Metallurgy
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
What is the ability of a metal to resist indentation or penetration called?
Hardness
The hardness test which uses a 10 mm (3/8” ) diameter ball as an indenter is called:
Brinell Hardness Test
As the carbon content of a steel increases, the weldability _________.
Decreases
What are two tests a steel fabricator could do on the jobsite to determine if a steel had high carbon content?
Spark Test
Chip test or File test
What would a Brinell Hardness of 100-150, 300, and 500 determine?
100 to 150 – File bites into surface easily
300 – Metal exhibits first real resistance to file
500 – File barely removes metal
What would the appearance of a chip look like if chip tested on mild steel?
The chip would be continuous and bend without breaking
What effect does carbon have as an alloying element in steel?
Principle hardening agent, gives steel its strength
What effect does aluminum have as an alloying element in steel?
Deoxidizes steels, reduces grain growth, produces fine grained steels, stronger than large grain.
What effect does chromium have as an alloying element in steel?
Hardening agent, increases strength, toughness and impact resistance at sub-zero temperatures, increases corrosion resistance.
What effect does copper have as an alloying element in steel?
Increases atmospheric corrosion resistance properties and increases strength of steel.
What effect does Manganese have as an alloying element in steel?
Offsets embrittlement and hot shortness in small percentages. In larger percentages, it gives greater toughness and hardenability.
What effect does Molybdenum have as an alloying element in steel?
Improves strength at high temperatures, increases hardenability and reduces high temperature creep.
What effect does Nickel have as an alloying element in steel?
Increases strength and toughness at low temperatures.
What effect does Tungsten have as an alloying element in steel?
Allows steel to retain its strength and hardness at high temperatures.
The weld and area immediately affected by the welding heat is called the _____________
Heat affected zone (HAZ)
If proper precautions are not taken, what can occur in the heat affected zone when using an Oxy-Fuel gas cutting torch?
Grain growth can occur in the HAZ and the cut face can become hardened.
Why are some high alloy steels unable to be cut with an oxy-fuel torch?
Many of the alloying elements have a much higher melting temperature than what is attainable with an oxy-fuel torch. They prevent the iron from being exposed and prohibit oxidization.
Cold working of metal takes place at temperatures_______________
Below the re-crystallization temperature for that metal.
The results of cold working a metal will be an increase in ______________.
Tensile strength and hardness
Hot working metal results in ____________in the elongating in the direction of forming.
Grains
Why is hot working necessary for some metals?
Some metals are not sufficiently ductile when cold to be able to be cold worked.
Hot working allows ________sections to be worked
Thicker
What causes distortion in a welded joint or structure?
Weld metal expanded when first deposited, then contracts/shrinks upon cooling and draws in the base metal.
What is residual stress?
Stresses that exist in the metal at room temperature
What is angular distortion?**
Weldment pulled out of the desired alignment.
What is longitudinal distortion?
Shrinkage along the length of the weld.
What is transverse distortion?
Shrinkage across the width of the weld.
Staggered or intermittent welding helps to_________________
Control distortion.
What does ASTM stand for?
American society of Testing Metals
What does ASME stand for?
American Society of Mechanical Engineers
What does AISI stand for?
American Iron & Steel Institute
What does SAE stand for?
Society of Automotive Engineers
Under the AISI material specification: What do the first, second, third & fourth digit represent? (e.g. C1015)
First digit: Type of Steel
Second digit: Major or dominant alloying element
Third & Fourth digit: Percentage of carbon in the hundredths
Describe a C1015 steel (AISI) in sentence form:
A plain carbon steel with no alloying elements and a carbon content of 0.15%
Describe an A36 steel (ASTM)
Carbon steel for general construction (Structural)
Describe an A515 steel (ASTM)
Intermediate and high temperature service with increased notch toughness (pressure vessel)
Describe an A516 steel (ASTM)
Medium to lower temperature service with increased notch toughness (pressure vessel)
Decsribe an A283 steel (ASTM)
Steel for tanks.
What element in steel gives corrosion resistant properties?
Chromium
Stainless steel’s specification system is designated by which organization? How many digits in it’s numbering system?
AISI
3 digit numbering system called a SERIES
For a 304L stainless steel, the L stands for__________:
Extra Low Carbon
What does the first digit, and the last two digits refer to in AISI stainless steel series designation?
First digit refers to the group/classification
Last two digits refer to the type OR specific alloys
What are the 4 general classifications of stainless steel, and what are their numbers?
2xx – Chromium-Nickel-Manganese
3xx – Chromium-Nickel
4xx – Chromium
5xx – Low Chromium Steel
What is Flame-Heat straightening?
Using heat to correct warpage or twisting from welding distortion, or other stress / force that misaligns.
When heated, metal becomes ______ and wants to expand_____
Plastic
Expand in all directions
If volumetric expansion of metal is restricted, the metal will expand in which direction?
Direction of least resistance.
What are the AISI / SAE steel class numbers from 1 to7?

What does ASTM A6 cover?
Rolled plates, shapes, sheet piling, and bars for structural use.
What does ASTM A20 cover?
Steel plates for pressure vessel use.
Metals are made up of many crystals called:
Grains
Where do grains in metal interconnect with each other?
At their grain boundaries
The smaller the grain size, the _______the steel will be:
Stronger and tougher
Grains will begin to form in the areas of molten steel that are __________
Cooling first
Grains will continue to grow in size as long as the steel is held at temperatures above _______
The upper critical temperature
What are the two atomic arrangements that iron can exist in? What are their Temperatures? How many atoms are in their arrangements?
Body centered cubic form (Below 1670F), 9 atoms
Face centered cubic form (Above 1670F), 14 atoms
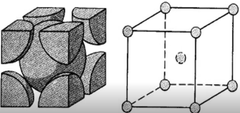
What is this crystal structure called?
Body-centered Cubic
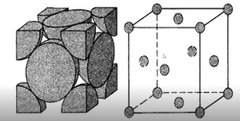
What is this crystal structure called?
Face-centered cubic
What is the lower critical transformation temperature of mild steel?
1333F (723 C)
The upper critical transformation of steel will vary depending on the:
Carbon content of the steel.
Define Austenite:
A solid solution of carbon/iron-carbide in the fcc cubic structure (face centered). Exists in steels above 1333 F
Define Cementite:
Hard and brittle iron-carbide. Below 1333 F
Define Ferrite:
Pure iron of the BCC Crystal structure, Soft and Ductile
Define Pearlite:
Continuous granular mixture, alternate plates/layers of ferrite and cementite. Exists below 1333 F
Define Martensite
Formed when steel is rapidly cooled from the upper transformation temperature.
Hard needle like crystals saturated with a solid solution of carbon in iron.
Forms when Austenite is quenched.
What is heat treatment?
Heating and/or cooling a steel to achieve a specific property or change in the metal’s characteristics.
Pre-heating a metal before welding reduces___________
Thermal Shock/stress
What is the approximate temperature and time held at that temperature for STRESS RELIEVING a welded structure?
Heat below Lower critical transformation temperature (1200F) for ONE HOUR per INCH of material thickness.
What is the purpose of stress relieving?
Heating and cooling at a uniform/controlled rate to remove residual stresses due to forming / welding.
What is an annealing heat treatment?
Heat to 100 F above the upper critical temperature (1700 F) and held there for a specified time then slowly cooled in a furnace. Soften steel for machining / working to be re-hardened afterwards.
How is a Normalizing Heat Treatment accomplished?
Similar process to annealing except the steel is cooled in still air at room temperature. Higher strength and hardness than annealed steels.
Pressure vessel plates are often normalized (SA516-70 MT <-- indicates normalizing)
The rapid cooling of a metal from an elevated temperature is called:
Quenching
What is tempering?
Final heat treatment, done below lower critical temperature.Increases toughness and impact strength. Reduces internal stresses and removes some degree of hardness.