Behavioral Science II Lesson 7: The Self
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Self-concept can be broken down into what two parts?
(A) The Existential and Rhetorical Self
(B) The Existential and Categorical Self
(C) The Rhetorical Self and Categorical Self
(D) The Rhetorical Self and Reflective Self
(B) The Existential and Categorical Self
Self-concept can be broken down into The Existential and Categorical Self.
CRB Many Self-Concepts can also fall under the umbrella of Self-Schemas. Which of the following would classify as a Self-Schema?
(A) A patient referring to me as Doctor
(B) Calling myself an Athlete
(C) Jennifer thinking about her role in her neighborhood
(D) Tommy's unique way of classifying animals as spotted or not-spotted.
(B) Calling myself an Athlete
Self-Schemas are self-given labels, and those labels usually imply I have a certain set of qualities. Only (B) involves a self-given label.
What is the difference between the Existential and the Categorical Self?
The Existential Self is understanding that you are a separate and distinct entity from others. It is constant and unchanging.
The Categorical Self is understanding the way in which you fit into the world (age, gender, traits, careers, etc). It can change.
Which of the following is not one of Carl Rogers' three components of self-concept?
(A) Self-Esteem
(B) Awareness of self
(C) Self-Image
(D) Ideal Self
(B) Awareness of Self
Carl Rogers' three components of self-concept are self-esteem, self-image, and ideal self.
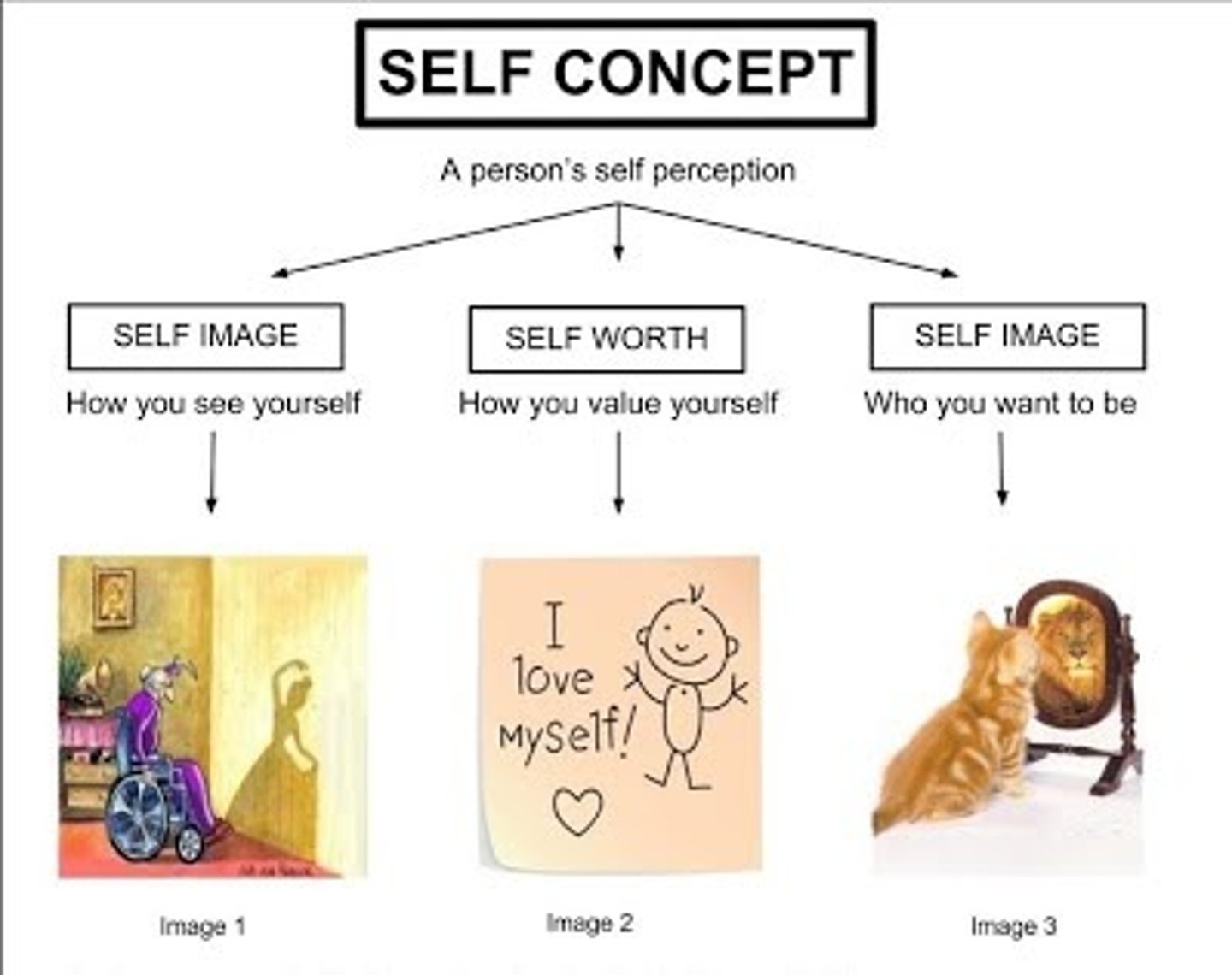
CRB Carl Rogers also believes that the ideal self is usually an unattainable standard, and the real self will fall short of that. Which term best describes this phenomenon?
(A) Learned Helplessness
(B) Low Self Efficacy
(C) Differentiated
(D) Incongruity
(D) Incongruity
When the real self falls short of the ideal self, the result is Incongruity, according to Rogers.
Sarah struggles with an eating disorder and body dysmorphia, meaning that she sees herself as being much fatter than she actually is. Because she is not as thin as the pictures she sees in magazines, she tends to feel bad about who she is. Describe how Carl Roger's Self-esteem, Self-image, and Ideal Self relate to this example.
Sarah feels a low Self-esteem as she views herself poorly. Her Self-image is skewed from reality as she sees herself as fatter than she really is. Her ideal self is likely based on the images she sees in the magazine. It is who she wants to be/thinks she should be.
CRB Opposing Carl Rogers' theory is the Self-Discrepancy Theory, which also maintains people are made up of three selves. Which of the following is NOT one of the three selves?
(A) Ought Self
(B) Ideal Self
(C) Self-Esteem
(D) Actual Self
(C) Self-Esteem
In the Self-Discrepancy Theory, the Actual self is how we see ourselves, the Ideal Self is who we would like to be, and the Ought Self is what we think that others believe we should be.
CRB True or false? The closer that these three selves are aligned, the higher someone's Self-Esteem or Self-Worth will be.
True. The closer that these three selves are aligned, the higher someone's Self-Esteem or Self-Worth will be.
CRB Before breaking down different types of identity, which of the following best defines Identity?
(A) A single self-concept that relates most to the groups someone belongs to.
(B) A collection of assigned concepts that someone must fit into.
(C) A collection of assigned concepts that accurately describe the groups someone belongs to.
(D) The individual components of self-concept that relate to groups that someone belongs to.
(D) The individual components of self-concept that relate to groups that someone belongs to.
The two parts of Social Identity Theory are Personal and Social. How do these differ from one another?
Personal is who we personally are (personality, etc).
Social is the groups we belong to/how we fit into the world.
CRB Chris Noble considers himself to be smart, funny and a good rapper. Would this be better described as his Personal or Social Identity, and why?
Because Chris is talking about his own sense of personal attributes, this would be an example of Personal Identity.
Social Identity says that there are three steps that we take to develop a Self Identity. Describe these three steps using yourself as an example:
1. Categorize
2. Identification
3. Comparison
1. Categorize - You associate different things with other things (i.e. jocks, nerds, drama queens, etc).
2. Identification - You adopt the identity of the group that you identify yourself as (i.e. "I am a nerd").
3. Comparison - You compare your group to other groups (i.e. "Nerds are so much smarter than Jocks").
CRB Another type of identity that could be tested on the MCAT is Gender Identity. Which of the following statements are true?
I. Gender Identity describes someone's appraisal of himself or herself on scales of masculinity and femininity.
II. It is possible to score highly or lowly on both Masculinity and Femininity.
III. Although gender identity is not necessarily tied to biological sex, in most Western Cultures the two concepts are closely related.
(A) II only
(B) I and II only
(C) I and III only
(D) I, II and III
(D) I, II and III
Each of the following statements about Gender Identity are true:
I. Gender Identity describes someone's appraisal of himself or herself on scales of masculinity and femininity.
II. It is possible to score highly or lowly on both Masculinity and Femininity.
III. Although gender identity is not necessarily tied to biological sex, in most Western Cultures the two concepts are closely related.
CRB Compare Androgyny and being Undifferentiated.
Androgyny would be scoring highly on both Masculinity and Femininity simultaneously, whereas low scores on both simultaneously would be Undifferentiated.
CRB True or false? The Theory of Gender Schema claims that the key components of gender identity are transmitted solely through societal means.
False. The Theory of Gender Schema claims that the key components of gender identity are transmitted through societal and cultural means.
CRB Compare Ethnic Identity and Nationality.
Ethnic identity refers to someone's ethnic group, which typically means a common ancestry, cultural heritage and language as members in that group.
Nationality is based on the political borders of countries, and would have a shared national history, media, and national symbols.
Jessica believes that she is good at playing basketball, but deep down she feels a sense of guilt about who she is. She doesn't like herself. How does Jessica's situation relate to Self-esteem and Self-efficacy?
Self-esteem is the respect that you have for yourself. In this case, Jessica has a low Self-esteem.
Self-efficacy is your belief in your capacity to do a specific thing. In this case, Jessica has a high amount of Self-efficacy for basketball.

There are four ways to develop Self-efficacy. Pretend that you want to get better at playing the piano, describe how each of these things may build up your self-efficacy:
1. Mastery of Experience
2. Social Modeling
3. Social Persuasion
4. Psychological Responses
1. Mastery of Experience - You practice the piano all the time, so you start to feel more confident.
2. Social Modeling - You see your friend who has been playing the piano as long as you, play really well.
3. Social Persuasion - Your friends compliment you and even tell other people that you are good at the piano.
4. Psychological Responses - You develop the ability to decrease your stress level and anxiety before a concert.
CRB Having an inappropriate amount of self-efficacy can lead to which of the following phenomena?
I. Misplaced Locus of Control
II. Overconfidence
III. Learned Helplessness
(A) I only
(B) I and II only
(C) II and III only
(D) I, II and III
(C) II and III only
Overconfidence can cause someone to attempt a task that they are not adequately prepared for. Learned Helplessness often presents as not attempting to change a fixable situation due to an extremely low self-efficacy.
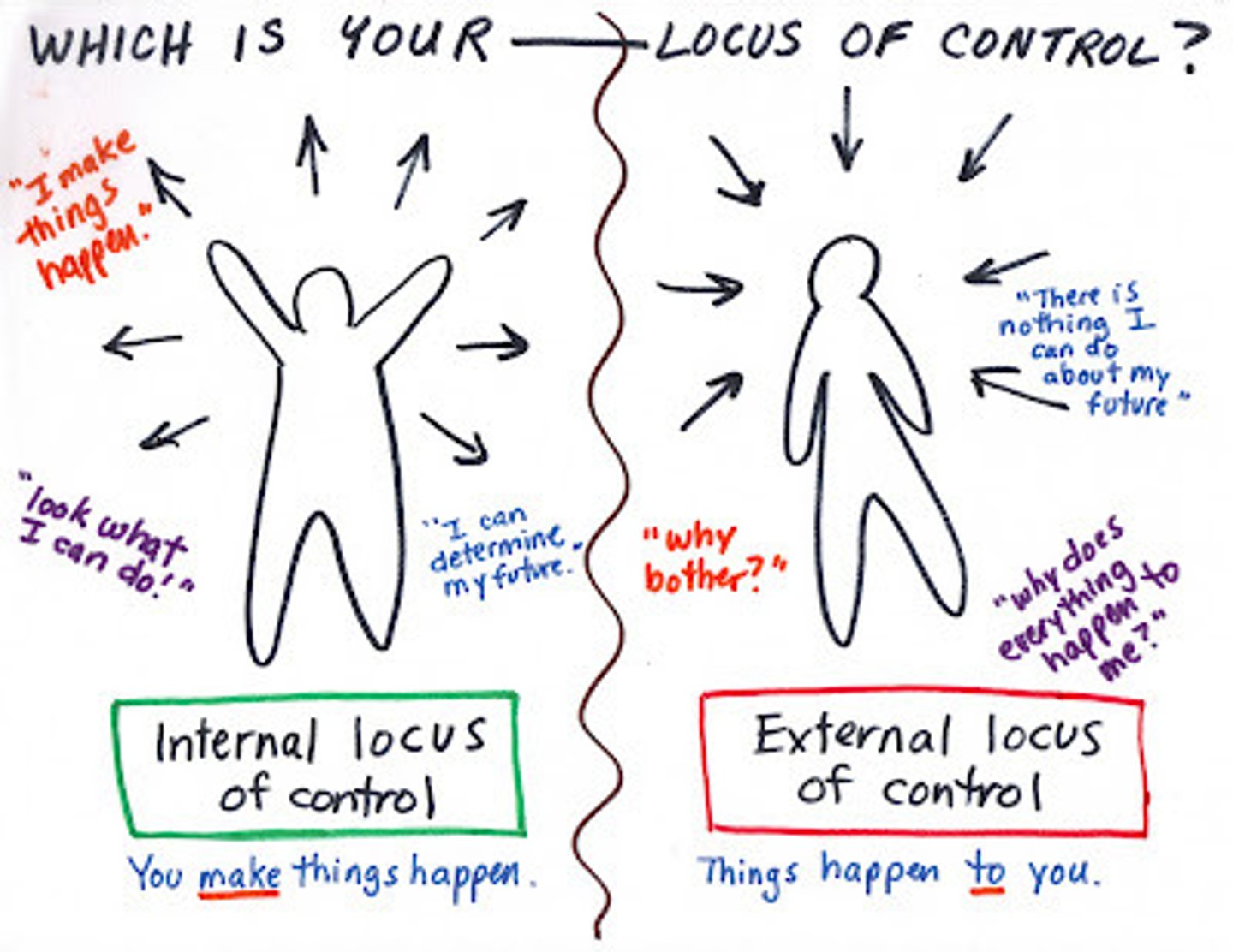
Jessica took a math test and got a terrible grade. She says, "I just didn't study hard enough." She has what kind of Locus of Control?
(A) Positive
(B) Negative
(C) Internal
(D) External
(C) Internal
Jessica is attributing her failure to internal issues, which is characteristic of an Internal Locus of Control.
If she had an External Locus of Control she may have said something like, "The teacher was not clear enough in the guidelines."
There is no such thing as having a Positive or Negative Locus of Control.
True or False? Babies develop a sense of their Existential Self within 12 to 21 days of birth.
True. Babies develop a sense of their Existential Self (idea that they are a separate, unique entity) within 12 to 21 days of birth. This is evidenced by studies on Imitation.
Which type of neurons are hypothesized to be responsible for our ability to imitate?
(A) Mirror Neurons
(B) Efferent Neurons
(C) Afferent Neurons
(D) Interneurons
(A) Mirror Neurons
Mirror Neurons are hypothesized to be responsible for our ability to imitate because they cause us to have similar brain activity to when we watch someone do something to when we actually do that same thing ourselves.

Which of the following examples best relates to the concept of a Reference Group?
(A) You look to the lifeguard to know if it is safe to swim in the water.
(B) Before getting married, a man asks his girlfriend's dad if he can have his permission to marry his daughter.
(C) A man uses a female shopping catalogue to know what gift to buy for his wife.
(D) A medical student tries to be a good doctor by thinking about the doctors he has shadowed in the past.
(D) A medical student tries to be a good doctor by thinking about the doctors he has shadowed in the past.
Reference Groups are groups that we look up to in order to know what beliefs, attitudes, and behaviors to adopt.

Compare how Charles Cooley and George Herbert Mead thought that other people can influence us.
Charles Cooley seemed to think that anyone can influence us at any time while Mead had a more restrictive view, thinking that only certain people can influence us at certain time points..
True or False? Mead believed that very young children are not influenced by others.
True. Mead believed that very young children are not influenced by others. He believed that children see themselves as the center of their own world.
Think of this as a parallel to Piaget's egocentrism stage.
Little Timmy sees himself as the center of the universe. Describe how the following stages may play a role in helping little Timmy start to be influenced by others:
1. Preparatory Stage
2. Play Stage
3. Game Stage
1. Preparatory Stage - Timmy starts imitating others, allowing him to realize that he is a distinct individual from others.
2. Play Stage - Timmy starts pretending that he is a lawyer like his daddy. He begins to see things better from other's perspectives.
3. Game Stage - Timmy starts to understand that his teachers at school also have home lives and families. He also starts to see himself from the perspective of others.

Little Timmy feels like most of the girls at his school think he is cute. The girls at his school are most likely part of what concept in Timmy's life?
(A) Vague Other
(B) Generalized Other
(C) Significant Other
(D) Attractive Other
(B) Generalized Other
They likely play into how Timmy thinks other people in general view him, which is most in line with the idea of the Generalized Other.
A Significant Other would be someone like Timmy's best friend or his parents.
Vague and Attractive Other are not sociological terms.
Little Timmy feels like other people like him. For this reason, Timmy tends to engage in activities with others readily. How might Mead's concept of the I vs. Me apply in this situation?
I is the part of yourself that is active and responds to how others view you. In this case it is Timmy engaging in activities.
Me is the part of yourself that is passive. It is the way Timmy is viewed by others.

True or False? The Looking Glass Self refers to how you view yourself through your own eyes.
False. The Looking Glass Self refers to how you view yourself through the eyes of others.
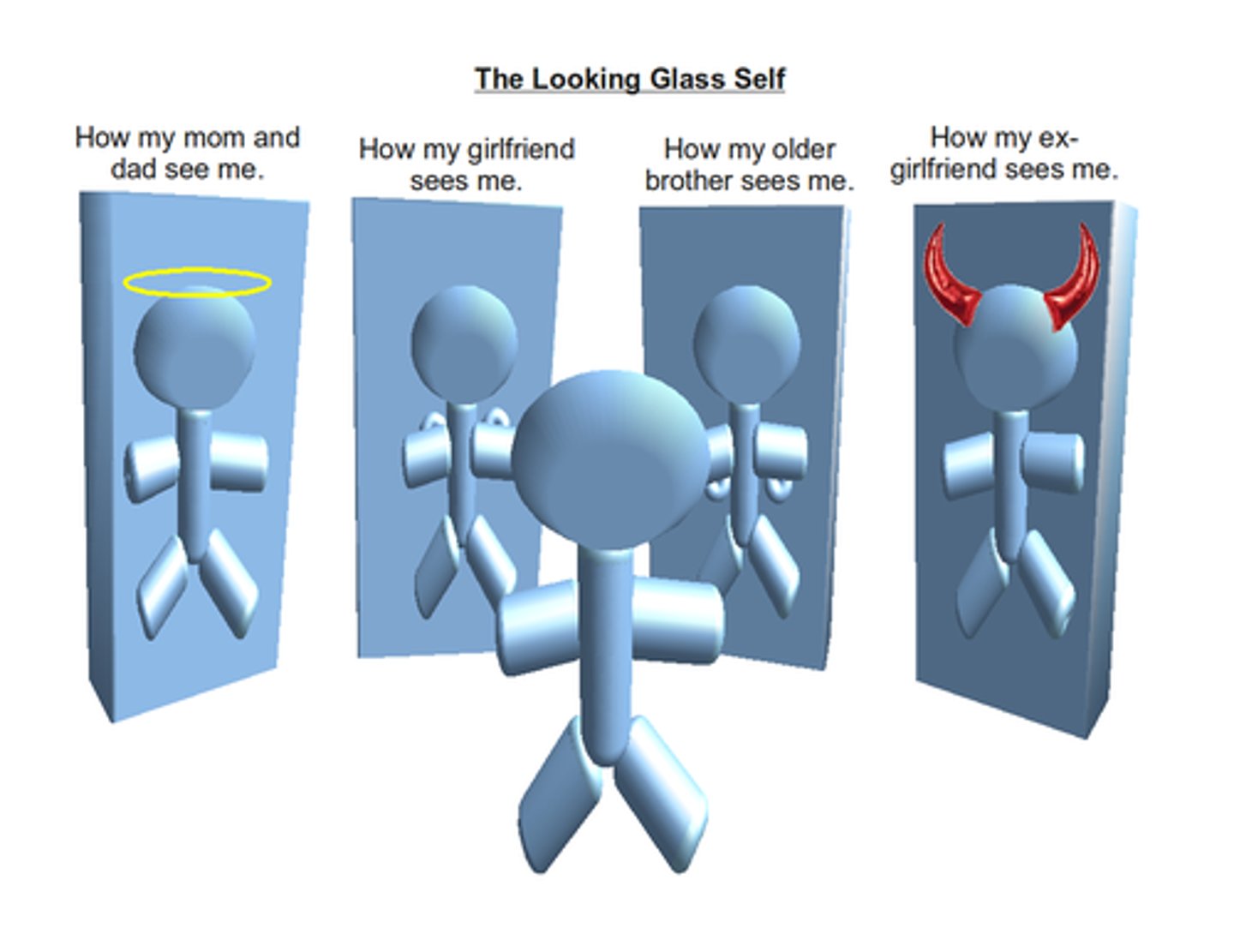
What three questions do we ask ourselves when developing our Looking Glass Self?
1. How do I appear to others? ("I walk upright")
2. What do others think of me? ("That guy is too serious")
3. How should this affect how I think about myself? ("Maybe I am a little to serious")
True or False? One's Looking Glass Self is extremely accurate due to it being based on the objective opinions of others and not our own thoughts about ourselves.
False. One's Looking Glass Self is extremely INaccurate because it is based on how we THINK others THINK about us. It is very subjective.
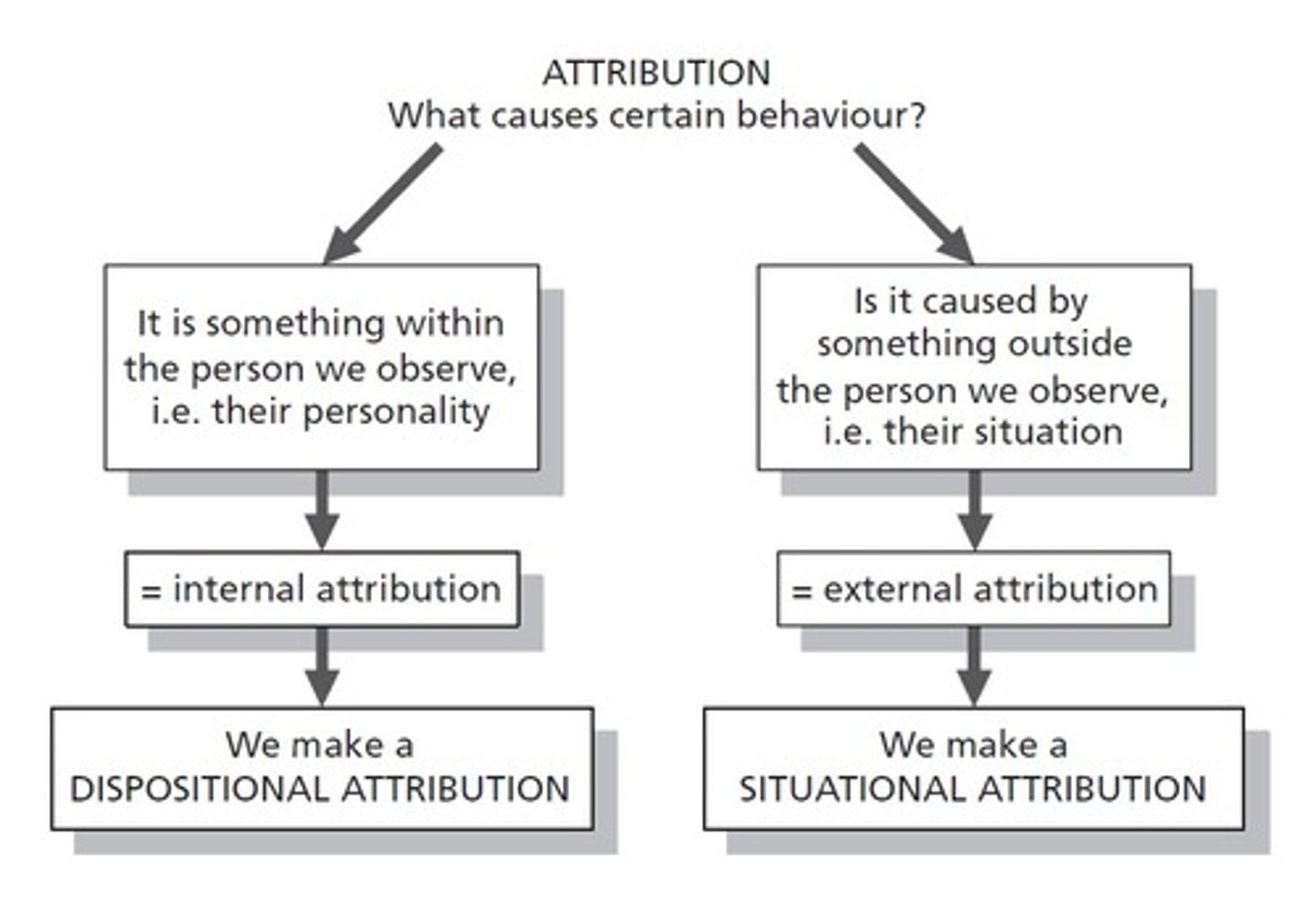
True or False. Attribution means inferring that someones behavior is caused by external factors.
False. Attribution is the act of inferring the cause of the behavior of others, whether that cause is internal or external.
When making an attribution concerning his professor, Jack notices that Dr. Marks wears a red shirt every Tuesday without fail, representing a _____________ cue. He also notices that Dr. Marks doesn't wear a red shirt on any other day of the week, representing a _____________ cue. Lastly, he realizes that Dr. Marks is the only professor on campus who acts this way, representing a _______________ cue.
(A) Consensus, Consistency, Distinctiveness
(B) Consistency, Distinctiveness, Consensus
(C) Distinctiveness, Consistency, Consensus
(D) Consensus, Distinctiveness, Consistency
(B) Consistency, Distinctiveness, Consensus
When making an attribution concerning his professor, Jack notices that Dr. Marks wears a red shirt every Tuesday without fail, representing a Consistency cue. He also notices that Dr. Marks doesn't wear a red shirt on any other day of the week, representing a Distinctiveness cue. Lastly, he realizes that Dr. Marks is the only professor on campus who acts this way, representing a Consensus cue.
See this article for more info: https://www.simplypsychology.org/attribution-theory.html
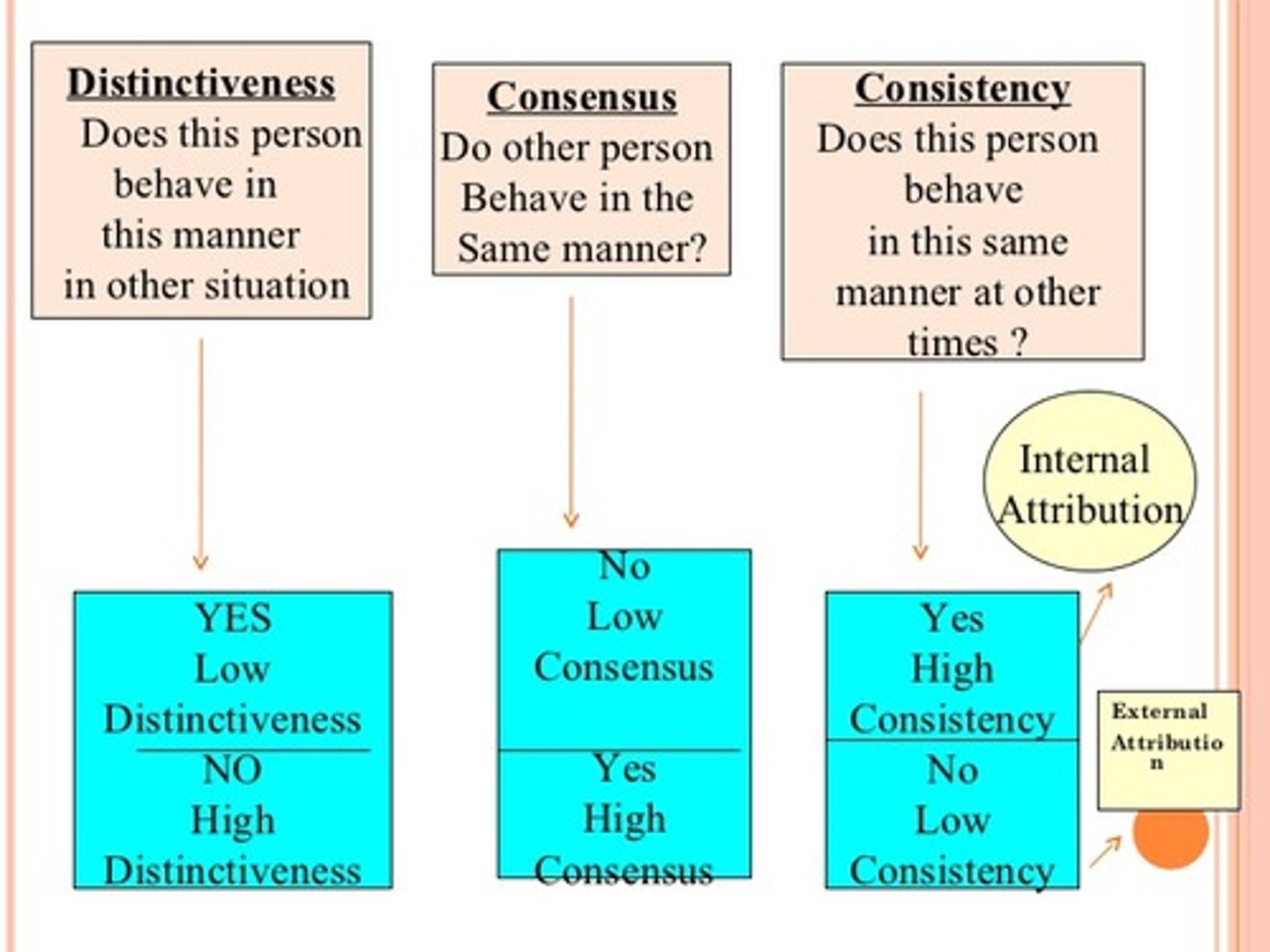
Referring to the previous example, which of the following cues would lead Jack to assume that Dr. Marks' behavior is resulting from the situation (i.e. That is is a Tuesday)?
I. Consistency
II. Distinctiveness
III. Consensus
(A) I Only
(B) II Only
(C) I and II Only
(D) I, II, and III
(B) II Only
Consistency is high in this case. When consistency is high, a behavior is attributed to the person's innate characteristics, not the circumstance (of being Tuesday).
Distinctiveness is also high, which would lead them to conclude that Dr. Marks is doing what he is doing because it is a Tuesday.
Consensus is low, however, which would lead the student to conclude that Dr. Marks is doing this because he is a unique individual on the inside. Something unique to Dr. Marks (not something about Tuesdays) is making him do what he does.
Jack finds himself in a Holocaust type of situation in which he is told to kill others. After this event, he is asked if he feels responsible for his actions. He responds, "No. I was just following orders. I only acted the way I did because of my situation." When asked about his fellow soldiers who did horrible things, he responds by saying, "they, on the other hand, are terrible people and did what they did because they are flawed." Is this a better example of the Fundamental Attribution Error or Actor-Observer Bias?
Because this scenario is both addressing Jack's actions and other soldiers' actions, this is a classic example of the actor-observer bias. Jack is attributing others' actions to their internal characteristics while attributing his own actions to his situation.
If there was no reference to his own actions, and Jack was strictly attributing soldiers' actions to internal dispositions or personality, rather than the circumstances, that would be an example of the Fundamental Attribution Error.
CRB George W. Bush often felt like the general public "misunderestimated" (his words not mine) him, blaming his failures on his personality and not giving enough credit to the impact of situations he was put in. Which Attributional Bias is the public guilty of here?
(A) Fundamental Attribution Error
(B) Actor-Observer Bias
(C) Self-Serving Bias
(D) Just World Phenomenon
(A) Fundamental Attribution Error
Fundamental Attribution Error is when people overestimate the impact of a person's character and underestimate the impact of the situations the person faces.
Compare the Self-serving Bias, Fundamental Attribution Error, and Actor-observer Bias.
Self-serving Bias - where you attribute your success to yourself but your failures to the external environment. (always serving your self basically). It is a mechanism to protect your own self-esteem.
Fundamental attribution error - tendency to attribute people's negative behavior to them personally rather than considering other circumstances/environment.
Actor-observer Bias - tendency to attribute your faults to outside factors but other's faults to their personality/personally.
True or False? The Fundamental Attribution Error is more common in Collectivist Cultures such as Asia.
False. The Fundamental Attribution Error is more common in Individualistic Cultures such as the United States due to a greater focus on individuals and their ability to control their situation.
In Collectivist Cultures, successes are universally much more likely to be credited to external factors, and failures blamed on internal factors. There is no differentiation or judgment differences based on whether it's your own or another's performance, as there would be in the Fundamental Attribution Error.
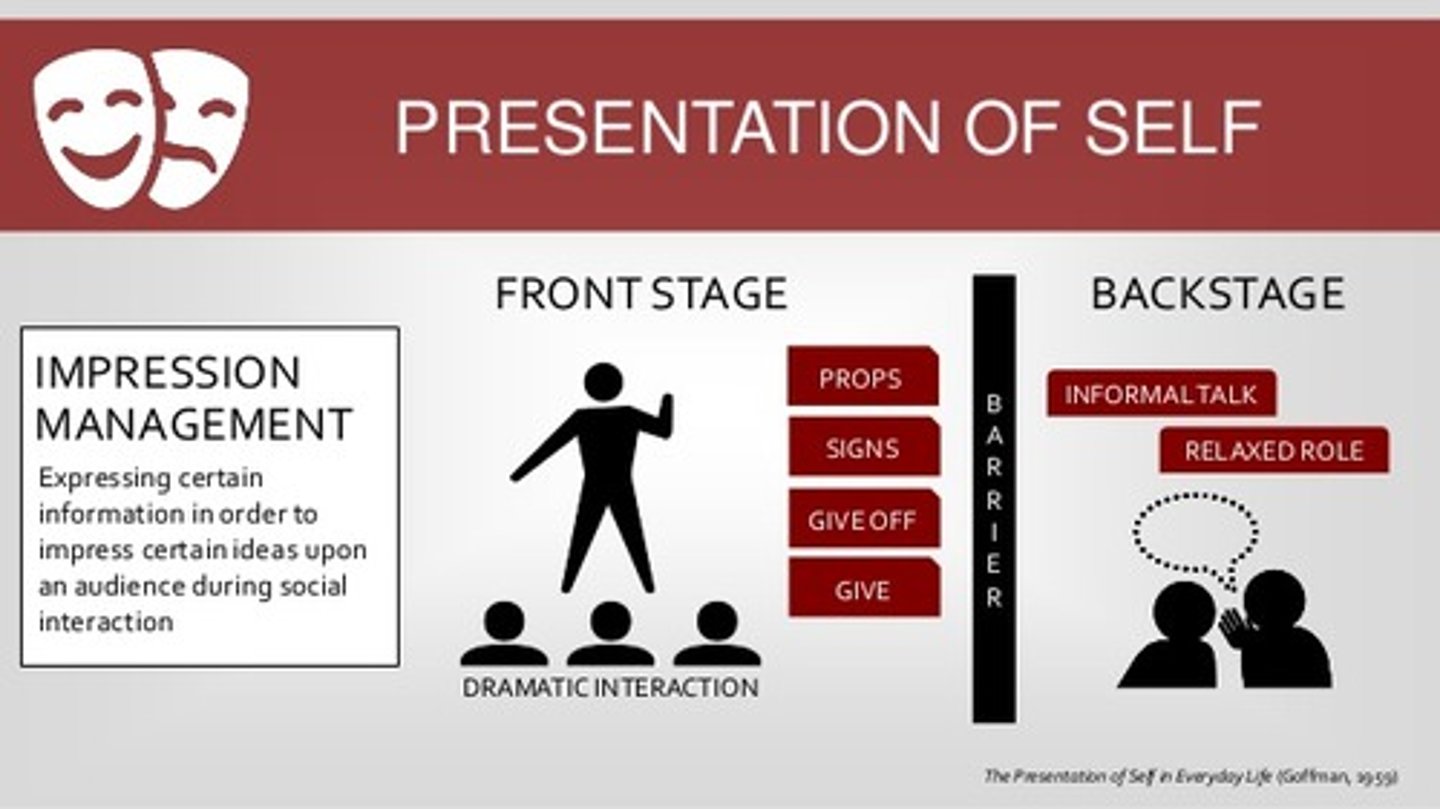
Which example best illustrates the difference between Front Stage and Back Stage Self?
(A) Sarah loves to sing in the shower, but not in front of others.
(B) Jim is better at sports he has practiced than those he hasn't in front of others.
(C) Gary feels anxious about meeting new people but he is very comfortable around friends.
(D) Elizabeth doesn't like people to be around her in the mornings because she isn't ready for the day.
(A) Sarah loves to sing in the shower, but not in front of others.
Front Stage Self is how we act when others are around as Sarah does not sing with others around.
Back Stage Self is how we act when others are not around as Sarah does when she sings in the shower.

Impression Management describes how we try to manage the way that:
(A) We act
(B) Others act
(C) We see others
(D) Others see us
(D) Others see us
Impression Management describes how we try to manage the way that others see us.

True or False? Impression Management is unrelated to the Backstage Self.
False. The Backstage is where you prepare for Impression Management (get dressed, put on makeup, practice singing, etc).