Biology Lab Practical #2
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
meiosis
cellular reproduction
strawberry DNA lab - how was the DNA extracted
smash the berries in bag and add in DNA extraction buffer and alcohol to precipitate the DNA
strawberry lab - how did you take the DNA out of the cone?
use a small stick and gently twirled it up
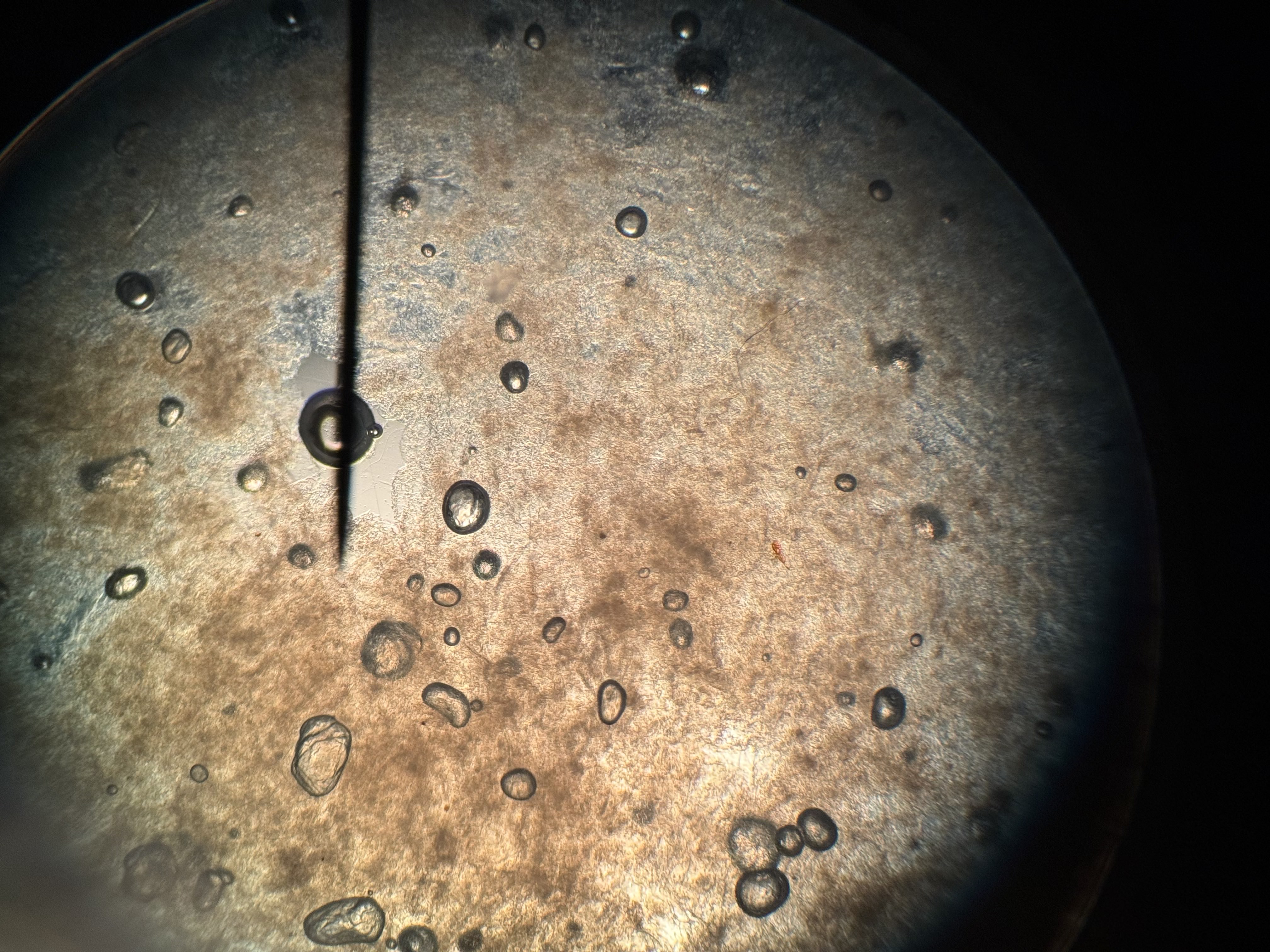
what is this?
strawberry DNA with no stain
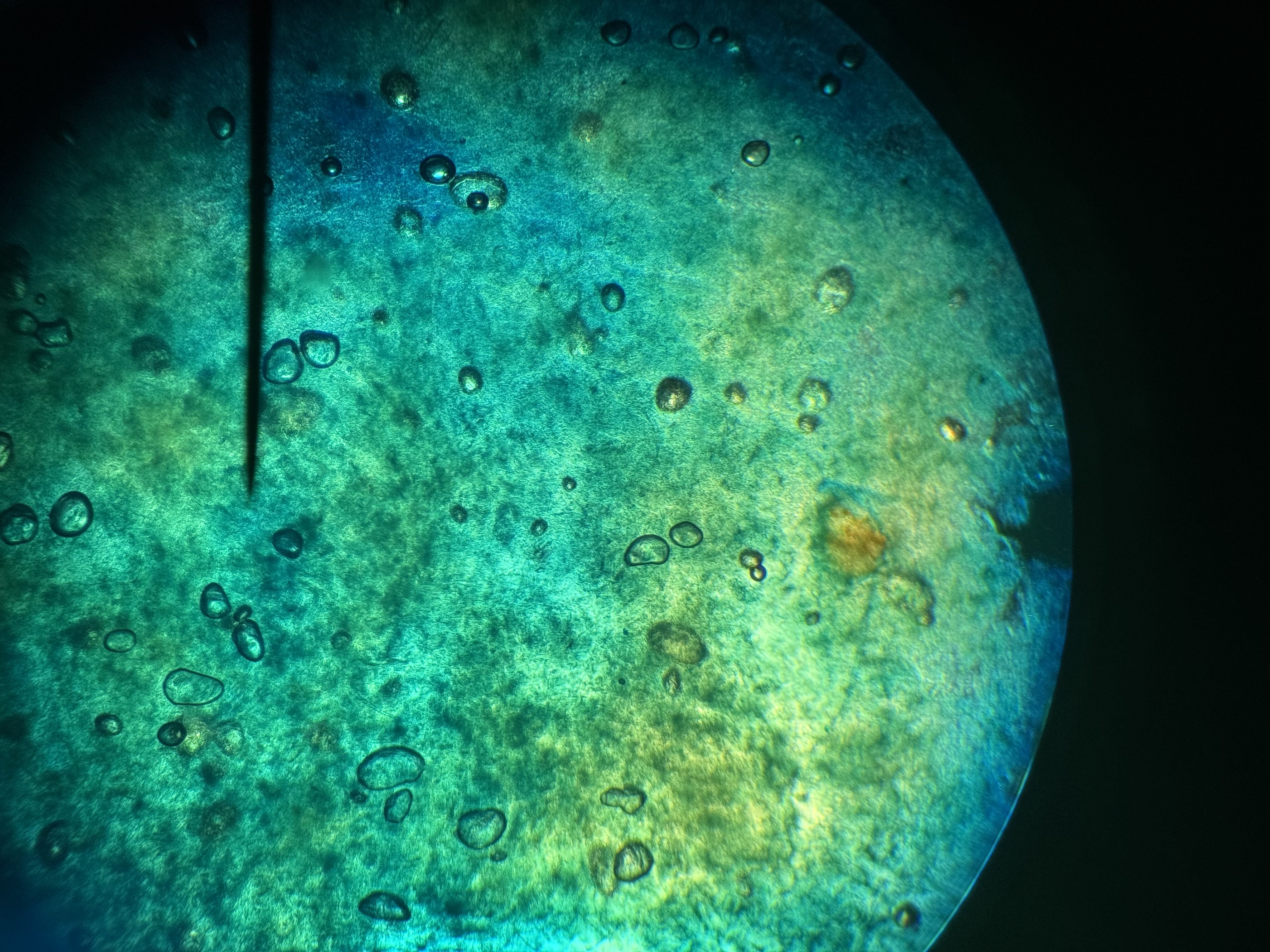
what is this?
strawberry DNA with stain
natural selection lab - what did we do
throw down sticks in grass and look for them
natural selection lab - what did we hypothesize?
that the sticks that were really dark would be easy to find
gel lab - what is the power supply
electrical current that passes through gel and allows DNA to move
gel lab - what is the gel box
plastic box that the gel is in and connects to power supply
gel lab - what is the buffer solution
electrolye solution that conducts electricity across the gel
gel lab - for DNA, what side do we set the combs in?
the negative side of the gel since DNA is charged and will go to the positive side
gel lab - the larger molecule substances will travel _____ comparatively to the smaller molecule substances
less
gel lab - what does it mean if something has traveled to the edge of the gel
it is the smallest molecule
gel lab - T.A.E. buffer solution stands for?
tris acetate edta soltution

gel lab - what is this?
micropipette

gel lab - what is this?
micropipette tips
gel lab - how can you tell if the power supply/set up is working properly once turned on?
the buffer begins to bubble
gel lab 1 - why is it important to place the wells in the center of the gel?
to allow for negative molecules to go towards the positive and vice versa
gel lab 1 - what is the purpose of the comb?
to make the wells to put the substance in
gel lab 1 - what are ways that can harm the micropipettor?
using wrong tip or letting liquid into barrel
gel lab 1 - what did we do? what did we put in the gels?
dye mixtures
gel lab 1 - what does it mean if bands were of the same color and were in the same place from the combs?
they came from the same dye
gel lab #2 - what did we do?? what did we put in the gels?
same DNA sample with different enzymes
gel lab 2 - what enzymes did we use?
BamHI, EcoRI, and HindIII
gel lab 2 - what was the control for this experiment
DNA with no enzyme

gel lab 2 - how can we make sure that we get all of the sample at the bottom of the tube?
spin in microfuge

gel lab 2 - how can we mix two solutions that are of very small quantities?
use microfuge
gel lab 2 - how long did we incubate DNA and enzyme for and at what temp?
45 minutes at 37 celsius
gel lab 2 - why did we add dye to the DNA samples?
without it, the samples would be clear and hard to monitor
gel lab 2 - what is special about the dye that we used for this lab?
can be exposed to UV light so we can see the bands
gel lab 2 - if a enzyme cut a DNA piece 4 times, how many pieces are made?
5
gel lab 3 - what did we do in this lab?
tried to identify crime scene DNA
gel lab 3 - what did we add to each DNA sample?
enzyme
gel lab 3 - why did we add enzyme to each DNA sample?
to see whether or not the DNA cut sites matched up
gel lab 3 - how did we stain the gel?
put it in dye and rinse with water
gel lab 3 - who was the culprit
suspect #3
last lab - what did we do?
put plasmid in DNA and put in agar plates with amp and no amp
last lab - what was the goal?
to see whether the DNA would take in the plasmid DNA and show it
last lab - how do we know that the DNA was taken in?
green proteins should be seen
last lab - in what case would there be no green proteins visible on the agar plate but should be there?
agar plate with plasmid and no amp
last lab - why is it that we cannot see the green proteins in the agar plate with plasmid and no amp?
there is no amp so the wild type bacteria grows over the green proteins since there is so much of it
last lab - what method did we use to get the plasmid dna into the bacteria?
heat shock
last lab - how can we make sure that the green proteins came from the plasmid?
take DNA from agar plate with green protein and the plate with amp and no growth and put into gel electrophoresis and look for any extra cuts on the green protein
last lab - what to do if see extra cut on green protein?
cut it out and send for sequencing to confirm that it is from plasmid
last lab - why do the green proteins have wild type colonies around it?
with the proteins comes the amp enzyme so where the protein is, the enzyme decreased the concentration of amp, allowing the wild type bacteria to survive
last lab - what bacteria did we use?
e coli
last lab - what did the agar plates have in them?
luria broth
last lab - what did we put into the tubes to help incubate the bacteria?
cold calcium chloride
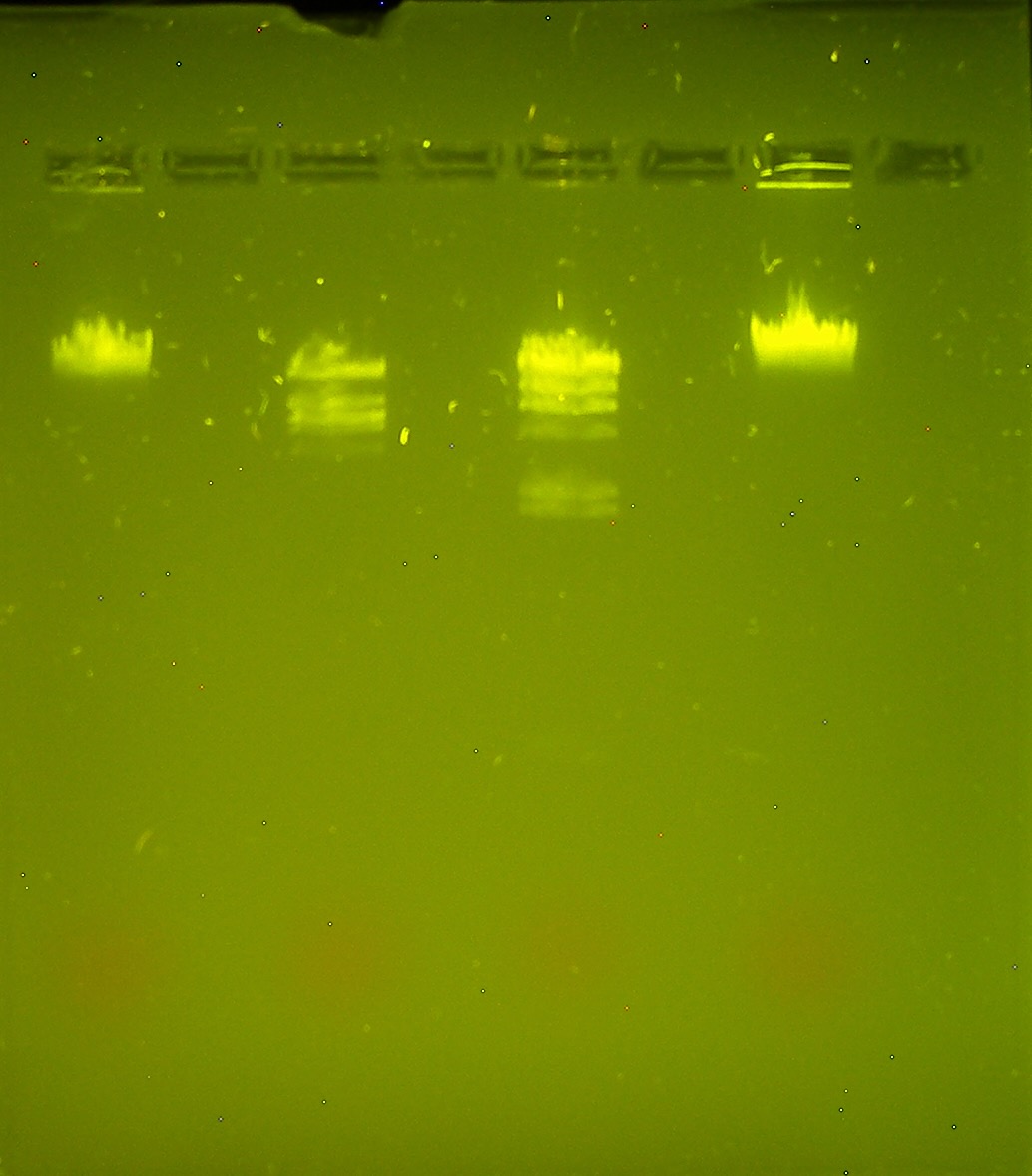
gel lab 2 - why did the BAM enzyme not cut?
it denatured
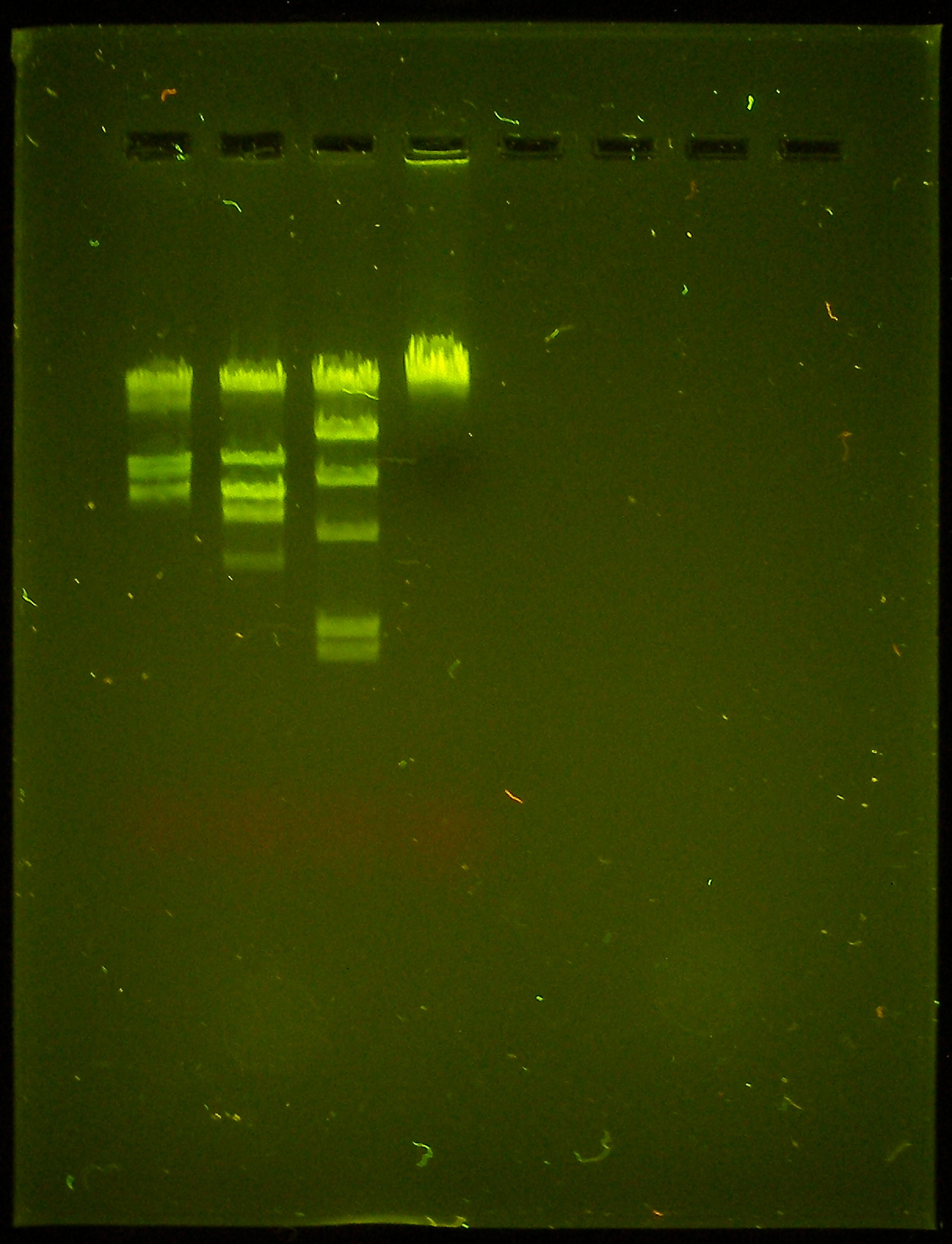
gel lab 2 - name the enzymes from left to right
BamHI, EcoRI, HindIII
gel lab 2 - why do bacteria have restriction enzymes?
to cut dna infected by phages
gel lab 2 - how many cuts were made by BamHI?
4
gel lab 2 - how many cuts did HindIII make?
7
gel lab 2 - what is restriction mapping?
use bands to map out relative size of other bands
last lab - what is a marker gene?
a piece of DNA included on same plasmid as gene of interest
last lab - what is ampicillin?
antibiotic that kills bacteria
exp 13 - how many haploid cells come from meiosis of 1 diploid cell?
4
exp 13 - how many chromosomes are in each haploid (human) cell after meiosis?
23
exp 13 - homologous chromosomes
non identical chromosomes with different alleles for same genes
exp 13 - sister chromatids
copies of each of the 46 chromosomes
exp 13 - prophase 1
chromosomes condense and form tetrads
exp 13 - synaptomal complex
proteins between homologous chromosomes in tetrads
exp 13 - what is synapsis
chromosomes in tetrads cross over
exp 13 - what is chiasmata
points of cross over
exp 13 - recombination nodules
areas where they mediate DNA recombination
exp 13 - centromere
area where kinetochore latches on
exp 13 - kinetochore
protein that pulls chromosomes
exp 13 - at what stage do tetrads form?
after prophase 1
exp 13 - nondisjuction
separation of chromosomes goes wrong
exp 13 - do x and y chromosomes cross over?
no
exp 13 - what sex chromosomes can cross over?
x and x or y and y
exp 14 - law of segregation
paired genes must segregate equally into gametes
exp 14 - law of independent assortment
the passing of genes is not influenced by other genes
exp 14 - dihybrid cross
cross between two true breeding parents
exp 14 - character
characteristic of an organism
exp 14 - locus
area on chromosome where gene is found
exp 14 - genes
heritable information in form of nucleotides
exp 14 - incomplete dominance
heterozygote is intermediate between two homozygotes
exp 14 - codominance
both alleles are expressed
exp 14 - epistasis
one gene modifies other gene
exp 14 - traits on homologous chromosomes are _________
not inherited independently
exp 14 - how can you tell if a trait is recessive on a pedigree?
it skips a generation
exp 15 - dna is made of linked _____
nucleotides
exp 15 - dna must be separated from blood cells before it can be sequenced. This also helps in doing what?
purifying DNA in order to clone a gene
exp 15 - why add the extraction buffer to the smashed strawberry??
to dissolve the cell and nuclear membrane
gel lab 1 - what is gel electrophoresis used for?
separating molecules of different size and charge
gel lab 1 - what gel do we use for gel labs?
agarose gels
gel lab 1 - how do pcr and gel electrophoresis work together?(in case of paternity test)
pcr causes dna to repeat in a chosen area and then put through a gel to see whether or not the short tandem repeats of the father and child match
gel lab 1 - microsatellites are the same as _____
short tandem repeats
gel lab 2 - molecular cloning
reproduce fragments of genome
gel lab 2 - transgene
foreign DNA
gel lab 2 - restriction endonucleases
recognize sequences and cut them out as defense
gel lab 2 - plasmids with foreign dna inserted in them
recombinant dna molecules
gel la 2 - recombinant proteins
proteins made from recombinant dna
exp 20 - what does competent mean in relation to bacteria?
ability of bacteria to pick up dna from environment
exp 20 - transformation
new dna entering a cell
exp 20 - what was the gene of interest?
pgreen
exp 20 - how did the plasmid enter the cell?
heat shock
exp 20 - what is a marker gene
way to identify that gene of interest has entered cell and can grow