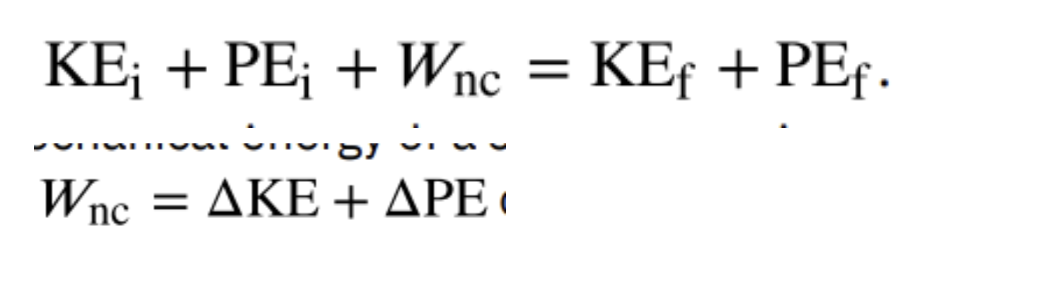Chapter 7: Work, Energy, and Energy Resources
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
basal metabolic rate
the total energy conversion rate of a person at rest
chemical energy
the energy in a substance stored in the bonds between atoms and molecules that can be released in a chemical reaction
conservation of mechanical energy
the energy in a substance stored in the bonds between atoms and molecules that can be released in a chemical reaction
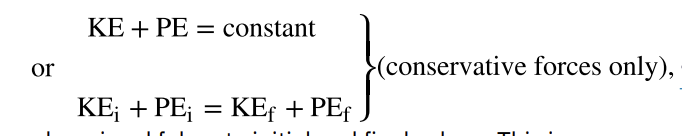
conservative force
a force that does the same work for any given initial and final configuration, regardless of the path followed
efficiency
a measure of the effectiveness of the input of energy to do work; useful energy or work divided by the total input of energy
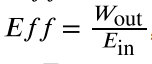
Electrical energy
the energy carried by a flow of charge
Energy
the ability to do work
fossil fuels
oil, natural gas, and coal
friction
the force between surfaces that opposes one sliding on the other; friction changes mechanical energy into thermal energy
gravitational potential energy
the energy an object has due to its position in a gravitational field
horsepower
an older non-SI unit of power, with 1hp = 746W
joule
SI unit of work and energy, equal to one newton-meter
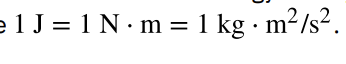
kilowatt-hour (kW x h)
unit used primarily for electrical energy provided by electric utility companies
Kinetic energy
the energy an object has by reason of its motion, equal to 1/2mv2 for the translational (i.e., non-rotational) motion of an object of mass m moving at speed v
law of conservation of energy
the general law that total energy is constant in any process; energy may change in form or be transferred from one system to another, but the total remains the same
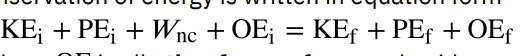
Mechanical energy
the sum of kinetic energy and potential energy
Metabolic Rate
the rate at which the body uses food energy to sustain life and to do different activities
net work
work done by the net force, or vector sum of all the forces, acting on an object
Nonconservative force
a force whose work depends on the path followed between the given initial and final configurations
Nuclear energy
energy released by changes within atomic nuclei, such as the fusion of two light nuclei or the fission of a heavy nucleus
Potential energy
energy due to position, shape, or configuration
Potential energy of a spring
the stored energy of a spring as a function of its displacement; when Hooke’s law applies, it is given by the expression 1/2kx2 where x is the distance the spring is compressed or extended and k is
power
the rate at which work is done
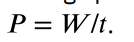
radiant energy
the energy carried by electromagnetic waves
renewable forms of energy
those sources that cannot be used up, such as water, wind, solar, and biomass
thermal energy
the energy within an object due to the random motion of its atoms and molecules that accounts for the object's temperature
useful work
work done on an external system
Watt (W)
SI unit of power, with 1W = 1J/s
work (W)
the transfer of energy by a force that causes an object to be displaced; the product of the component of the force in the direction of the displacement and the magnitude of the displacement
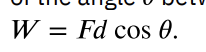
work-energy theorem
the result, based on Newton’s laws, that the net work done on an object is equal to its change in kinetic energy
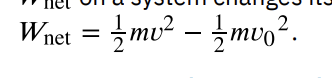
Translational Kinetic Energy Formula
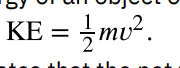
Change in Gravitational Potential Energy
also equals to the negative value of change in Kinetic Energy
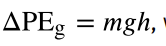
Work done by a nonconservative force