Lecture 6.1 Nicotine
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
desired effects of stimulants (1)
elation, euphoria; exciteent; increased alertness; increased energy; reduced fatigue
side effects of stimulants (1)
incrase BP and HR; dilated pupils; increased talkativeness, restlessness, irritability; erratic behaviour, mania; incomnia; reduced appetite; increased sweating; anxiety, paranoia, panic; increased aggressiveness.
tolerance of stimulants (2)
rapid
stimulants risk of physical dependence (2)
moderate
stimulants risk of psychological dependence (2)
high
stimulants fatal overdose potential (2)
moderate to high
stimulant routes of adminstration (3)
smoke, absorbed across skin and mucosal membranes of mouth and nose
stimulants duration of effect (3)
short (2hr half life)
neurotransmitter directly affected by stimulants (3)
acetylcholine (also dopamine)
tolerance of stimulants (3)
moderate/high
physical dependence of stimulants (3)
moderate/high
psychological dependence of stimulants (3)
moderate/high
stimulants withdrawal symptoms (3)
craving, irritability, headaches, increased appetite, abnormal sleep
stimulants schedule (3)
legal
forms of nicotine (6)
chewing tobacco, cigars/pipes, cigarettes, vaporizers, nicotine patch, nicotine gum
nicotine routes of administration (6)
oral through buccal membranes (e.g., chewing tobacco, cigars, pipes, nicotine gum), inhaled (e.g., cigarettes, vaporizers), transdermal (e.g., patch)
smoking rates in western vs developing nations (8)
declining in western nations, rising in developing nations
when do most smokers begin smoking? (10)
in adolescence
how many chemicals in a cigarette? (11)
around 8000
how long does a puff take to deliver nicotine to the brain? (12)
around seven seconds
what impacts absorption of nicotine? (13)
how densed the tobacco is packed, length of cigarette, characteristics of the filter, number of cigarettes smoked throughout the day, volume of smoke inhaled, pH of the tobacco.
biggest increase of absorption (13)
length and volume of a drag (how big, how long they hold it)
where in the body does nicotine travel? (14)
everywhere (e.g., brain, placenta, all body fluids, breast milk)
nicotine metabolite (15)
cotinine
metabolism of nicotine men vs women (15)
women have a faster metabolism since the enzyme expression is increased by estrogen
why are there menthol cigarettes (15)
menthol decreases the metabolism of nicotine
nicotine half life (16)
2 hours
how is nicotine eliminated (16)
its metabolite is mainly extreted through the urine
nAChRs (17)
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor; ionotropic; in the brain and autonomic nervous system
composition of nAChRs (18)
varies; 5 subunits with a pore; most common in 3 beta-2 with 2 alpha-4 and has high affinity; some have all alpha-7 and is locatted presynaptically.
speed of high-affinity nAChRs desenitization (21)
rapid; cell cannot fire again until the nicotine is removed;
smoking’s effects ont he sympathetic and parasympathetic systems (22)
wide range of effects; arouses the brian to a state of increased alertness; increases heart rate and blood pressure; at high levels, relaxes muscles and triffers the release of endorphins, natural opiates the may reduce stress; reduce circulation to extremites; suppresses appetitie for carbohydrates
dual motivations for nicotine consumption (25)
direct reward/reinforcement pathway (via mesolimbic DA pathway), cognitive enhancement (via mesocortical DA pathway
nicotine cognitive enhancement in smokers vs nonsmokers (27)
may be present in nonsmokers; increases in smokers but animals show performance deficits when withdrawing from chronic nocotine treatment
nicotine reinforcement in females vs males (28)
females are more sensitive to nicotine reinforcement
nicotine reinforcement in adolescents vs adults (28)
Adolescents show greater nicotine reward and reinforcement compared to adults
pharmacodynamic tolerance of nicotine (30)
receptor desensitization is possible with acute use; receptor upregulation is possible with chronic use
states of compulsion to use tobacco (32)
wanting → craving → needing
6 month relapse rate of nicotine (32)
high (70-80%)
nicotine withdrawal symptoms (32)
anxiety, irritability/frustration, decreased heart rate, difficulty concentrating, increased appetite/weight gain, restlessness, cigarette cravings, depression/dysphoria
nicotine withdrawal throughout the day (33)
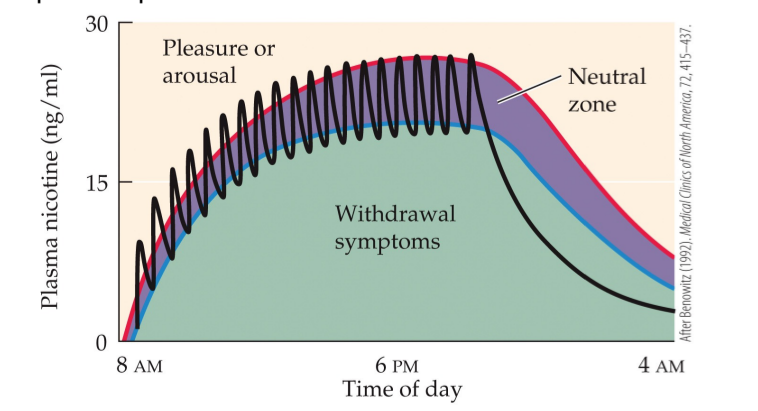
nicotine withdrawal timeline (34)
can begin as quickly as 3 hours after cessation of smoking; symptoms reach a peak around 1 week post-cessation, and will gradually diminish over several weeks
varenicline (36)
partial agonist at high-affinity nAChRs expressed in the VTA; stimulates the nicotinic receptor on dopamine neurons, minicking the effects of nicotine but to a lesser degree.
tabacco related deaths per year in Canada (37)
47,000
how many puffs per year for a pack-a-day smoker? (42)
at least 50,000