Edexcel A Level Chemistry: Transition metal colours
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
[Cu(H₂O)₆]²⁺
Pale blue Solution
[Fe(H₂O)₆]²⁺
Pale green solution
[Fe(H₂O)₆]³⁺
Yellow Solution
[Mn(H₂O)₆]²⁺
Pale Pink Solution
[Cr(H₂O)₆]³⁺
Green Solution
Orange to yellow
both +6 oxidation states of chromium
CrO4 2- - yellow
Cr2O7 2- - orange
Cu(OH)₂
Pale Blue precipitate
Fe(OH)₂
green precipitate, turning brown on exposure to air
Fe(OH)₃
red-brown precipitate
Cr(OH)₃
Green PPT
[Cr(OH)₆]³⁻
Dark green solution
Cr₂O₇²⁻
Orange solution
[Cu(NH₃)₄(H₂O)₂]²⁺
Dark blue solution
[CuCl₄]²⁻
Yellow solution
[Cr(NH₃)₆]³⁺
Violet solution
Purple solution → grey green precipitate → violet solution
CrO₄²⁻
Yellow solution
Permanganate ion
MnO₄⁻, oxidising agent, purple in solution, reduces from +7 to Mn 2+ in colourless solution
Dichromate ion
Cr₂O₇²⁻
Chromate ion
CrO₄²⁻
[Co(H₂O)₆]²⁺
Pink solution
[CoCl4]2-
Blue solution
[Co(H₂O)₄(OH)₂]
Blue precipitate ANHYDROUS
pink HYDRATED.
Co(H2O)6 2+ → [Co(NH₃)₆]²⁺
pink solution → brown solution which darkens on standing
[Co(NH₃)₆]³⁺
A deep red-brown solution
Observation adding some OH⁻ to Chromium (III) ions
Green solution → green precipitate
Observation adding XS OH⁻ to Chromium (III) ions
Green solution → green precipitate → dark green solution
What happens when Fe(OH)₂ is left exposed to air
Fe(OH)₂ is oxidised to Fe(OH)₃
stability constant, Kstab
The equilibrium constant for the formation of a complex ion in a solvent from its constituent ions
Large Kstab means
stable complex
Small Kstab means
unstable complex
Observation adding XS OH⁻ to Iron (II) ions
green precipitate remains, no further change
Observation adding some OH⁻ to Iron (III) ions
yellow solution → red-brown precipitate
Observation adding XS OH⁻ to Iron (III) ions
red-brown precipitate remains, no further change
Observation adding some OH⁻ to cobalt (II) ions
pink solution → blue precipitate
Observation adding XS OH⁻ to cobalt (II) ions
blue precipitate remains, no further change
Observation adding some OH⁻ to copper (II) ions
blue solution → blue precipitate
Observation adding XS OH⁻ to copper (II) ions
Blue precipitate remains, no further change (NON AMPHOTERIC)
Observation adding some OH⁻ to group II ions
white precipitate forms
Observation adding XS OH⁻ to group II ions
white precipitate remains, no further change
Observation adding some OH⁻ to group I ions
no visible change
Observation adding XS OH⁻ to group I ions
no visible change
Observation adding some NH₃ to Chromium (III) ions
green solution → green precipitate
Observation adding XS NH₃ to Chromium (III) ions
green precipitate slowly dissolves forming a violet solution
Observation adding XS NH₃ to Iron (II) ions
pale green solution → pale green precipitate (FeOH2H2O4), further oxidation to red-brown precipitate (FeOH3), precipitate darkens
Observation adding some NH₃ to Iron (III) ions
yellow solution → red-brown precipitate of [Fe(H2O)3(OH)3]
NH3 acts as base, not as ligand here
Observation adding some NH₃ to Iron (II) ions
green solution → green precipitate
Observation adding XS NH₃ to Iron (III) ions
red-brown precipitate remains, no further change
Observation adding some NH₃ to cobalt (II) ions
pink solution (hexaaquaion) → blue precipitate (CoNH36)
Observation adding XS NH₃ to cobalt (II) ions
Pink solution (Co2+) → green precipitate (Co OH2) → brown solution, which darkens to a red-brown solution on standing (oxidation of Co2+ to Co3+)
Observation adding some NH₃ to copper (II) ions
Blue solution → blue precipitate
Observation adding XS NH₃ to copper (II) ions
Blue precipitate → deep blue solution
Ligand
particle with lone pair of electrons that bonds to metals by a co-ordinate bond
Complex
metal ion with co-ordinately bonded ligands
Co-ordinate number
number of co-ordinate bonds from ligands to metal ion
Coordinate (dative) bond
A covalent bond in which both electrons come from the same atom
Monodentate ligands
A ligand which can donate one pair of electrons to a central metal ion
Monodentate ligand examples
NH₃, OH⁻, Cl⁻
Bidentate ligand
A ligand which has 2 pairs of electrons which can be donated to the same central metal ion
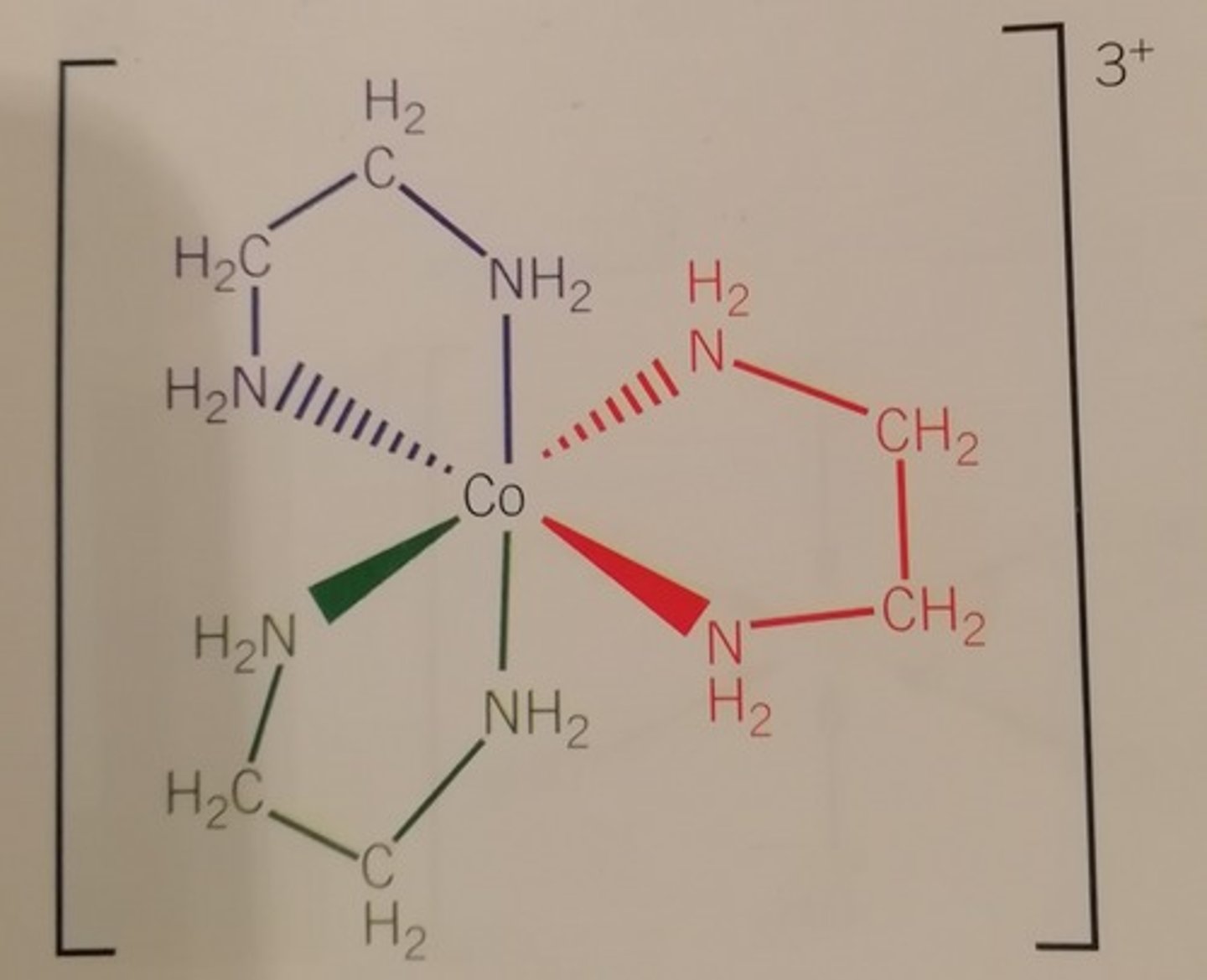
Bidentate ligand examples
Diaminoethane, Ethanedioate
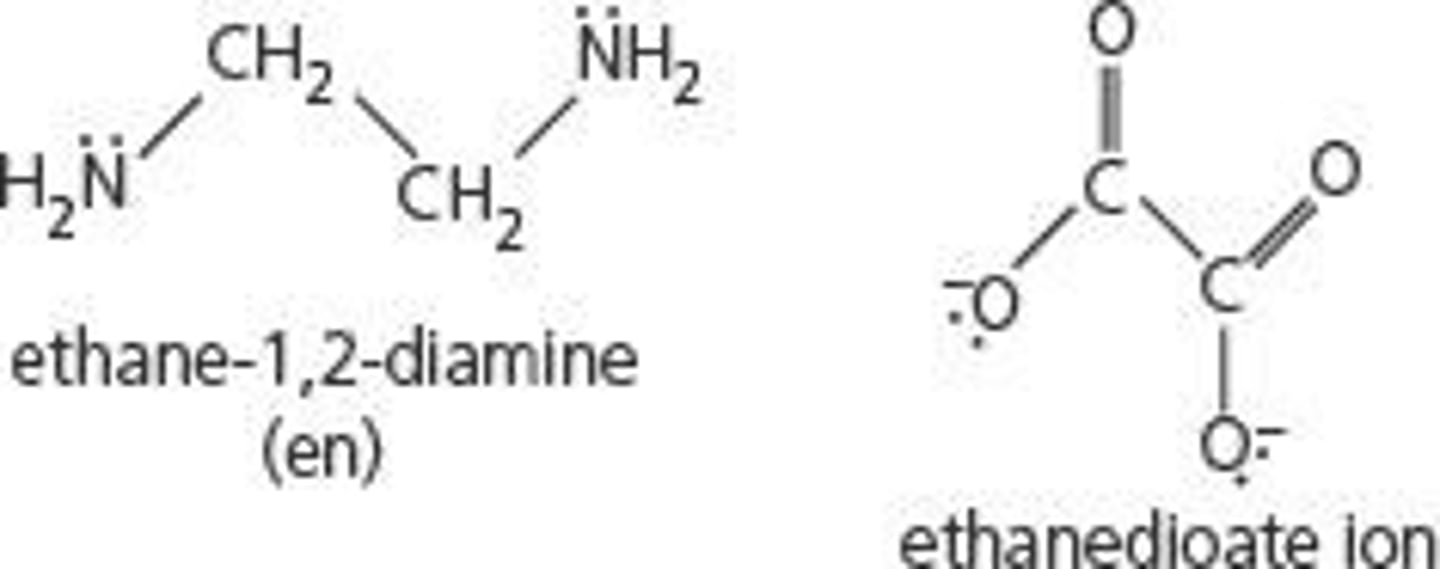
Polydentate ligands
a ligand that is attached to a central metal ion by bonds from two or more donor atoms
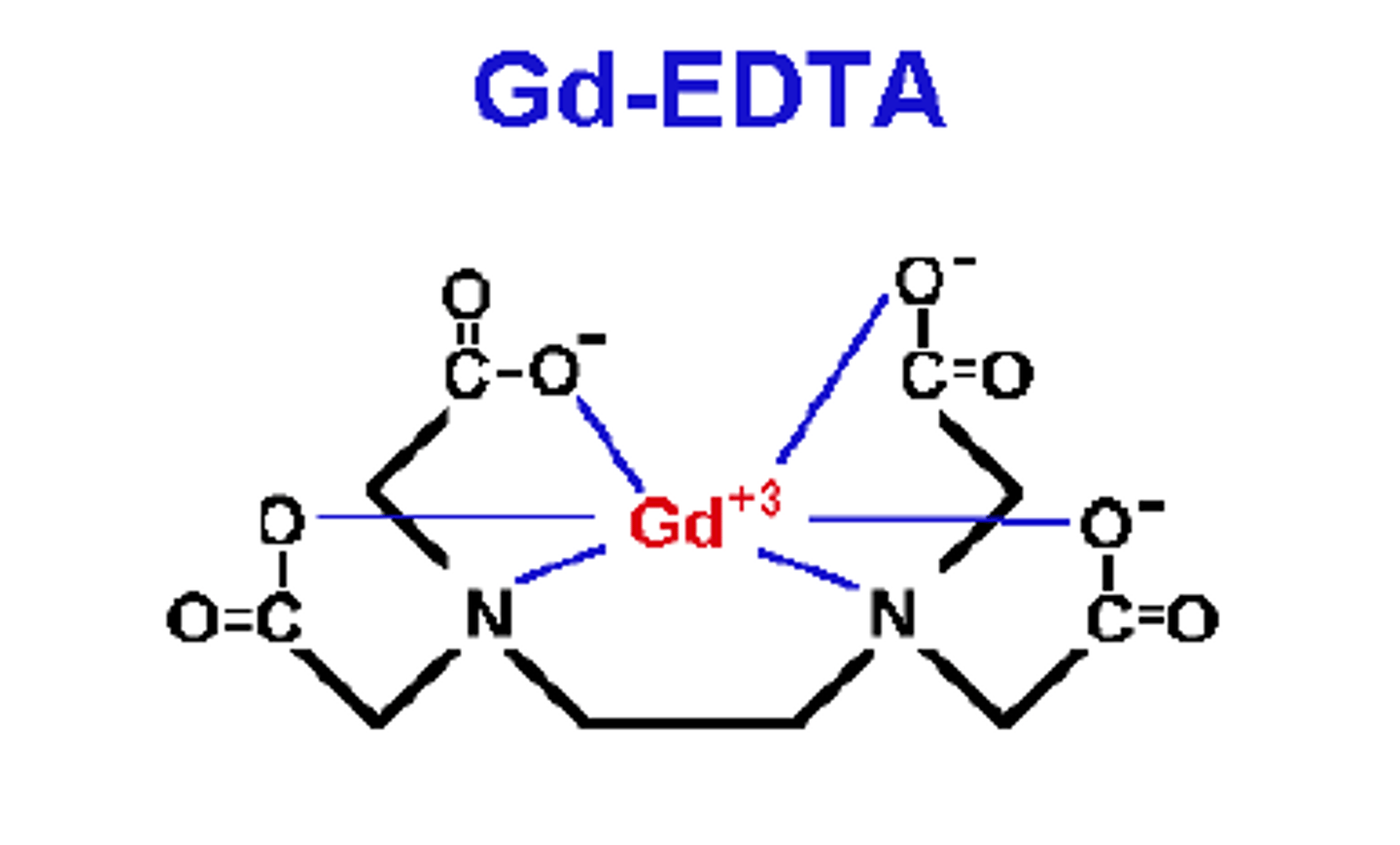
EDTA⁴⁻
Hexadentate ligand