daddys home
1/642
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
643 Terms
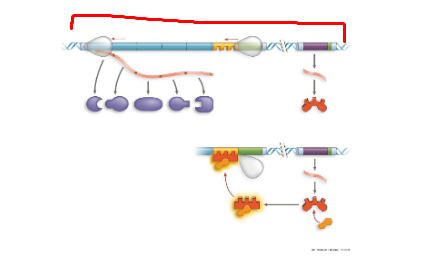
What system + what structure
TRP operon, polypeptide subunits that make up enzymes for trp synthesis
Inducible operon
Default off, add something = on, example=lac operon
Repressible operon
Default on, add something = off, example=trp operon
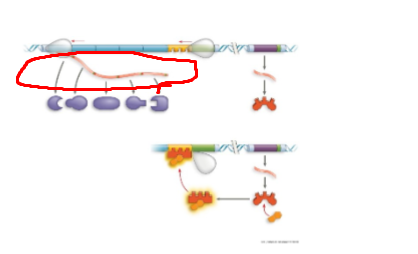
What system + what structure
TRP operon, mRNA strand, provides blueprint for ribosome to build proteins
What system + what structure
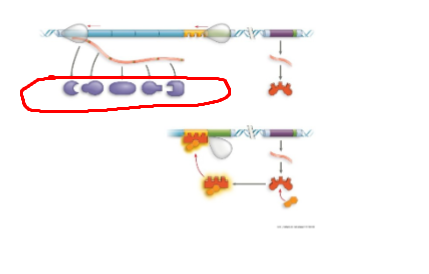
TRP operon, default on,
What system + what structure
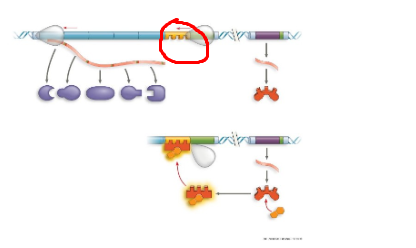
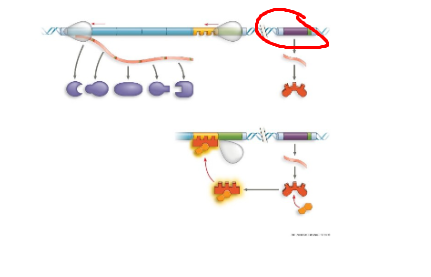
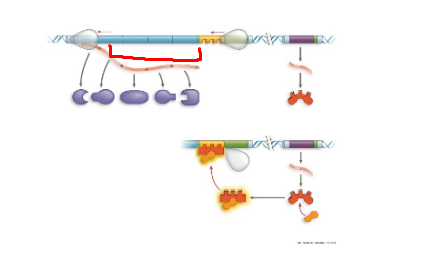
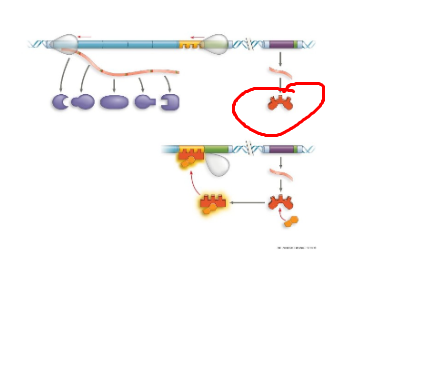
TRP operon, operator, region where rna pol binds to start transcription. when trp high, protein binds to promoter region, blocking transcription
What system + what structure
TRP operon, trpR, regulatory gene that codes for trp repressor protein
What system + what structure
TRP operon, genes of operon, encode for enzymes needed to synthesize trp
trpa - trpe
What system + what structure
TRP operon, inactive repressor, protein cant bind to promoter region, resulting in active trp operon
What system + what structure
TRP operon, active repressor, protein binds to promoter region resulting in inacctive trp operon, no trp made
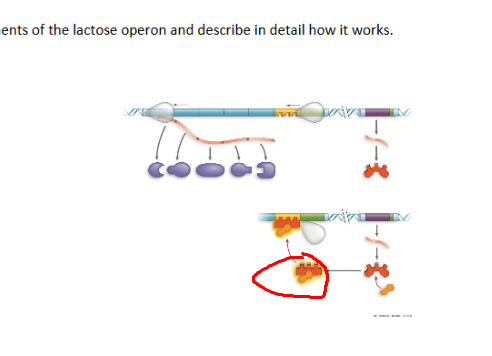
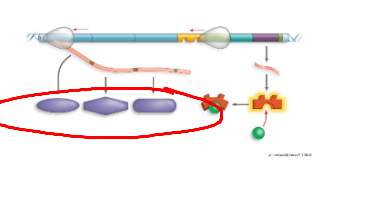
What system + what structure
inactive lac operon as no lactose present, does not want to work for something absent
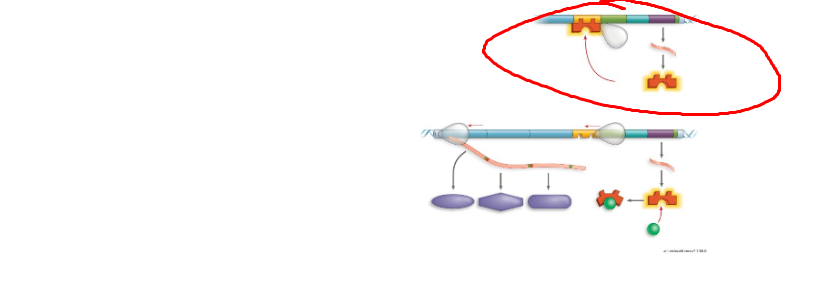
What system + what structure
Lac operon, allolactose, an inducer that binds to a protein changing shape allowing no binding to promoter, resulting in an active operon
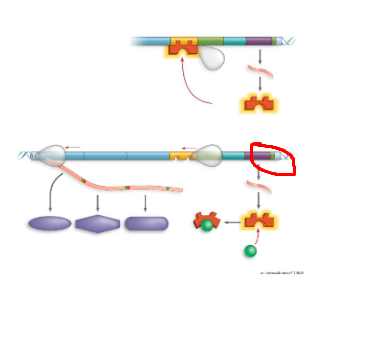
What system + what structure
Lac operon, lacI, separate gene, not structural gene, creates the lac repressor protein
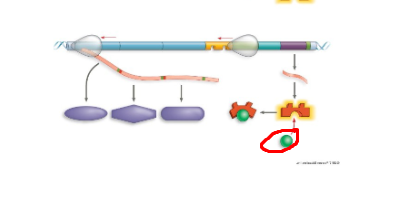
What system + what structure
lac operon, enzymes for using lactose, lacZ,lacY,LacA
Mayr concept name
Biological species concept
Mayr idea
Species is a group that
-connected by gene flow
-ability to produce viable fertile offspring
-potential to interbreed (separated by geography but still have ability to breed if met)
-reproductively isolated from other groups (prezygotic/postzygotic)
Define allopatric speciation
one species split into two, once separated they evolve independently, overtime reproductively isolatated
steps to allopatric speciation
split-isolating-divergence-reproductive isolation
step 1 allopatric speciation
one species, connected by gene flow, reproducing is fine
step 2 allopatric speciation
geographic isolation, something physically splits population so individuals on one side cant mate with other
step 3 allopatric speciation
populations are now independent, mutations arise randomly in each population
step 4 allopatric speciation
separated groups have adopted new adaptations that create a difference so large, they can no longer reproduce
what is sympatric speciation
single population splits into two reproductively isolated species WITHOUT any barrier
most common form of sympatric speciation in plants
polyploidy, error in meiosis or mitosis resulting in 4n individuals instead of 2n, new 4n individuals can only mate with other 4n.
sympatric speciation bp
some females strongly prefer one type of male trait, over time this reduces interbreeding resulting in reproductive isolated individuals
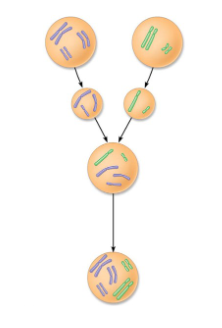
Explain what’s happening
Two different species mate and create a sterile hybrid with 5 chromosomes, a mitotic error doubles
How Can Small Genetic Changes Result in Large Changes in Phenotype?
Two gene categories, structural and regulatory, structural codes for enzymes, regulatory controls when where and how much expressed, single mutation in regulatory change location amount timing
Small genetic change = big phenotype change example
Pitx1 gene in stickleback fish removes expression in pelvis=lose pelvic spines and girdle
How did Walter Hering show insect and vertebrae eyes use the same master eye gene
turned on fly eye gene in wrong places, flies grew extra eyes there, then he put mouse frog version of that gene into flies and it also grew extra eyes.
Define hox gene
master regulatory gene that tells cells where they are and what to build there.
define homeobox
DNA sequence that regulates large scale anatomical features in embryonic development
fruit fly vs vertebrate hox genes
fruit flies have one hox cluster split into two parts, resulting in fewer hox genes. vertebrates have 4 hox clusters, many more complex patterns to control
importance of hox genes
tell embryo what to build and where, shared by almost all animals, small changes in hox genes cause big changes in phenotype
The mating of a horse and a donkey produces a mule. Does this mean that horses and donkeys are the same species? Why or why not?
No, not same species as they cant produce viable offspring. horse = 64 chrom donkey = 62 chrom, mule =63, odd number, sterile
advantage of sex vs asex reproduction
sexual reproduction results in genetic variation, creating new combinations that allow faster adaptation to environments
why is asex reprod weak
makes clones=harmful mutations build overtime
how was dolly cloned
1.take nucleus of donor
2.remove nucleus from egg from 2nd donor
3.put nucleus from 1st donor into empty egg
4.grow in culture
5.when embryo, implant into surrogate mom
6.lamb with same nuclear dna born
steps to add foreign dna into a plasmid and insert plasmid into bacterium
1.cut plasmid with restriction enzyme
2.mix cut plasmid and cut dna together, glue with ligase, resulting in recomb dna
3.introduce plasmid to bacterial cell
4.plate bacteria and add antibiotic that kills those that arent recomb dna plasmid
5. those who survive form colonies
estimated that human cells have about 25,000 genes, however there are many more proteins
produced. How is that possible? Explain
single gene can be cut and pasted in different ways. (alt splice)
how are proteins modified to increase diversity
proteins can change activity location and interactions so one sequence can act as multiple functional forms
1st step of creating bacteria to produce euk protein
isolate mrna from target cell which already has its introns removed by euk splicing
2nd step of creating bacteria to produce euk protein
add reverse transcriptase from a retrovirus plus nucleotides and a primer to create cDNA
what is a reverse transcriptase
enzyme that copies rna into dna
3rd step of creating bacteria to produce euk protein
degrade mRNA strand for dna pol to synthesize a second dna strand using cDNA as template, now you have double straned cDNA copy
4th step of creating bacteria to produce euk protein
glue with dna ligase, creating recombinant plasmid
5th step of creating bacteria to produce euk protein
transofrm ecoli with this, plate then use antibiotic so only recombinant survives.
adaptive radiation
rapid evolution of multiple species from one ancestor
how does adaptative radiation often occur
mass extinctions leave many niches empty
bottleneck effect
drastic drop in population size, randomly changes allele freq, resulting in less genetic diversity
divergent evolution
starts with common ancestor, two or more related species become more diff overtime as they adapt to different environments or niches
convergent evolution
unrelated species independently evolve similar traits because they live in similar environment or niches.
The analytical approach to understanding the diversity and relatedness of both extant and extinct organisms is called __________.
systematics
What is the focus of the branch of biology called taxonomy?
The classification of life-forms by their similarities and differences
The binomial system assigns to each organism a unique name that describes its __________.
genus and species
The two-part format of the scientific name, referred to as binomial, ensures that __________.
each species is assigned a unique name
systematists can easily specify the closest relatives of any species
each species has a name that is understandable regardless of language barriers among scientists
Which of the following is the correct taxonomic name for the African forest elephant?
Loxodonta cyclotis
A taxon __________.
is a formal grouping at any given level
Rabbits and guinea pigs both belong to class Mammalia. This means they must also both belong to __________.
phylum Chordata
Species A and species B are in the same phylum. Species A and species C, but not species B, are in the same order. From this information you can conclude that __________.
species C could be in the same class as species A and B
What does a branch point in a phylogenetic tree represent?
A branch point represents a point at which two evolutionary lineages split from a common ancestor.
Which of the following methods to establish phylogenetic relationships among organisms has been developed most recently?
comparing the amino acid sequences of proteins and nucleotide sequences of nucleic acids
Which of the following would be the LEAST useful in determining the relationships among various species
analogous structures
Researchers can use molecular homologies to __________.
reveal the number of mutations in a particular sequence that has occurred in each species since they diverged from a common ancestor
A phylogenetic tree of bird families constructed by cladistic analysis would be a hypothesis about which of the following?
evolutionary relationships among bird families
Many researchers who study the kingdom Protista argue that all of these organisms should NOT be placed in the same kingdom, because these organisms could not have evolved from a common ancestor. In other words, they argue that the kingdom Protista is __________
polyphyletic
Using cladistic analysis, a taxonomist wishes to construct a phylogenetic tree showing the relationships among various species of mammals. Which of the following would be the LEAST useful for this purpose?
the fact that all mammals have hair
Which statement below is true about an outgroup?
The outgroup should be from a lineage known to have diverged before the lineage that includes the ingroup.
Unlike a regular phylogenetic tree, phylogenetic trees with branch lengths proportional to time can be used to __________.
represent the chronological time that has passed since two groups diverged from a common ancestor
Which statement below is true of parsimonious trees?
The most parsimonious tree requires the fewest evolutionary events to have occurred in the form of shared derived characters.
Birds and mammals have a four-chambered heart, but most reptiles have a three-chambered heart. How does this fact affect the construction of phylogenetic trees for these groups?
The most likely tree is not always the most parsimonious.
If you wanted to determine the lineage of plants that have evolved on a relatively young archipelago—approximately 15,000 years old—what type of nucleic acid should you compare?
mtDNA
Paralogous genes __________
result from gene duplication
What is the evolutionary significance of paralogous genes?
They increase the size of the genome and provide more opportunity for the evolution of novel characteristics.
What is the evolutionary significance of orthologous genes
The high percentage of orthologous genes found in vastly different organisms emphasizes the many biochemical and developmental pathways shared by all organisms.
The idea of using molecules as clocks to time evolutionary events is very attractive, but there are many problems in actually applying the technique. What seems to be the best way to get reliable results?
It is important to use as many genes as possible. With this approach, fluctuations in evolutionary rate will tend to average out.
Question 25:By applying a molecular clock, researchers have proposed that the first HIV-1 M invasion into humans occurred in the ________
1930s
Universal phylogenetic trees built from different genes sometimes give inconsistent results. What basic assumption on which phylogenetic trees are based has probably been violated during the history of life?
Genes are passed vertically from one generation to the next.
Define phylogeny
Evolutionary path a species took
Define Systematics
the field that classifies organisms and determines their evolutionary relationship
Homo Sapiens
Binomial, homo=man sapien=wise
Two components of every binomial
Genus name and Specific epithet (species name)
Taxonomic categories
Domain
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
Organisms in the same order or same phylum, which is more closely related
order, lower on taxonomic bracket, more related
How is phylogeny and Systematics used to develop phylogenetic trees
Phylogeny is the goal, its the historical pattern of descent, systematics is the toolkit, it uses data (anatomy, protein sequence) to reconstruct phylogeny trees
Branch point
represents most recent common ancestor, also called a node
Sister taxa
Two groups that share an immediate common ancestor not shared not with anyone else
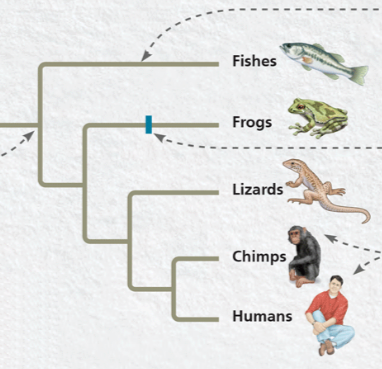
Identify the sister taxa
Chimps and humans, share the most recent branch point, ancestor isn’t shared with anything
What does it mean for a phylogenetic tree to be rooted?
A rooted phylogenetic tree has a single, defined starting point that represents the most recent common ancestor (MRCA) of ALL taxa in the tree
What three key points about phylogenetic relationships cannot be determined from
phylogenetic trees?
1.Actual age of species or divergence events
2.Which species is more evolved
3.Whether one living species descended directly from another.
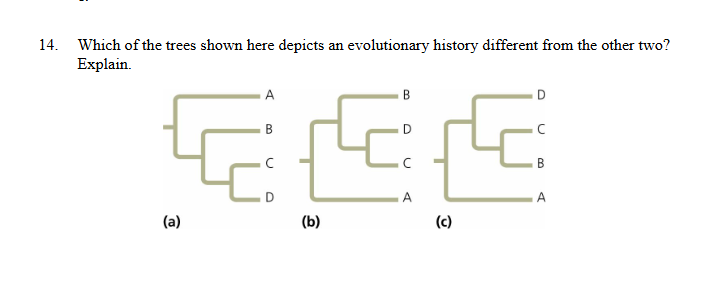
Which shows a different evolutionary history
c
How could convergent evolution be a confusing factor in developing phylogenetic trees?
Produces traits that look similar but do not come from a common ancestor
Why is it important to sort homologous from analogous structures? Which are appropriately used in creating phylogenetic trees?
Homologous traits reflect shared ancestry, analogous doesnt, they evolve independently. only homologous is used
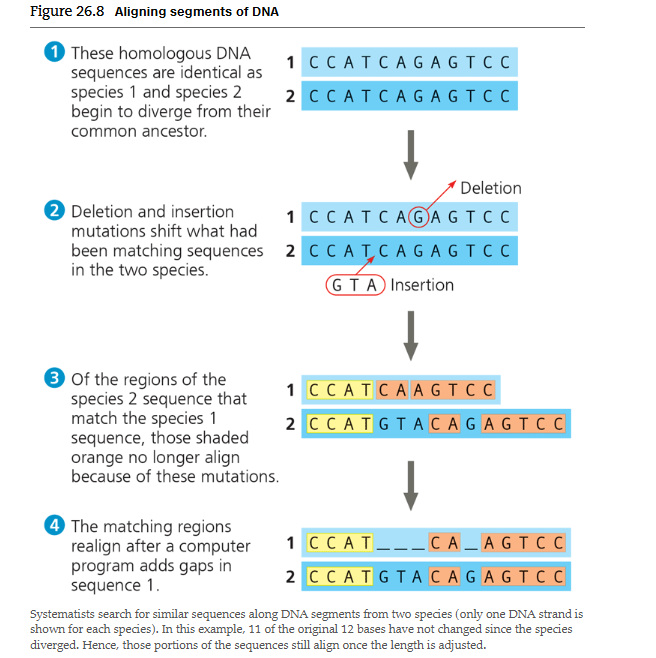
How can DNA homologies be detected after mutations occur
Computer adds gaps to compensate for missing or extra base. After alignment, the conserved regions that still match between species reveal the homologous DNA inherited from their common ancestor.
Species A and B have similar appearances but different divergent gene sequences
Species B and C have different appearances but similar gene sequences
Which pair is more closely related
B and C due to similar gene sequences. physical appearance similarities can be shaped by convergent evolution
Define clades
group of organisms with a common ancestor and all of its descendents
Clades are developed using shared derived characters, what are these
Shared derived characters (synapomorphies) are traits that are new, evolutionary innovations that first appeared in a common ancestor of a group and are shared only by its descendents
Why is hair a shared derived character but a backbone is a shared ancesteral character
Hair evolved in MRCA of mammals and is unique to mammals
Backbone evolved long before mammals existed, since many groups outside mammals also have backbones, the backbone is ancestral
Synapomorphy vs plesiomorphy
plesiomorphy is an older trait that evolved before the clade and is shared by clade and other groups
synapomorphy is a trait evolved in MRCA of a clade and is only found in that group
Shared derived character and shared ancestral character scientific names
Synapomorphy and Plesiomorphy
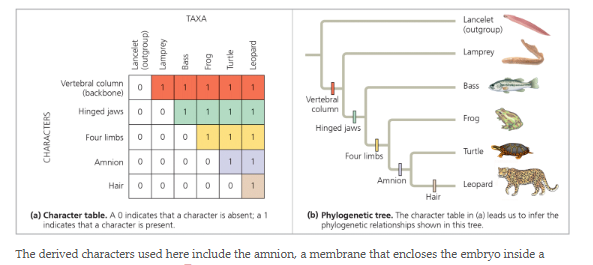
Why is the lancelet considered the outgroup
Most distantly related organism in the phylogeny, it has ancestral traits but lacks derived traits