Gluteal Region, Hip, Posterior Thigh
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What is the two function of the lower extremety? What are the five joints of the lower extremity?
Support body weight
Articular surfaces are shaped to “lock”
This reduces muscular energy
Locomotion
Combination of several movements across multiple joints
Joints:
Hip joint
Knee joint
Tibiofemoral joint
Patellofemoral joint
Tibiofibular joint
Ankle joint
Joints of the foot
Describe the superficial and deep fascia of lower limb. What is the Fascia Lata? What is the IT Band?
Superficial Fascia
Delicate over the gluteal region
Contains fat and cutaneous nerves & vessels
Deep Fascia
Deep gluteal fascia
Fascia Lata
A thick, stocking-like fascia that surrounds the thigh
Iliotibial Band - a thickened portion of the fascia lata
Describe the hip joint
(Articulation? Joint? AKA? Consists of?)
Articulation: head of femur + acetabulum of pelvic bone
Ball-socket Synovial joint
Aka Os Coxae
Consists of 3 fused bones: Ilium, Ischium, Pubis
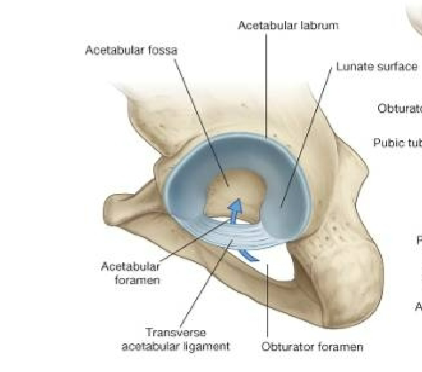
Describe the acetabular labrum. Where is the transverse acetabular ligament and why is this important?
Acetabular Labrum: fibrocartilage collar that surrounds and Deepens the acetabulum
Transverse acetabular ligament has vessels passing through it
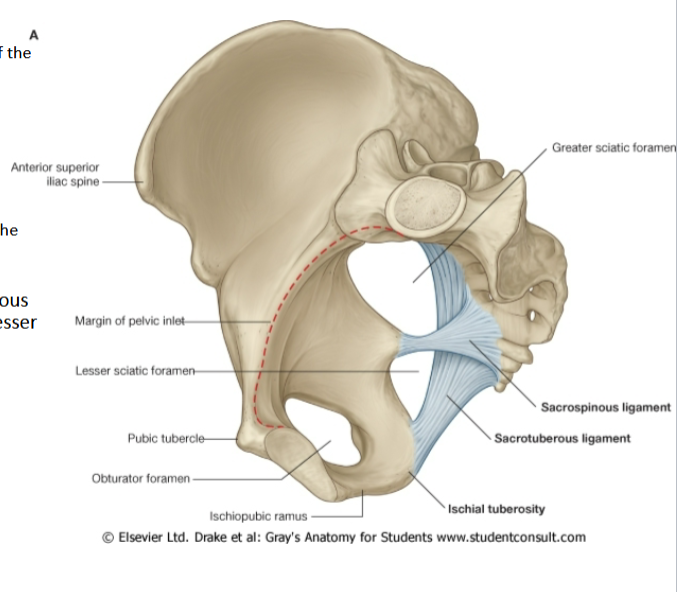
Differentiate between the sacrospinous and sacrotuberous ligaments
Sacrospinous Ligament
Attachments: Anterior surface of sacrum + Ischial Spine
Forms greater sciatic foramen
Sacrotuberous Ligament
Attachments: Lateral margin of sacrum + Ischial tuberosity
Sacrospinous + Sacrotuberous = lesser sciatic foramen
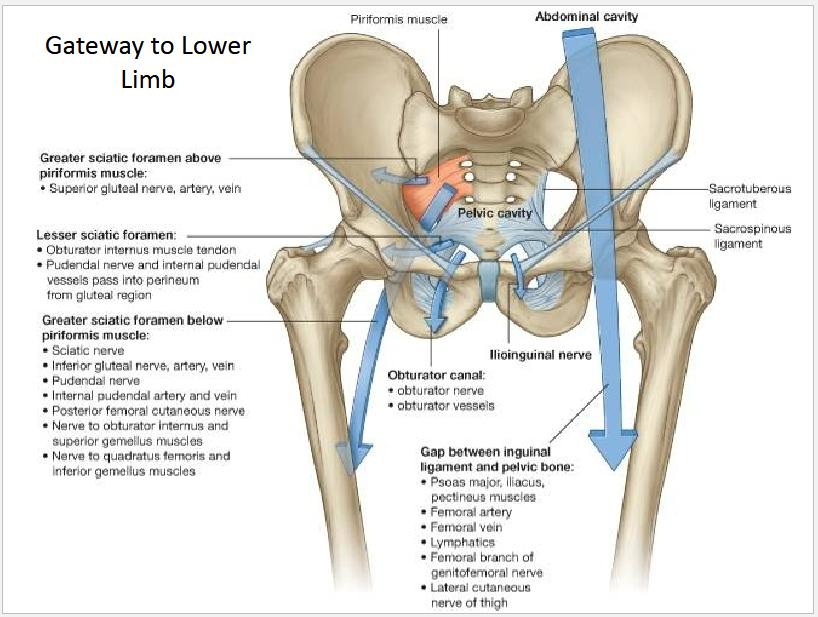
Describe what goes through the Greater sciatic foramen (above and below piriformis) and lesser sciatic foramen
Describe the SI joint’s function and sources of pain. Describe what the pain feels like
Sacro-Iliac Joint
small and very strong
Transmits forces of upper body → pelvis (hips) and legs
shock-absorbing structure
Source of Pain
Too much movement — hypermobility or
instabilityToo little movement — hypomobility or
fixation.typically felt on one side of the low back or buttocks, and can radiate down the leg
What are the hip flexors muscles (Origin/insertion/innervation)? What is the tensor fascia lata (function/innervation)?
Hip Flexors
Iliacus
• Iliac fossa
• Lesser trochanter
• Femoral nervePsoas
• T12-L5
• Lesser trochanter
• Anterior rami
Tensor fascia lata
stabilization of both knee and hip joints
innervated by superior gluteal n.
Differentiate between the gluteus maximus, medius, and minimus
Gluteus maximus
extension of the femur at the hip
Inferior gluteal n.
Gluteus medius
abducts & medially rotates femur at the hip
Superior gluteal n.
Gluteus minimus
abducts and medially rotates femur
Superior gluteal n.
What are the deep muscles of the gluteal region? Function?
Deep Muscle:
Piriformis
Obturator internus
Superior & Inferior Gemelli
Quadratus femoris
Function:
laterally rotate extended femur or abduct flexed femur
Describe the biomechanic of the hip joint during gait
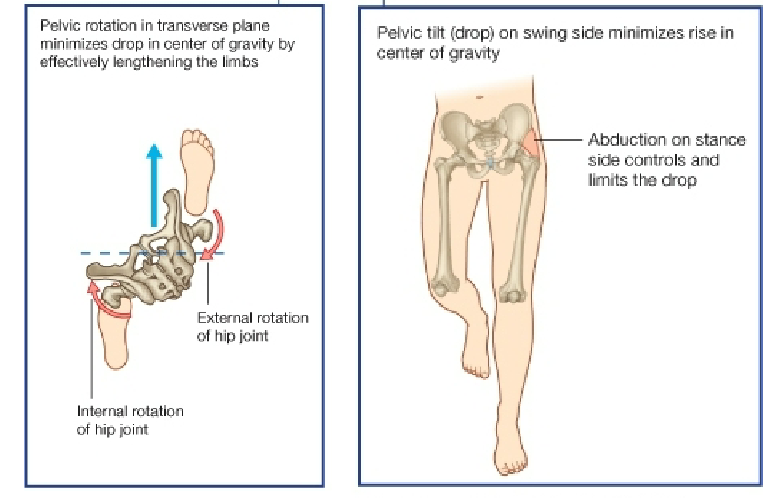
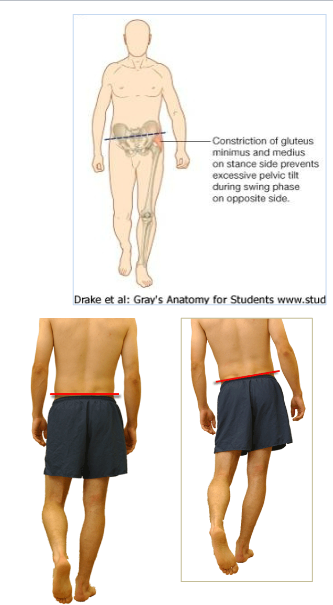
Describe the Trendelenberg sign/gait
Paralysis of Gluteus Medius + Minimus = (+) Trendelenburg sign
Sign: pelvis opposite the affected side drops when the affected side is supporting the body
patient will leans her trunk toward the affected side to maintain balance
What are the nerves to lower limb?
Nerves to lower limb:
Obturator
Femoral
Sciatic
Superior/Inferior gluteal nerves
Cutaneous nerves
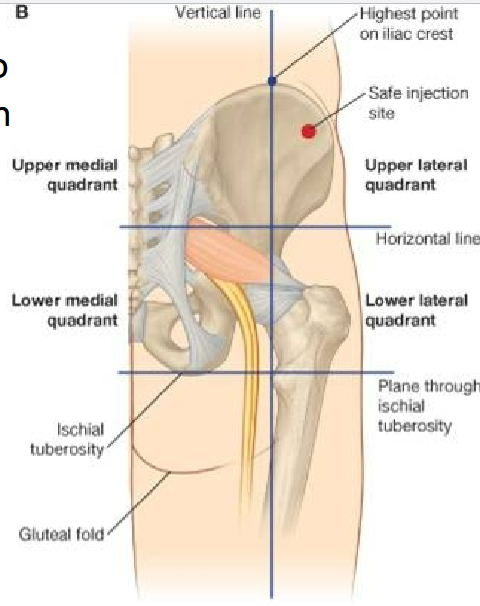
What are the nerves to gluteal region? How do you inject into the gluteal region?
Superior gluteal nerve
Inferior gluteal nerve
Sciatic nerve
Safe = Upper lateral quadrant
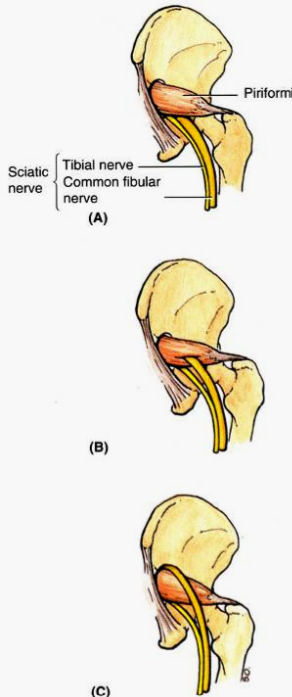
What is piriformis syndrom? What occurs in 12% of the population? What plays a role in this disease? What type of occupation could lead to this?
Sciatic nerve can become irritated or compressed by the piriformis muscle → pain and/or paresthesia in the gluteal region and posterior thigh
An early division of the sciatic n. occurs in about 12% of the population and may predispose a person to this condition
Hypertrophy of the piriformis plays a role as well
Dancers, ice skaters, cyclists, etc.
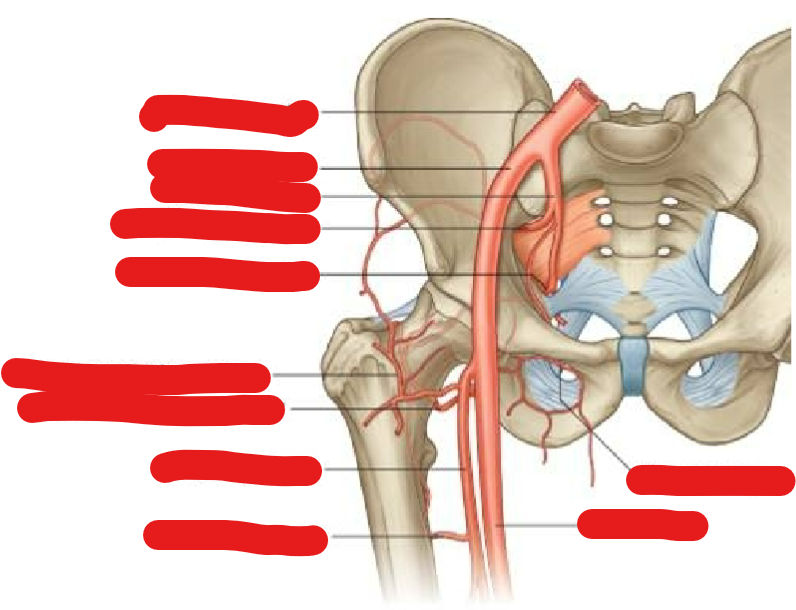
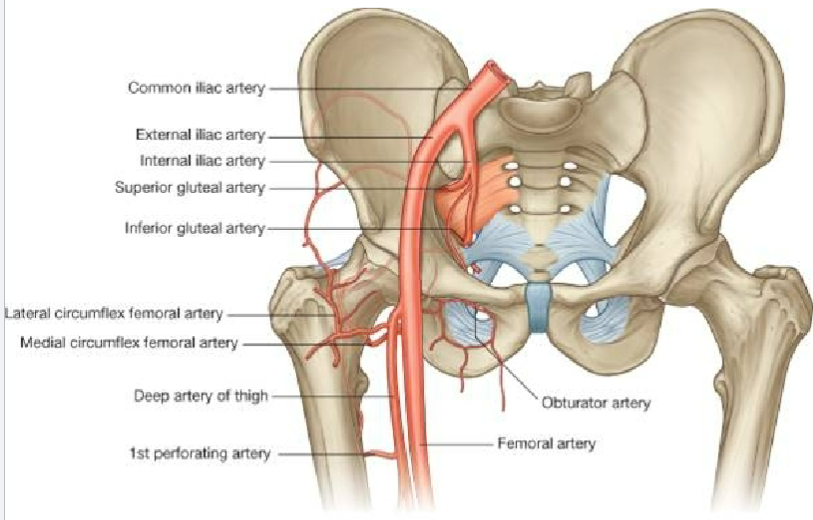
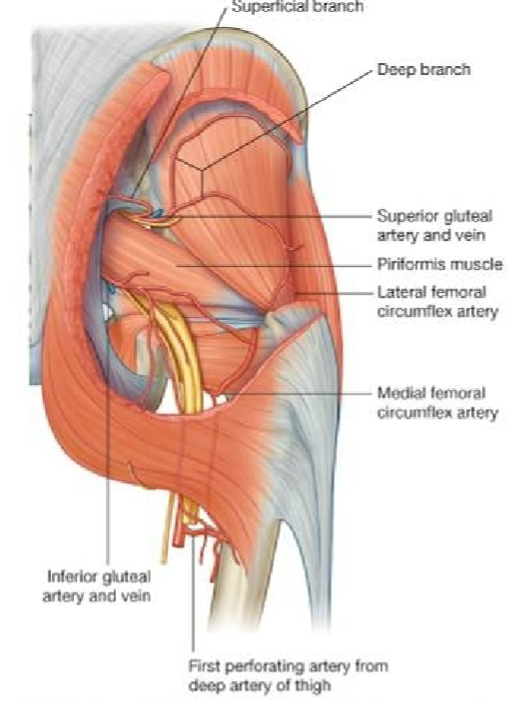
Describe the vasculature of the head of femur
Extracapsular arterial network around head and neck of femur
Branch from medial & lateral circumflex arteries
Only one small artery to the head of the femur (branch of obturator)
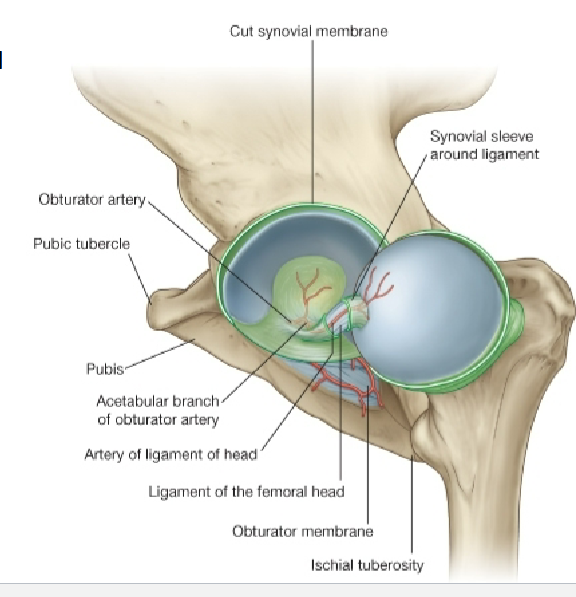
How does avascular necrosis could happen to the head of the femus?
Medial circumflex artery feeds epiphyseal arteries (posterio-lateral aspect of femoral neck
Disruption of this blood supply leads to avascular necrosis of femoral head
What are the anterior ligaments of the hip? Compare and contrast them
(Shape? Attachments? tightened when…?)
Iliofemoral Ligament
Y shaped ligament located anterior to hip joint
Attachments: ilium btw AIIS / margin of acetabulum + femur along intertrochanteric line
tightened by extension of femur
helps reduce muscular energy required to maintain a standing position
Pubofemoral Ligament
triangular shaped ligament located anteroinferior to hip joint
Attachments: Pubic bone + iliofemoral ligament
(Exact attachments vary from text to text)
Tightens w/ extension and abduction of the femur
Describe the ischiofemoral ligament?
(Location? Attachments? Function?)
Location: posterior to hip joint
Attachments: Ischium + neck/greater trochanter of femur
Function: similar to Iliofemoral and pubofemoral but not as strong
Describe Hip Replacement Surgery
(procedure? type? common problem post op?)
Removes damaged cartilage and bone → replaces w/ artificial parts
Types:
Joint resurfacing
Hemiarthroplasty
Total joint replacement
common problem post-op: hip dislocation because artificial hip is smaller than the original joint
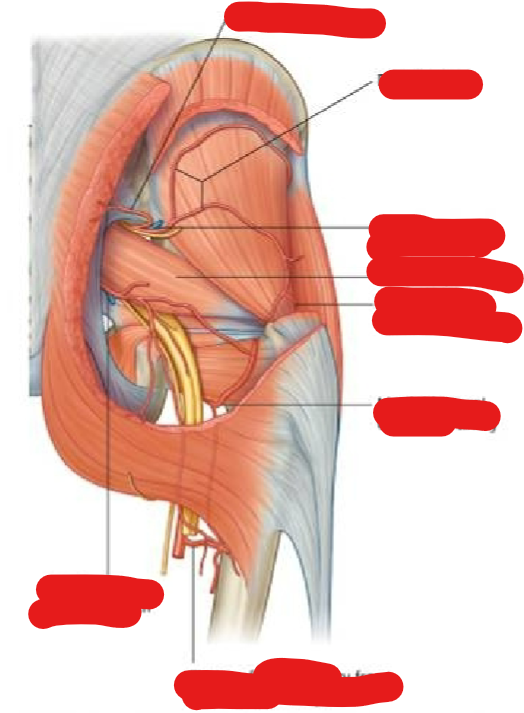
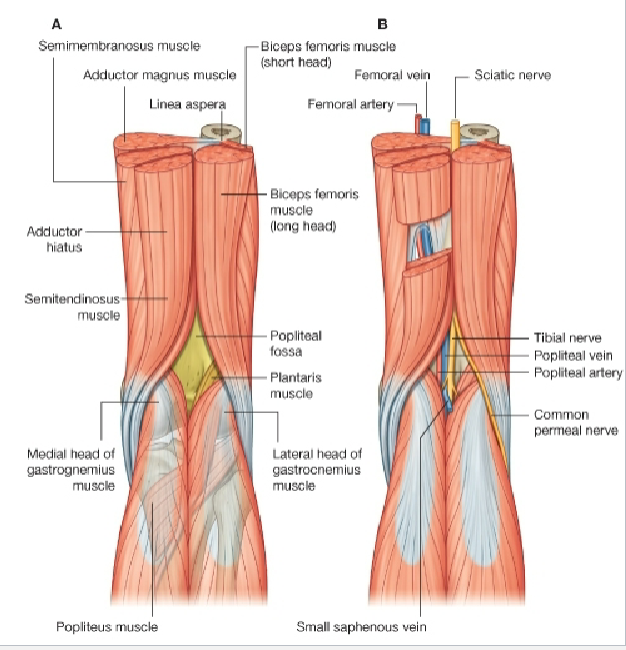
What are the Posterior Thigh Muscles (action? Innervation? Attachment?)
Semimembranosus & Semitendinosus
Flex leg at knee
Extend thigh at hip
Medially rotate lower limb
Biceps Femoris
Flexes leg at knee
Extends thigh at hip
Laterally rotates lower limb
All supplied by sciatic nerve
Note proximal attachment on ischial tuberocity (2 joint muscle)
Describe the divisions of the sciatic nerve
Divides into two divisions in distal thigh (Sometimes divided within pelvis)
Tibial Division
Medial thigh: Adductor magnus, hamstring part
Posterior thigh: Long head of biceps femoris, Semitendinosus, Semimembranosus
Common Fibular Division
Posterior thigh: Short head of biceps femoris
Divides into deep and superficial fibular nerves
Old name “peroneal nerve”
Describe the boundaries and content of the popliteal fossa?
What is the difference between between Gluteals and Hamstring?
Gluteal: extends hip getting up
Hamstring: Exten hip when standing
Describe how hamstrings could cause Low Back Pain.
Hamstring muscles are tight → pull on their attachment at the bottom of the pelvis → backwards tilting of
the pelvis →rounding out the natural inward lower back arch and causing slouching
If your muscles have tightened up then blood has been squeezed out of them therefore your muscles are working at less than 100 % of capacity and your performance will be down as a result