DNA Profiling
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Uses of DNA profiling
Paternity tests
Forensics
Assessing disease risk
Classification/species identification
Introns
Non-coding regions of the DNA
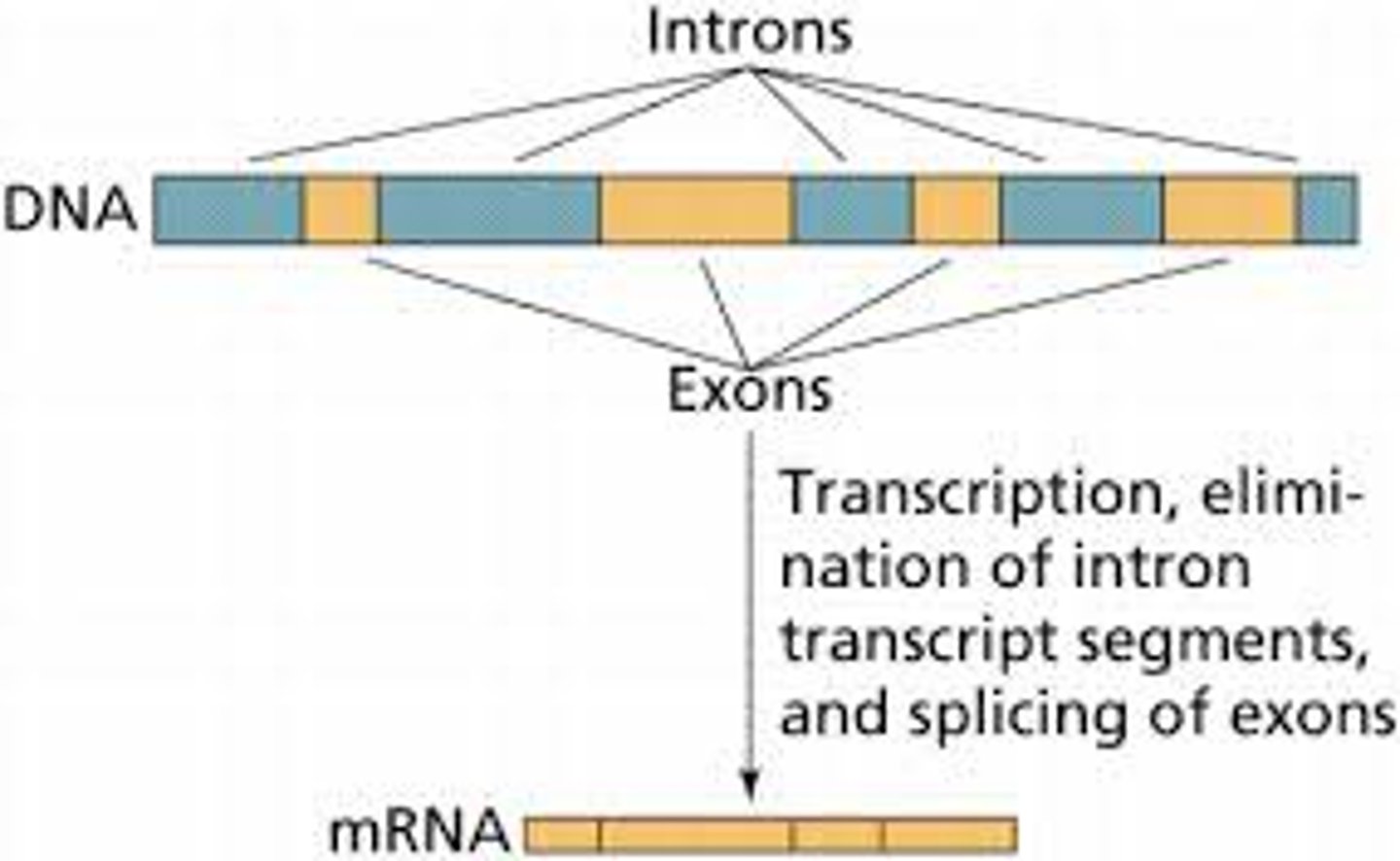
Explain why some regions of DNA can be described as non-coding
These regions are not present in mature mRNA and are not translated
Suggest why non coding regions of DNA show more variation
They aren’t selected against. They don’t affect survival.
Why do we use introns for genetic profiles?
- In most people, the genome is very similar
- Using coding sequences of DNA would not provide unique profiles
- Introns contain repeating sequences
STRs
Short tandem repeats
2-4 base pairs repeated 5-15 times
VNTRs
Variable number tandem repeats
20-50 base pairs repeated from 50 to several 100 times
What is the name for the sequence of bases that is repeated in Short tandem repeats (STRs) and variable number tandem repeats (VNTRs)?
The core sequence
1) DNA Profiling
Extract the DNA
2) DNA Profiling
Amplify the DNA fragment with PCR
3) DNA Profiling
Cut the DNA with restriction enzymes
4) DNA Profiling
Separate DNA fragments using electrophoresis. The DNA will be separated based on their mass.
5) DNA Profiling
Transfer fragments to paper
6) DNA Profiling
Apply a radioactive probe.
Use x-rays to view the position of DNA fragments
7) DNA Profiling
As a result, you create genetic profiles, which can be used in paternity tests, forensics, and for analysis of disease risk.