Physiology Lecture Exam 1 SG
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/115
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:30 AM on 2/1/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
116 Terms
1
New cards
What is blood made of?
liquid CT (fluid CT)
2
New cards
Blood is
continuously regenerative
3
New cards
Arteries carry oxygenated blood
AWAY from the heart to the body
4
New cards
Arterial blood would be
bright red because it is carrying oxygenated blood
5
New cards
Veins carry deoxygenated blood
TOWARDS the heart
6
New cards
Blood carried through veins would be
blue/ dark red because it is deoxygenated
7
New cards
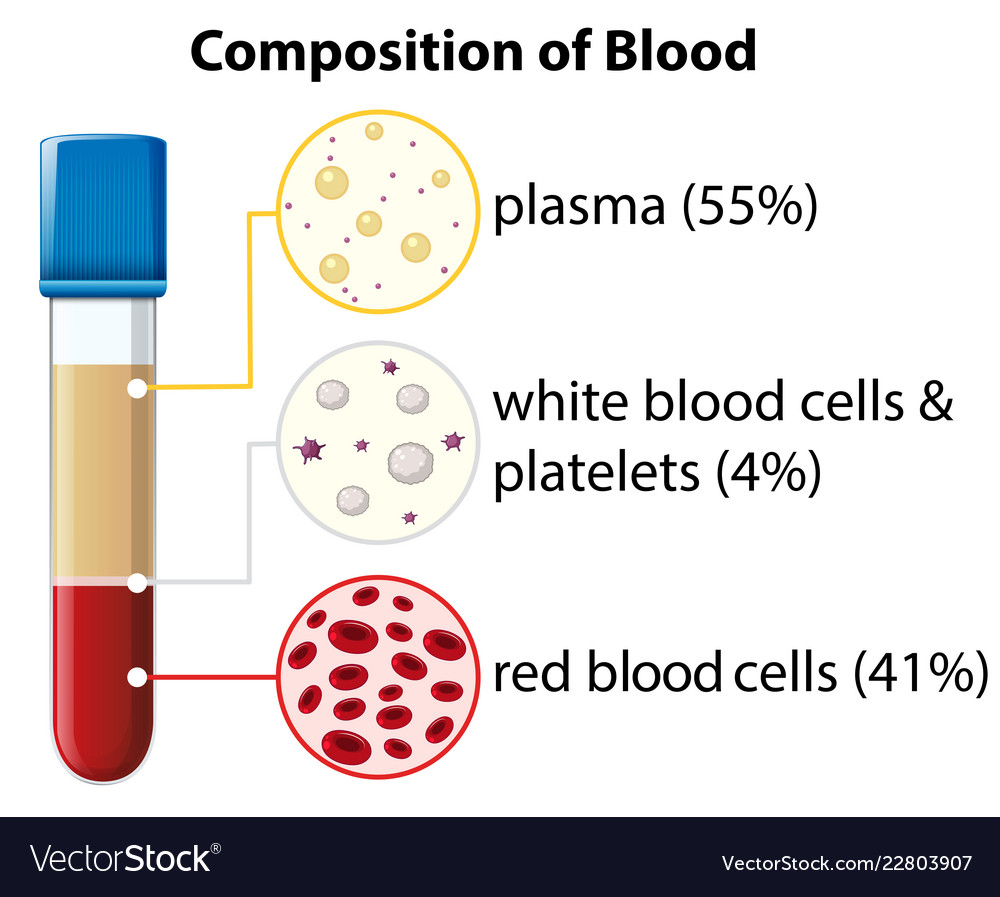
What is the composition of blood?
55% plasma
41% red blood cells (erythrocytes)
4% leukocytes (WBCs) and platelets
41% red blood cells (erythrocytes)
4% leukocytes (WBCs) and platelets
8
New cards
Blood functions in
transportation
regulation
protection
regulation
protection
9
New cards
How is blood transported?
through veins, capillaries, and arteries
10
New cards
How does blood function in regulation?
Regulates hormones, temperature, pH, and fluid balance
11
New cards
How does blood function in protection?
blood clotting +
contains leukocytes, plasma proteins, and other molecules protecting against microbes.
contains leukocytes, plasma proteins, and other molecules protecting against microbes.
12
New cards
What is the composition of plasma?
mostly water + plasma proteins and other solutes
13
New cards
Solutes in plasma
proteins- big molecules: albumin (60%), globulins (35%); antibodies or immunoglobulins, + transport proteins, fibrinogens (4%); function in blood clotting, other/ regulatory proteins (1%)
nutrients- water soluble vitamins B1-11
electrolytes- sodium, chloride, potassium, calcium, magnesium
waste products
respiratory gases
nutrients- water soluble vitamins B1-11
electrolytes- sodium, chloride, potassium, calcium, magnesium
waste products
respiratory gases
14
New cards
Erythrocytes (RBCs)
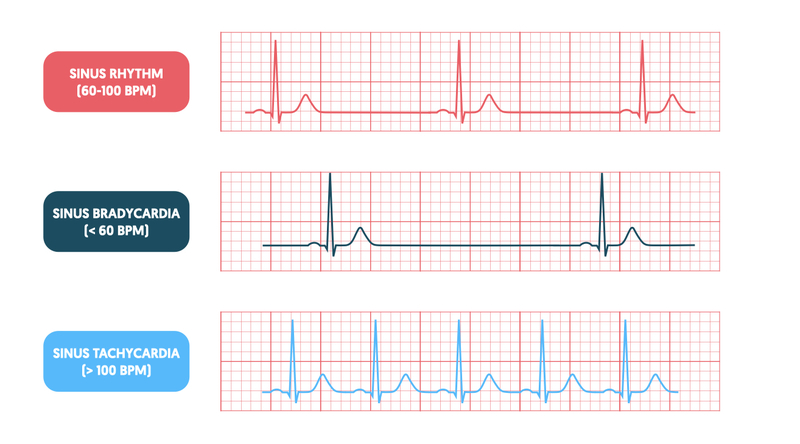
vast majority of the cells in the blood
hemoglobin, oxyhemoglobin, deoxyhemoglobin, oxygen
hemoglobin, oxyhemoglobin, deoxyhemoglobin, oxygen
15
New cards
What is the life expectancy of RBCs?
120 days
16
New cards
RBCs function to
transport respiratory gases in the blood
17
New cards
Leukocytes (WBCs)
contribute to defending body against pathogens, infection, disease.
18
New cards
Leukocytes are
immune cells
19
New cards
Leukocytosis
high white blood cell count.
normal immune response.
normal immune response.
20
New cards
Granulocytes
WBCs with secretory granules in its cytoplasm
21
New cards
What are the 3 granulocytes?
Neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils
22
New cards
Neutrophils
most abundant type of granulocytes.
40-70% of WBCs in humans.
vital for protection against bacterial infection.
40-70% of WBCs in humans.
vital for protection against bacterial infection.
23
New cards
Eosinophils
immune cell that fight against parasites.
24
New cards
Basophils
have a low count in blood.
25
New cards
Agranulocytes
account for about 30% of all leukocytes and are produced either in the bone marrow or the lymphatic system.
26
New cards
Lymphocytes
a type of Agranulocyte.
large- natural killer cells
small- divided into B and T lymphocytes
large- natural killer cells
small- divided into B and T lymphocytes
27
New cards
Monocytes
a type of Agranulocyte.
once in tissue can become with macrophages and dendritic.
once in tissue can become with macrophages and dendritic.
28
New cards
Thrombocytes
aka platelets.
absolutely essential in the process of blood clotting.
absolutely essential in the process of blood clotting.
29
New cards
ABO blood group system is determined by
the red blood cell.
30
New cards
Antigen
anything a recipient will recognize as being a foreigner.
31
New cards
Immunoglobulin
aka antibodies.
M, IgM
M, IgM
32
New cards
Blood group Rhesus factor
either dominant (present) or recessive (absent) on the RBC.
Rh-, Rh+.
Rh-, Rh+.
33
New cards
Chromosome
Rhesus factor is coded by a dominant gene.
34
New cards
A dominant gene is
one that would be expressed if present.
35
New cards
Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn
aka Eryhtroblastosis Fetalis.
Rh- mother, Rh+ father. Fetus Rh+.
Factor incompatibility- blood can mix during birth or at the end of pregnancy.
There are no naturally occurring antibodies to the Rhesus factor in the plasma.
Rh- mother, Rh+ father. Fetus Rh+.
Factor incompatibility- blood can mix during birth or at the end of pregnancy.
There are no naturally occurring antibodies to the Rhesus factor in the plasma.
36
New cards
When does the heart begin to develop?
in the third week of gestation; with the formation of two heart tubules.
37
New cards
Where does the heart develop/ form from?
the mesoderm in embryo.
38
New cards
The heart begins to beat on or around day
22
39
New cards
Cardiovascular system consists of
the heart and blood vessels.
40
New cards
Adequate perfusion is
the sufficient delivery of blood to maintain cells’ health.
41
New cards
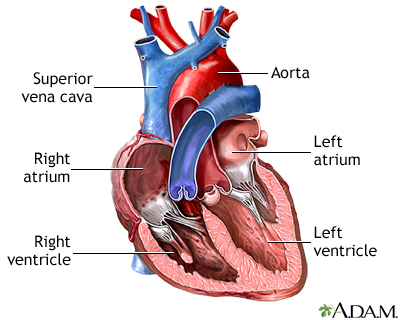
Ventricules
inferior chambers that pump blood away.
located inferior to atria.
located inferior to atria.
42
New cards
The left ventricle lining is
thicker than the right ventricle.
43
New cards
The interventricular septum
separates the right and left ventricles.
44
New cards
Why is the interventricular septum important?
it separates the ventricles to prevent oxygenated and deoxygenated blood from mixing.
45
New cards
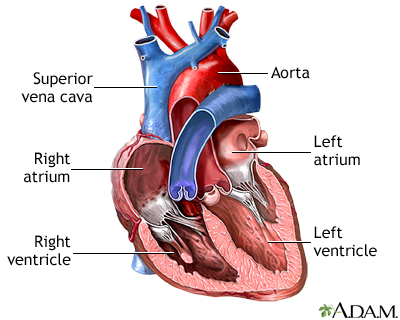
Aorta
receives oxygenated blood pumped from the left ventricle.
46
New cards
What kind of blood will you find in the aorta?
oxygenated
47
New cards
Oxygenated blood is received by the ____ pumped from the ____ ventricle.
aorta, left
48
New cards
The aorta is
the largest blood vessel in the body.
49
New cards
Heart valves
prevent back flow to ensure one way blood flow.
50
New cards
Valves on the left side of the blood
left atrioventricular valve (AV)/ bicuspid valve/ mitral valve.
aortic valve.
aortic valve.
51
New cards
Pulmonary artery
carries blood AWAY from heart TO lungs for oxygenation.
52
New cards
Atria
superior chambers that receive blood and send it to ventricles.
53
New cards
Valves on the right side of the heart
right AV valve/ tricuspid valve.
pulmonary valve.
pulmonary valve.
54
New cards
Vena cava/ right atrium
drain deoxygenated blood into right atrium.
55
New cards
Pulmonary circulation
transports blood from the right side of the heart to the alveoli of the lungs for gas exchange, and back to the left side of the heart.
56
New cards
Systematic circulation
transports blood from the left side of the heart to systematic cell of the body for nutrients and gas exchange, and back to the right side of the heart.
57
New cards
What is the first step of blood flow?
Blood enters through the superior/ inferior vena cava from the superior/ inferior parts of the body respectively.
58
New cards
Describe the process of blood flow
Blood enters through the superior/ inferior vena cava from the superior/ inferior parts of the body respectively > enters right atrium > flows through tricuspid/ right AV valve > into right ventricle > leaves right ventricle through pulmonary valve > deoxygenated blood to lungs where gas exchange occurs > pulmonary veins (oxygenated blood) > left atrium > left AV/ bicuspid/ mitral valve > left ventricle > put through aortic valve > into aorta > back to body/ system.
59
New cards
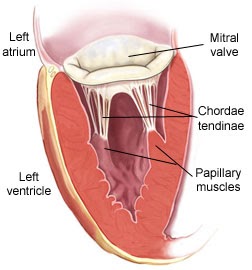
Tendinous cord/ chordae tendineae
holds AV valves in place while heart pumps blood.
60
New cards
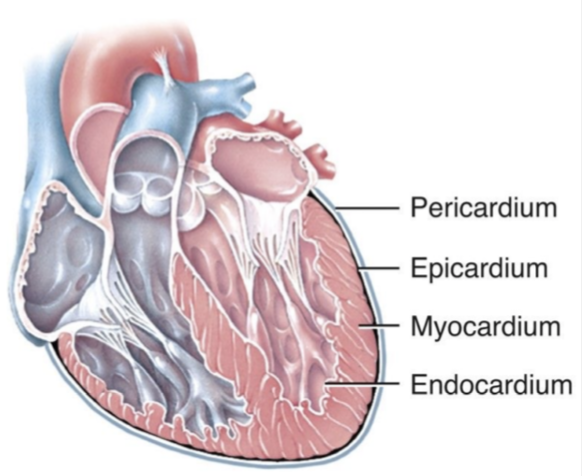
Layers of the heart
pericardium, endocardium, myocardium
61
New cards
Heart conduction system
specialized cardiac muscle cells within the heart located internal to the endocardium
62
New cards
What happens in the cardiac circle?
atria contracts first, ventricles will contract from the bottom up
63
New cards
SA node (sinoatrial node)
generates an electrical signal that causes atria to contract.
pacemaker of the heart.
pacemaker of the heart.
64
New cards
Heart electrical system
SA node generates an electrical stimulus. Atria are activated. Electrical stimulus travels down through conduction pathways and causes ventricles to contract and pump out blood.
65
New cards
AV node (atrioventricular node)
Collects signals from SA node. Serves as a gate that slows electric current before signal is permitted to pass down through to the ventricles.
66
New cards
Bundle of His
a group of fibers that carry electrical impulses from AV node to bundle branches.
67
New cards
Bundle branches
There are 2- left and right.
The bundle of His is divided into these two bundle branches.
The bundle of His is divided into these two bundle branches.
68
New cards
Left bundle branch
conducts impulses to left ventricle
69
New cards
Right bundle branch
conducts electrical impulses to right ventricle
70
New cards
Purkinje fibers
Deliver electric signals to ventricles, making them contract.
71
New cards
Components of the heart electrical system
SA node
AV node
Bundle of His
Left and right bundle branches
Purkinje fibers
AV node
Bundle of His
Left and right bundle branches
Purkinje fibers
72
New cards
Heart conduction system
Starts at SA node > action potential distributed through aorta > reaches AV node > action potential delayed at AV node (delay allows ventricles to fill before the contract) > action potential travels through AV bundle to Purkinje fibers (AV node > AV bundle > bundle branches > Purkinje fibers) > action potential spreads through ventricles (ventricles contract simultaneously)
73
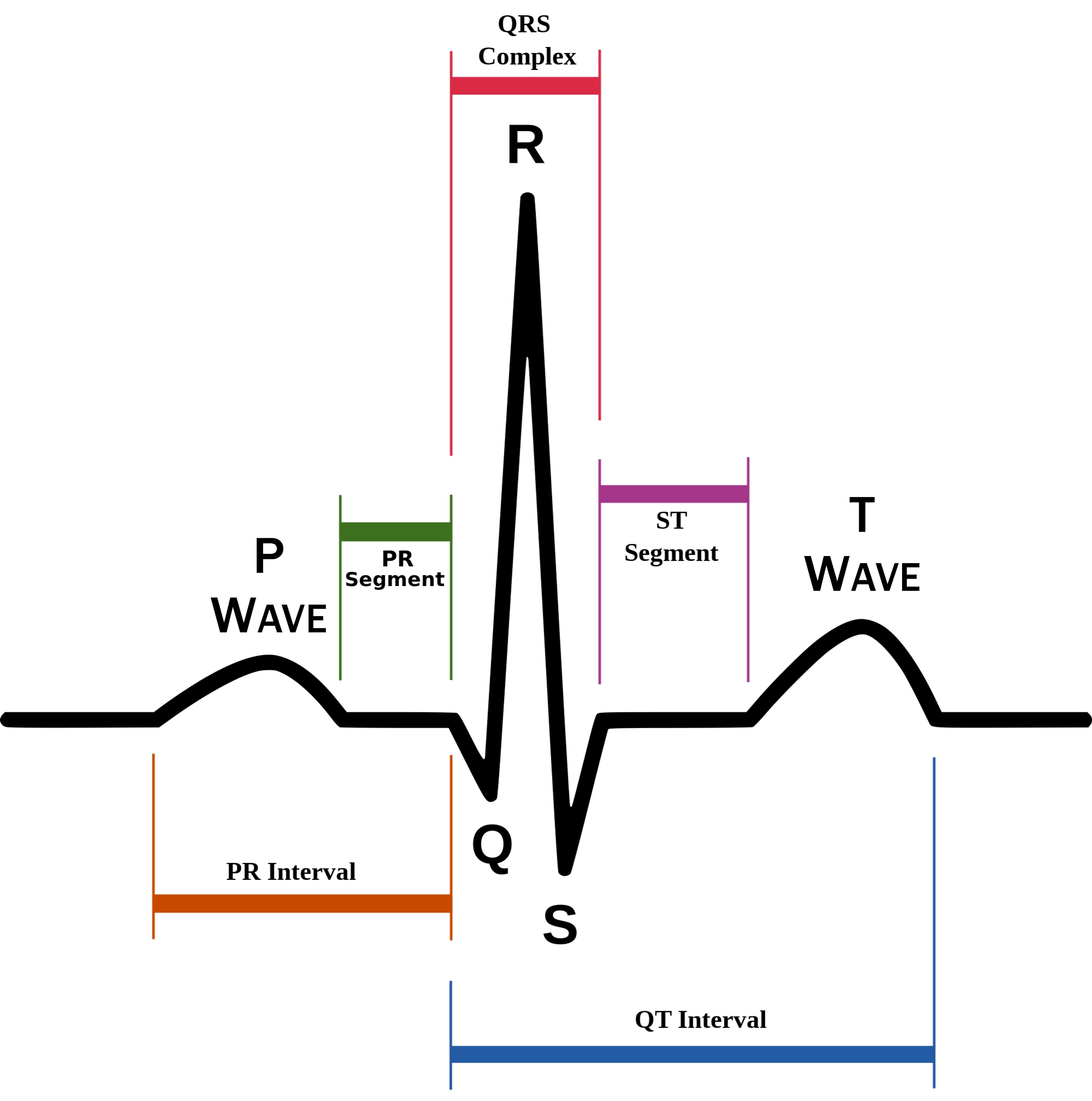
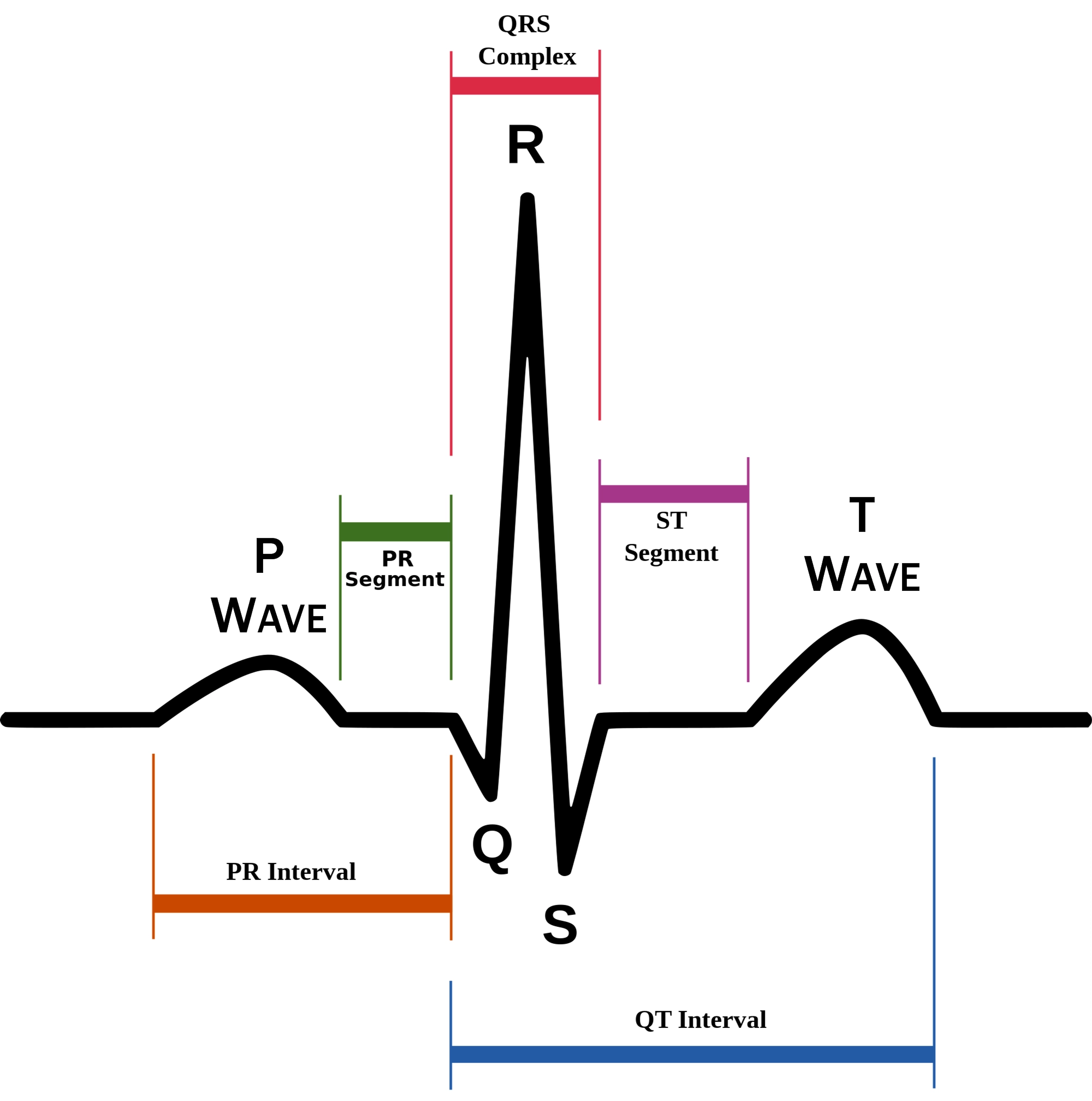
New cards
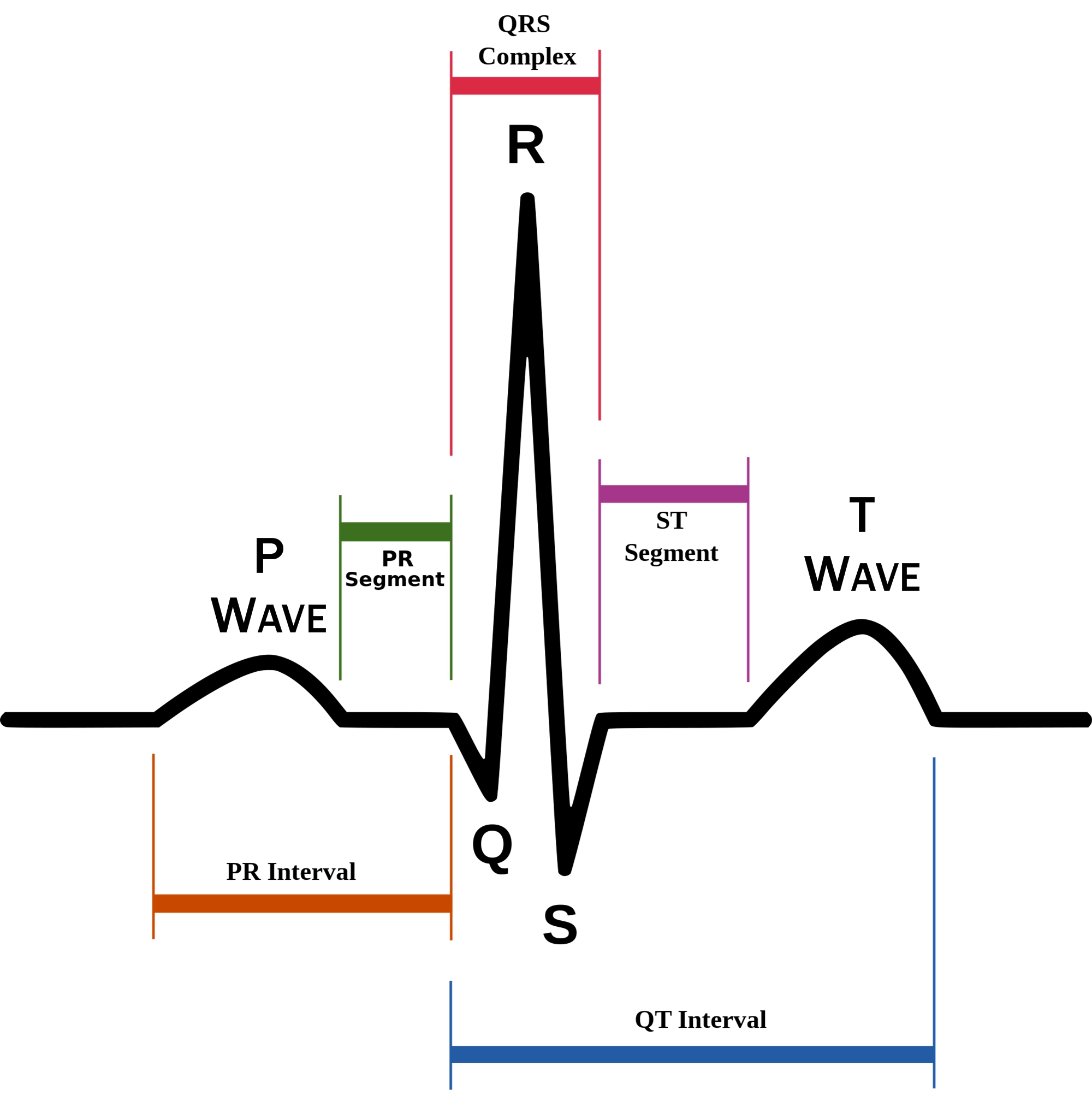
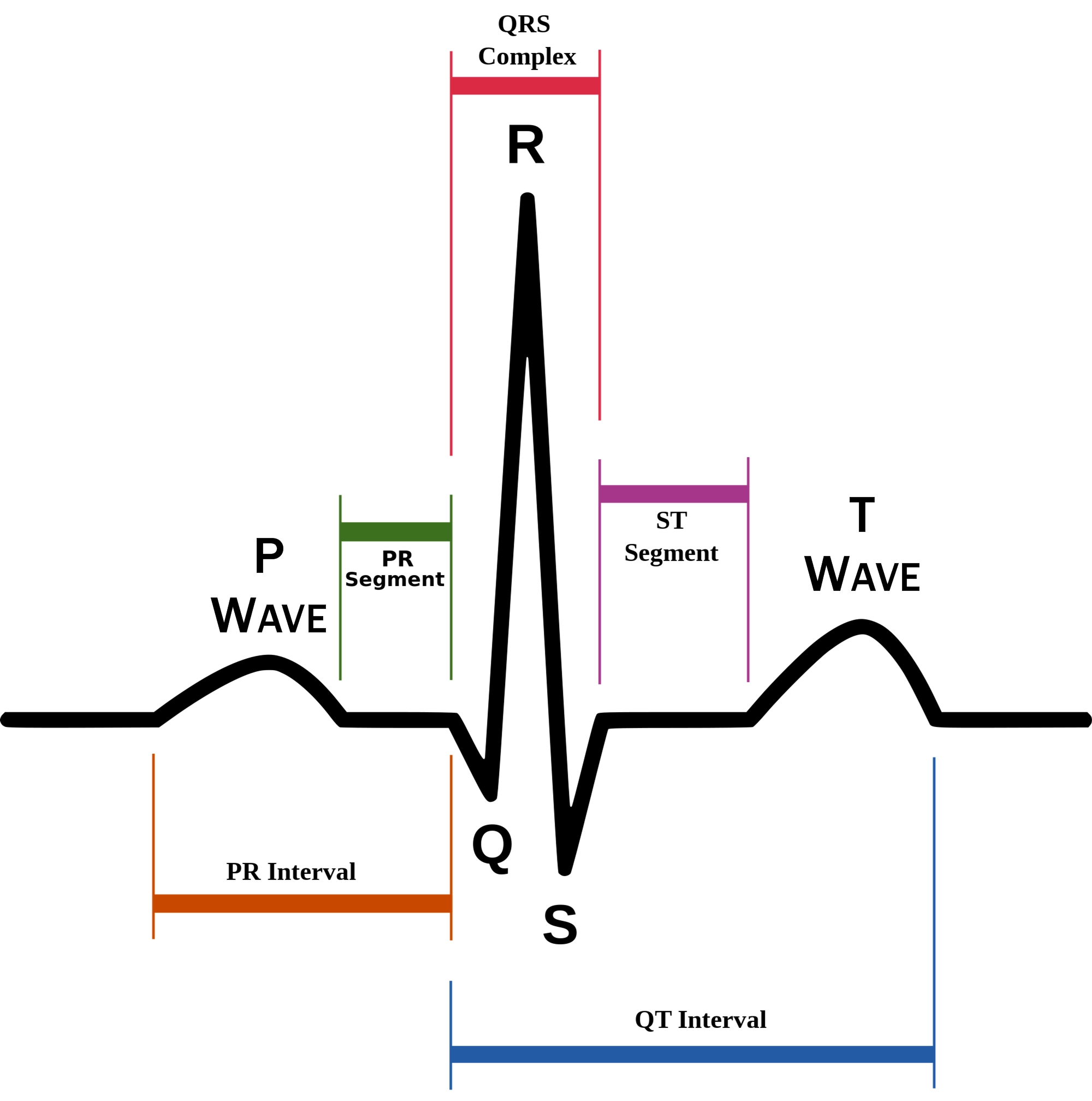
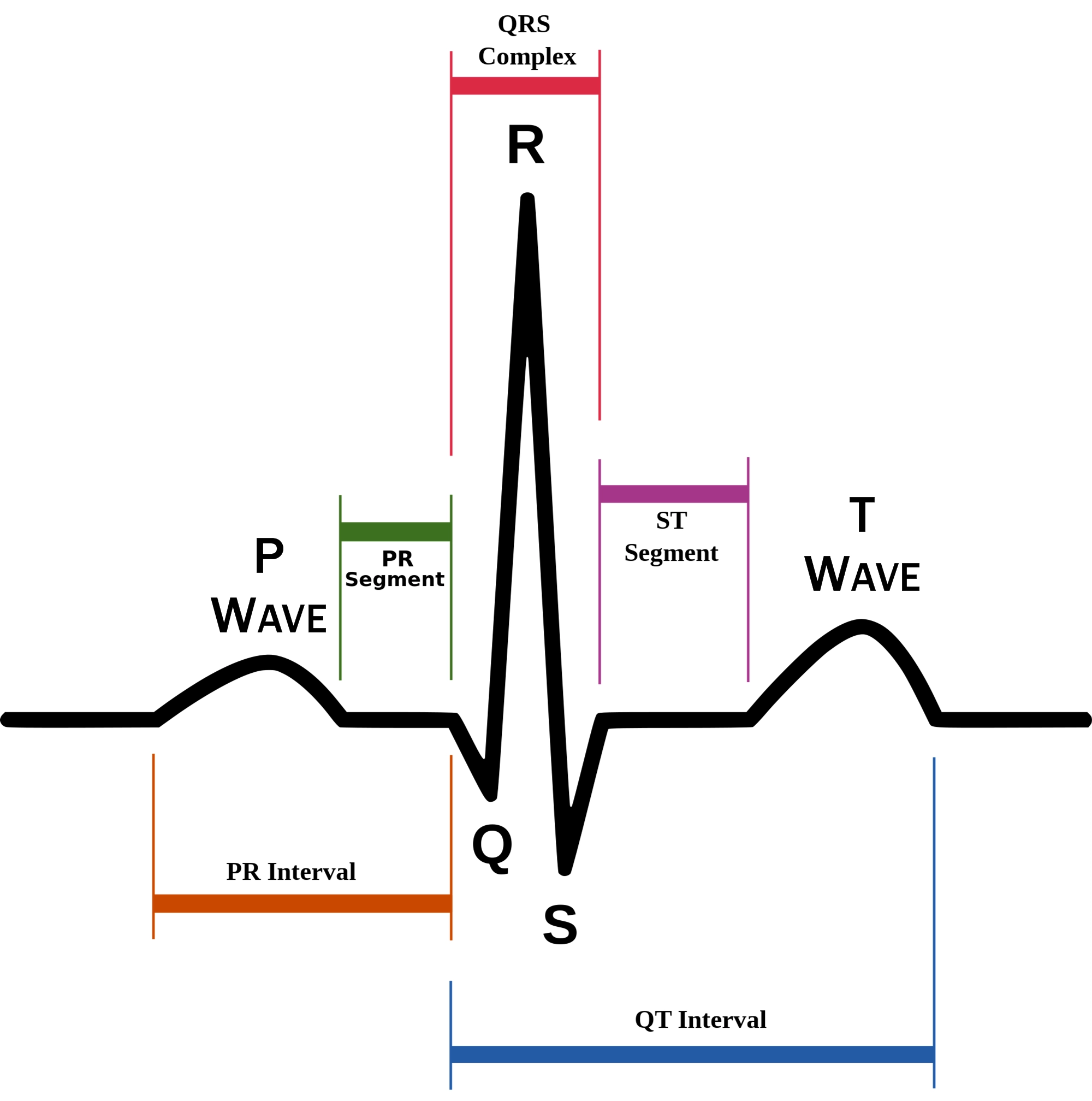
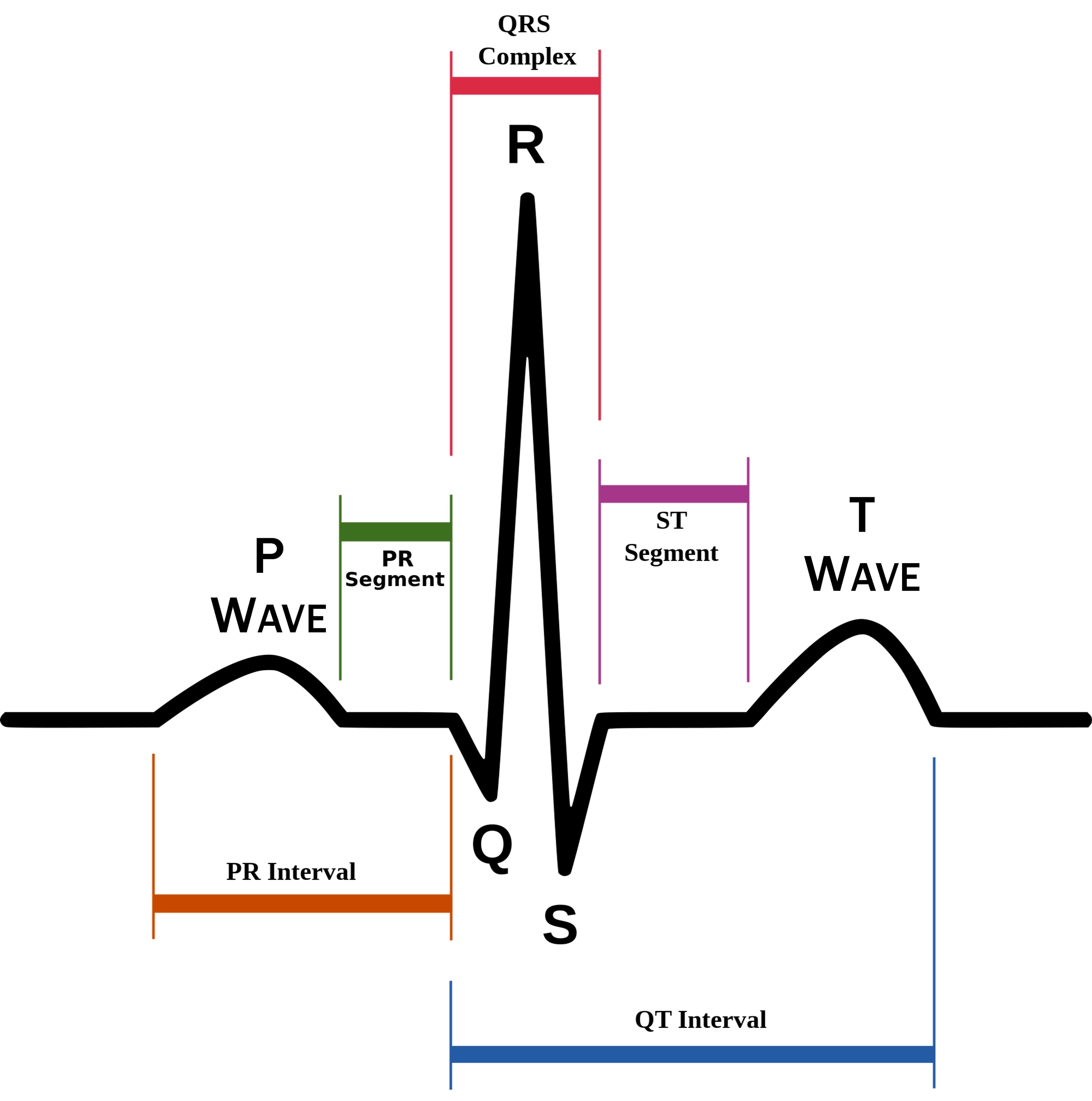
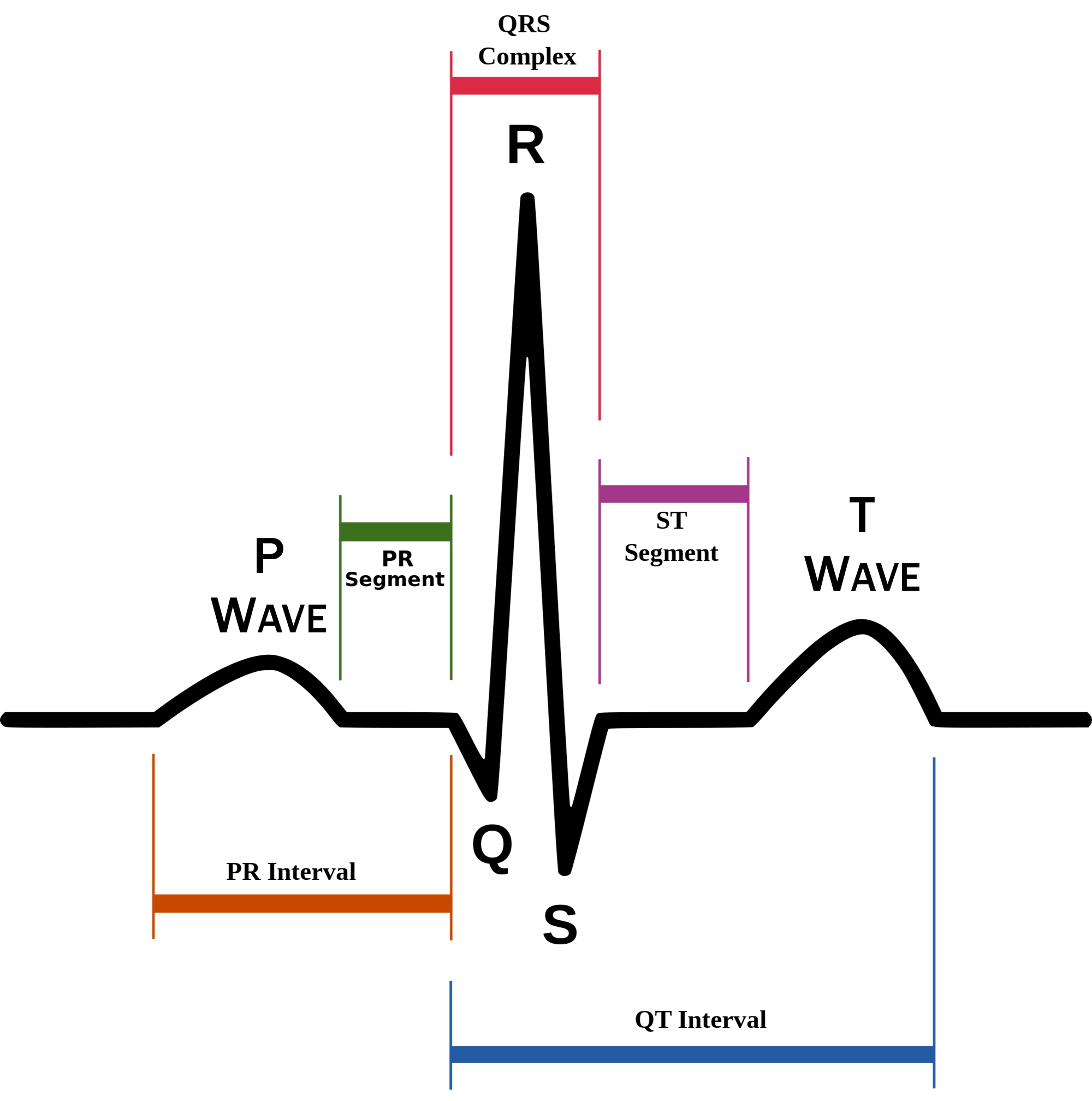
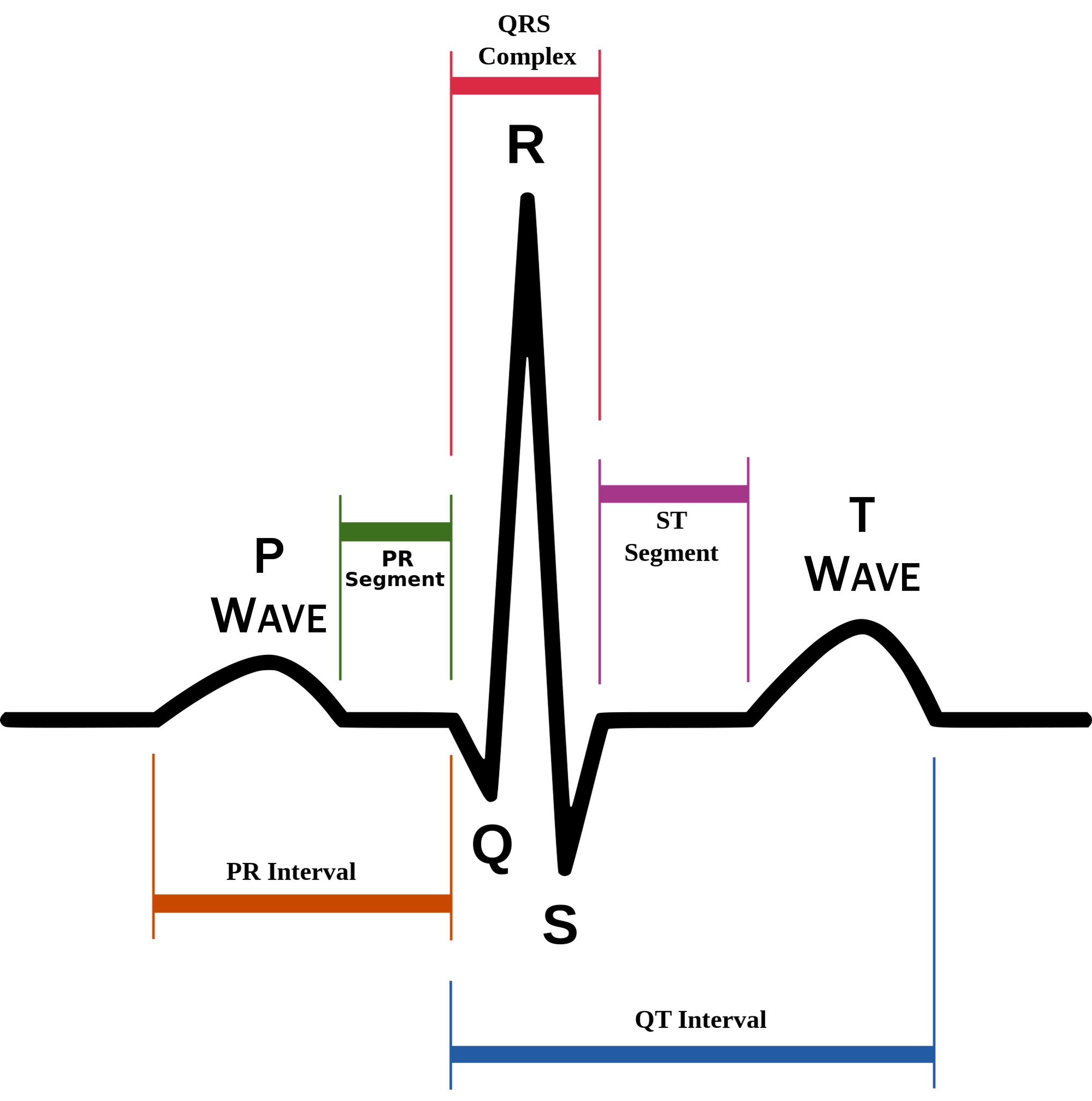
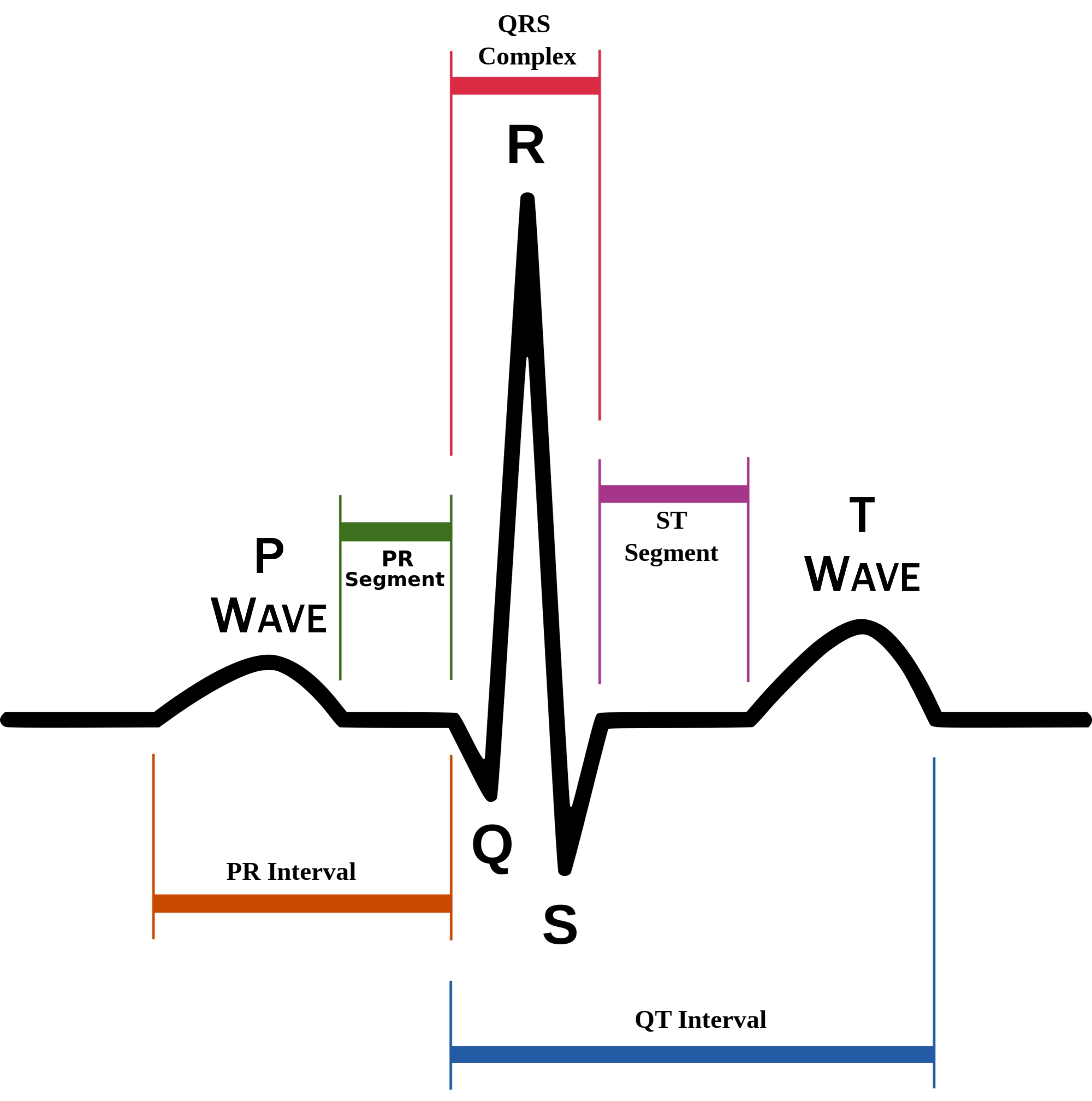
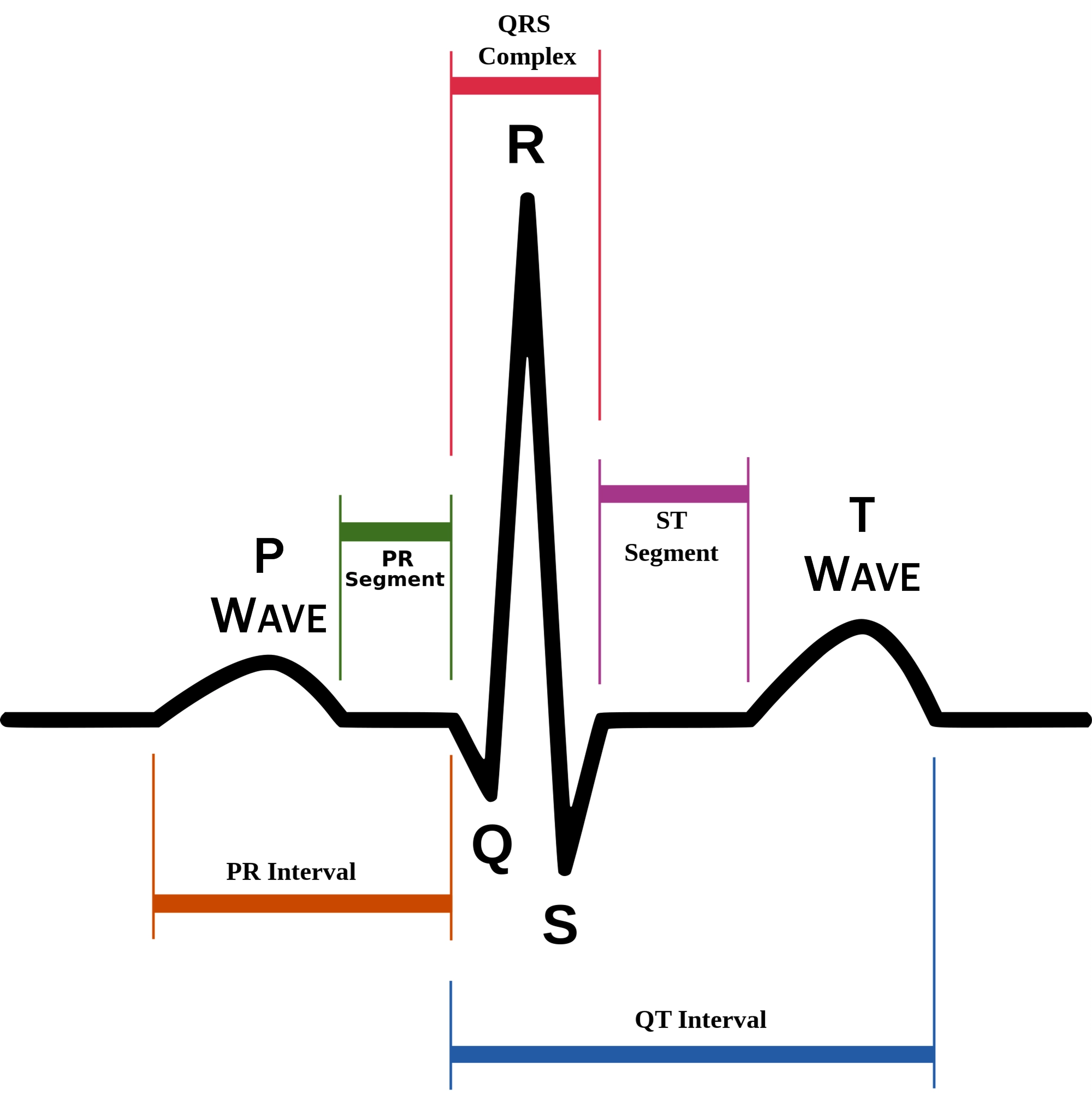
P wave
atrial depolarization (contraction) originating in SA node
74
New cards
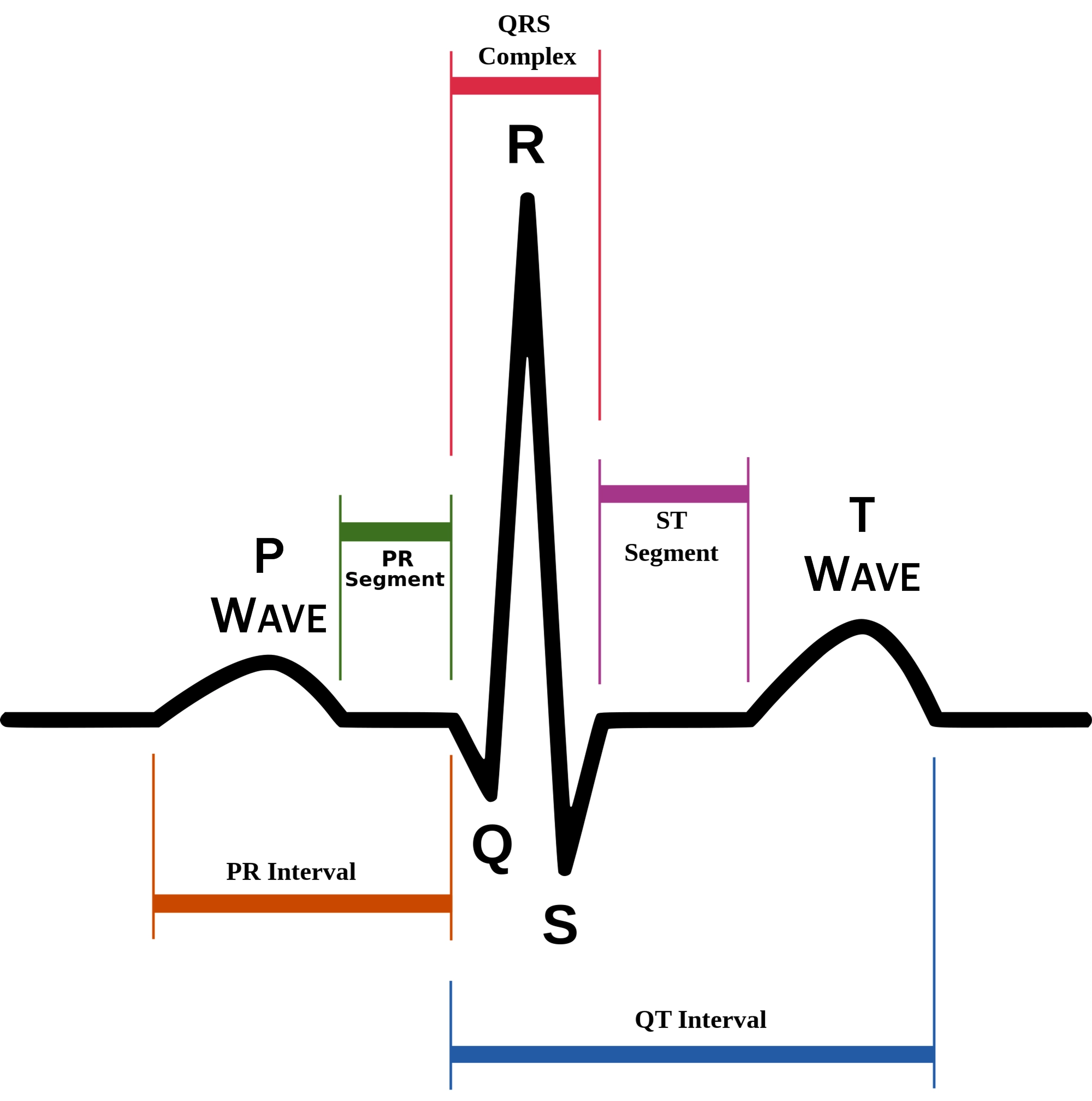
QRS complex
ventricular depolarization.
atria also simultaneously repolarizing.
atria also simultaneously repolarizing.
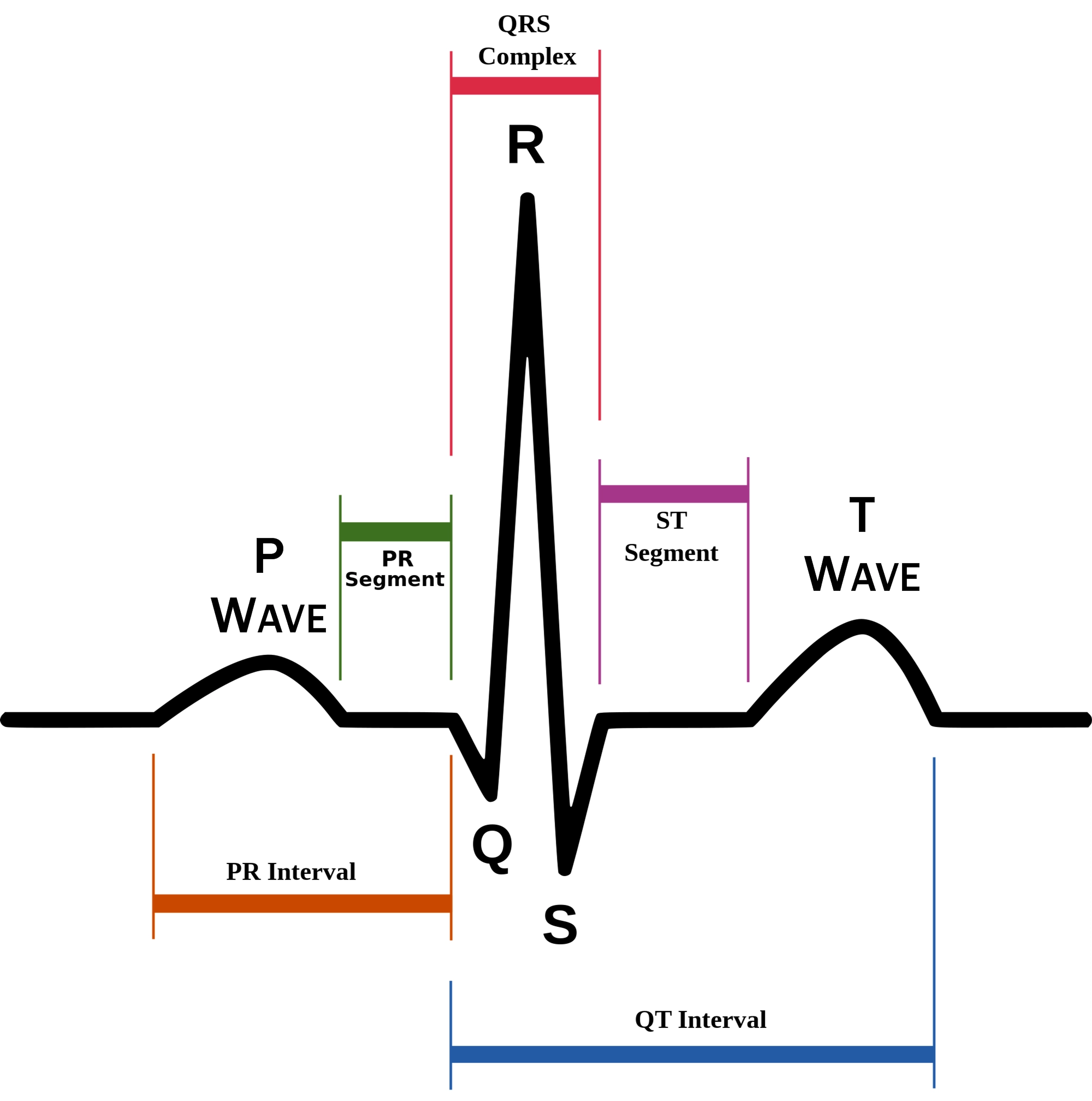
75
New cards
T wave
ventricular depolarization (rest)
76
New cards
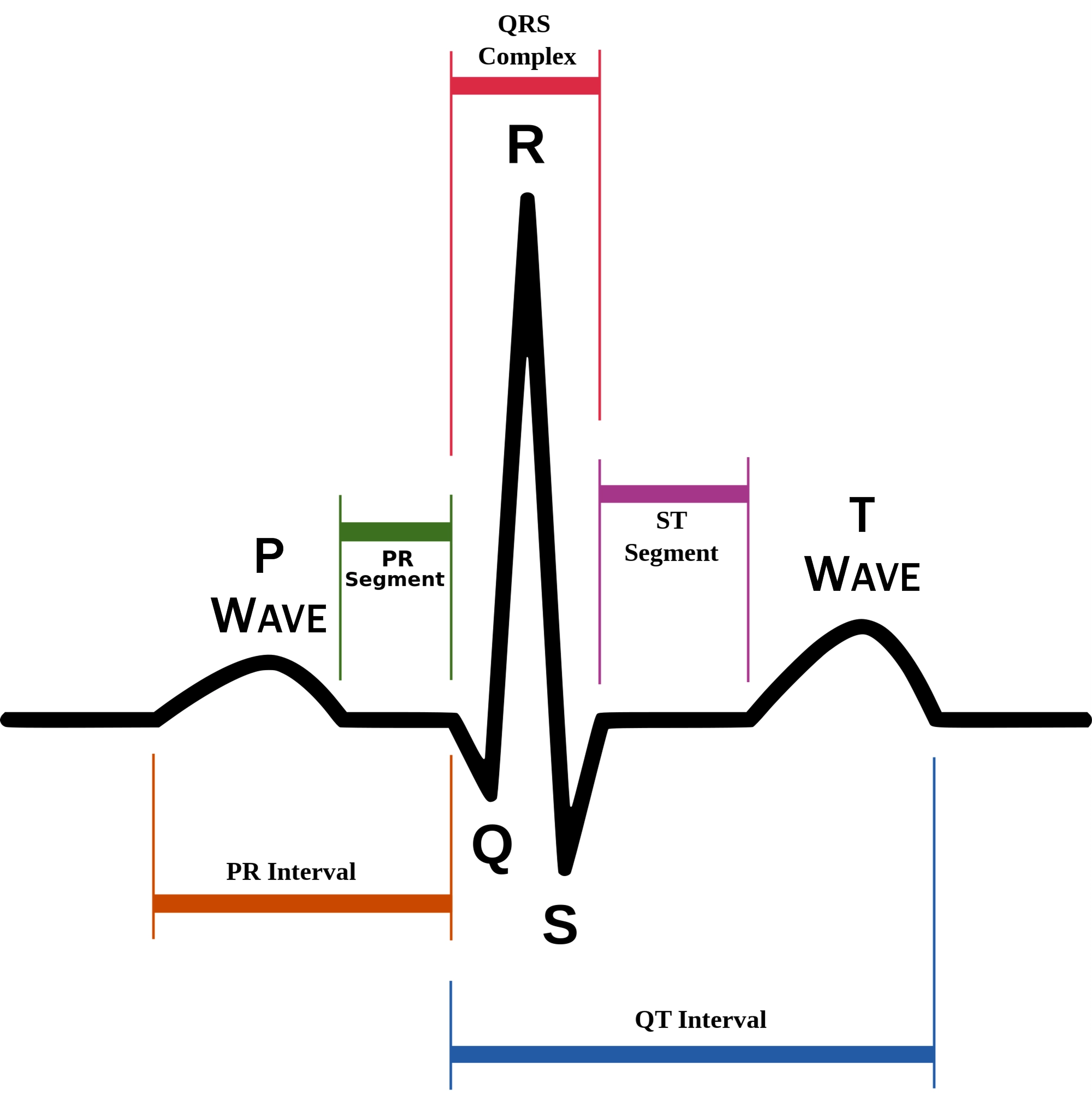
EKG segments
two segments between waves correspond to plateau phases of cardiac potentials (NO ELECTRICAL CHARGE)
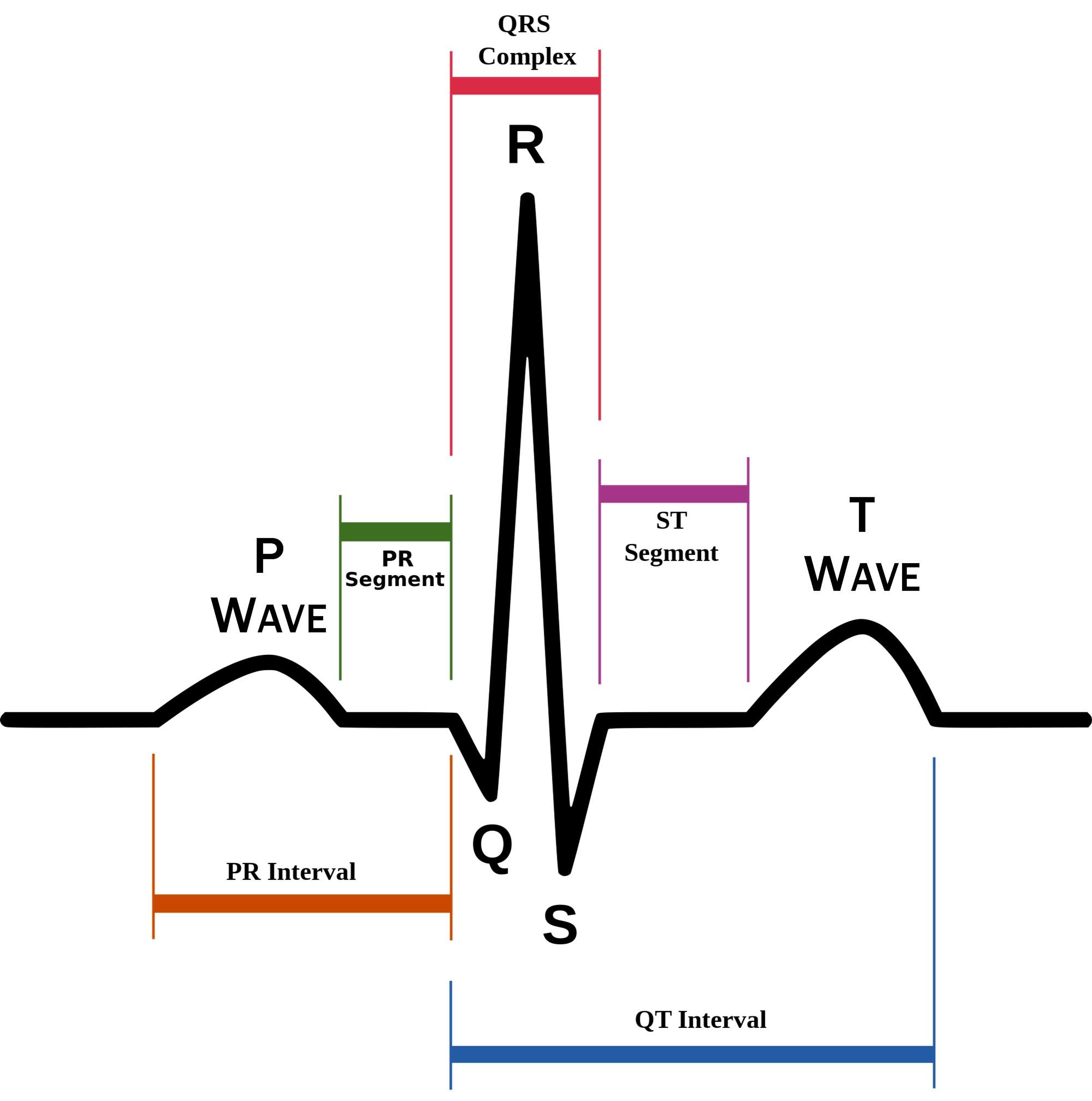
77
New cards
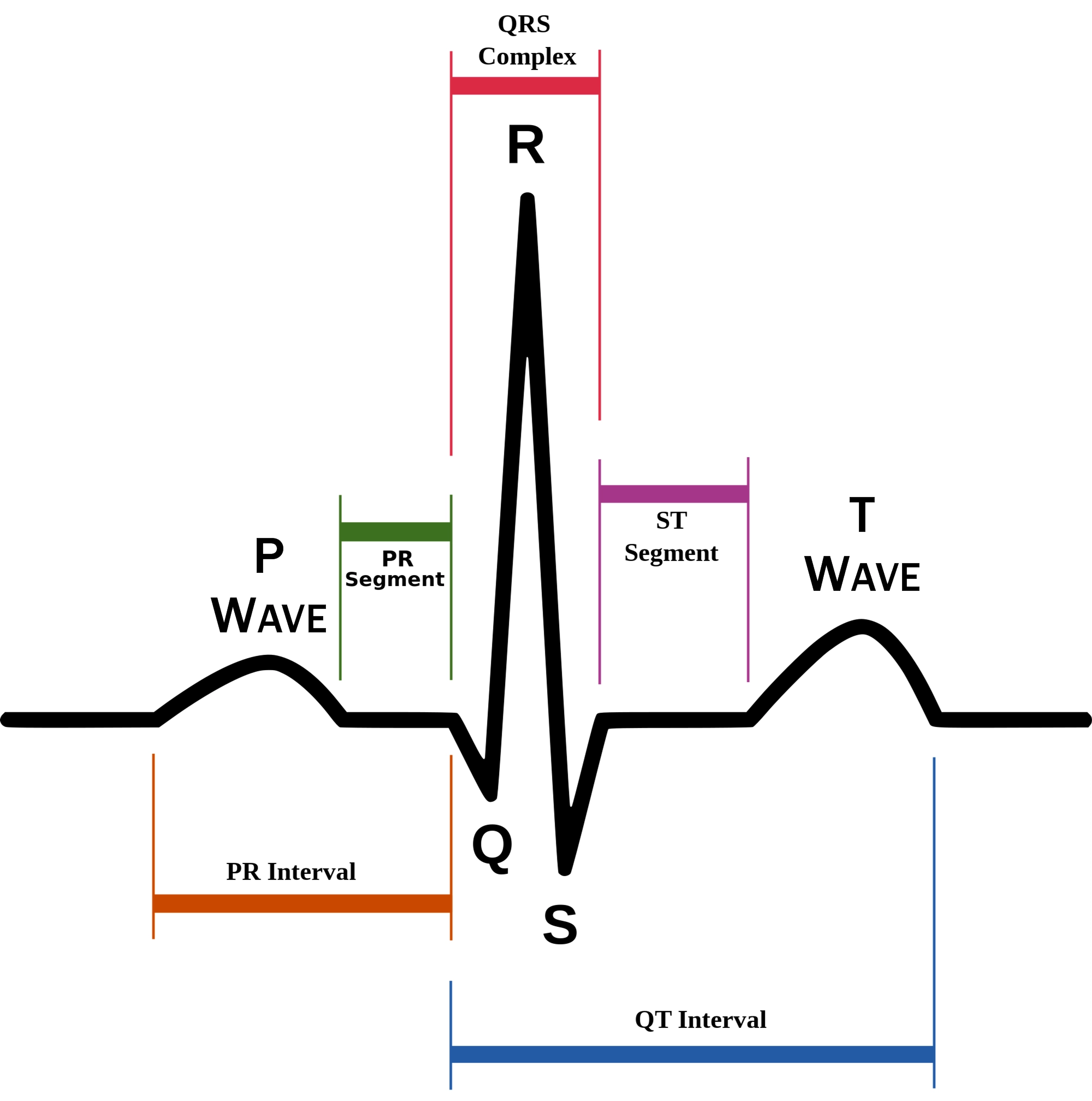
P-Q segment
atrial cell’s plateau (atria are contracting)
78
New cards
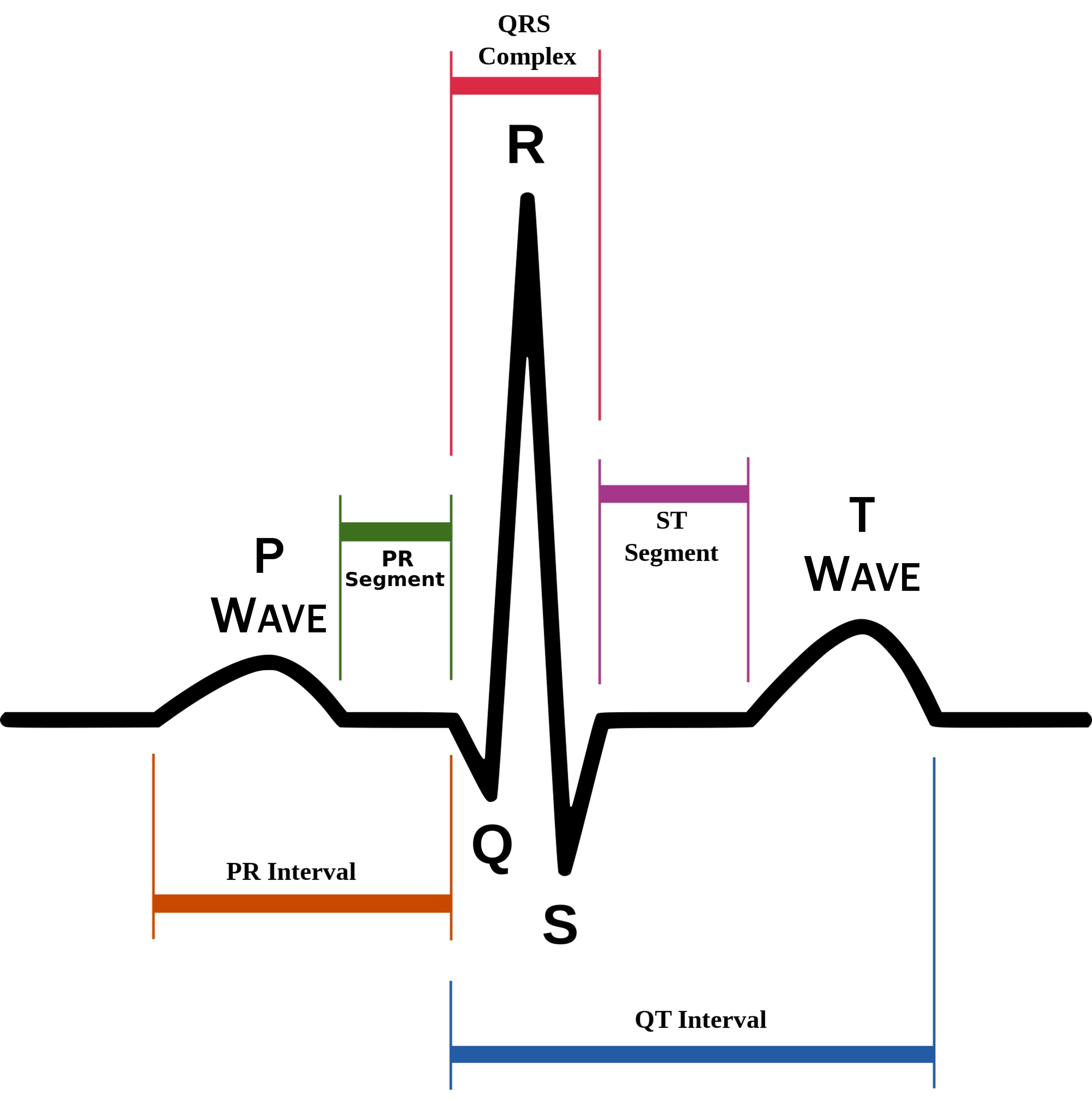
S-T segment
ventricular plateau (ventricles contracting)
79
New cards
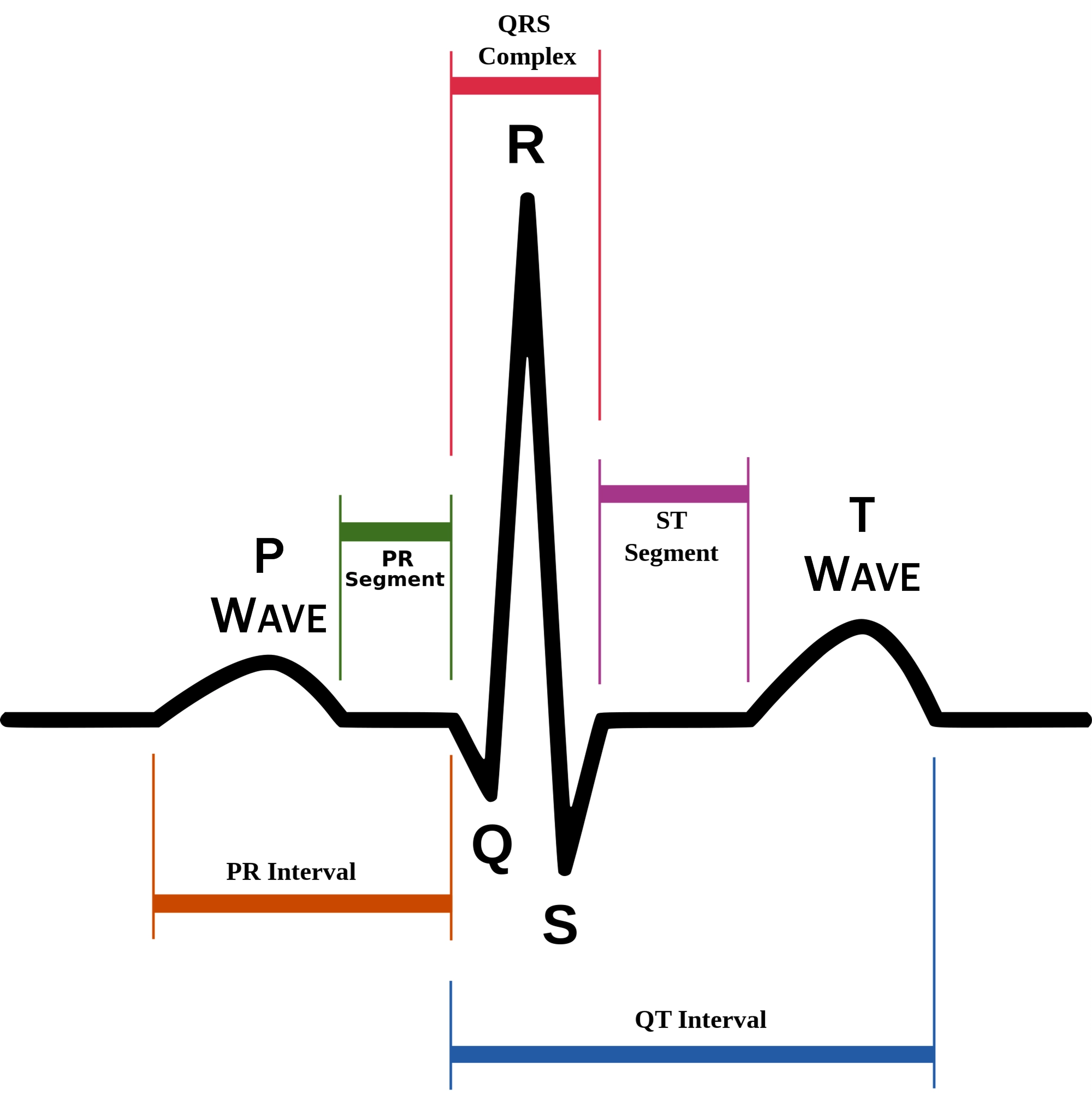
Atrial depolarization
P wave
80
New cards
Atrial plateau- muscle cells of atria contract and relax
PQ segment
81
New cards
Atrial depolarization
not visible on EKG
82
New cards
Ventricular depolarization
QRS wave
83
New cards
Ventricular plateau- ventricles contract and relax
ST segment
84
New cards
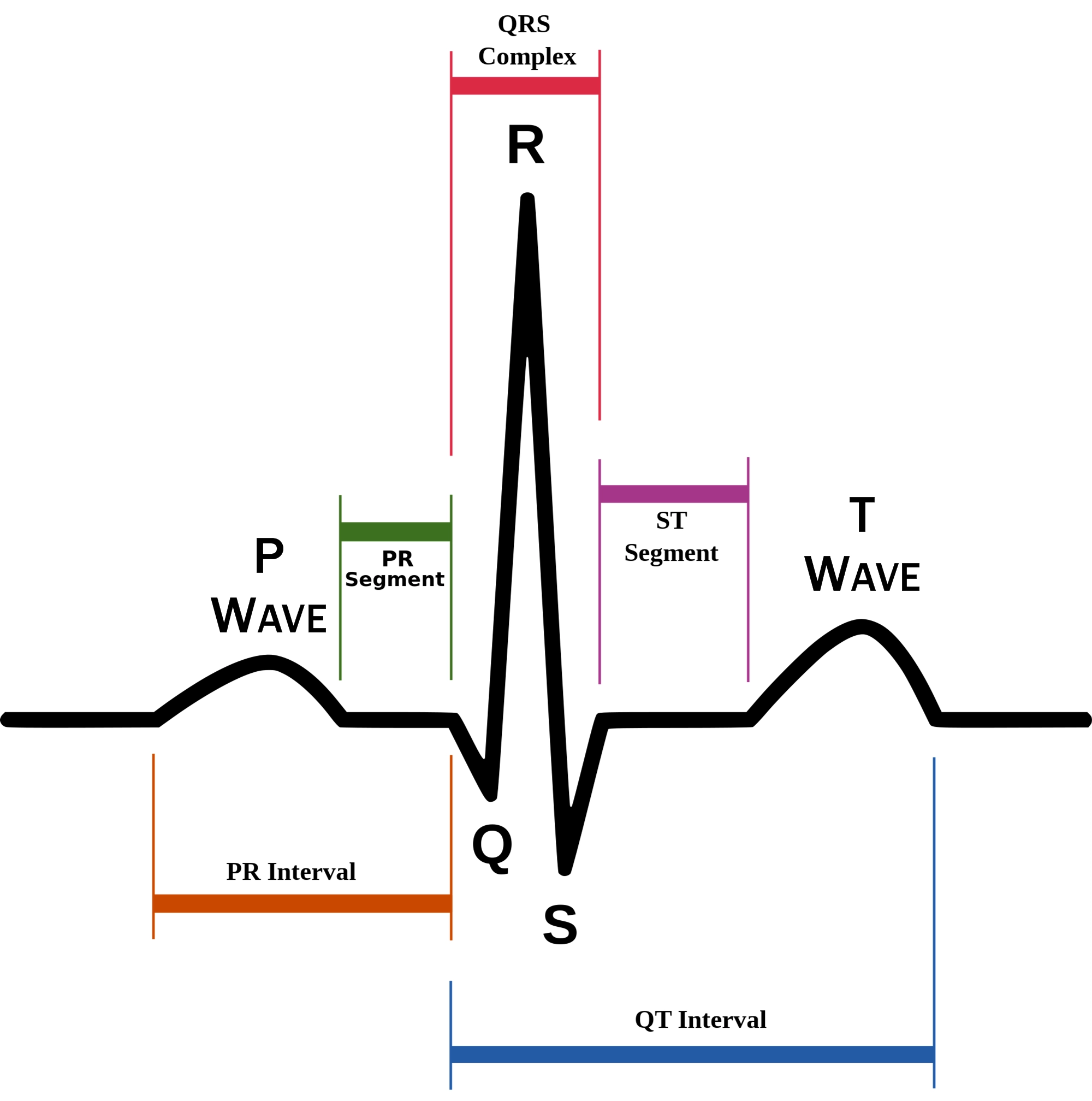
Ventricular depolarization
T wave
85
New cards
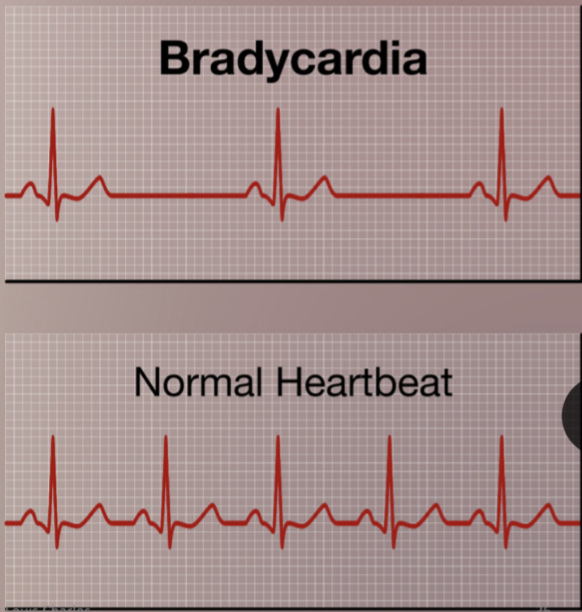
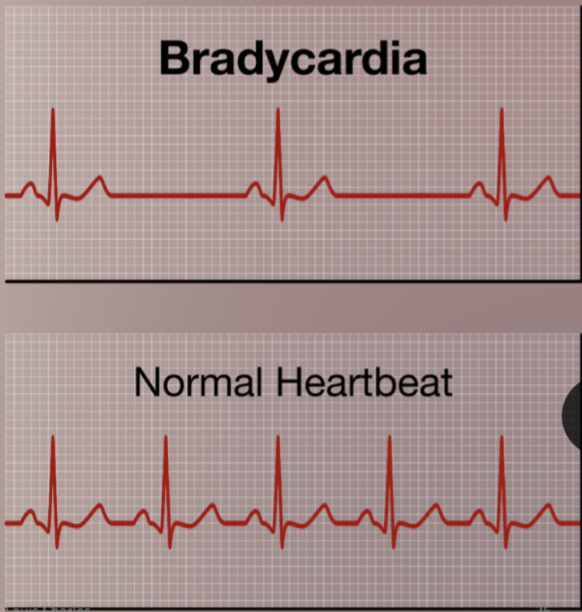
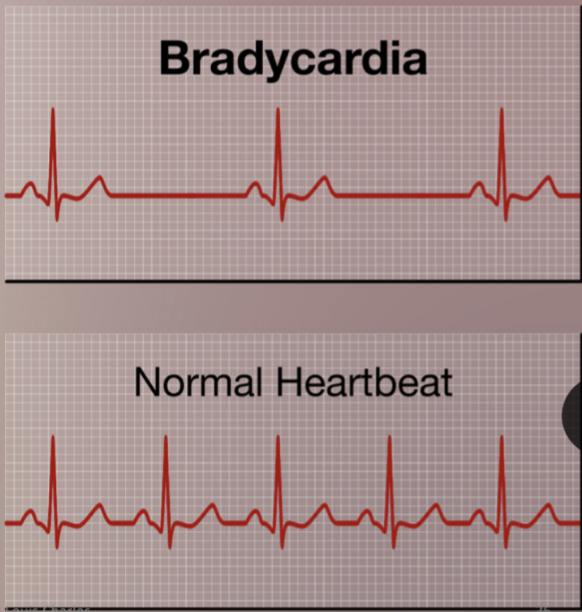
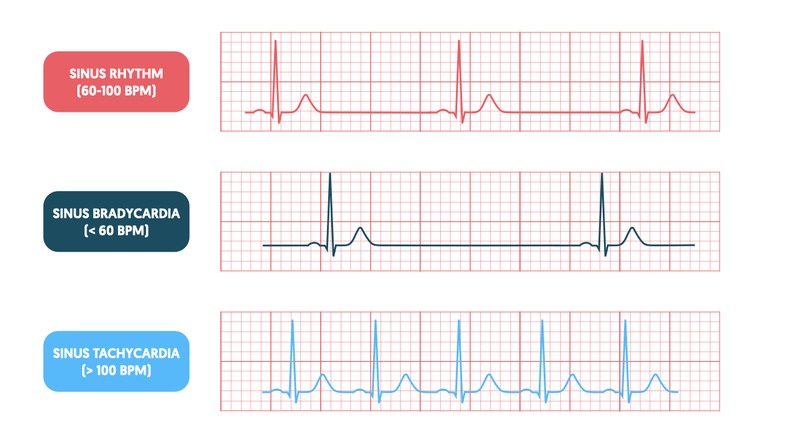
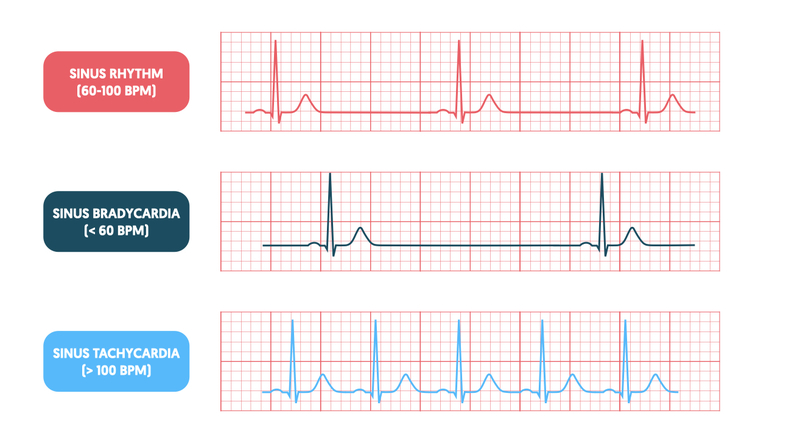
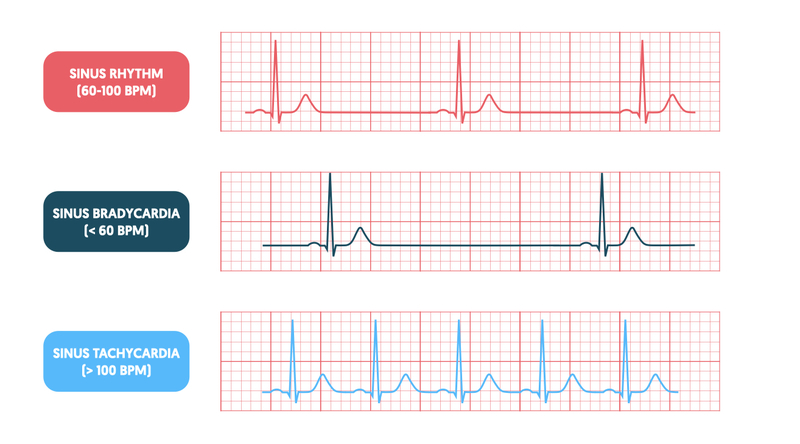
Bradycardia
Persistently low heart rate in adults (normal change in athletes).
Abnormal due to hypothyroidism, electrolyte imbalance, congestive heart failure
Abnormal due to hypothyroidism, electrolyte imbalance, congestive heart failure
86
New cards
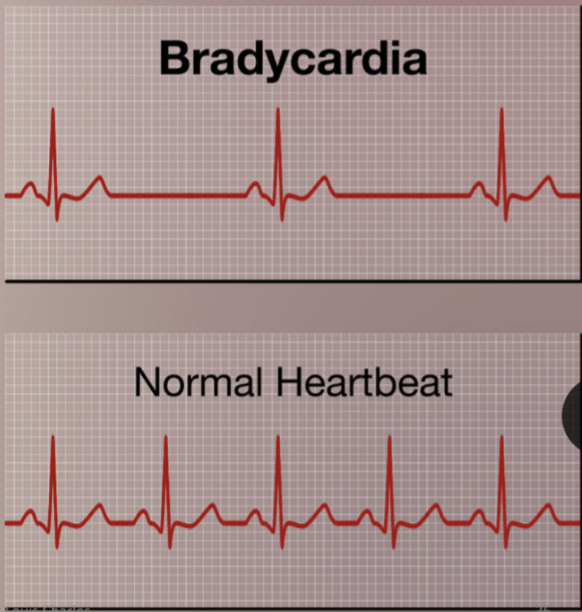
Bradycardia heart rate
below 60 beats/ minute
87
New cards
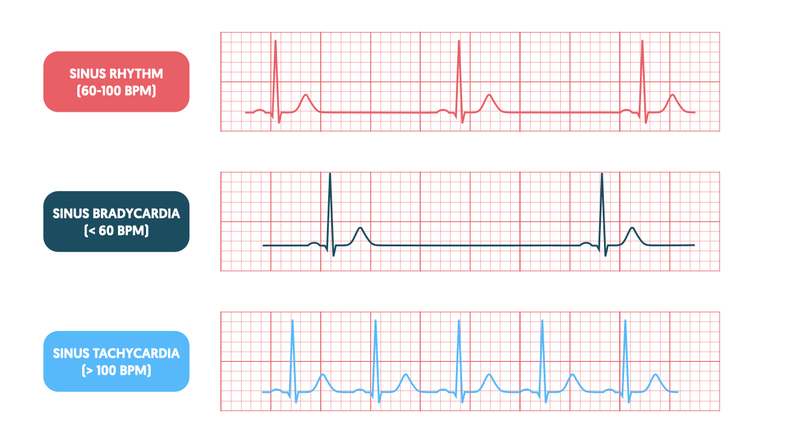
Tachycardia
Persistently high resting heart rate
Caused by heart disease, fever, anxiety
Caused by heart disease, fever, anxiety
88
New cards
Tachycardia heart rate
over 100 beats/ minutes
89
New cards
Types of blood vessels
arteries
capillaries
veins
capillaries
veins
90
New cards
Arteries blood flow
Oxygenated blood away from heart > tissues
91
New cards
Do arteries contain a valve?
No. Blood moves by pressure of contraction of heart
92
New cards
Veins blood flow
From body toward the heart
93
New cards
Valves are present in most veins
True
94
New cards
Systematic veins
transport blood low in oxygen
95
New cards
Pulmonary veins
transport blood high in oxygen
96
New cards
Vessels are composed of layers called
tunica
97
New cards
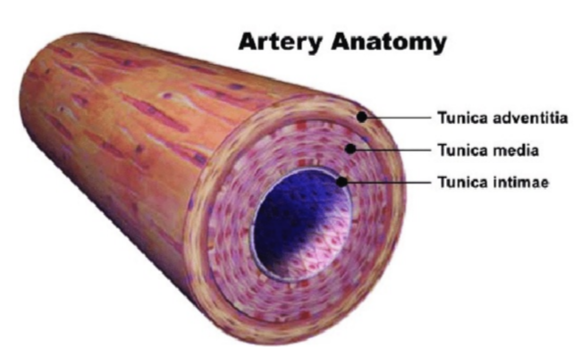
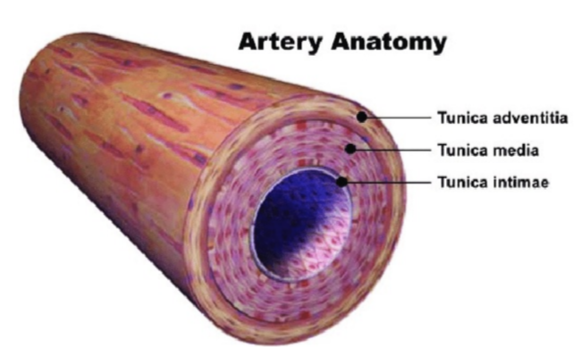
tunica intima/ interna
innermost layer of blood vessel
98
New cards
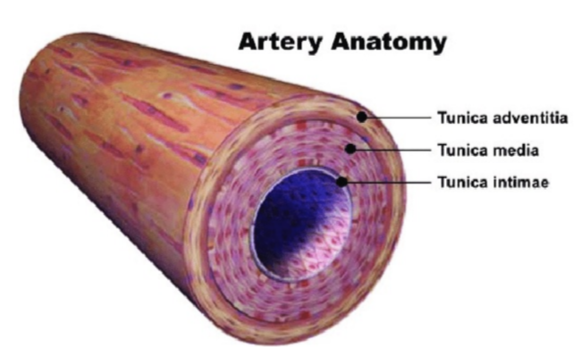
tunica media
middle layer
thicker, muscular wall
mostly smooth muscle + elastic tissue
thicker, muscular wall
mostly smooth muscle + elastic tissue
99
New cards
Vasucular endothelium
inner cellular lining of blood vessels.
in direct contact with blood.
inside lining of lumen.
allows for smooth blood flow.
increase diameter of artery to increase blood flow.
found in large arteries.
one cell thick- simple endothelium.
in direct contact with blood.
inside lining of lumen.
allows for smooth blood flow.
increase diameter of artery to increase blood flow.
found in large arteries.
one cell thick- simple endothelium.
100
New cards
Vascular endothelium maintain
vascular homeostasis