2.4 Biomes, Zonation, and Succession
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
biome
a collection of ecosystems sharing similar climatic conditions
biosphere
That part of the Earth inhabited by organisms. It extends from the upper part of the atmosphere down to the deepest parts of the oceans which support life.
freshwater biomes
swamp forests, lakes and ponds, streams and rivers, bogs
marine biomes
rocky shore, mud flats, coral reef, mangrove swamp, continental shelf, deep ocean
deserts
a barren region with little or no rainfall, usually sandy and without trees; can be hot or cold
forests
land dominated by trees and other woody vegetation and sometimes used for commercial logging; tropical, temperate and boreal (taiga)
grassland
Biome where grasses are the main plant life with few trees; tropical or savanna and temperate
latitude
distance north or south of the equator
altitude
height above sea level
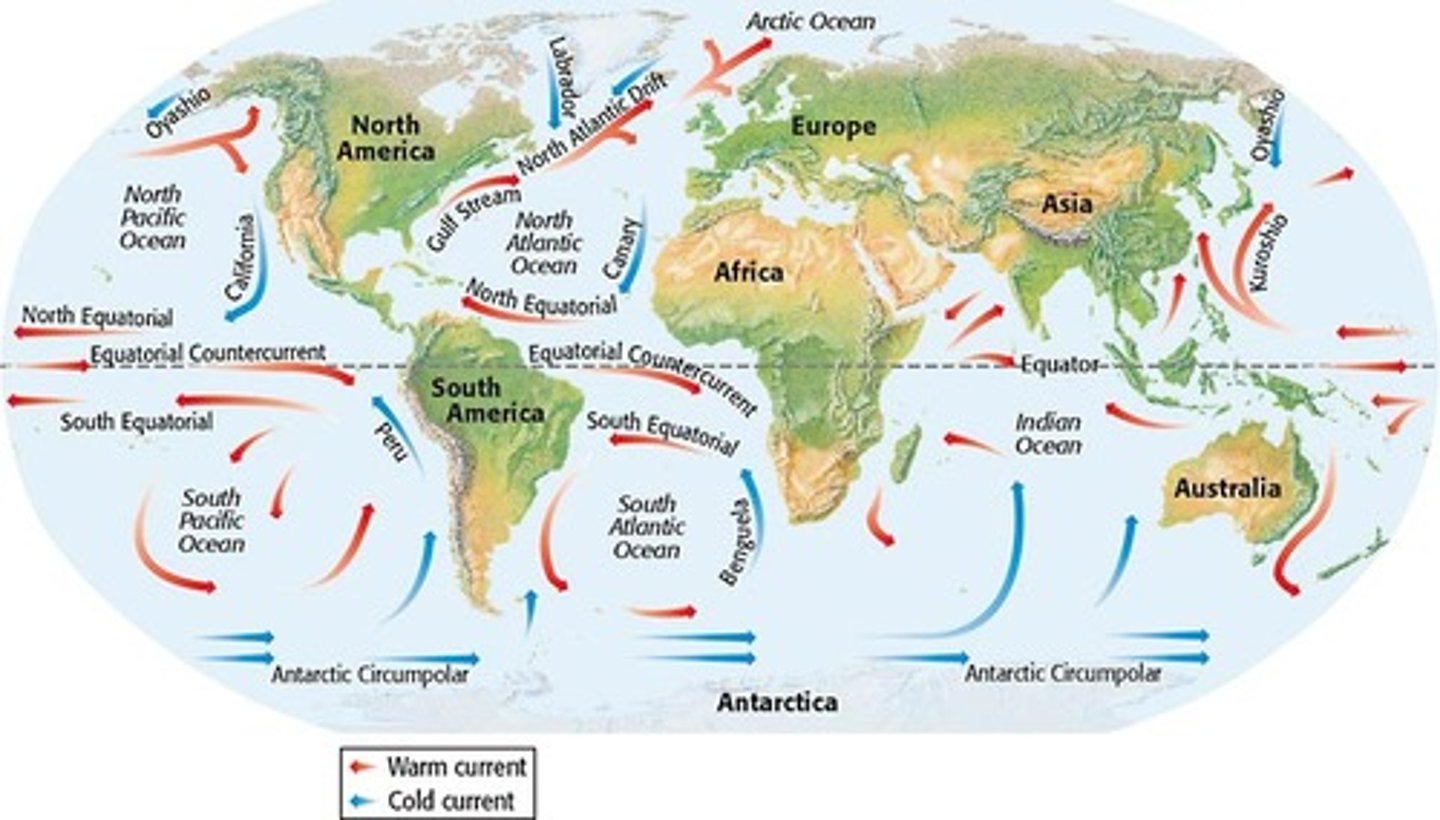
ocean currents
a movement of ocean water that follows a regular pattern
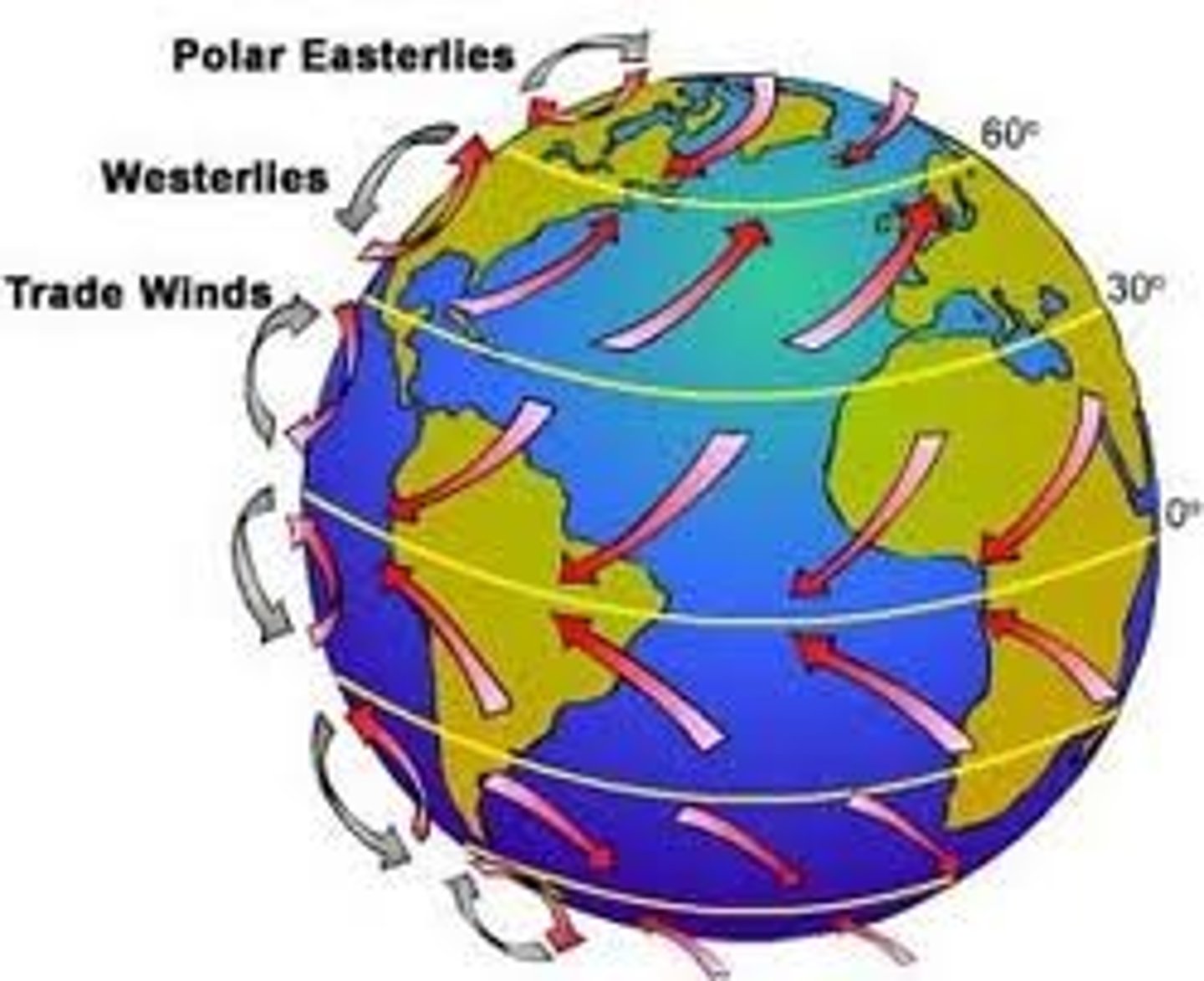
winds
These are formed due to unequal heating of the atmosphere that causes air pressure differences; they move from high to low pressure areas
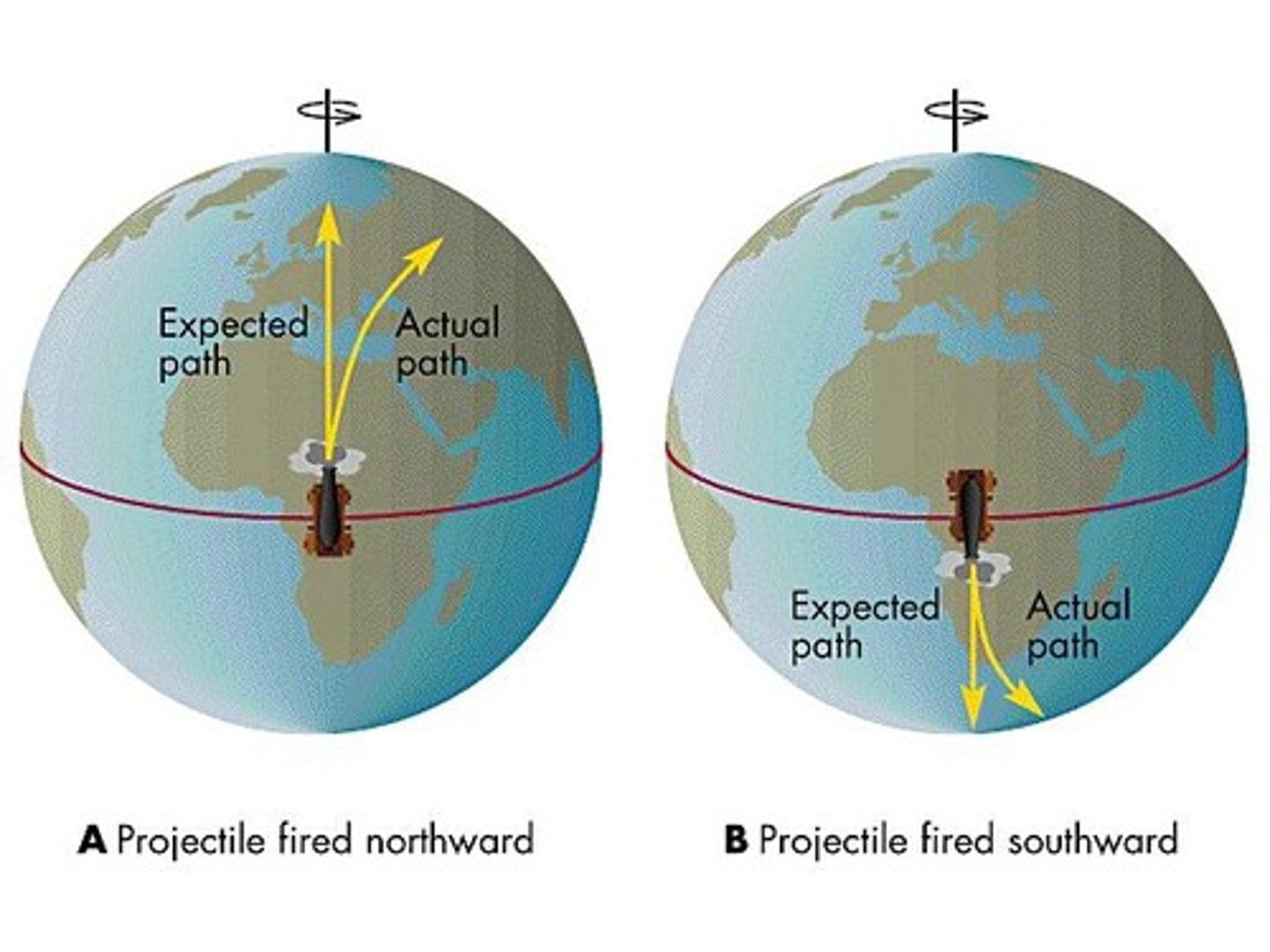
Coriolis effect
The effect of Earth's rotation on the direction of winds and currents; causes moving air and water to turn left in the southern hemisphere and turn right in the northern hemisphere.
latent heat
heat absorbed or radiated during a change of phase at a constant temperature and pressure
insolation
incoming solar radiation
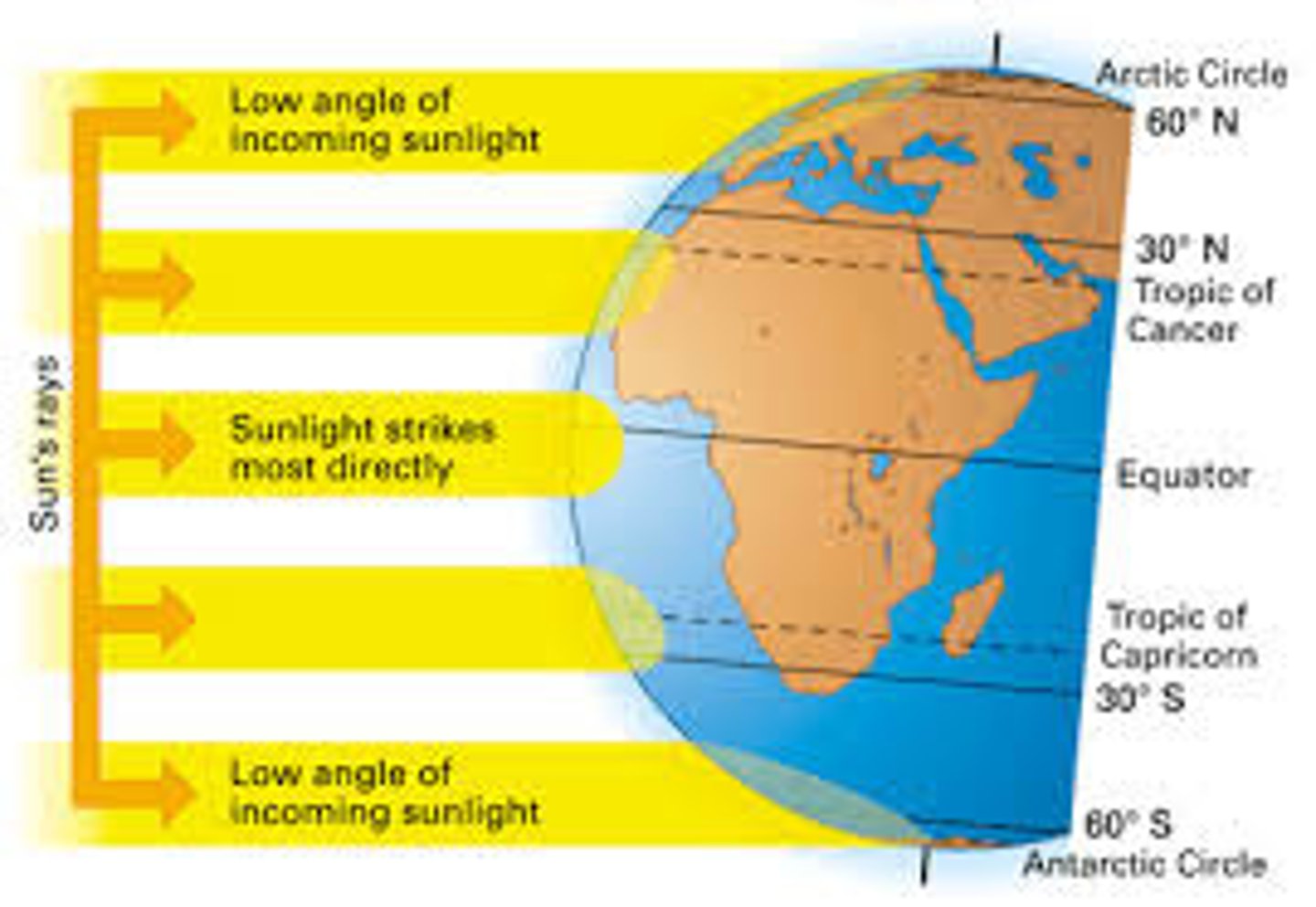
uneven heating of Earth's surface
cause by angle of the sun's rays , tilt of the Earth on its axis; affects the climates and biomes that exist on the planet
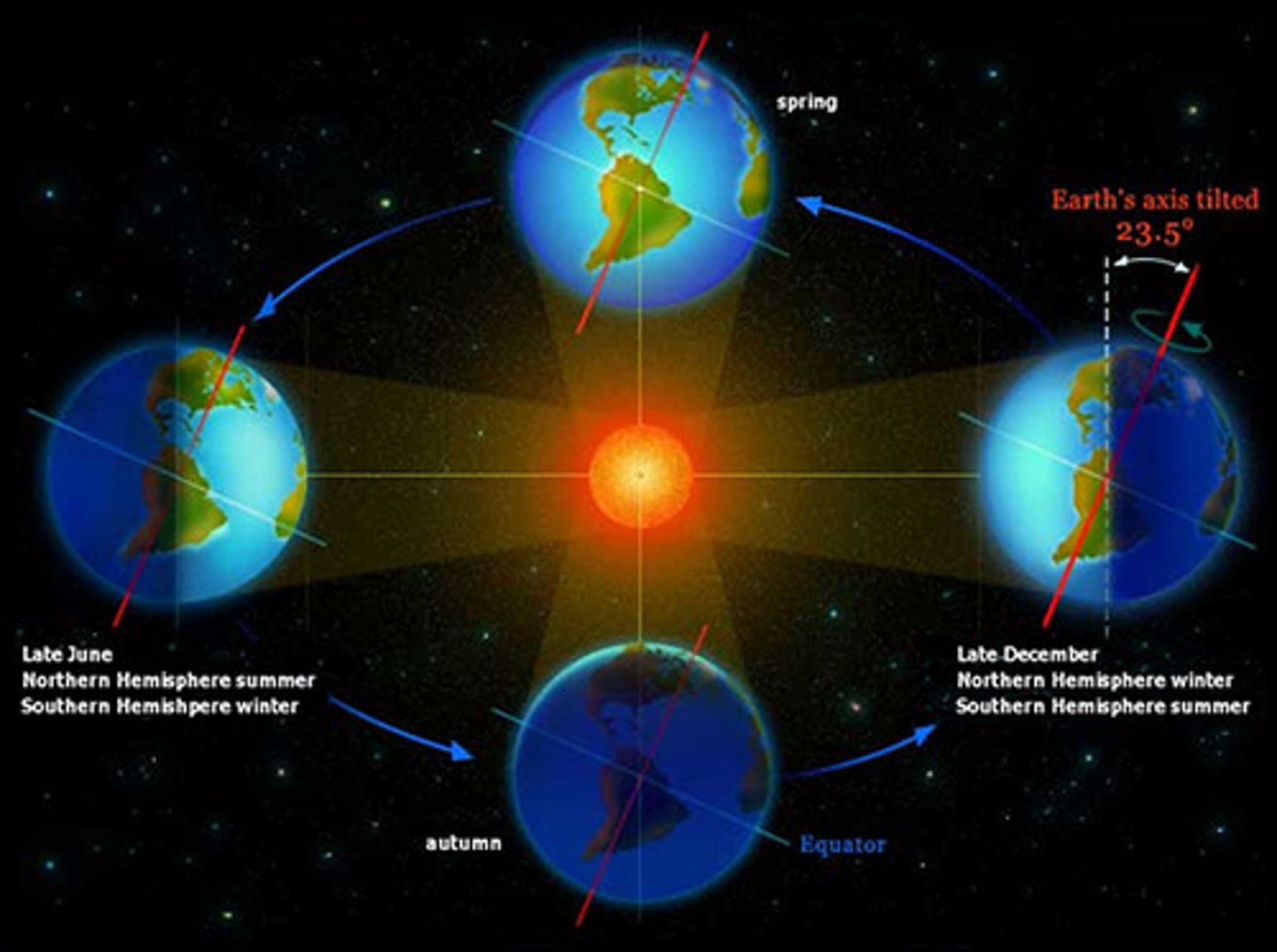
Earth's seasons
• Caused by the tilt of the Earth on its axis and its revolution around the sun.
• Hemisphere with most direct sunlight- summer.
• Hemisphere with indirect sunlight- winter.
precipitation to evaporation ratio
Amount of fallen precipitation/Amount of evaporated precipitation
If P/E ratio > 1 : A lot of precipitation and evaporation rates are low. Then there's leaching in the soil when soluble minerals are washed downwards.
If P/E ratio < 1 : Water moves upwards through the soil and evaporates on surface. This leaves salt behind and salinity increases, stopping plants from growing (salinisation).
If P/E ratio ~ 1 : Precipitation is about the same as evaporation, the soils tend to be rich and fertile.
productivity
greater in low latitudes (near the equator) and lower in high latitudes (near the poles
- GPP and NPP are higher near the equator
- GPP and NPP are lower nearer to the poles
annual precipitation and temperature
Main two factors, after latitude, that affect biome distribution
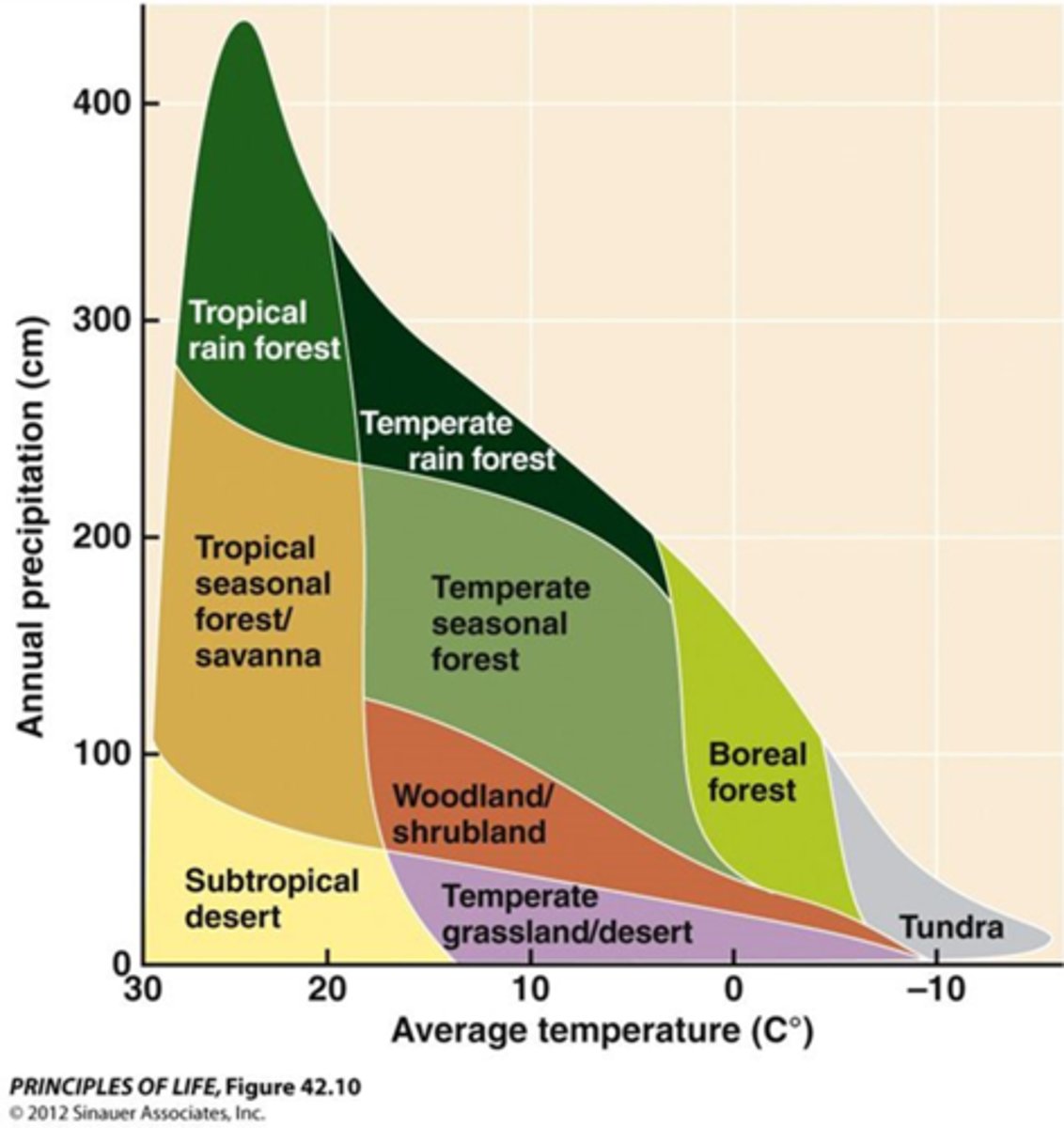
Tropical Rainforest
Forests in which rainfall is abundant - more that 200 cm (80 in) per year - and temperatures are warm or hot year-round; found mostly near the equator
Deserts
covers about one fifth of the Earth's surface and occur where rainfall is less than 50 cm/year. Most deserts occur at low latitudes, have a considerable amount of specialized vegetation, as well as specialized animals. Soils have abundant nutrients, need only water to become productive, and have little or no organic matter.
Temperate Grassland
biome characterized by deep, nutrient-rich soil that supports many grass species
Temperate Forests
Forests that exist between 25 and 50 degrees latitude in both hemispheres, which typically have high humidity, heavy rainfall, large, tall trees and wide leaves.
Arctic Tundra
a biome characterized by low average temperatures, brief growing seasons, the presence of permafrost, and limited precipitation largely in the form of snow in which the dominant vegetation are low shrubs, lichens, mosses, and small herbaceous plants
Deep Ocean
this biome has lots of pressure, is dark and has many creepy fish and sea creatures
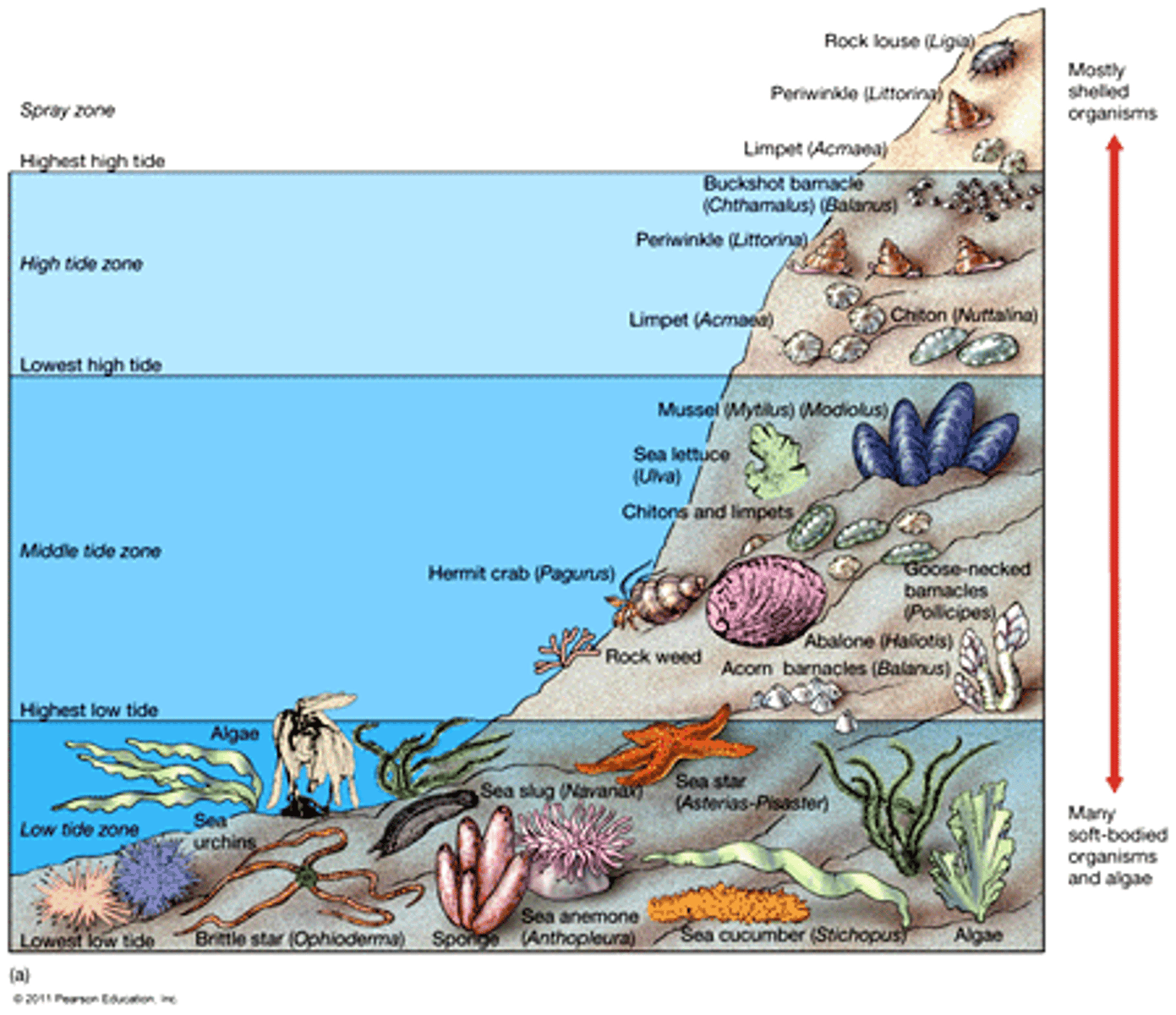
Zonation in Aquatic Biomes
Many aquatic biomes are stratified into zones or layers defined by light penetration, temperature, and depth
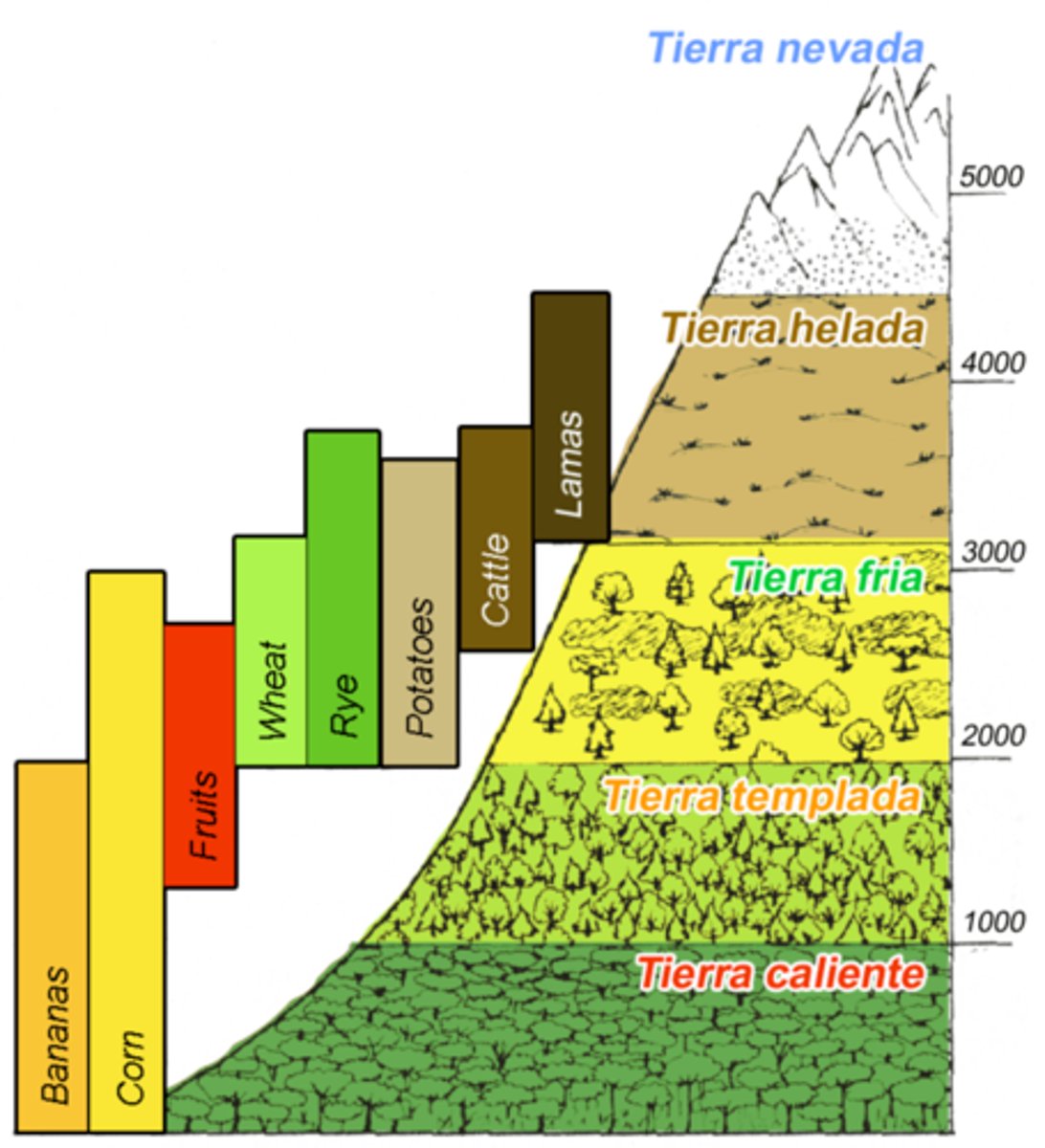
Zonation in Terrestrial Biomes
The arrangement or patterning of plant communities or ecosystems into parallel or sub-parallel bands in response to change in altitude and latitude.
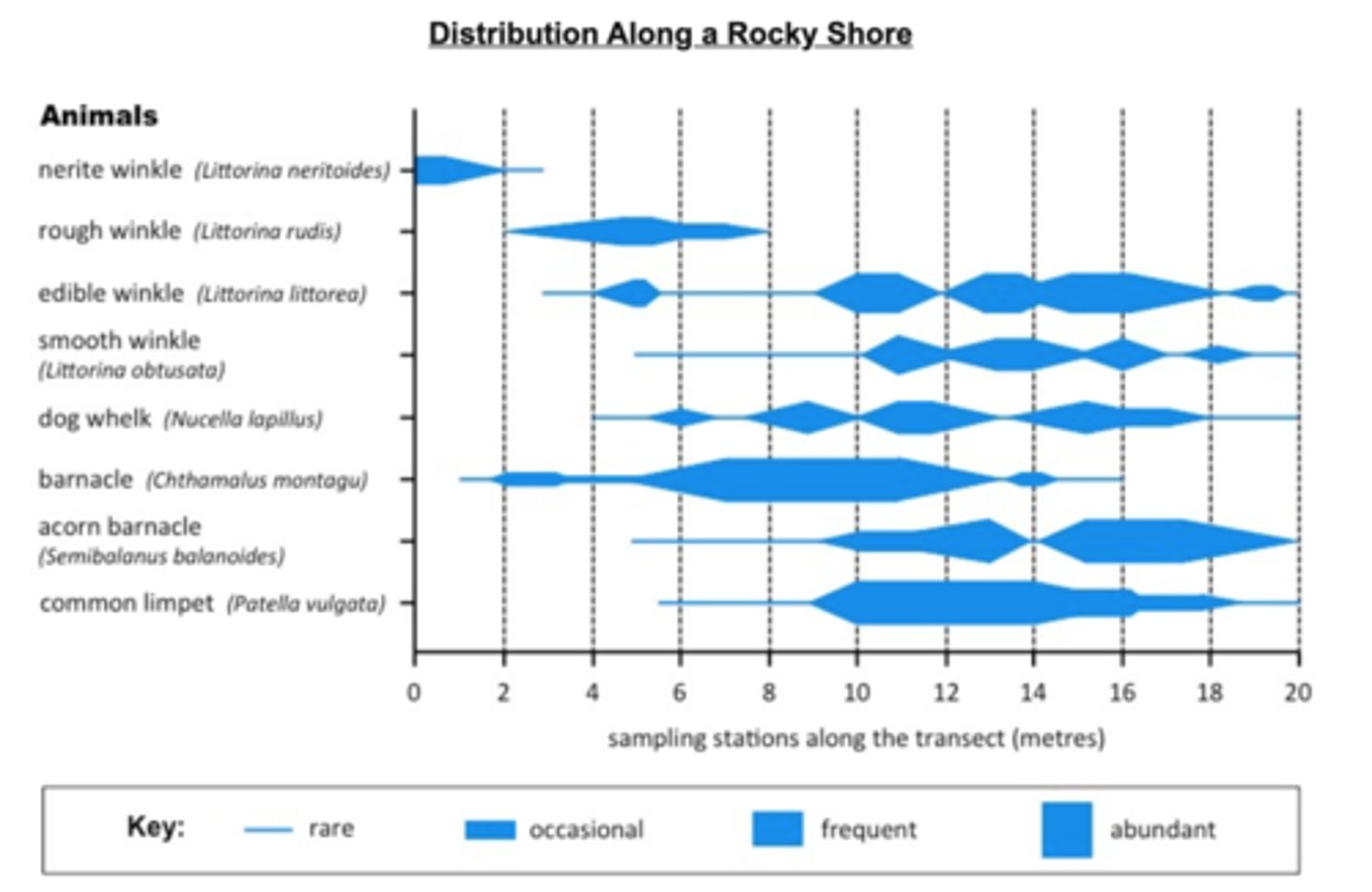
Kite Diagram
A diagram used to visualise the abundance and distribution of different species, using belt transect data
Zonation
the distribution of plants or animals into specific zones according to such parameters as altitude or depth, each characterized by its dominant species.
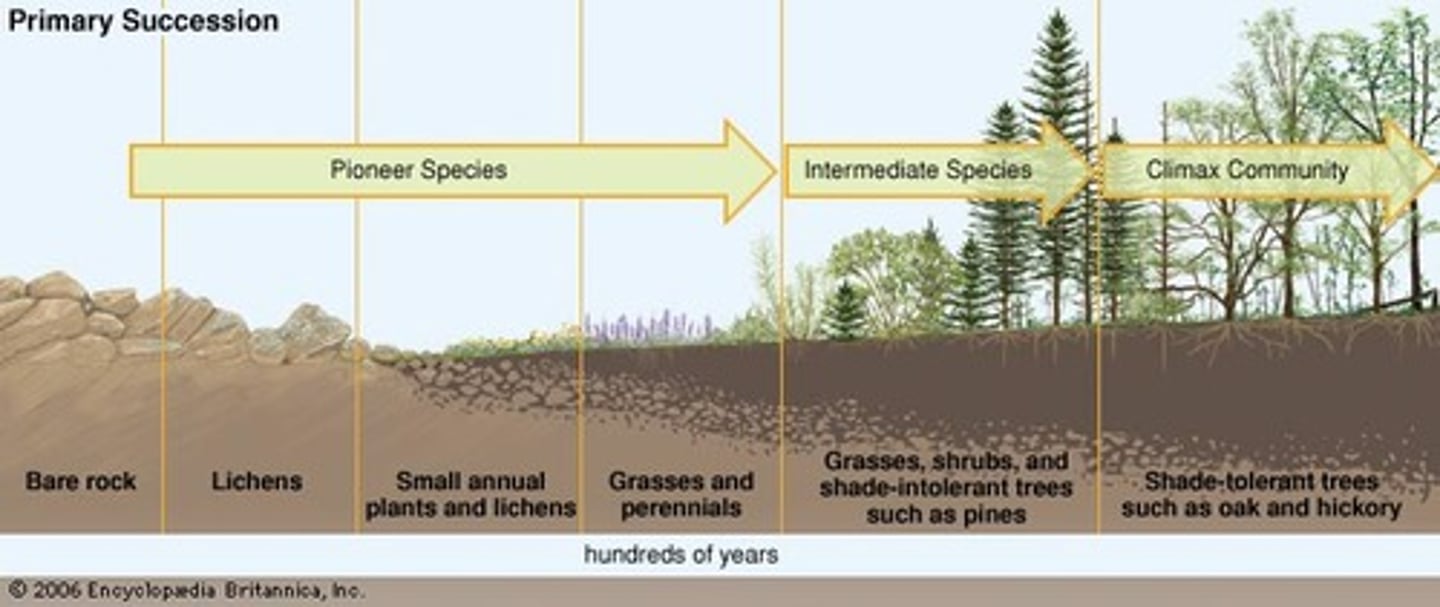
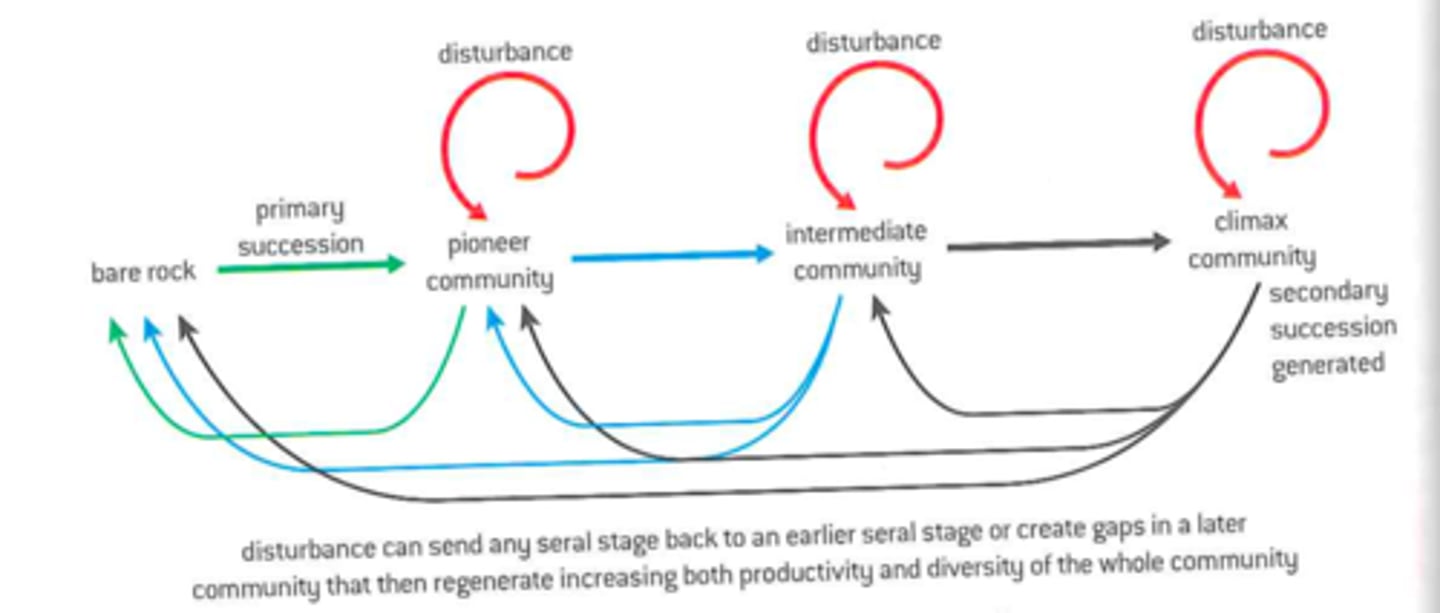
Succession
(ecology) the gradual and orderly process of change in an ecosystem brought about by the progressive replacement of one community by another until a stable climax is established
primary succession
An ecological succession that begins in an area where no biotic community previously existed
secondary succession
type of succession that occurs in an area that was only partially destroyed by disturbances
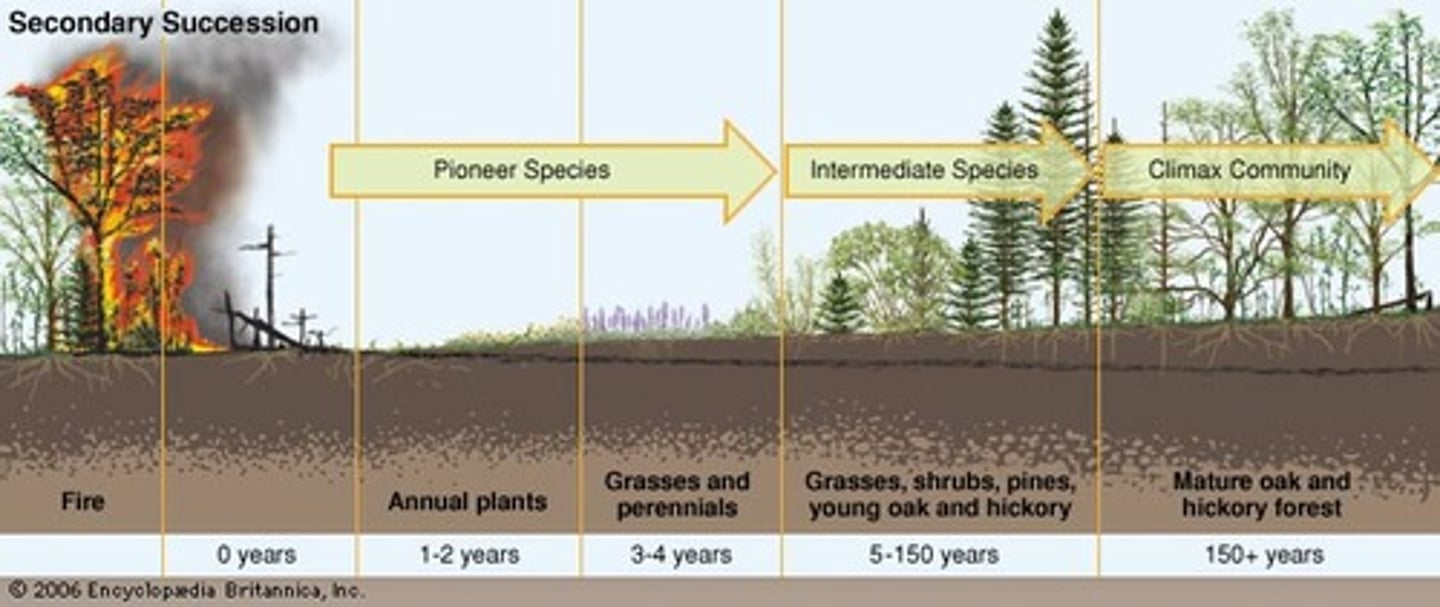
pioneer species
First species to populate an area during primary succession
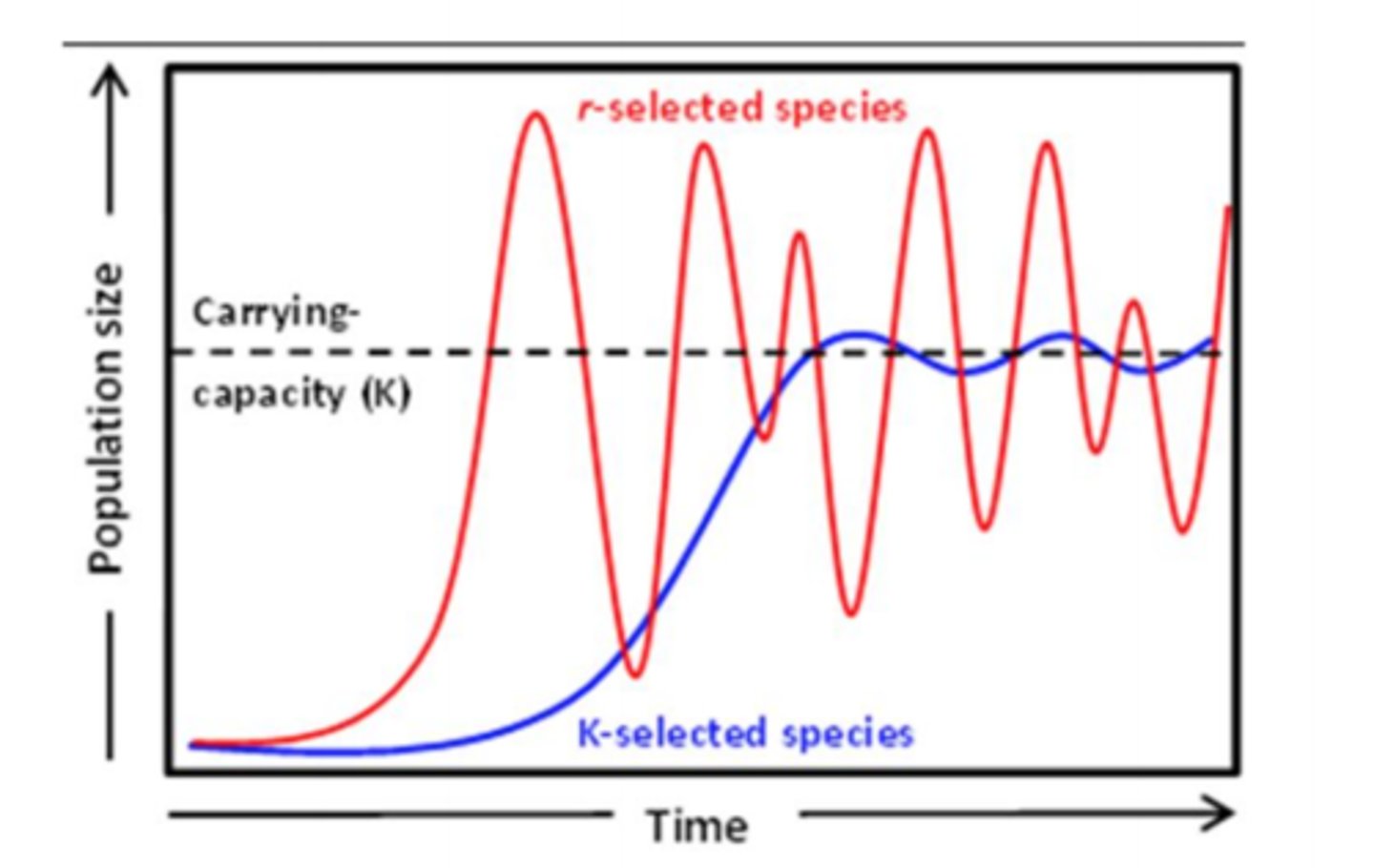
r-selected species
a species that has a high intrinsic growth rate, which often leads to population overshoots and die-offs
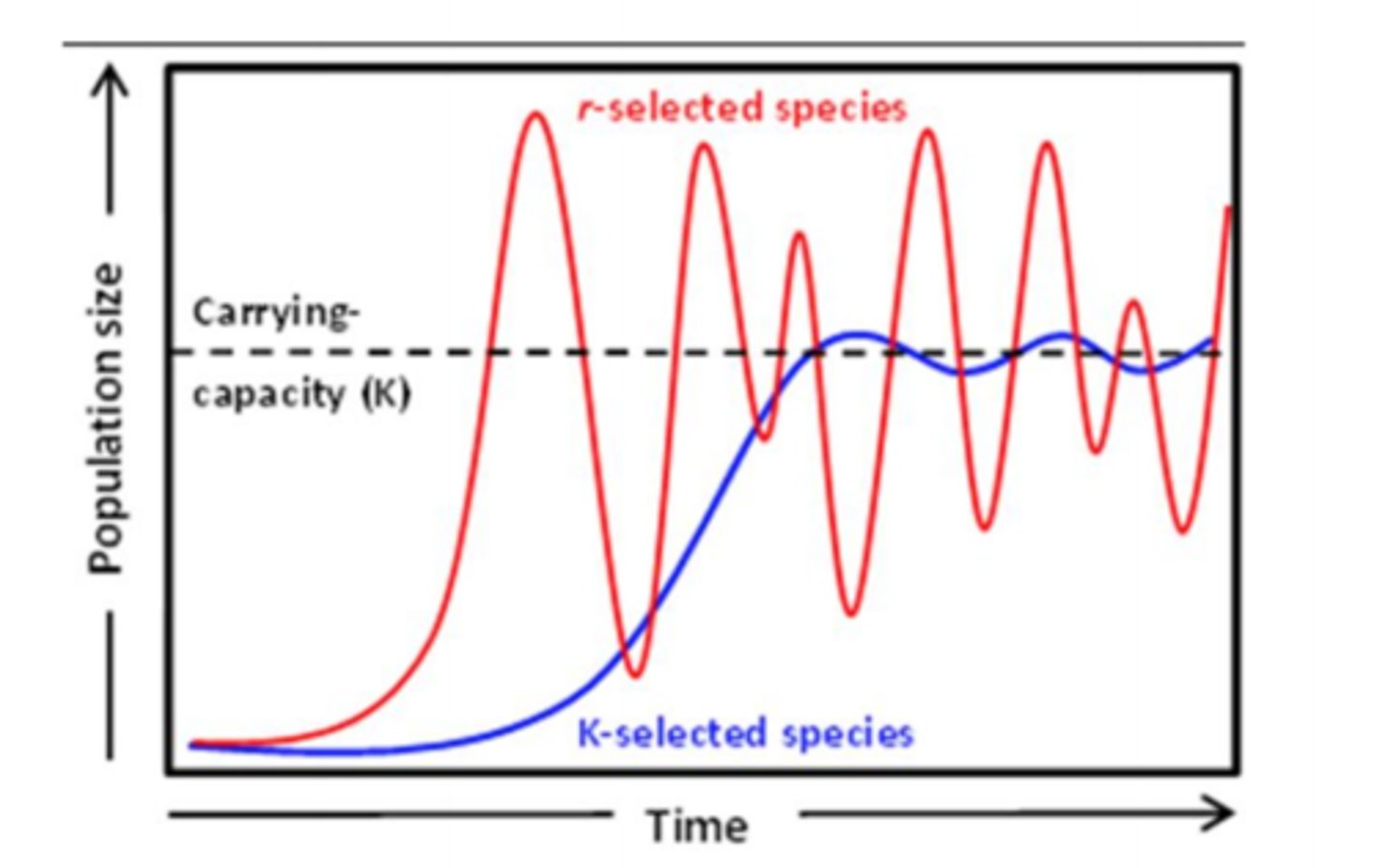
K-selected species
a species with a low intrinsic growth rate that causes the population to increase slowly until it reaches carrying capacity
climax community
A stable, mature community that undergoes little or no change in species over time
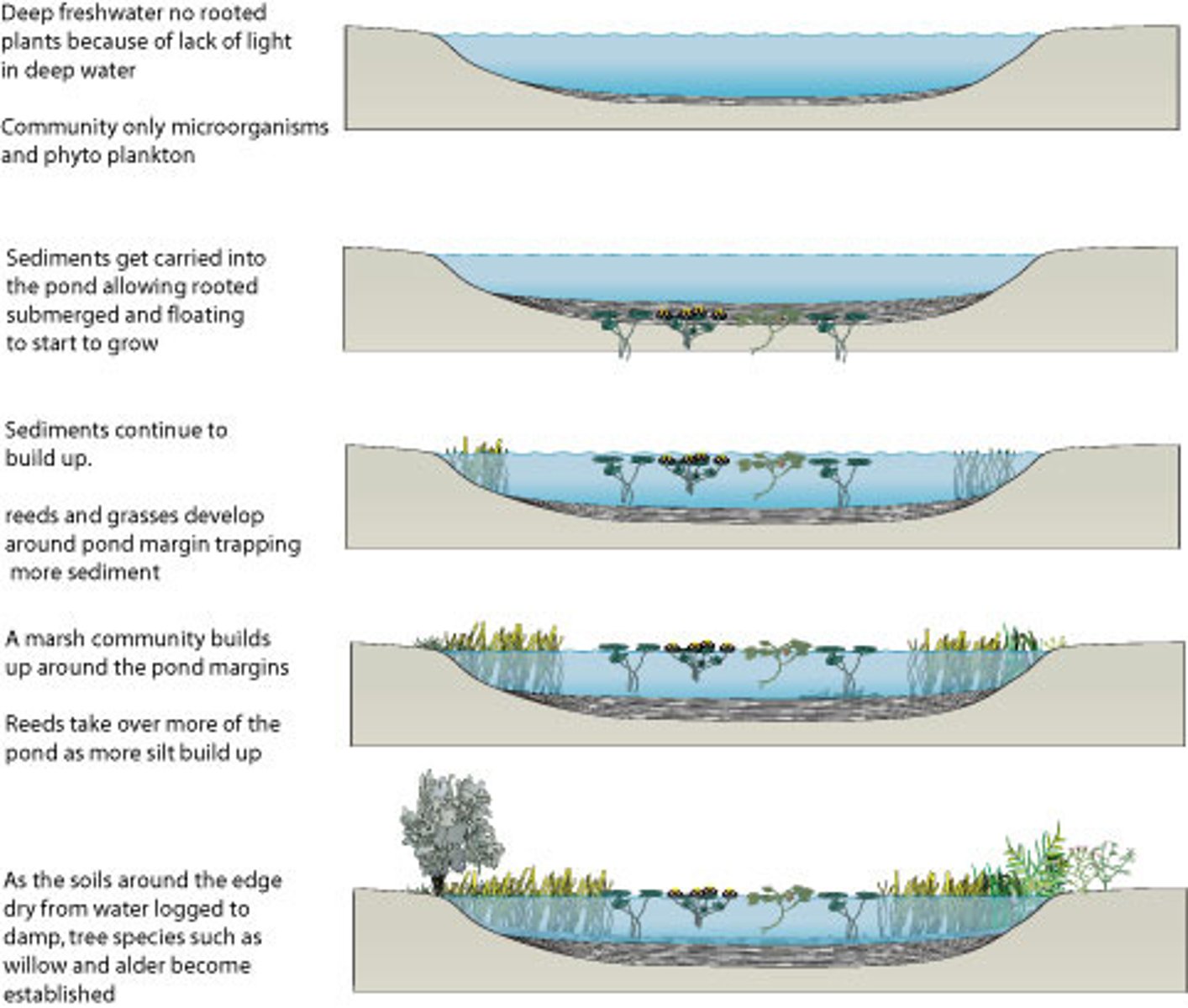
hydrosere
Succession in water
disturbance
An event, such as storm, fire, flood, drought, overgrazing or human activity, that changes a community and alters resource availability.
Climatic climax vegetation
The final stage in succession, the richest community for a climate
sub-climax community
succession is 'arrested' at a stage by an abiotic factor. This community will only develop if the limiting factor is removed
plagioclimax community
an area or habitat in which the influences of the humans have prevented the ecosystem from developing further
biodiversity
the variety of life in the world or in a particular habitat or ecosystem.
mineral cycling
The cycle in an ecosystem of a mineral element (i.e. carbon, nitrogen, sulfur, water, oxygen etc) through living and nonliving parts of the natural world.