoid
a large, triangular-shaped muscle located on the shoulder. Shoulder muscle; lifts the arm in all directions.
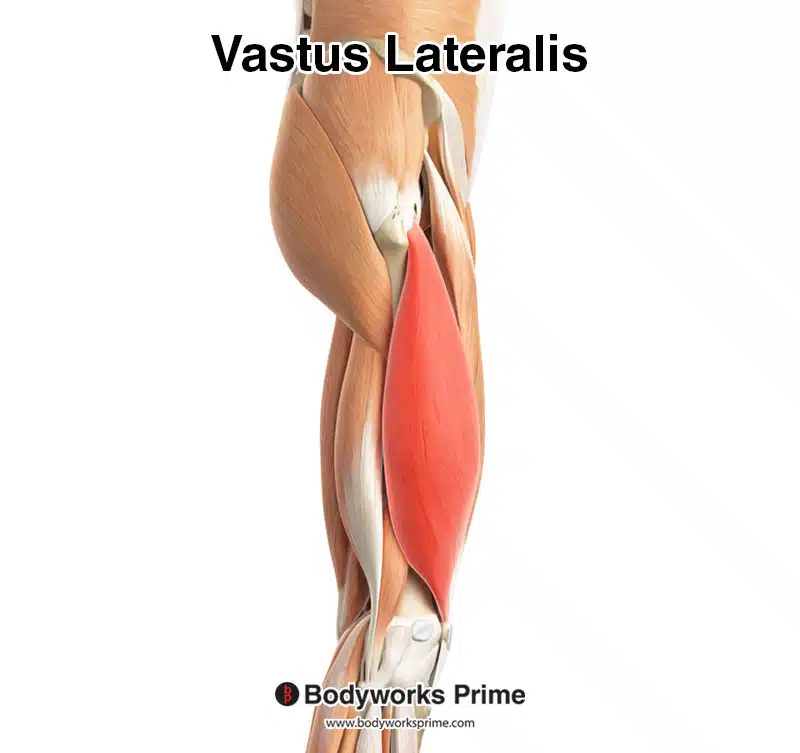
Vastus lateralis
the largest muscle of the quadriceps femoris group, located on the lateral (outer) side of the thigh, and functions primarily to extend the knee joint.
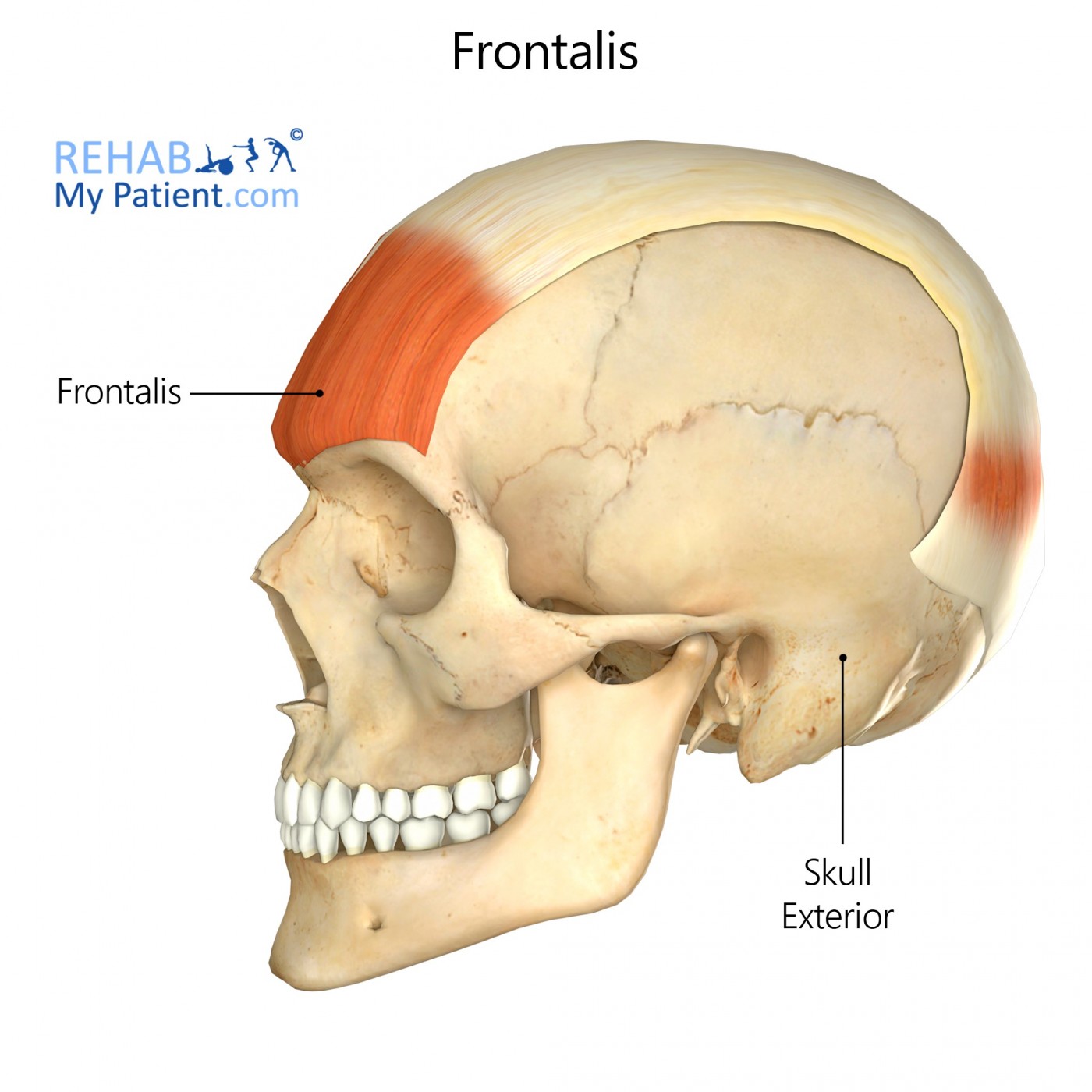
Frontalis
a paired facial muscle located in the forehead, responsible for raising the eyebrows and wrinkling the forehead.
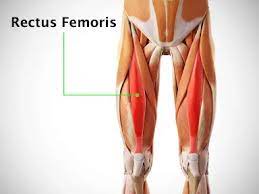
Rectus femoris
the anterior thigh compartment's most superficial and nearly vertically oriented muscle. This bipennate structure is a component of the quadriceps muscle complex, one of the knee's most important dynamic stabilizers.
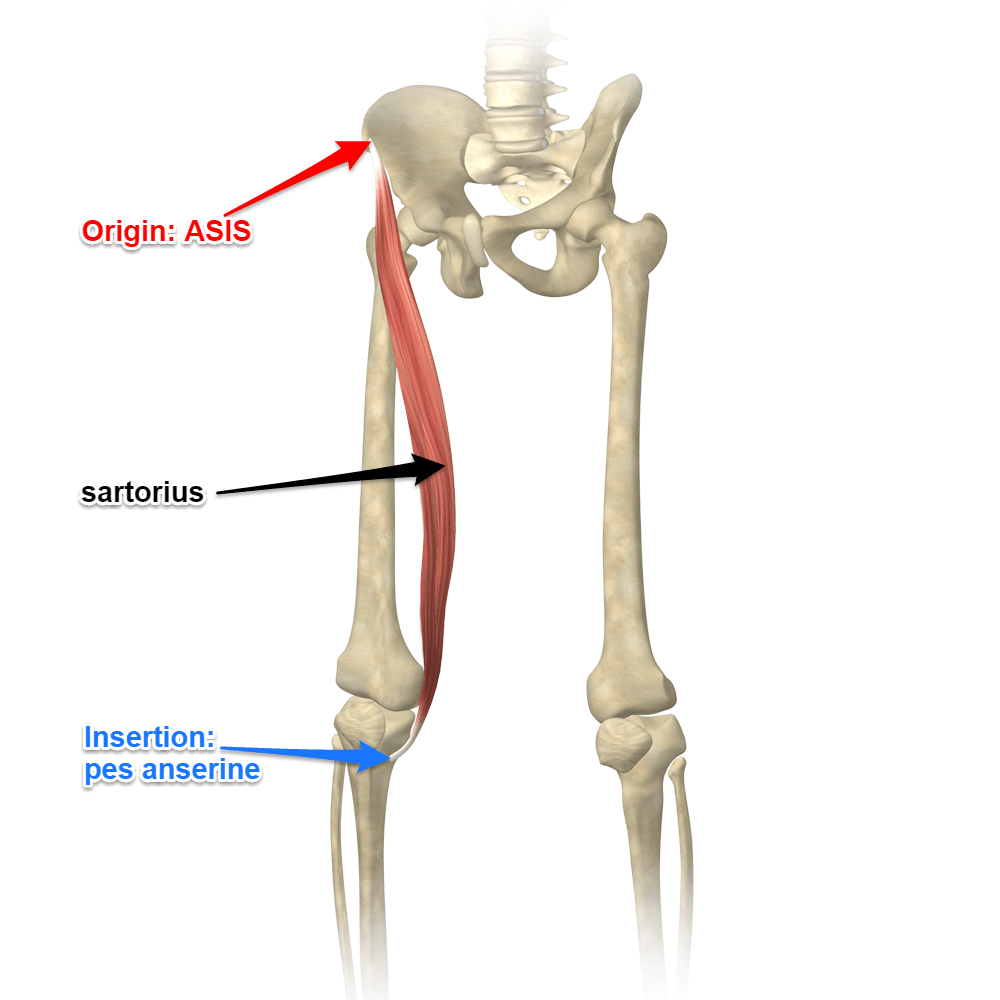
Sartorius
the longest muscle in the human body, spanning from the anterior superior iliac spine to the medial aspect of the tibia, and is involved in hip flexion, abduction, and lateral rotation, as well as knee flexion and medial rotation.
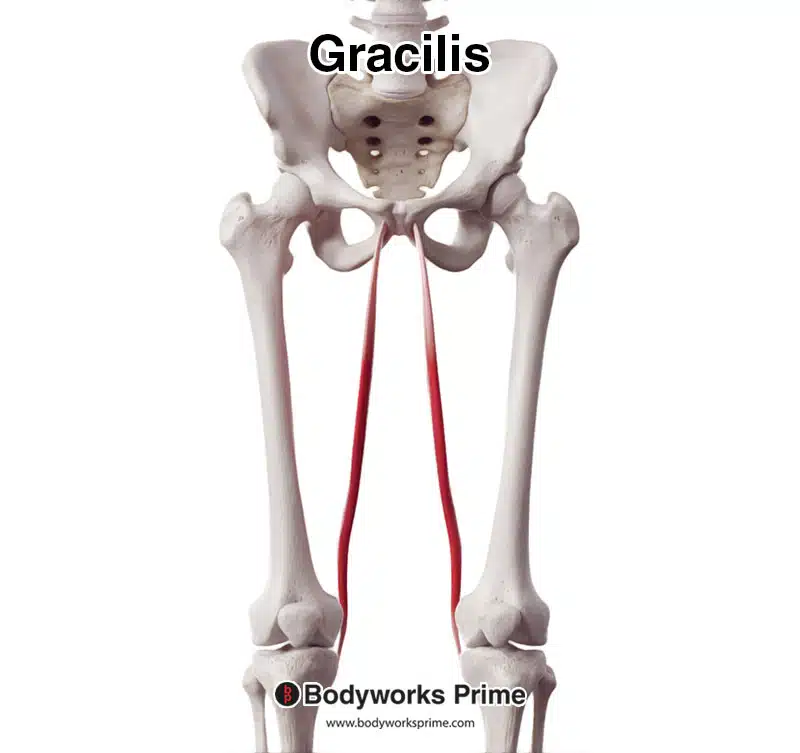
Gracilis
a long, thin muscle located on the medial (inner) side of the thigh, acting as a hip adductor and knee flexor, originating from the pubis and ischium and inserting on the tibia as part of the pes anserinus.
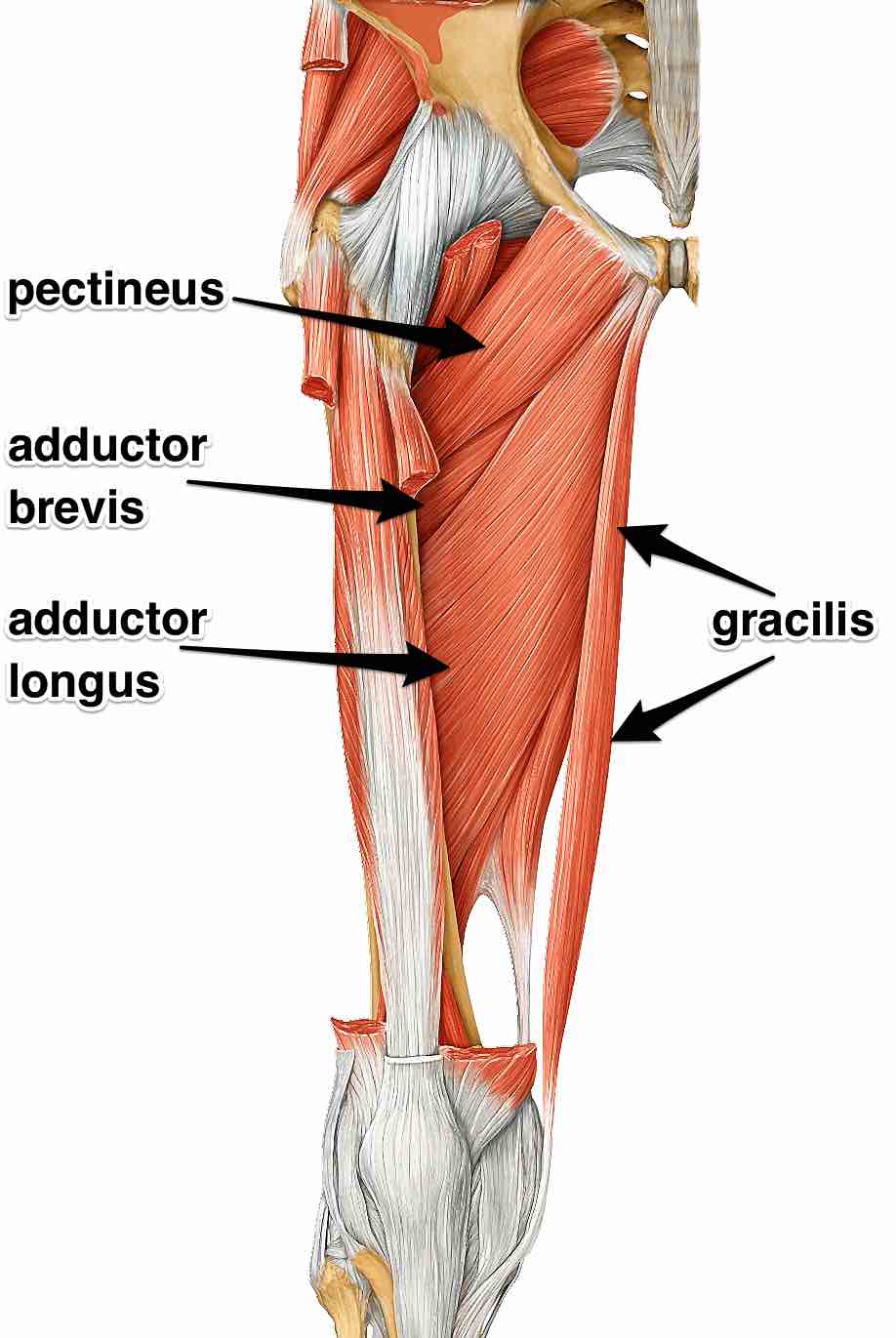
Adductor group
muscles that draw a part of the body towards the midline or toward the axis of an extremity, specifically the muscles on the inner thigh that pull the leg towards the body's center.
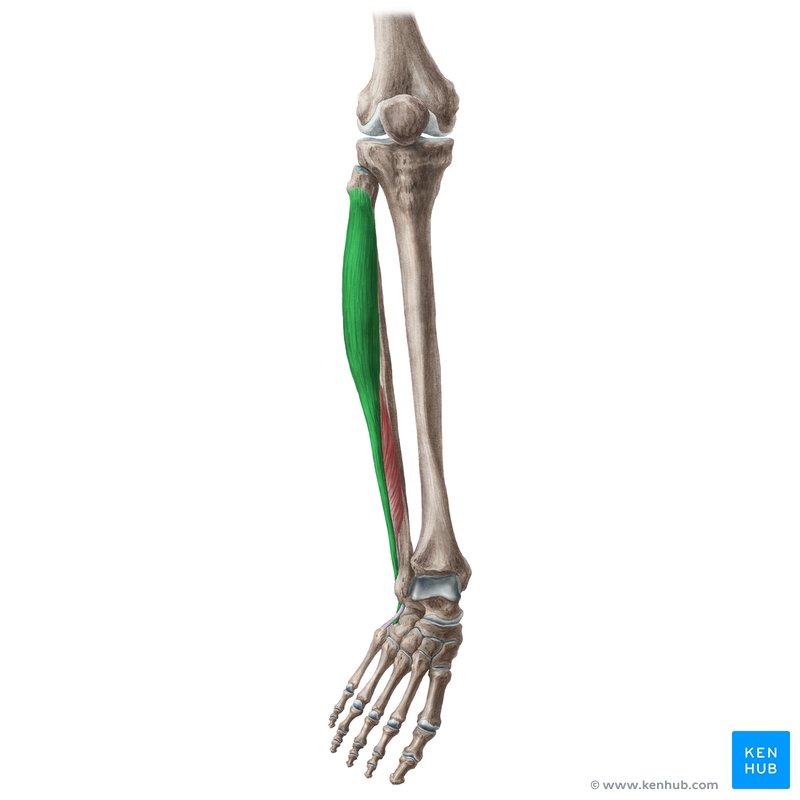
Fibularis Longus
a long muscle located superficially in the lateral compartment of the leg, together with the fibularis brevis muscle.
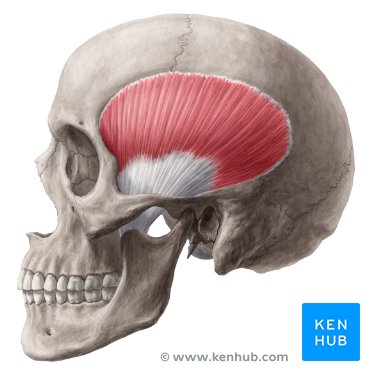
Temporalis
a fan-shaped muscle located on the side of the head within the temporal fossa, playing a crucial role in mastication (chewing) by elevating and retracting the mandible (lower jaw).
Orbicularis oculi
a ring-shaped muscle, also known as a sphincter muscle, located around the eye that functions to close the eyelids, contributing to blinking, and protecting the eye from damage.

Zygomaticus
a slender band of muscle on each side of the face that arises from the zygomatic bone, inserts into the orbicularis oris and skin at the corner of the mouth, and acts to pull the corner of the mouth upward and backward when smiling or laughing.
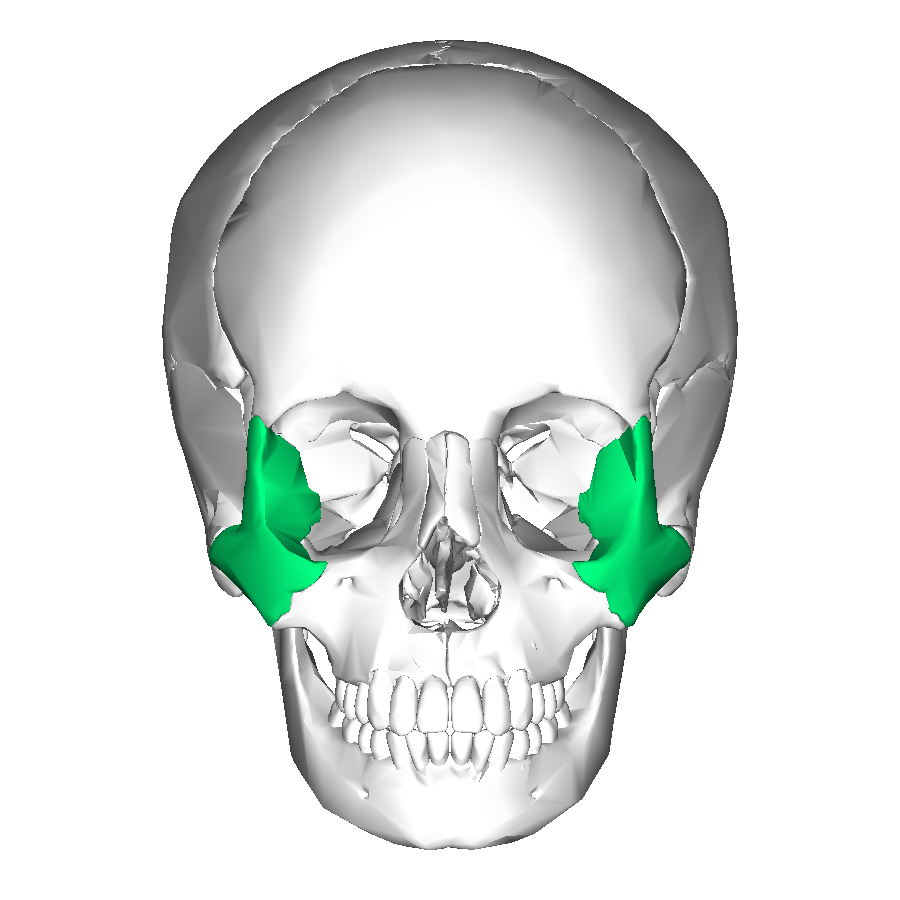
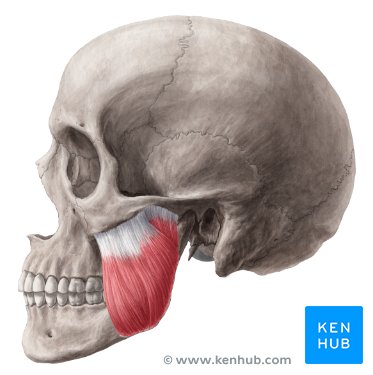
Masseter
a thick, quadrangular-shaped muscle located on the side of the face, below the cheekbone. It is one of the four muscles involved in chewing (mastication).
Vastus medialis
a muscle located on the inner (medial) part of the thigh, part of the quadriceps muscle group, that extends the knee.
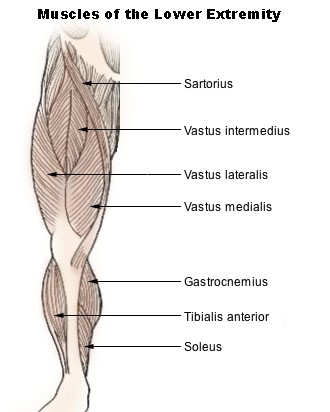
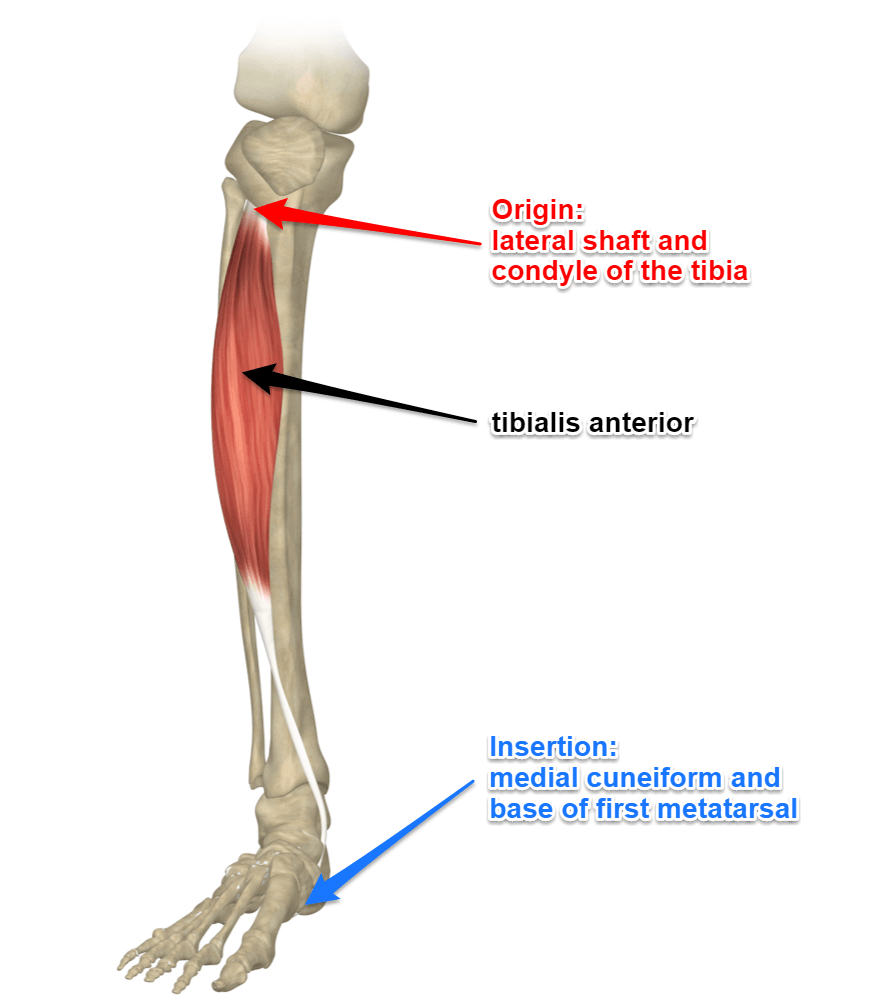
Tibialis anterior
originates from the tibia and inserts into the medial cuneiform and first metatarsal bones, acting to dorsiflex and invert the foot.
Transversus
efers to a muscle, like the transversus abdominis, whose fibers run horizontally or across the body, as opposed to vertically.
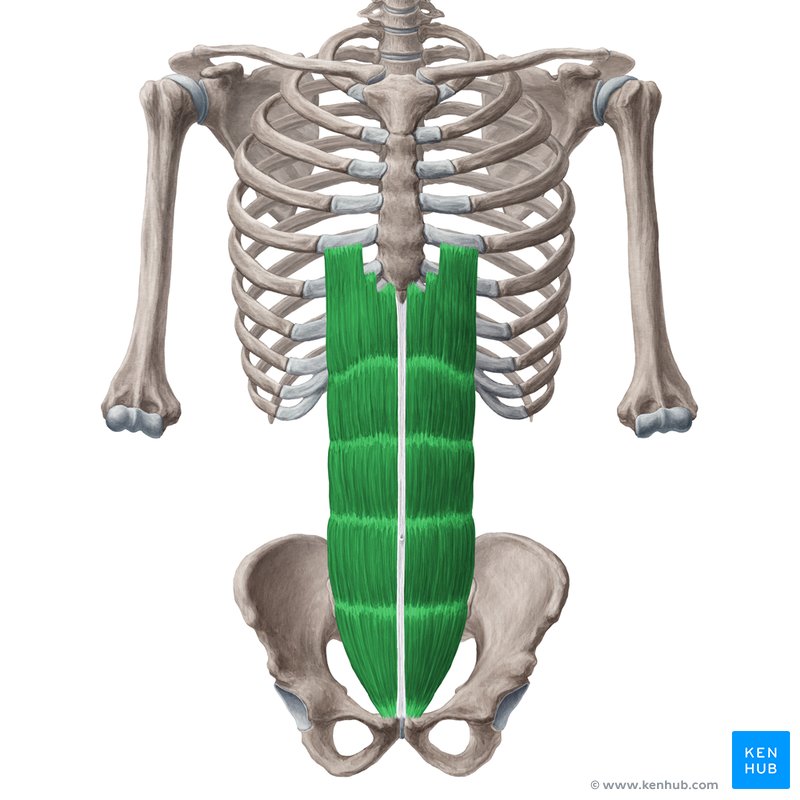
Rectus abdominis
a long, flat muscle located on the anterior (front) of the abdomen. It extends vertically from the pubis (pelvis) to the ribs.
Sacromere
The basic contractile unit of muscle fiber, made up of repeating patterns of actin (thin) and myosin (thick) filaments. It shortens during muscle contraction.
Thin fliaments
Made of actin, along with tropomyosin and troponin, these are pulled by myosin to shorten the sarcomere.
Thick filaments
Made of myosin, these interact with actin to produce contraction.
Motor unit
A single motor neuron and all the muscle fibers it innervates. The more fibers per neuron, the more forceful (but less precise) the contraction.
ADP/ATP cycle
ATP (adenosine triphosphate) provides energy when its third phosphate is removed, forming ADP (adenosine diphosphate). ADP is then recharged back into ATP using energy from various sources.
ATP/CP cycle
An immediate energy system where ATP is rapidly replenished by creatine phosphate, useful for bursts of activity lasting about 10 seconds.
Creatine phosphate
A high-energy molecule stored in muscles that quickly donates a phosphate to ADP to regenerate ATP during short, intense activity.
Aerobic respiration
The process of producing ATP using oxygen. It occurs in the mitochondria and is the main source of ATP for long-duration, moderate-intensity activities.
Myoglobin
An oxygen-binding protein in muscle tissue that stores oxygen and helps maintain oxygen supply during muscular activity.
Oxygen debt
The amount of extra oxygen the body needs after exercise to restore normal metabolic conditions, including converting lactic acid back into glucose.
Fatigue
A decline in a muscle’s ability to generate force, often due to lack of ATP, buildup of lactic acid, or nervous system limits.
Fast twitch
Contract quickly, fatigue quickly, use anaerobic metabolism; ideal for sprinting or weightlifting.
Slow twitch
Contract slowly, fatigue-resistant, use aerobic metabolism; ideal for endurance activities.
Red fibers
Rich in myoglobin and mitochondria, high endurance (slow-twitch).
Isometric contraction
Muscle length doesn't change (e.g., holding a plank). Force is produced without movement.
Tone
The constant, low-level contraction of muscles that helps maintain posture without producing movement.
White fibers
Low in myoglobin, adapted for fast, powerful bursts (fast-twitch).
Isotonic Contraction
Concentric: Muscle shortens.
Eccentric: Muscle lengthens under tension.
1st Class Lever
Fulcrum is between the load and effort (e.g., nodding the head).
2nd Class Lever
Load is between fulcrum and effort (e.g., standing on tiptoes).
3rd Class Lever
Effort is between fulcrum and load (e.g., biceps curl). Most common in the body.
Work
The energy transferred when a force moves an object. Equation: W = Force x Distance
Energy
The capacity to do work. Comes in various forms (kinetic, potential, chemical, etc.).
Kinetic energy formula
KE= 1/2 mv²
Potential energy formula
PE = mgh (m=mass, v=velocity, g=gravity, h=height)