Neuro Module 5
1/134
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
135 Terms
Passive Signal Propagation
Electrotonic spread of depolarization in the membrane
Active Signal Propagation
Repeated regeneration of depolarization through voltage-gated channels.
Oligodendrocytes
Cells that produce myelin in the central nervous system.
Myelin
Lipid-rich insulation around axons, produced by oligodendrocytes or Schwann cells.
Nodes of Ranvier
Gaps in the myelin sheath where action potentials are renewed.
Astrocytes
Glial cells that regulate brain homeostasis and are diverse controllers of the CNS microenvironment.
Tripartite Synapse
Involvement of astrocytes in synapse formation and function.
Microglia
Immune cells in the CNS that contribute to brain health and disease control.
Microglia Activation
Microglia change from ramified to amoeboid morphology during activation, leading to active phagocytosis and a graded cytokine response.
Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB) Integrity
Microglia activation influences BBB integrity, with pro-inflammatory microglia reducing astrocyte support, leading to leukocyte infiltration, while anti-inflammatory microglia promote astrocyte support and release protective neurotrophins.
Gene
A gene is part of chromosomal DNA that encodes a specific protein, with non-coding regions (RNAs) also playing crucial roles.
Regulation of Gene Expression
Each human cell contains ~25,000 protein-coding genes, and the regulation of gene expression is essential for the diversity of cell types and functions.
Monogenic Diseases
Gene therapies are evolving for monogenic diseases caused by single gene defects, such as Huntington’s disease and Leukodystrophies, which are largely heritable and independent of environmental factors.
Viral Gene Therapy Vectors
Viral vectors like Adenovirus and Adeno-associated virus are used for gene delivery, with episomal vectors being safer for targeting terminally differentiated cells.
Motor Neurons
Lower motor neurons directly innervate skeletal muscles, forming the final common path for conveying movement commands, while upper motor neurons regulate local circuit neurons and alpha-motor neurons.
Motor Unit
A motor unit consists of a motor neuron and the skeletal muscle fibers it innervates, with different motor units varying in size and types of muscle fibers they innervate.
Henneman’s Size Principle
Motor unit recruitment follows a systematic order according to size, with small motor units activated first during weak contractions and larger units recruited as force requirements increase.
Local Circuit Neurons
located in the spinal cord and in the motor nuclei of the brainstem cranial nerves ; they regulate activity of lower motor neurons
Upper Motor Neurons (UMNs)
Cell bodies located in the cerebral cortex or brainstem; essential for initiation of voluntary movements and complex skilled movements; synapse with local circuit neurons and lower motor neurons.
Cerebellum and basal ganaglia
regulate activity of the upper motor neurons without direct access to either the local circuit neurons or lower motor neurons
Basal Ganglia
Suppresses unwanted movements; prepares upper motor neuron circuits for movement initiation; dysfunction leads to Parkinson’s and Huntington’s disease.
Spinal Reflex
Involuntary response mediated through spinal pathways; now viewed as highly modifiable with reflex modulation predominating.
Proprioception
Perception of body position, limb location, and effort in movement; integrates signals from muscle spindles, Golgi tendon organs, joint receptors, vestibular system, and skin mechanoreceptors.
Muscle Spindles
Sensory organs within muscles detecting changes in muscle length and velocity of movement; activated by gamma motor neurons to maintain sensitivity.
Muscle Stretch Reflex
Maintains muscle length through feedback control; detected by muscle spindles to excite alpha-motor neurons for muscle contraction.
Golgi Tendon Organs (GTO)
Distributed in tendons to provide information about muscle tension; negative feedback system to regulate muscle force and maintain steady force levels.
Protective Reflexes
Include flexion reflex pathways triggered by nociceptors; involve polysynaptic pathways and descending regulation to modulate responses.
Motor System Diseases
Include motor neuron diseases, peripheral neuropathies, neuromuscular junction disorders, myopathies, and basal ganglia-related conditions like Parkinson’s and Huntington’s disease.
Contracture
Permanent structural shortening of a muscle or joint due to prolonged hypertonic spasticity.
Babinski sign
Reversal of cutaneous flexor reflex, seen as abnormal fanning of toes and extension of the big toe.
Extensor response
Fanning out of smaller toes in infants due to incomplete myelination of corticospinal pathways.
Lower Motor Neuron (LMN) degeneration signs
Weakened reflexes, flaccidity, muscle cramps, fasciculation, muscle wasting.
Upper Motor Neuron (UMN) loss effects
Spasticity, clonus, muscle wasting, increased tendon reflexes.
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
Motor neuron disease affecting UMN and LMN, leading to weakness, wasting, spasticity, and hyperreflexia.
Progressive bulbar palsy
Affects brainstem motor neurons causing symptoms like swallowing difficulty, speech loss, and emotional lability.
Primary lateral sclerosis (PLS)
UMN disorder affecting limbs and face, progressing slowly without affecting lower motor neurons.
Progressive muscular atrophy (PMA)
Slow degeneration of lower motor neurons, leading to muscle weakness, wasting, and potential progression to ALS.
Spinal Muscular Atrophy
Hereditary disease affecting lower motor neurons, caused by deficits in the SMN1 gene, leading to muscle weakness.
How it voltage across the membrane affected after injection?
Internal Resistance
Membrane resistance
What does current leakage depend on?
Membrane resistance and internal resistance
Conduction Velocity =
Speed of impulse propagation
What is conduction velocity inversely proportionate to?
The time constant (smaller time → charge spreads faster)
How can you increase conduction velocity?
Increase axon diameter and increase insulation
What does myelin consist of ?
Condensed phospholipid bilayers helically wrapped around axons
what is the g-ratio?
The thickness of the myelin sheath relative to the axon size
What does a lower g-ratio indicate?
Faster conduction velocity
Saltatory impulse propagation speeds up…
Active signal propagation
In saltatory conduction, the signal …
jumps from node to node
Electrical insulation
enables saltatory impulse propagation (decrease capacitance and increase membrane resistance)
Potassium buffering
promotes sufficiently rapid recovery from repetitive firing → seizure prevention
Trophic support
provides energy requires to sustain repetitive action potential firing
Paranode
Attachment of myelin membrane via Caspr, Contactin & NF155
Juxtaparanode
Clustered voltage-gated potassium channels, Na+/K+ ATPase
Internode
Compact Myelin, Na+/K+ ATPase
Long axons need ____ to function properly
Trophic support
Axonal transport is…
Slow, meaning axons need a lot of energy
What provides trophic support to meet energy needs ot active neurons?
Oligodendrocytes
Oligodendrocytes transfer glycolysis products _____ and ____ to axons through MCT transporters which is metabolised in neuronal ____ (axon) to generate energy required for impulse propagation
pyruvate, lactate, mitachondria
Exosomes transfer proteins and RNAs between….
oligodendrocytes and neurons
_____ myelination is critical for learning
Adaptive
What is the effect of inhibition of oligodendrocytes differentiation?
New skill acquisition, learning and memory are impaired
What is the effect of prolonged decrease in axonal firing?
Decreased myelination of an axon
Myrf
transcription factor driving oligodendrocyte maturation and myelination
What has a longer distance between Nodes of Ravier: Schwann Cells or Oligodendrocytes?
Schwann Cells
Myelin compacting protein of Schwann Cells
P0, PMP2
Myelin compacting proteins of Oligodendrocytes
PLP1, MBP
What is Schwann cell myelin covered by?
A basal lamina
Where are astrocytes located?
Only the CNS.
One astrocyte occupies…
one region alone
What is the role of an astrocyte in homeostasis?
Each astrocyte has local control of homeostasis within the defined area its processes reach.
Extensive interaction and communication through ___ ___ with other astrocytes along ___ ___
Gap junctions, regional boundaries
How do astrocytes communicate?
Through Ca2+ waves triggered by neurotransmitters, gliotransmitters or insult
Astrocyte number, size and connections is proportional to….
brain size and cognitive capabilities
What role can astrocytes play in synapse formation, function, and decay?
Astrocytes can regulate synapse formation, function, and decay through processes such as neurotransmitter recycling and gliotransmitter secretion
Astrocytes regulate ___ ___ and ____ ____ at the neurovascular junction
nutrient supply and osmotic homeostasis
The nutrient supply and osmotic homeostasis that astrocytes maintain includes:
Local regulation of blood flow, regulation of ions pH and water, contributes to blood-brain-barrier integrity
Astrocyte Ca2+ levels control the release of:
Vasodilators and vasoconstrictors
Leber’s congenital amaurosis
Is an early onset severe retinal dystrophy and responsible for 10%-20% of all childhood blindness
3 features of monogenic diseases
Caused by a single gene defect, largely environment and lifestyle dependent, 100% heritable
3 features of polygenic diseases
Multiple genetic alterations combined cause disease, environment and lifestyle triggered, less than 100% heritable
in vivo gene therapy
Delivers the therapeutic DNA or gene therapy vector directly into the patient
ex vivo cell-based gene delivery step 1
extract patient’s stem cells
ex vivo cell-based gene delivery step 2
Add gene therapy vector to stem cell in a dish
ex vivo cell-based gene delivery step 3
Modify genome with therapeutic DNA (replacement, regulation, gene editing)
ex vivo cell-based gene delivery step 4
Expand and test modified cells in a dish
ex vivo cell-based gene delivery step 5
return modified cells to patient
How is ex vivo gene therapy different from in vivo gene therapy?
Ex vivo gene therapy involves integrating viral vectors into the host chromosome, which is passed on with cell division.
What is a characteristic of an episomal viral vector when used in vivo?
It does not integrate into the host genome and is lost in cell divisions.
Are episomal vectors safer?
Yes, but they are used to target terminally differentiated cells that do not divide any longer
properties of the gene therapy vector should…
match the pathophysiological requirements dictated by the disease.
Ex vivo gene therapy diagram
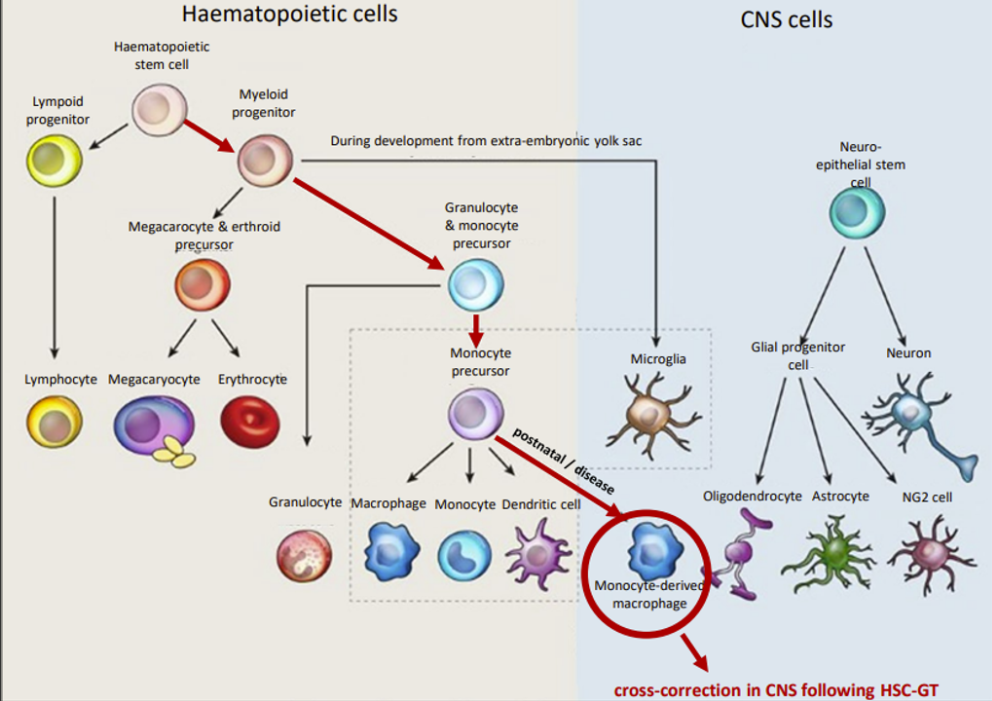
Viral vectors in gene therapy are replication…
incompetent
Three requirements of viral gene therapy vectors
Host cell tropism - uptake by the cell
Gene expression - transcription in the target cell
Immune response - against vector or transgene
Experiment found that promoters in gene therapy vectors can…
restrict transgene expression i.e., different promoters can target different outcomes
Gene therapies for CNS disorders are complicated by…
Brain encased in skull, blood brain barrier and the fact most neural cells do not divide
Autosomal defect
Gene defect on autosome, not sex chromosome
Recessive disease gene
One healthy copy is sufficient to prevent disease
Cause of MLD
mutations in ARSA gene → toxic accumulation of sulfatides in the CNS and spinal cord
Antisense oligonucleotide (ASO) to treat SMA
Are short synthentic oligonucleotides, that elimate/reduce/modify mRNAs, are very stable but struggle to cross BBB
SMN2
A mutated gene duplication of SMN1 with an unknown function, and shows frequent exon 7 skipping leading to a non-functional protein