MOD 1 - The Basics
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
frontal/coronal plane
splits front & back
sagittal plane
splits into left & right
midsagittal: equal left & right parts
transverse/axial plane
splits superior & inferior
prone
lying on belly
face & palms down
supine
lying on back
face & palms up
caudad
towards the tail/posterior part of body
cephalad
towards the head/anterior end of body
anechoic
without echos
hyperechoic
having many echoes
hypoechoic
having few echoes
isoechoic
having the same echogenicity
acoustic shadowing
an area through which sound waves fail to propagate
acoustic enhancement
refers to the increased echoes deep to the structures that transmit sound exceptionally well
complex
consists of both solid & cystic components
homogeneous
of uniform composition
heterogeneous
of differing compositions
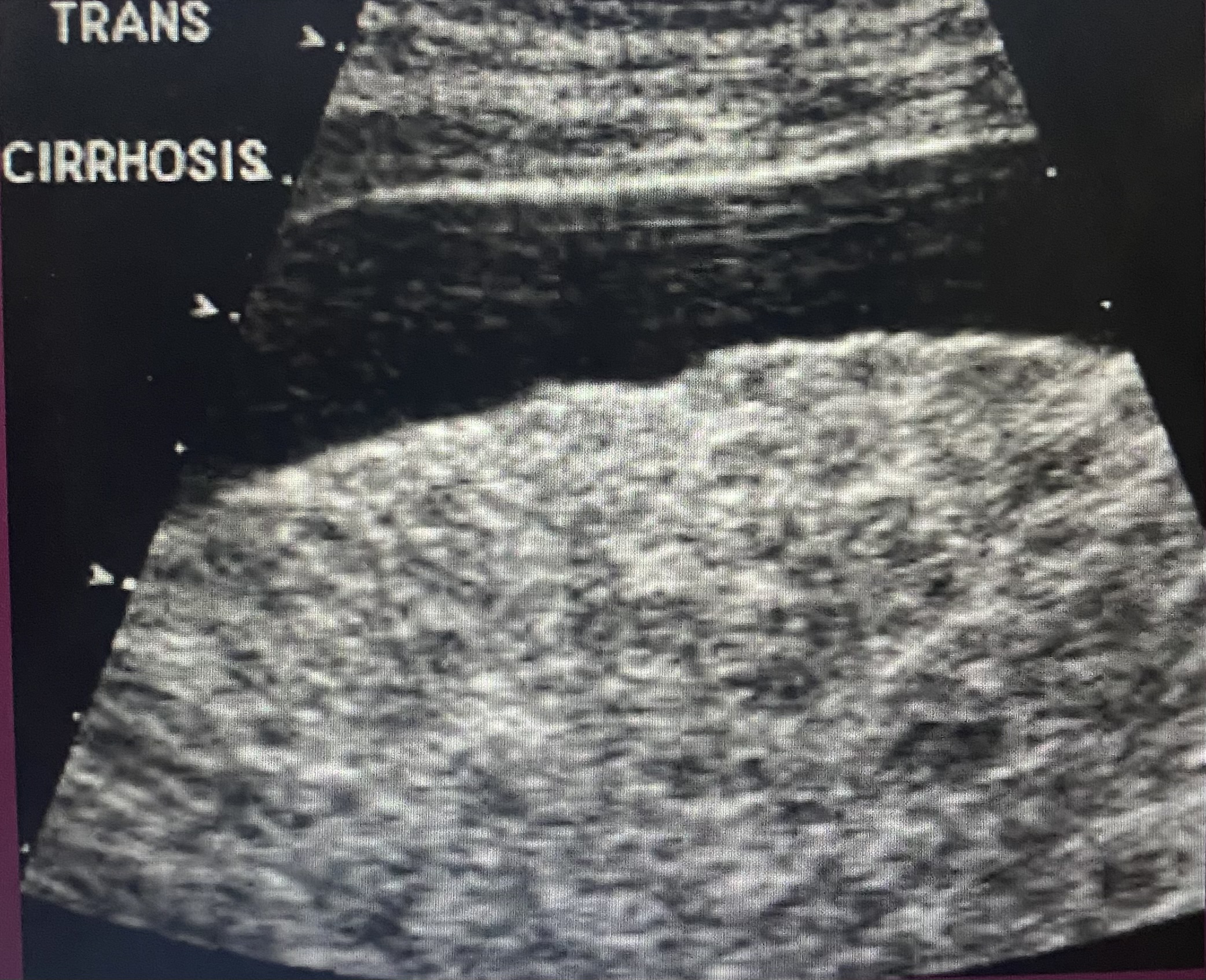
acoustic shadowing
characterized by a signal void behind structures that strongly absorb or reflect ultrasonic waves
a form of imaging artifact
happens most frequently w solid structures, such as bones or stones
acoustic enhancement
refers to the increased echoes deep to structures that transmit sound exceptionally well
characteristic of fluid-filled structures such as cysts, urinary bladder, and gallbladder
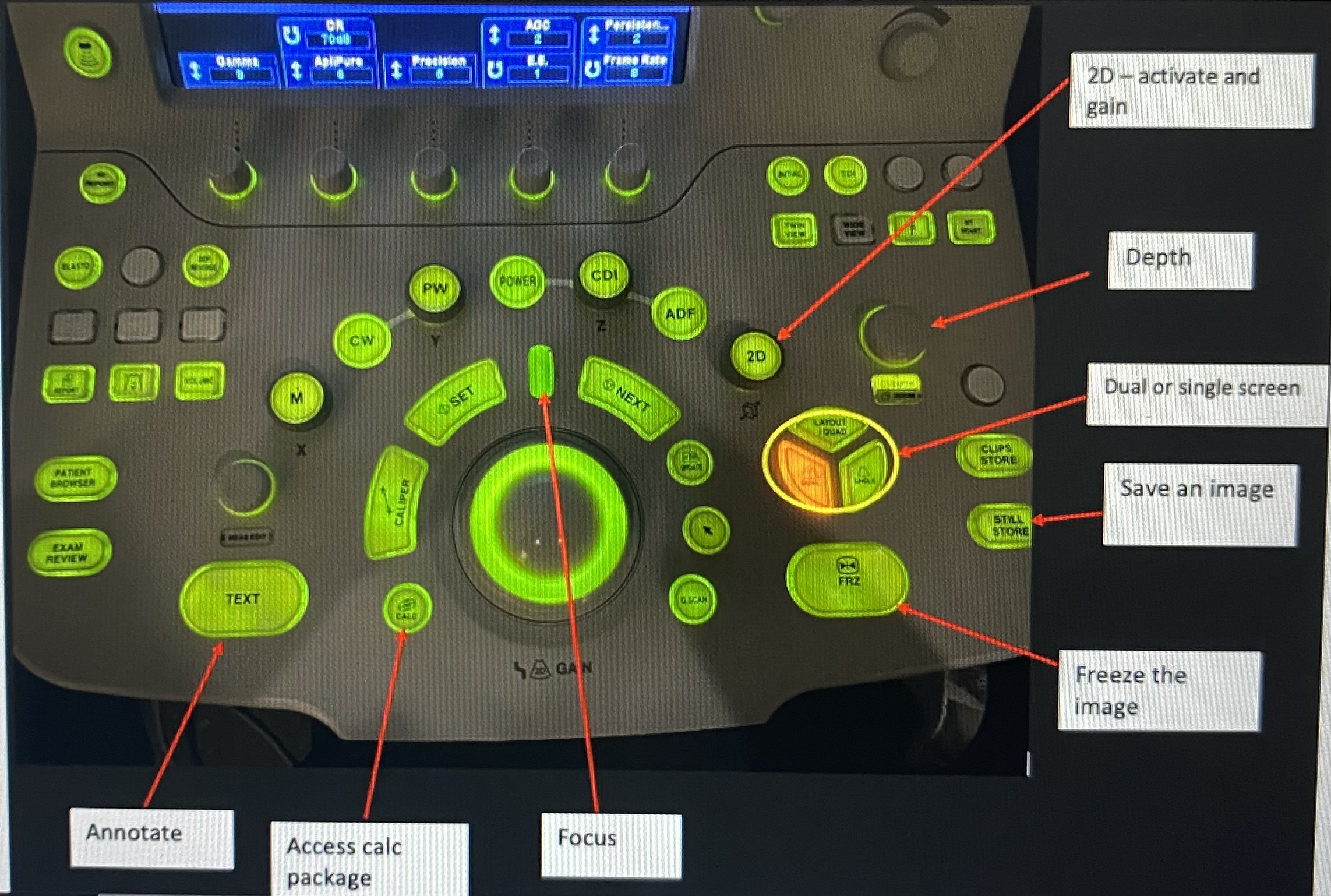
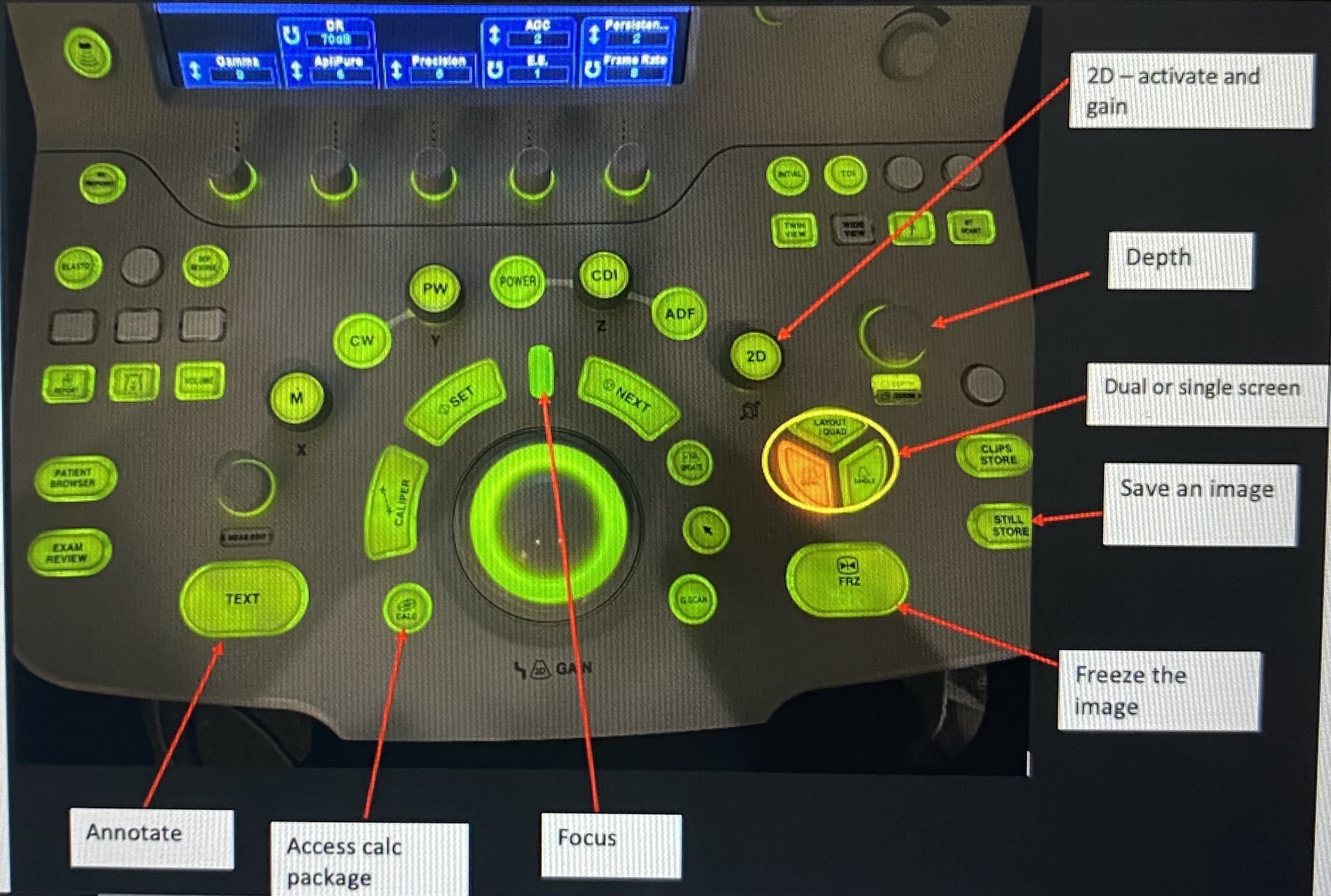
depth
to display information only to a certain depth
focus
defines where the focal point of the beam is in the body
gain
defines how much amplification is applied to echoes returning from the body
increasing makes it brighter
decreasing makes it dimmer
tgc
defines how much amplification is applied to echoes diff depths
freeze
freeze the imagine to allow for annotation & measurement before saving
still store
save the image
calc
access the calc package to enter measurements
dual
divides the screen into two images that you can toggle between
sector width
defines how wide our image is on the screen
text
annotate your images
anechoic
hyperechoic
hypoechoic
isoechoic
acoustic shadowing
acoustic enhancement
complex
homogeneous
heterogeneous
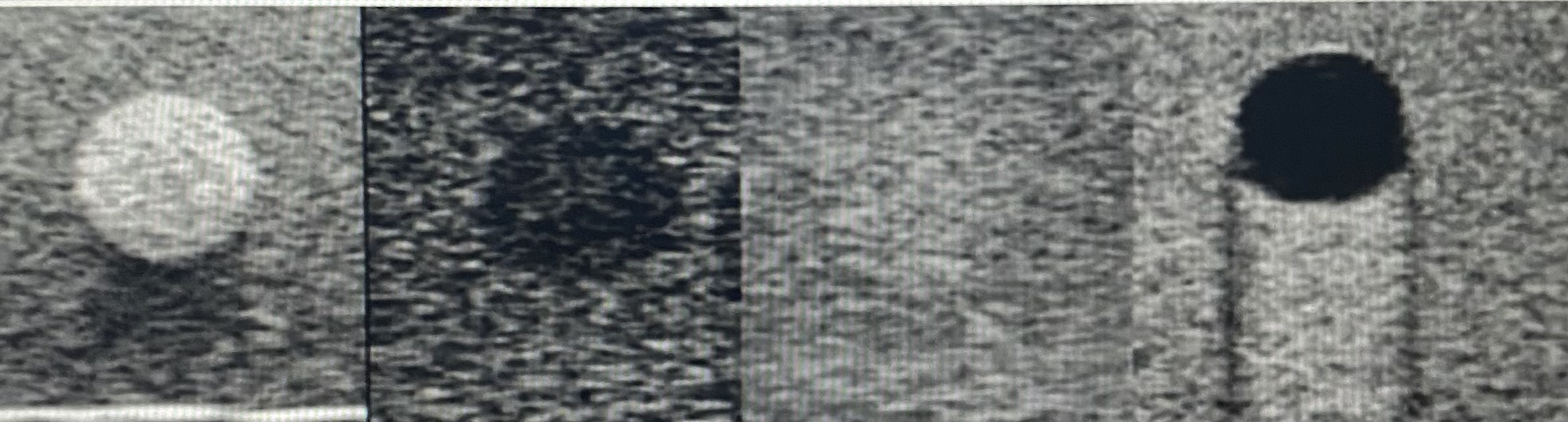
echogenic
hypoechoic
isoechoic
anechoic
which vessel sits left of the midline of the body?
abdo aorta
which vessel sits to the right of the midline of the body?
IVC
which vessel sits posterior to the liver?
IVC
which vessel travels through the posterior portion of the liver?
IVC
which vessel pulses with the heart?
abdo aorta
which vessel expands and collapses with respiration?
IVC
which vessel has thicker walls?
abdo aorta
which vessel has thinner walls?
IVC
which vessel drains directly into the right atrium of the heart?
IVC
which statement is incorrect when comparing the aorta and the IVC?
a) the distal order is more anterior than the IVC at that level
b) the proximal aorta travels through the posterior portion of the liver, anterior to the caudate lobe
c) the IVC responds to respiration
d) the IVC is located to the right of the spine and the aorta to the left
b) the proximal aorta travels through the posterior portion of the liver, anterior to the caudate lobe
what is the most proximal branch of the abdominal aorta?
celiac trunk
true or false?
the superior mesenteric vein is normally located to the right if the superior mesenteric artery
true
the correct way to measure the distal abdominal aorta is in a ___ plane
transverse
where do you place the anterior caliper when measuring the abdominal aorta?
anterior outer wall edge
where do you place the posterior caliper when measuring the abdominal aorta?
posterior outer wall edge
the correct place to measure the distal abdominal aorta is ___
just above the bifurcation
what is the normal diameter of the aorta?
1.5cm-2.5cm