Chemistry Exam 3
1/38
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Alcohol
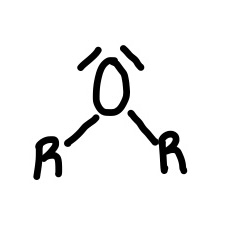
Ether
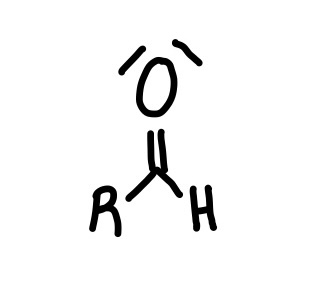
Aldehyde
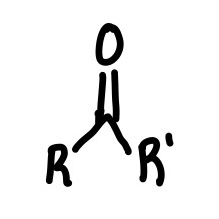
Ketone
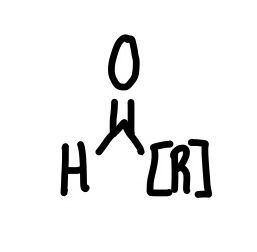
Carboxylic Acid
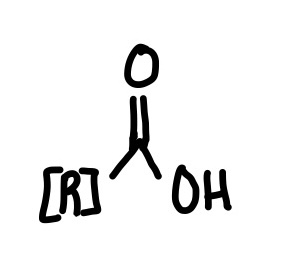
Ester
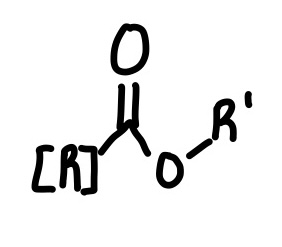
Amide
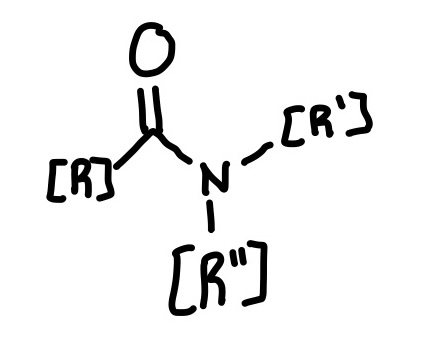
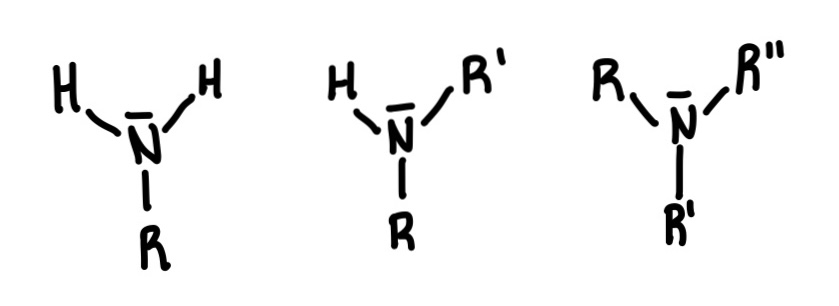
Amine
Methane
CH4
Ethane
C2H6
Propane
C3H8
Butane
C4H10
Pentane
C5H12
Hexane
C6H14
Heptane
C7H16
Octane
C8H18
Nonane
C9H20
Decane
C10H22
London Dispersion Force (LDF)
larger cloud = stronger force
more surface area = stronger force
dipole-dipole
greater separation of positive and negative charges = stronger attractions
orientation: positive end needs to attract a negative end
dipole induced dipole
stronger dipole moment = stronger force
larger atom = stronger force (more polarizable)
ion induced dipole
higher charges = stronger forces
larger atoms = stronger forces (more polarizable)
ion-ion
greater charge = stronger force
closer together = stronger interaction
High melting and boiling point
stronger IMFs; more energy is required to break the interaction
Low melting and boiling point
weak IMFs; less energy needed to overcome the forces
Polarizability
how easily an electron cloud can be distorded
induced dipole
a temporary dipole created in a nonpolar molecule due to an external electric field or nearby charge; causes the electron cloud to shift and creates a region of partial positive charge and a region of partial negative charge
Solids
Molecular Structure: closely packed, don’t freely move
IMF: strongest, keep molecules in a fixed shape and volume
KE: low
Liquids
Molecular Structure: close but not fixed arrangement
IMF: weaker but strong enough to keep molecules near each other; allows for a defined volume but not a fixed shape
KE: molecules can partially overcome IMF enabling movement but not seperation
Gases
Molecular Structure: far apart in constant random motion
IMF: weak and often negligible
KE: high, allowing to completely overcome IMF allows free movement in all directions
Intramolecular Force
forces that hold atoms together within a molecule forming chemical bonds
covalent, ionic, and metallic bonds
breaking requires a chemical reaction and are in the range of 100-1000 kJ/mol
Intermolecular Force (IMF)
forces of attraction between separate molecules
LDR, Dipole-Dipole, hydrogen bonds
determine physical changes rather than breaking apart
forces range from 1-50 kJ/mol
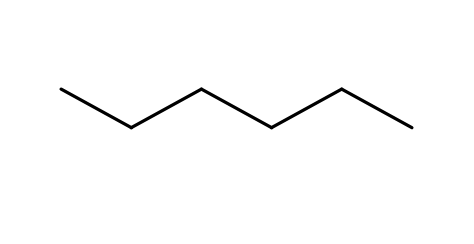
Alkane
CnH2n+2
saturated with single bonds
strong and nonpolar
combustion and substitution reactions
high stability
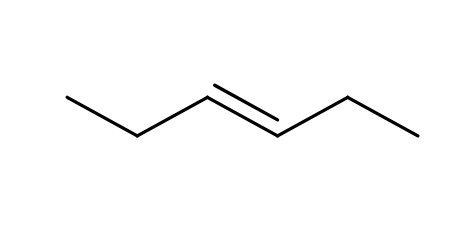
Alkene
CnH2n
Unsaturated with at least one double bond
addition reactions
less stable than alkanes
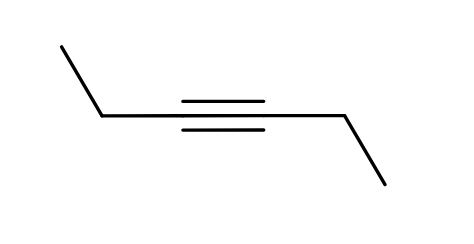
Alkyne
CnH2n-2
Unsaturated with at least one triple bond
addition reactions
less stable than alkenes and alkanes
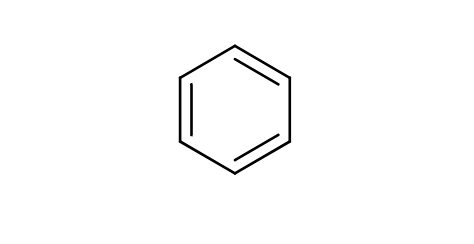
Aromatic
a ring of carbon atoms with alternating single and double bonds
electrophilic substitution reactions
high stability makes them less reactive
Isomer
a molecule that shares the same molecular formula as another molecule but differs in the arrangement
Geometric Isomer
some molecular formula and some connectivity but different arrangements
look for restricted rotation (double bonds or rings)
Constitutional Isomer
same molecular formula but atoms are connected differently
atoms bonded in different orders