the carbon cycle and energy security
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
1
New cards
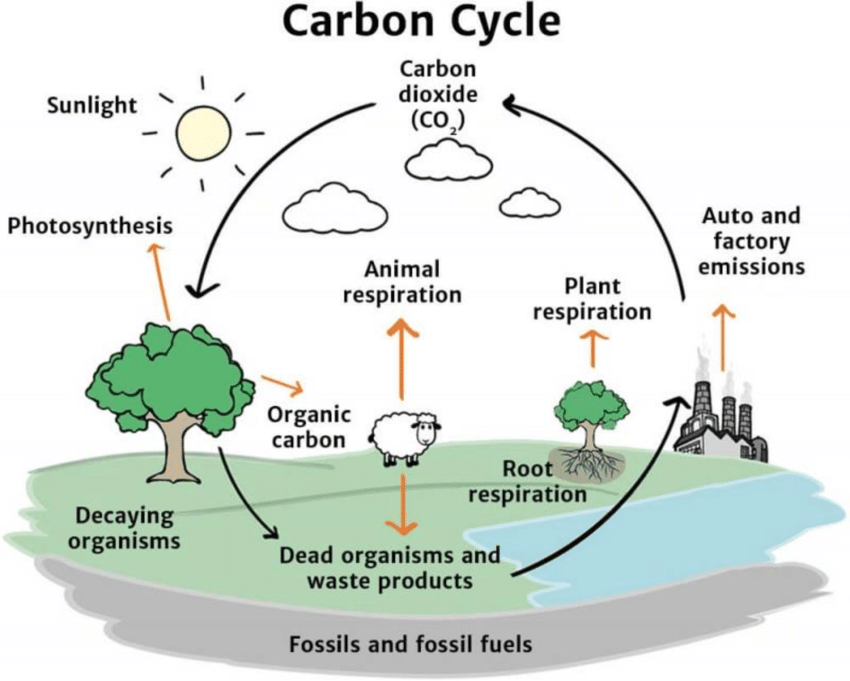
the carbon cycle
the process in which carbon atoms circulate through Earth's land, ocean, atmosphere, and interior.
2
New cards
ocean uptake
the process of the ocean absorbing CO2 from the atmosphere
3
New cards
carbon stores
long term
* earths crust
* deep ocean
\
short term
* soil
* ocean surface (in phytoplankton)
* atmosphere
* terrestrial ecosystems
* earths crust
* deep ocean
\
short term
* soil
* ocean surface (in phytoplankton)
* atmosphere
* terrestrial ecosystems
4
New cards
how is carbon measured
petagram or gigatonne
5
New cards
carbon flux
is the amount of carbon exchanged between Earth's carbon sinks
\
largest flux= photosynthesis
smallest flux= rivers
\
largest flux= photosynthesis
smallest flux= rivers
6
New cards
if sources= sinks then….
the system is in equilibrium
7
New cards
reservoir turnover
the rate at which carbon enters and leaves a store is measured by
\
the mass of carbon in any store / the exchange flux
\
the mass of carbon in any store / the exchange flux
8
New cards
however changes in the system may result in +ive or -ive feedback
\-ive feedback (stabilizing) - how the system usually works which is stabilizing and prevents the system moving beyond a certain threshold
\
\+ive feedback (amplifying) - occurs when a change in one component causes a change in the next- causing an overall change to the system
\
\+ive feedback (amplifying) - occurs when a change in one component causes a change in the next- causing an overall change to the system
9
New cards
sequestration
the natural storage of carbon by physical or biological processes such as photosynthesis
10
New cards
the biological carbon pump
caused by phytoplankton- a single celled organism which can photosynthesise and therefore store carbon
\
so when they die they sink and bring carbon to the bottom of the ocean
\
**thermohalide circulation** also helps with this
\
so when they die they sink and bring carbon to the bottom of the ocean
\
**thermohalide circulation** also helps with this
11
New cards
phytoplankton bloom
phytoplankton populations rapidly increase as conditions are ideal
\
conditions-
* stratification of water temps (as they need both cold nutrient rich water and warm water to grow)
\
conditions-
* stratification of water temps (as they need both cold nutrient rich water and warm water to grow)
12
New cards
ways fluxes can vary
diurnally- changes form day to night
seasonally- changes between seasons
seasonally- changes between seasons
13
New cards
factors decreasing terrestrial sequestration
* deforestation
* deciduous forests (have -ive NPP for part of the year)
* deciduous forests (have -ive NPP for part of the year)
14
New cards
CASE STUDY- deforestation
* brazil and china
15
New cards
the enhanced greenhouse effect
The disruption to Earth’s climate equilibrium caused by the increased concentrations of greenhouse gases has led to an increase in the global average surface temperatures
16
New cards
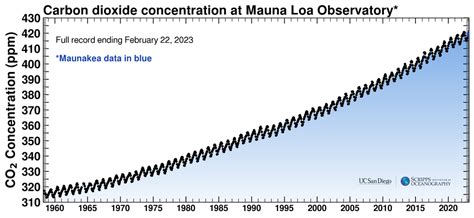
keeling’s curve
shows fluctuation in CO2 seasonally but an overall increase over past decades
17
New cards
anthropogenetic (human related) causes of climate change and CASE STUDIES
* burning fossil fuels (eg BP & electricity generating companies)
* transport (eg ships and vans for amazon products)
* industry
* deforestation (brazil for soy and cattle)
* cattle farming (mcdonalds and tesco etc)
* transport (eg ships and vans for amazon products)
* industry
* deforestation (brazil for soy and cattle)
* cattle farming (mcdonalds and tesco etc)
18
New cards
energy security
the uninterrupted availability of energy sources at an affordable price
\
consists of
* availability of energy
* whether energy mix in domestic or imported
* whether supply is interrupted or not
* energy price
\
consists of
* availability of energy
* whether energy mix in domestic or imported
* whether supply is interrupted or not
* energy price
19
New cards
CASE STUDY
USA vs q France energy mix/security
20
New cards
uses of energy
* communication
* electricity
* heating
* manufacturing
* electricity
* heating
* manufacturing
21
New cards
the worlds energy consumption trend
countries with higher GDP have a higher energy consumption
* as they can afford more/ access and transport it easier
and higher population= higher consumption
* as they can afford more/ access and transport it easier
and higher population= higher consumption
22
New cards
energy intensity
a measure of how affectively a country uses energy
* generally decreases as a country becomes more developed as cost per unit of GDP decreases as energy is used more effectively
* generally decreases as a country becomes more developed as cost per unit of GDP decreases as energy is used more effectively
23
New cards
CASE STUDY
UK energy mix
24
New cards
things that impact energy consumption
* cost
* standard of living
* environmental priorities
* population
* climate
* public perception (eg in german CASE STUDY)
* development level/ technology
* standard of living
* environmental priorities
* population
* climate
* public perception (eg in german CASE STUDY)
* development level/ technology
25
New cards
CASE STUDY
german energy mix (disapproval on nuclear power) and france (large use of nuclear power)
26
New cards
energy stakeholders
* TNCs (provide investment)
* OPEC (Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries)
* Governments
* consumers (must pay)
* OPEC (Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries)
* Governments
* consumers (must pay)
27
New cards
CASE STUDY
coal exports
28
New cards
CASE STUDY
oil exports
29
New cards
CASE STUDY
gas exports
30
New cards
disruption to energy pathways (and CASE STUDIES)
* wars (Russia and Ukraine)
* supplies diminishing
* changing to renewable energy
* changes in cost (cost of living in UK)
* trade issues
* damaged pipes
* OPEC reducing global productions
* supplies diminishing
* changing to renewable energy
* changes in cost (cost of living in UK)
* trade issues
* damaged pipes
* OPEC reducing global productions
31
New cards
CASE STUDY
OPEC
32
New cards
CASE STUDY
deep water oil drilling in brazil
33
New cards
CASE STUDY
Canadian tar sands
34
New cards
CASE STUDY
USA fracking
35
New cards
renewable energy
an energy resource that is replaced rapidly from an existing natural process such as wind or sun
36
New cards
recyclable energy
an energy resource that can be reused once people or nature have processed it such as HEP and nuclear
37
New cards
\+ives and -ives of renewable energy
\- cost
\+ no pollution
\- but nuclear energy can be damaging
\- harder to store and transport
\+ cheaper long term
\+ no pollution
\- but nuclear energy can be damaging
\- harder to store and transport
\+ cheaper long term
38
New cards
biomass
organic matter used as a biofuel to generate electricity
39
New cards
biofuel
a fuel derived from from living matter
* can be primary or secondary (1= woodchips, 2= biodiesel as it requires processing)
* can be primary or secondary (1= woodchips, 2= biodiesel as it requires processing)
40
New cards
CASE STUDY- bad energy mixes
brazil (biofuels)
41
New cards
harmful activities of humans
* land conversion
* deforestation
* marine degradation
* deforestation
* marine degradation
42
New cards
land conversion
change of a natural ecosystems to an alternative use
43
New cards
deforestation
the action of clearing a wide area of trees.
\
impacts
* increases surface runoff as it decreases interception
* decreases infiltration
* so erosion of soil is faster
* increases flood risk
* less photosynthesis and transpiration (impacts water cycle)
\
impacts
* increases surface runoff as it decreases interception
* decreases infiltration
* so erosion of soil is faster
* increases flood risk
* less photosynthesis and transpiration (impacts water cycle)
44
New cards
marine degradation (eg cargo ships, overfishing, oil spills)
causes
→ coral bleaching/ ocean acidification (reduces biodiversity)
→ phytoplankton death (disrupts carbon cycle)
→ temperature increase
→ coral bleaching/ ocean acidification (reduces biodiversity)
→ phytoplankton death (disrupts carbon cycle)
→ temperature increase
45
New cards
CASE STUDY- marine degradation
ARCTIC
46
New cards
CASE STUDY
climate change impact on amazon rain forest / drought
47
New cards
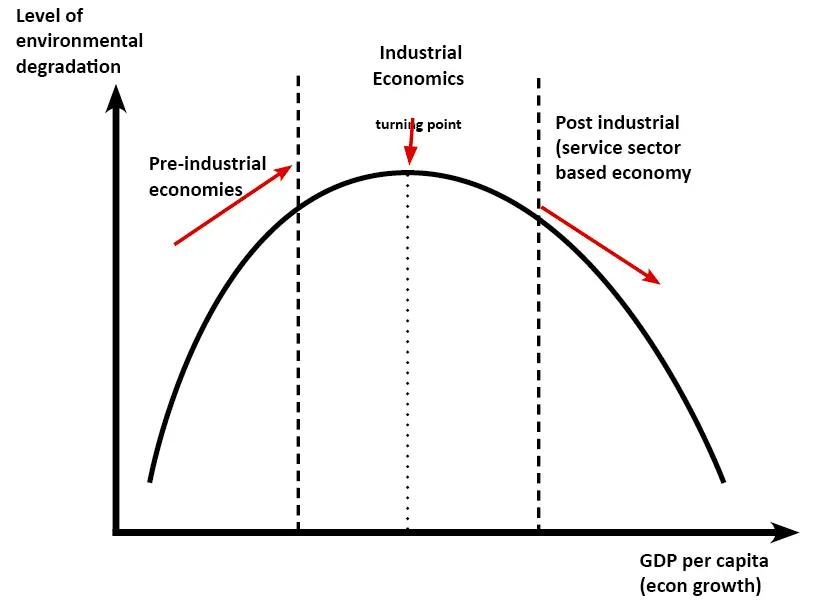
carbon cycle and human well being is represented Kuznets Curve
pre → post industrial rev
primary → 3 and 4 jobs
rural living → urban
low technology → high
low environmental awareness → higher
primary → 3 and 4 jobs
rural living → urban
low technology → high
low environmental awareness → higher
48
New cards
causes of uncertainty for the carbon cycle
natural
* carbon sinks and reservoir turnover
\
human
* population growth
* economic growth (development → kuznets curve)
* change in energy sources
\
feedback mechanisms-
* forest dieback rates (more or less changes in CO2 absorbed)
* peatland and permafrost CO2 released due to drying or melt
* thermohaline circulation- change how heat is transferred around the world which impacts ice sheets (containing carbon)
* carbon sinks and reservoir turnover
\
human
* population growth
* economic growth (development → kuznets curve)
* change in energy sources
\
feedback mechanisms-
* forest dieback rates (more or less changes in CO2 absorbed)
* peatland and permafrost CO2 released due to drying or melt
* thermohaline circulation- change how heat is transferred around the world which impacts ice sheets (containing carbon)
49
New cards
mitigation
strategies to prevent or reduce condition changes
50
New cards
adaptation
strategies to adjust to condition changes
51
New cards
adaptation strategies to climate change and environmental degradation
* water management + conservation
* resilient agriculture systems
* land use planning
* flood risk assessment
* solar radiation management
* resilient agriculture systems
* land use planning
* flood risk assessment
* solar radiation management
52
New cards
water management + conservation
* use more grey (recycled) water
53
New cards
resilient agriculture systems
* using GM crops that are more tolerant to drought, reduced famine
54
New cards
land use planning
* soft management
* building restrictions on high risk flood area
* reduces costs of damage and loss of life long term
* building restrictions on high risk flood area
* reduces costs of damage and loss of life long term
55
New cards
flood risk assessment
* hard engineering such as flood defences, river dredging and permeable tarmac
* reduces flood risk
* reduces flood risk
56
New cards
solar radiation management
* the use of orbiting satellites to reflect radiation back into space
* this has not yet been tried and tested
* this has not yet been tried and tested
57
New cards
mitigation strategies to climate change and environmental degradation (CASE STUDIES)
* carbon taxation (2015 changes)
* renewable switching (the climate change levy)
* energy efficiency (the green deal scheme)
* afforestation (the big three plant campaigne)
* carbon capture storage (Canadas boundary dam)
* renewable switching (the climate change levy)
* energy efficiency (the green deal scheme)
* afforestation (the big three plant campaigne)
* carbon capture storage (Canadas boundary dam)
58
New cards
CASE STUDY- long term international climate change mitigation
Kyoto protocol