Apes Unit: 1
1/128
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
129 Terms
Population
group of individuals of same species
Community
all living organisms in an area
Ecosystem
all living & nonliving things in an area (plants, animals, rocks, soil, water, air)
Biome
the plants and animals found in a given region (determined by climate) Ex: (tropical rainforest)
Competition
organisms fighting over a resource like food or shelter; limits pop. size
Predation
one organism using another for energy source (hunters, parasites) due to the 10% rule they have to have a low population
Mutualism
relationship that benefits both organisms (coral reef)
Commensalism
relationship that benefits one organism & doesn’t impact the other (birds nest in trees)
Herbivores
(plant eaters) eat plants for energy (giraffe & tree)
Parasitoids
lay eggs inside a host organism; eggs hatch & larvae eat host for energy Ex: parasitic wasps, bot fly
Symbiosis
Any close and long-term interaction between two organisms of different species
Resource partitioning
different species using the same resource in diff. ways to reduce competition
Temporal partitioning
using resource @ different times, such as wolves & coyotes hunting @ different times (night vs. day)
Spatial partitioning
using different areas of a shared habitat (different length roots)
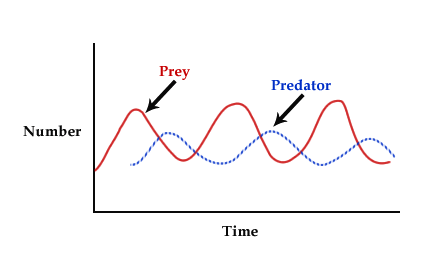
Predator/Prey Relationship
Helps control population growth and has a negative feedback loop that oscillates
omnivores
Eat plants and animals
Intraspecific competition
Competition amoung members of the same species can be reduced if: young disperse, exhibiting strong territoriality, and resource partitioning between generations, results in overall increased fitness
interspecific competition
competition between members of different species
Biogeochemical Cycle
The complete path a chemical takes through the four major components – or reservoirs – of Earth’s systems Atmosphere, Hydrosphere, Lithosphere, Biosphere
Major Chemical cycles
Water, Carbon, Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Sulfer
Atmosphere
the envelope of gases surrounding the earth or another planet.
Hydrosphere
total amount of water on a planet
lithosphere
A lithosphere is the rigid, outermost rocky shell of a terrestrial planet or natural satellite
Biosphere
the regions of the surface, atmosphere, and hydrosphere of the earth (or analogous parts of other planets) occupied by living organisms.
Limiting Factors
When chemical elements are not available at the right times, in the right amounts, and in the right concentrations relative to each other, life cannot “happen” as it should
Macronutrients
Elements required in large amounts by all life Include the “big six” elements that form the fundamental building blocks of life: (CHONPS)
Micronutrients
Elements required either in small amounts by all life or moderate amounts by some forms of life and not at all by others
Average residence time
a substance in a reservoir is a factor of the size of the reservoir and the flow into or out of the reservoir
Inputs and outputs
going between reservoirs can determine the size of the reservoir and the change in the reservoir over time
Reservoirs
components of the biogeochemical cycle that contain the matter, including air, water and organisms
sink
when atoms and molecules get stored in the reservoir
source
each reservoir can serve as a of the element when atoms and elements leave a reservoir
7 Processes drive the carbon Cycle
Photosynthesis, cellular respiration, exchange, sedimentation, burial, extraction and combustion
Carbon Reservoirs
Ocean - large reservoir of carbon, air/ocean gas exchange Sediments of plants/animals/ Geosphere -soils, fossil fuels/ Biosphere - living organisms/ Atmosphere - fast carbon cycling, short turnaround
Fast steps of the Carbon cycle
involves living organisms - cellular respiration, photosynthesis/ Exchange of CO2 between air/water/ combustion of fossil fuels (CO2) - oil, coal, natural gas
Slower step of the carbon cycle
Carbon in rocks- in form of limestone, calcium carbonate/ In soil such as petroleum hydrocarbons/ Sedimentation and burial
Carbon Cycle
Movement of molecules that contain Carbon (CO2, glucose, CH4,) between sources and sinks
Carbon sink
reservoir that take in more carbon than it releases
Carbon source
reservoir that releases more carbon than it takes in
Photosynthesis in Carbon cycle
sink
Cellular respiation
source
photosynthesis
Solar energy+ 6h2O+6CO2———C6H12O6+6O2
Cellular respiration
Energy+6H2O+6CO2—————-C6H12O6+6O2
Direct exchange in Carbon cycle
CO2 moves directly between atmosphere & the ocean by dissolving into & out of ocean water at the surface
Negative effects of ocean carbon cycle
Because of direct exchange, increasing atmospheric CO2 also increases ocean CO2, leading to ocean acidification
Sedimentation
calcium carbonate precipitates out as sediment & settles on ocean floor
Burial
over, long, periods of time, pressure of water compresses C-containing sediments on ocean floor into sedimentary rock (limestone, sandstone) - long-term C reservoir
Fossil Fuels (FF)
formed from fossilized remains of organic matter into coal (ex.
Extraction & Combustion
digging up or mining FFs & burning them as energy source; releases CO2 into atmosphere
upwelling current
circulates nutrients from the ocean floor back to the surface
cold water
holds more oxygen
bethic
bottom of ocean system
Pelagic
water column above the bottom in the ocean system
littoral zone
near shore
deep ocean
biological desert and slow growth
chemosythesis
Deep ocean animals and plants form of energy
Coral reefs
Aggerations of coral polyps that live symbiotically with algae
coral bleaching
global warming causes coral to expel their algal partners, wich can lead to mortality
Mangroves
important trees that grow in saltwater along tropical coastline
Estuaries
bays or semi-enclosed bodies of brackish water that form where rivers enter the ocean
salt marshes
costal wetlands flooded regularly or occasionally by sea water
Tide pools
Depressions in a rocky shoreline that are flooded at high tide but retain some water at low tide
intertidal zone
where ocean meets the land between high and low tide
barrier islands
Narrow islands made of sand that form parallel to a coastline
Epilimnion
warm-upper layer of lake system
Hypolimnion
Cold, deeper layer that does not mix
Thermocline
distinctive temp transition zone that separates warm upper layer and deeper cold layer
Wetlands
land surface is saturated or covered with water at least part of the year
swamps
wetlands with trees
Marshes
Wetlands without trees
Marshes
Wetlands without trees
Fens
Waterlogged soils that lend to accumulate peat ground water
Bog
Waterlogged soils that lend to accumulate peat
greatest aquatic concern for the biologist
Wetlands because of high productivity
determining biomes
temp and percipiation
ideal plant growth
hot and wet
no growth
zero degrees
tropical rain forest
humid regions in the tropical that support one of the most complex and biologically rich biomes
cloud forest
high mountains where fog and mist keep vegetation continually wet
tropical rain forest soil
acidic and nutrient-poor because 90% of nutrient are tied up in living organisms/ rapid decomposition
seasonal temp tropical rain forest
minimale seaonl temp flux
temperate Rainforest
a cool, rainy forest often enshrouded in fog

temperate regions
the mild temperature area located between the subtropical and the polar region
taiga/boreal forests
Cold winters, short growing season, primarily coniferous trees

savannas
warm temp with distinct wet and dry seasons, prone to fire, soil fertile, mandy migratoery grazors
adapation for savanna
water conservation in long roots or in stem
desert
Characterized by low moisture levels
temperate grassland
cold hard winter and hot/dry summers, prone to fires, few trees, large daily/seasonal temp flux, farm land

over graxing problems z
erosion and dead plants
temperate shrubland (Mediterranean)
warm, dry summers and cool moist winters think cali

Tundra
Treeless landscape that occurs at higher latitudes or on mountaintops

perma frost
an impermeable, perminatiely frozen layer in the soil
Nitrogen required for
proteins, nucleic acid/ DNA and RNA
usable nitrogen
NH4(ammonium) and NO3(Nitrate)
Nitrogen cycle speed
fast
main N resvior
atmosphere
biotic fixation
bacteria doing nitrogen fixation
abiotic fixation
lighting going nitrogen fixtion
Nitrogen fixation
Process of N2 being converted to biologically avaibale NH3(ammmonia) or N3(nitrate)
Assimilation
plants & animals taking N in and incorporating it into their biomass