Bacterial Transformation Using pGLO in E. Coli
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What is the purpose of performing bacterial transformation experiments?
To practice methodology and appreciate the significance of bacterial transformation for producing useful human proteins like insulin.
Which strain of bacteria is used in the transformation experiment?
An unharmful strain called Escherichia Coli or E. coli.
What is the name of the genetically engineered plasmid used in the experiment?
pGLO.
What are the three genes of interest in the pGLO plasmid?
1. A mutant GFP gene (Green fluorescent protein) from jellyfish. 2. A gene for ampicillin resistance that expresses Betalactamase. 3. A gene called ARA C that acts as a regulatory switch for the GFP gene.
What role does the ARA C gene play in the pGLO plasmid?
It acts as a regulatory switch to turn on the GFP gene only in the presence of Arabinose sugar.
What happens to the GFP gene when Arabinose is present?
The ARA C gene is turned on, leading to the transcription and translation of the GFP gene, causing the colonies to glow under UV light.
What occurs if no Arabinose is present during the transformation?
The ARA C gene is off, preventing GFP transcription and resulting in no glowing bacteria.
What should be observed if the bacterial transformation was successful?
Bacterial colonies growing on agar with ampicillin and fluorescing under UV light when exposed to Arabinose.
What does the presence of ampicillin in the agar indicate about the transformed bacteria?
The bacteria have ampicillin resistance due to the plasmid, allowing them to grow in the presence of the antibiotic.
How does the GFP protein expression relate to the presence of Arabinose?
GFP protein is expressed only when Arabinose is present, activating the GFP gene through the ARA C regulatory switch.
What happens to the plasmid in the progeny of the transformed bacteria?
The progeny will inherit the inserted plasmid for each generation.
What is the significance of using UV light in the experiment?
To visualize the expression of the GFP protein in transformed bacteria.
What is Betalactamase and what is its function?
Betalactamase is an enzyme expressed by the ampicillin resistance gene that breaks down the antibiotic Ampicillin.
What is the expected outcome when transformed colonies are exposed to UV light after adding Arabinose?
The colonies will fluoresce, indicating successful expression of the GFP gene.
What is the role of pharmaceutical companies in relation to bacterial transformation?
They manufacture many medications using bacterial transformation to produce proteins like insulin.
What does the term 'genetically engineered' refer to in the context of the plasmid?
It refers to the plasmid being modified to include specific genes for desired traits, such as GFP and antibiotic resistance.
What is the significance of the GFP gene in the experiment?
It allows for the visual confirmation of successful transformation by causing the bacteria to glow under UV light.
What is the relationship between bacterial transformation and protein harvesting?
Bacterial transformation allows for the insertion of plasmids that enable bacteria to produce and harvest useful proteins.
What is the function of the pGLO plasmid in the context of the experiment?
It carries the genes that enable E. coli to express GFP and resist ampicillin.
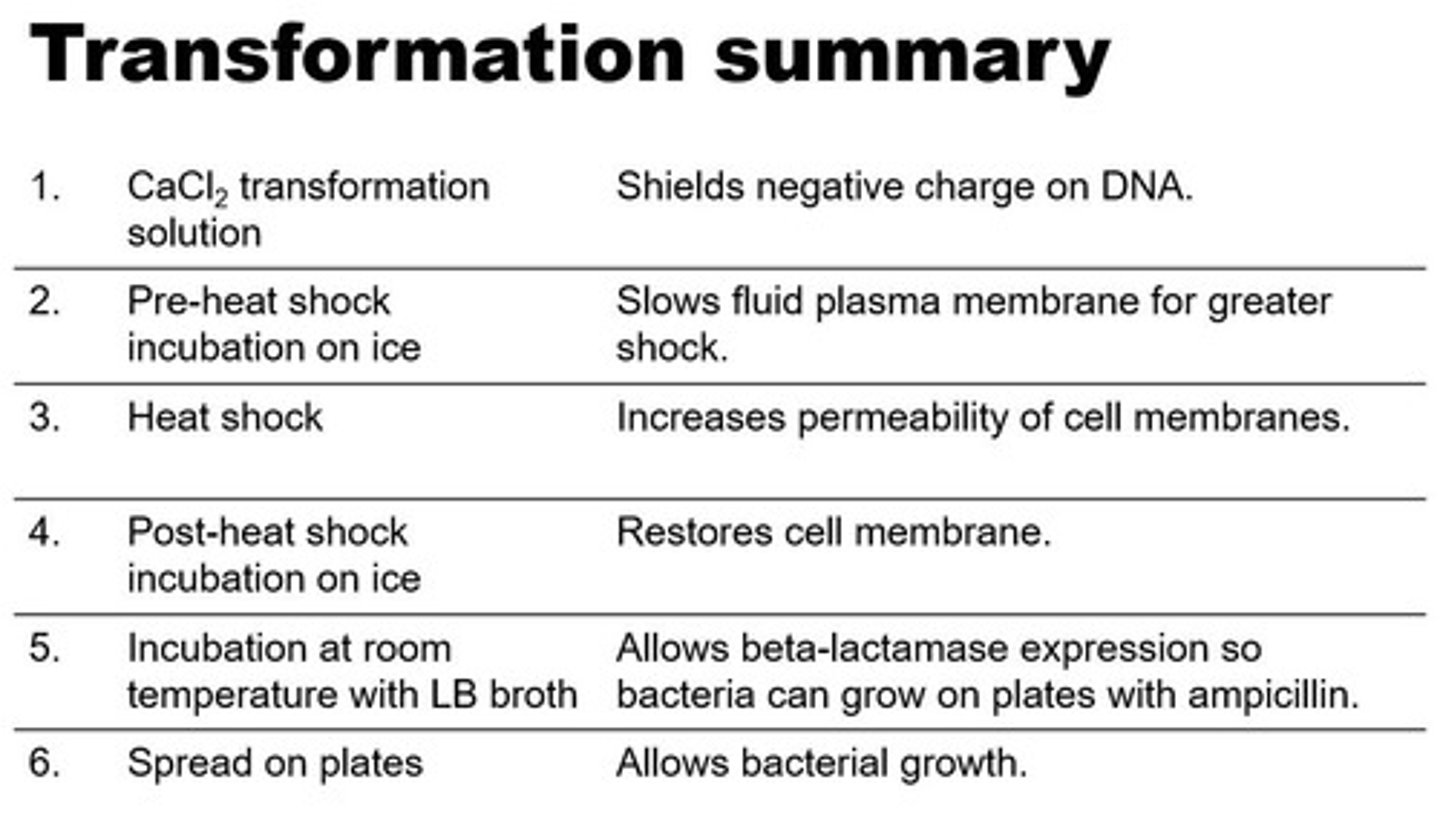
CaCl2 transformation solution
Step 1- shields negative charge on DNA
Pre-heat shock incubation on ice
Step 2- shows fluid plasma membrane for greater shock
Heat Shock
Step 3- increases permeability of cell membranes
Post- heat shock incubation on ice
Step 4- restores cell membrane
Incubation at room temp w/ LB broth
Step 5- allows beta lactamase expression so bacteria can grow on plates w ampicillin
Spread on plates
Step 6- allows bacterial growth