ESS SL - Semester 1 Term 1 - 2.1-2.4
1/193
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
194 Terms
What is Ecology?
Study of the living and non-living parts that interact within an ecosystem.
What are Abiotic Factors?
Non living, physical factors in the ecosystem that may influence an organism or a system.
What are the examples of abiotic factors?
Sunlight influences temperature and evaporation rates, which also influences precipitation levels.
Temp
Water
All these abiotic factors are interdependent.
What are the major biotic and abiotic components of an ecosystem?
Precipitation
Oxygen
Carbon Dioxide
Producer
Decomposers
Water
Soluble mineral nutrient
Secondary Consumer
Ecosystem
A community of interdependent organisms and the interactions with the physical environment in which they live.
What are the different levels of organization?
Species
Population
Community
Ecosystem
Biome
Biosphere
What is an ecosystem?
A community of interdependent organisms and the interactions with the physical environment in which they live. Or, The abiotic and biotic factors and the interactions between them.
What is the key of an ecosystem?
The interaction between organisms and environment
What’s a species?
A group of the same type of organisms that is able to reproduce and produce fertile offspring.
What are scientific names?
They are used by scientists to identify a specific species.
How many parts does scientific names contain?
It contains two parts: Genus Species
What are the characteristics of Scientific Names?
It contains two parts: Genus Species
Always underlined, or in italics
Genus always capitalizes & species all lower case
What are keystone species?
Species that are crucial to the maintenance of their ecosystem
What’s vital in determining the nature and structure of the entire ecosystem?
Keystone species
What’s a habitat?
Where an organism lives
What should a habitat provide for its living organisms?
It should provide:
Food
Water
Shelter
What’s a niche?
Where, who, what and how an organism lives.
A niche ranges from what-to-what?
It ranges from unidimensional space to a multidimensional space.
What does a niche include?
Space utilisation
Food consumption
Temperature range
Moisture requirements
A niche should not?
Have two identical or similar niches (bc they cant live in the same habitat)
No two species can have the same ecological niche in the same place at the same time.
What’s fundamental niche?
The entire range of conditions in which a species could live.
What’s realized niche?
The actual conditions under which the species lives (usually due to competition)
Case Study: Joseph Connell’s barnacles
Both of these barnacle species could live anywhere between the high tide and low tide lines-their fundamental niche.
But abiotic environmental conditions and competition for resources (a biotic factor) limit the size of each species-realized niche.
What are the Characteristics of a population?
Able to interbreed
Populations can be separated by geography eventually stopping interbreeding
Formation of a new species
Predation equals to?
Hunting
Herbivory equals to?
Hunting plants
What’s parasitism?
One species depends on another for nutrition, harming the host organism in the process.
What does mutualism equal to?
It’s when two species benefit from one another
What are the 2 types of competition?
Intraspecific, and interspecific.
What’s competition?
Fighting for the same resources
What’s Amensalism?
One unaffected the other harmed
What’s Neutralism?
Two organisms do not affect each other. No relationship.
What’s population Dynamics?
The study of the change in populations over time.
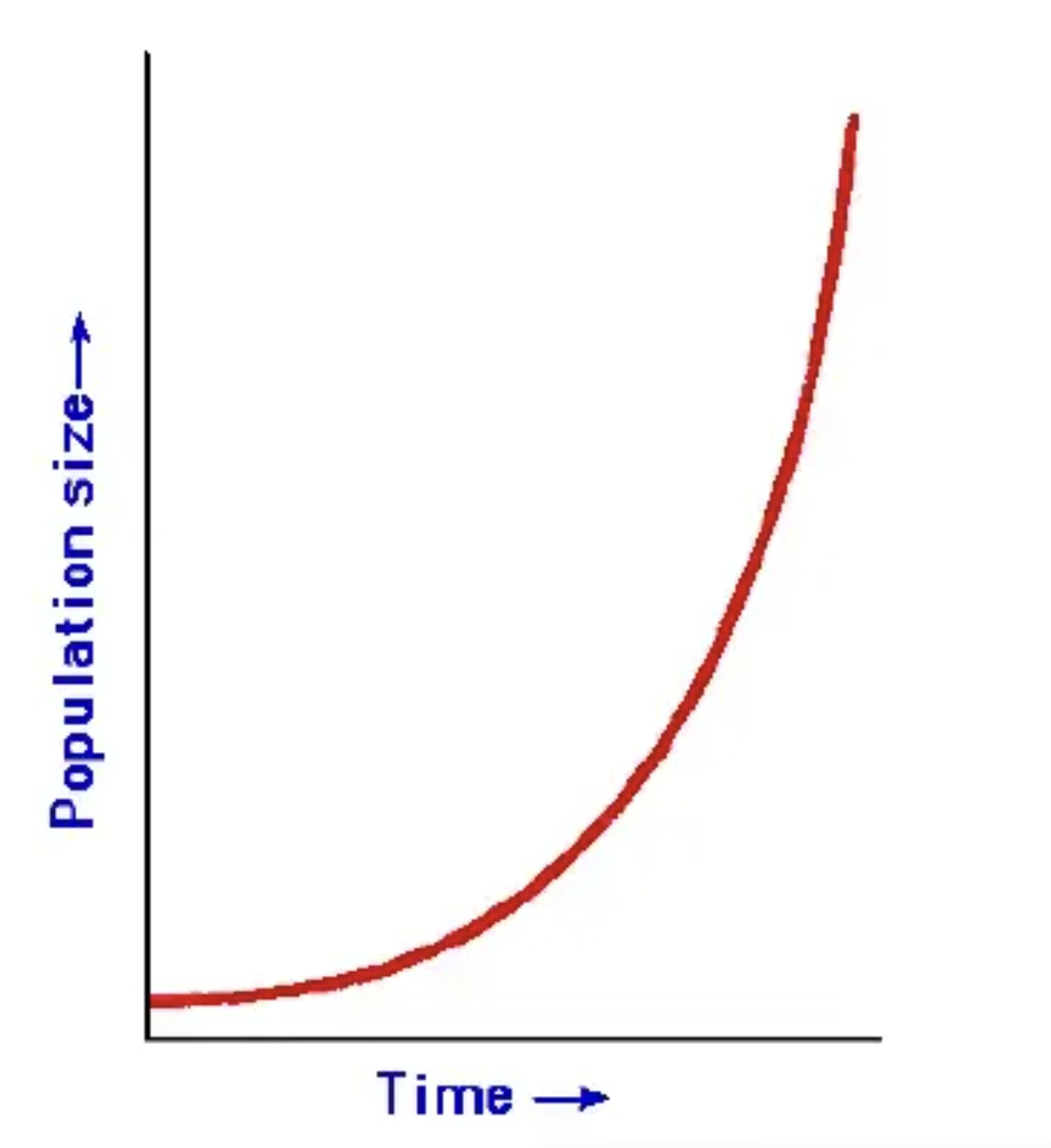
What would happen when there’s no limiting factors?
It will result in exponential growth (there is nothing limiting population size).
What happens during the ‘Exponential Growth Phase’?
the ecosystem provides its species/ living organisms with abundant food, space, and light
What happens during the ‘Transitional Phase’?
Competition
What happens during the ‘Plateau Phase’?
When population reaches carrying capacity (K) there is no longer growth.
What’s Carrying Capacity?
The maximum number of organisms of a single species that an ecosystem can support.
What are limiting factors?
Factors in an ecosystem that limit the population size if there are too much or too little for it.
What does limiting factor cause?
It causes a reduction in population growth as they become short in supply for resources.
What’s density dependent factors?
It increases or decreases the carrying capacity of a population based on the size of the population.
Carrying Capacity K and r Strategists
Plotting the growth of a population from an initial growth realization factor of 1 to a final factor of 0 produces a curve like this, called the logistic growth curve or S-shaped curve of growth.
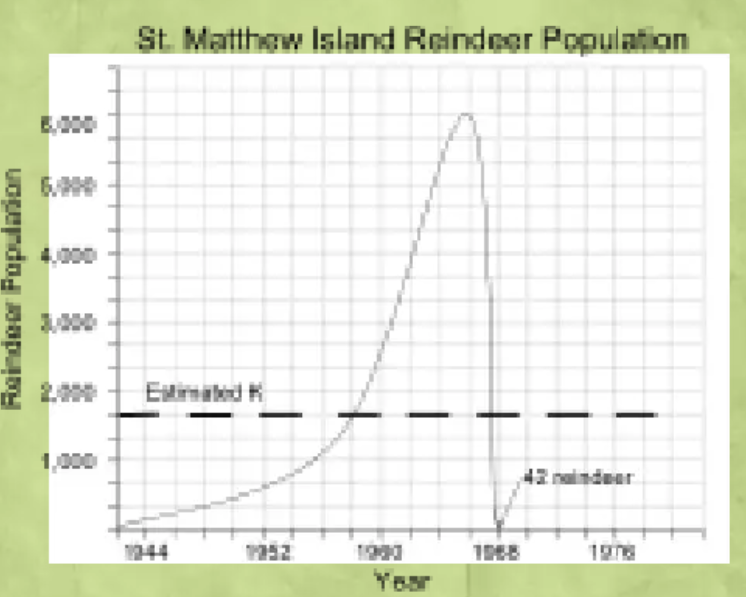
Case Study: Reindeer on St Matthew Island
Small island in the Bering Sea
Reindeer (Rangifer tarandus) introduced in 1944, increased from 29 to k in 1963.
Crash die-off the following winter to less than 50.
Community
A group if interacting species, living in the same ecosystem
Population
All he individuals of the same species in a community
Individual
A single organism of one species
Ecosystems and Communities are part of a bigger…?
Ecological organisational structure
Photosynthesis and respiration can be viewed as systems, which means?
they have inputs processes and outputs.
It is important to remember that producers (autotrophs) undergo…?
photosynthesis and respiration simultaneously, while consumers (heterotrophs) only respire.
Respiration
Oxidation of glucose to release energy, then used in all activities in the organism.
How energy is formed
Energy is stored in chemical bonds of glucose, and as the glucose is broken down the energy released is used to create another chemical, which our cells can readily use.
Respiration in word equation
Glucose + Oxygen → Carbon dioxide + water
Photosynthesis in word equation
Carbon Dioxide + Water yields glucose + Oxygen
Trophic level
Position an organism occupies in the food chain
What does T1 in model trophic levels mean
Producer
What does T4 or T5 in model trophic levels mean
terrestrial ecosystem T4 is the highest due to losses of energy between trophic levels.
Producers (Autotrophs)
Plants or algae that produce their own food using photosynthesis and form the first trophic level in a food chain.
Chemosynthetic Organisms
Produce food without sunlight
Feeding relationships involve
Producers, consumers, and decomposers.
Models to illustrate feed relationships
Food chains
Food webs
Ecological Pyramids
Food chain
Linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass as one organism, and eats another.
Pros of food web
it shows all of the relationship between all organisms in a community, and it shows how different food chains interact withe achother, and overlap.
Ecological pyramid
Graphical representation designed to show the biomass or bio productivity at each trophic level in a given ecosystem.
3 types of ecological pyramids
Pyramid of energy
Pyramid of Biomass
Pyramid of numbers
Pros of Ecological pyramid
Quantitative models to show information about the organisms at each trophic level.
Pyramid of numbers
numbers of organisms
pyramid biomass
mass of organic matter
pyramid of productivity
flow of biomass or energy overtime
Pros of pyramid of numbers
Simple overview of community structure
Non-destructive method
Useful in comparing changes in a number of individuals over time
Weakness of pyramid of numbers
All organisms included (regardless of size)
Numbers can be too great to represent accurately
Some animals feed at more than one trophic level (omnivore)
pyramid of biomass (definition)
standing stock/ storage of each trophic level, measured in units (grams of biomass per square meter), or Joules per square meter)
pyramid of biomass calculates
dry mass and energy content
Pyramid of biomass represents
standing stock
pyramids of biomass can show greater quantities at higher trophic levels because
they represent the biomass present at a fixed point in time, though seasonal variations may be marked.
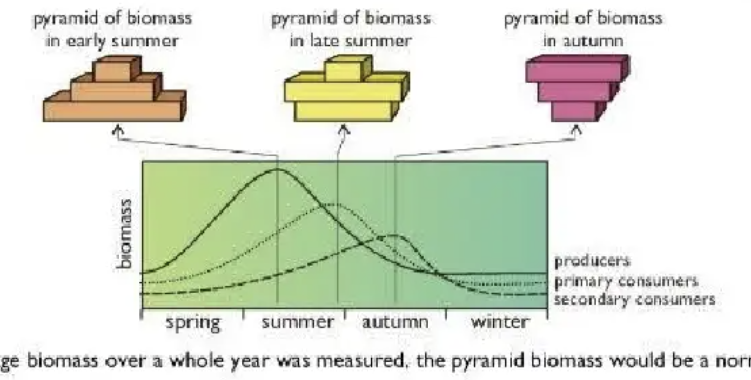
pyramid of biomass inverted
occurs w aquatic ecosystems when growth is rapid, and seasonal.
strength of pyramid of biomass
overcome the issue of counting seen in PN
limits of pyramid of biomass
seasonal variation
destructive and unethical
not all organisms have the same calorific value
pyramid of productivity
flow of energy through a trophic level, indicating the rate at which that storage is being generated.
pyramid of productivity shows
turnover of biomass at each trophic level
the clue that you need to find when dealing with pyramid of productivity loss is…?
time
pyramid of productivity for entire ecosystems over a year always shows…?
a decrease along the food chain
strengths of pyramid of biomass
Most accurate, because they show actual energy available.
Ecosystems can be compared
Solar input can be added.
Limits of pyramid of biomass
Difficult data collection
Species can be difficult to assignment to particular trophic level
Pyramid of productivity in a healthy ecosystem will form a…?
pyramid shape, due to the 10% rule and energy efficiency.
Why are the pyramids more narrow towards the apex?
Due to the tendency for numbers of biomass and energy to decrease along food chains.
Biomagnification
Increase in concentration of non-biodegradable pollutants along a food chain.
Toxins
poisonous materials
Persistent chemicals/ toxins/ nonbiodegradable pollutants
Unable to breakdown in the organism/trophic level, so it stays.
Dangers of Biomagnification
it accumulates in the food chain, and damage organisms (Especially the predators).
Toxins that cause problems in the food chain
heavy metals, and organic pollutants
Bioaccumulation
Inc in concentration of persistent or non-biodegradable pollutants along a food chain.
Toxins (eg. DDT, and mercury) accumulate along the food chains due to…?
Decrease of biomass and energy
Similarities of Biomagnification, and Bioaccumulation
Toxins are ingested
Bioaccumulation may lead to biomagnification
Concentration inc overtime
Difference in Biomagnification, and Bioaccumulation
Biomagnification: Accumulation with an organism, & Toxins are ingested at a higher rate than they are eliminated.
Bioaccumulation: Organisms (at higher rank), are more at risk, &Inc in concentration of a toxin as it moves from one trophic level to the next.
what animals are most susceptible to changes in the environment?
Apex predator, or top carnivore.
Case Study: Minamata Bay
Minamata a small town in Japan, was polluted by mercury and methylmercury from a factory known as Chisso (a factory that produces fertilizers and plastics). This caused the Minamata citizens to have a neurological disease.
what happens during insolation?
Solar radiation enters the earth, they become unavailable for ecosystems bc its absorbed by inorganic matter or reflected back into the atmosphere.
Albedo
Reflectivity of a surface
Albedo (dark colors)
Low albedo
Albedo (Light colors)
high albedo