Ch05 Chemical Messengers
1/70
Earn XP
Description and Tags
APK2105C @ UF | Dr. Nguyen | Module 2 | Ch05 Chemical Messengers
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
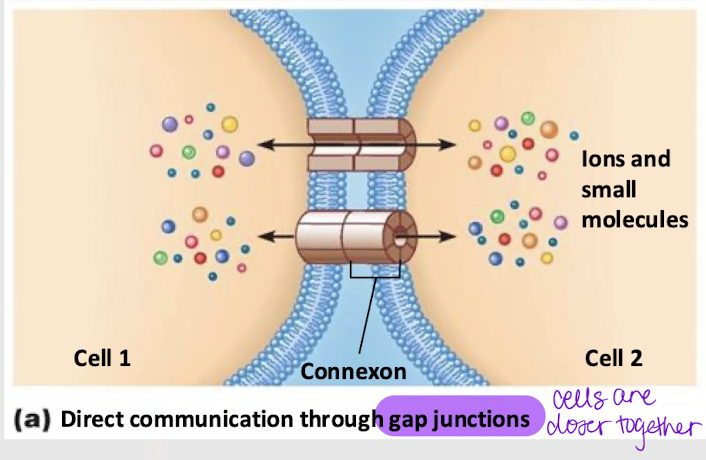
gap junctions
Intercellular communication that occurs through _____ ________, including via electrical and metabolic coupling.
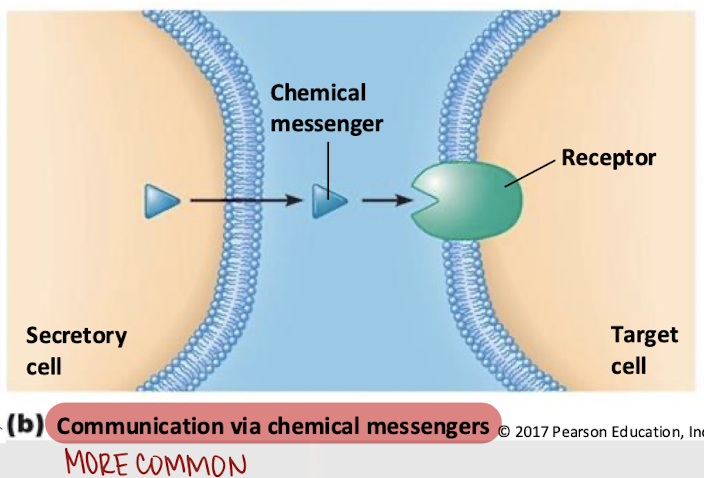
chemical messengers
Most common method of intercellular communication, involving the use of ________ __________ and ligands.
ligand
chemical messenger molecule which binds proteins reversibly
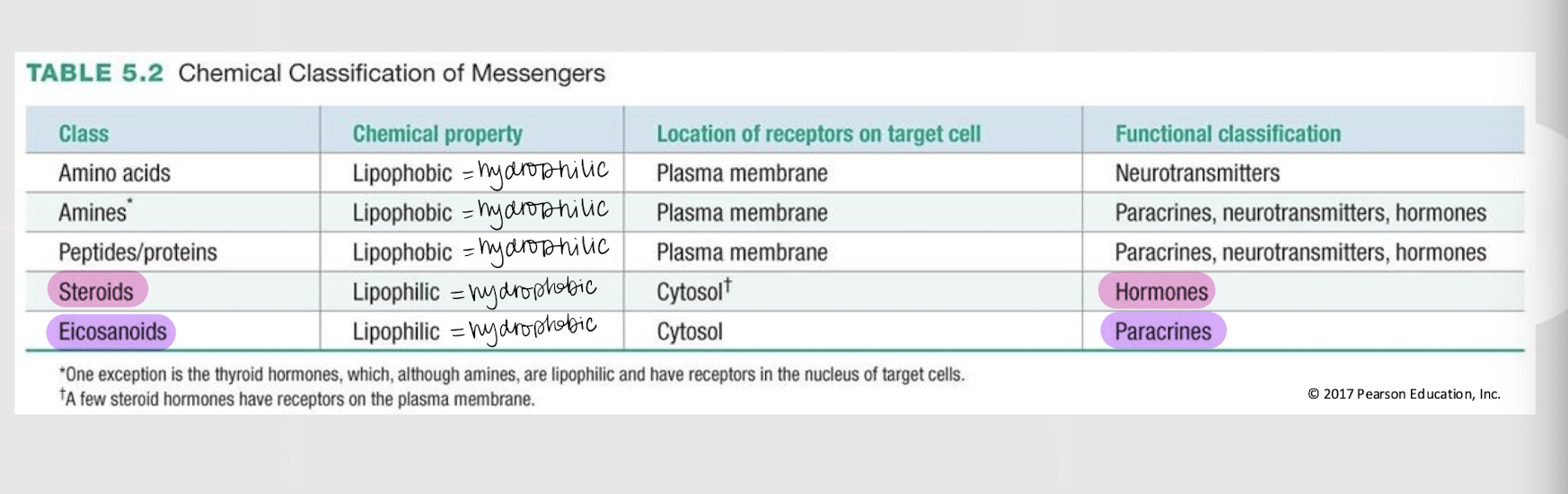
paracrines, neurotransmitters, hormones
What are the 3 functional classes of chemical messengers?
paracrines
Chemical messengers that reach target (adjacent/nearby) cells via simple diffusion.
autocrines
Chemical messengers that act on the cell that secreted them (if it has the receptor).
neurotransmitters
Chemical messengers involving synaptic signaling and that are synapse-specific (e.g. ACh → muscle cells).
hormones
Chemical messengers that are usually released from glands (exception: neurohormones) into the bloodstream. All cells are exposed, but only those w/ receptors are affected.
histamine
An example of a paracrine is ________, which is part of the inflammation response (increased blood flow to the area).
capillaries, leaky
Histamine breaks down _______, causing them to be more “_____.”
antihistamines
Side effects (e.g. drowsiness) of ___________ result b/c they block histamine receptors universally.
chemical structure
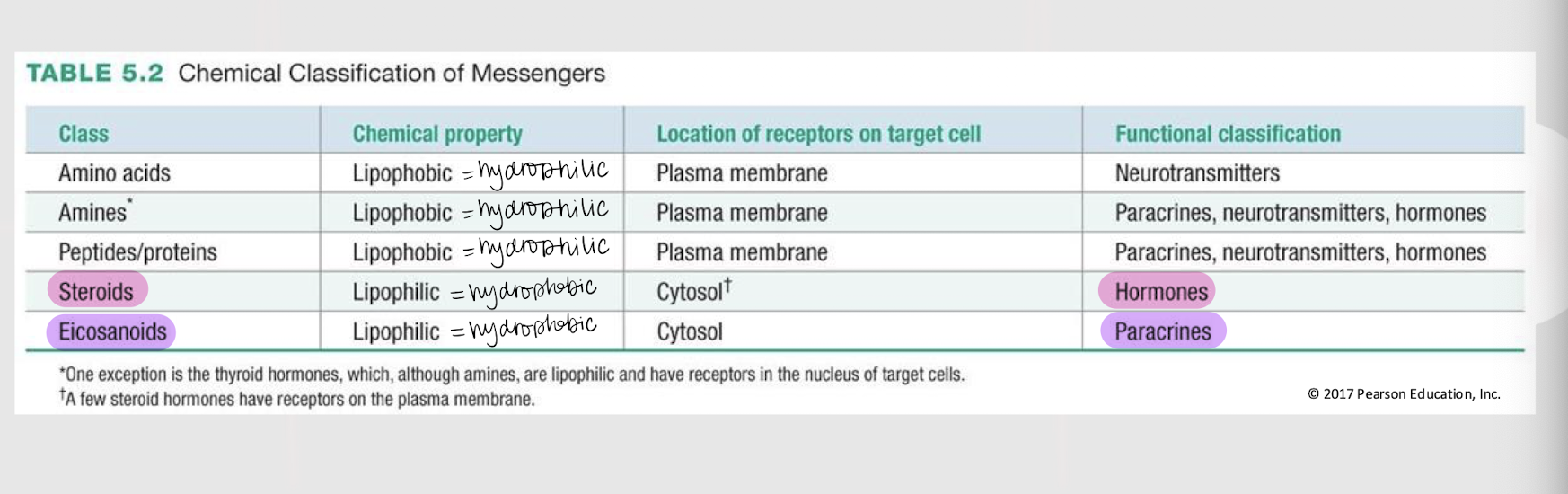
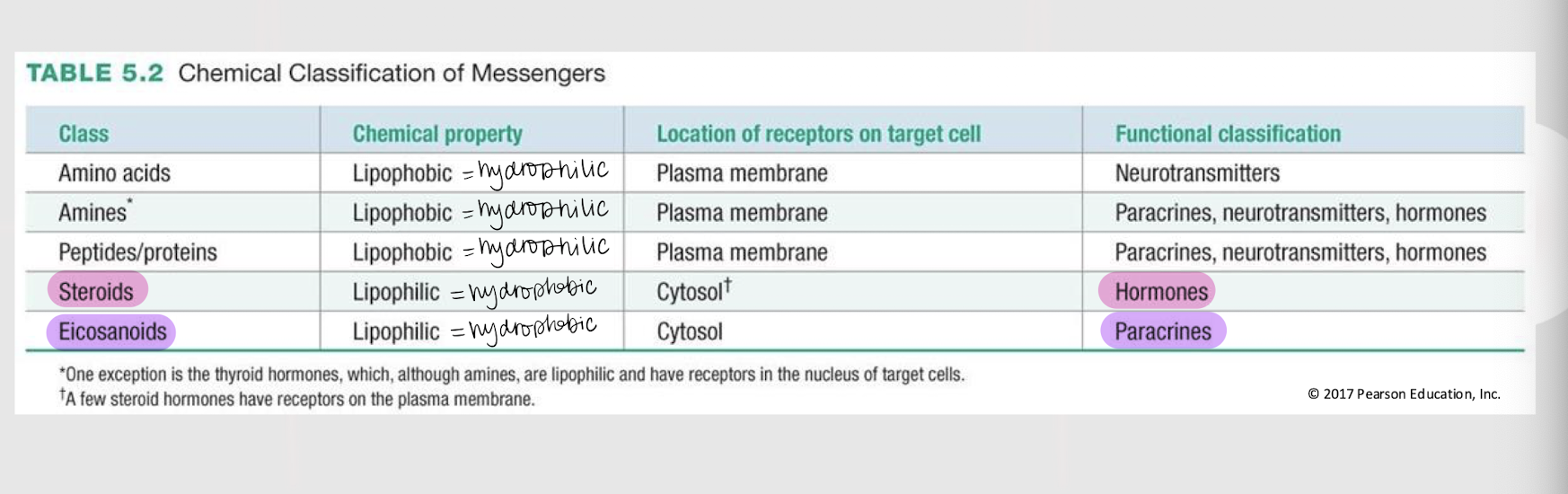
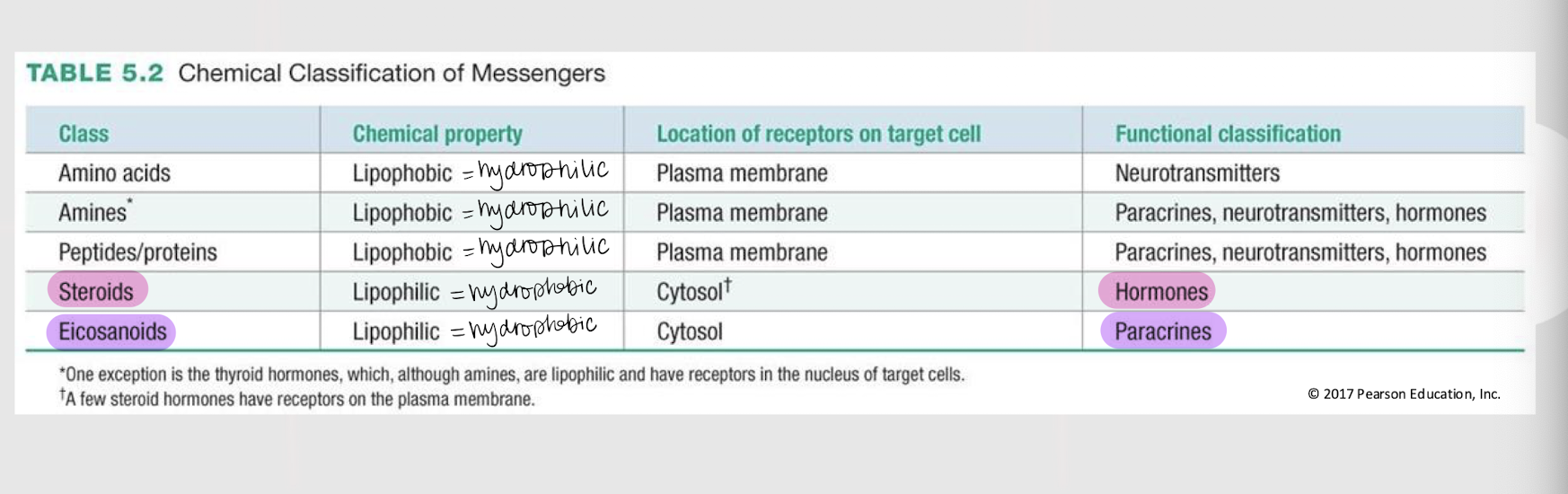
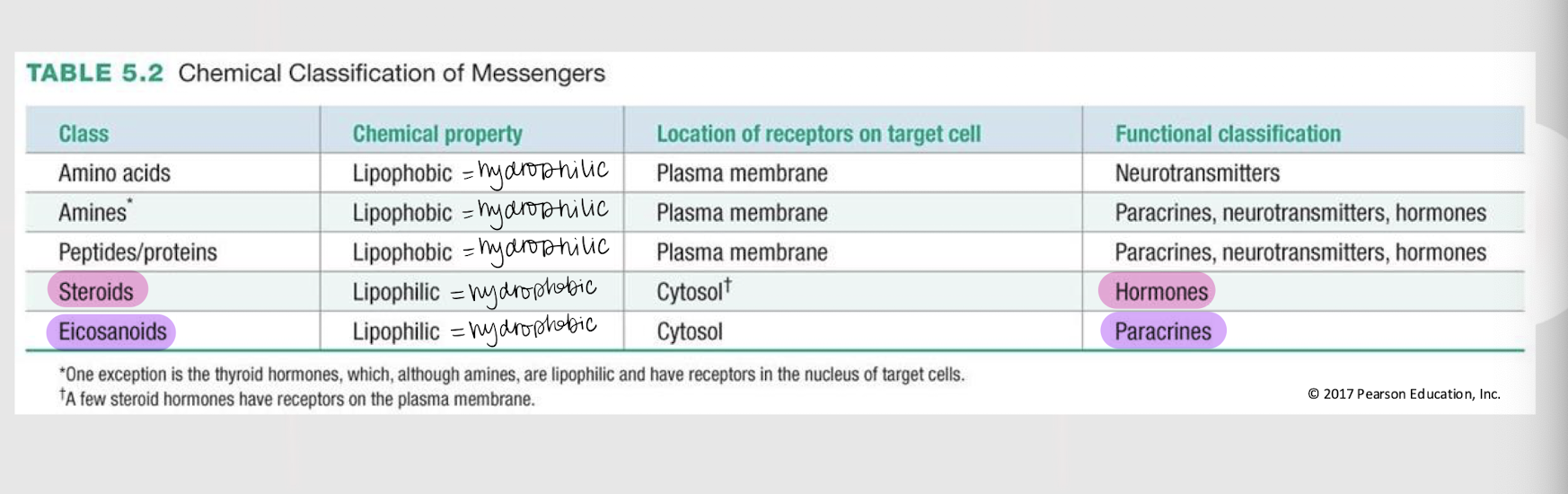
A molecule’s _______ ________ determines its mechanisms of synthesis, release, transport, and signal transduction.
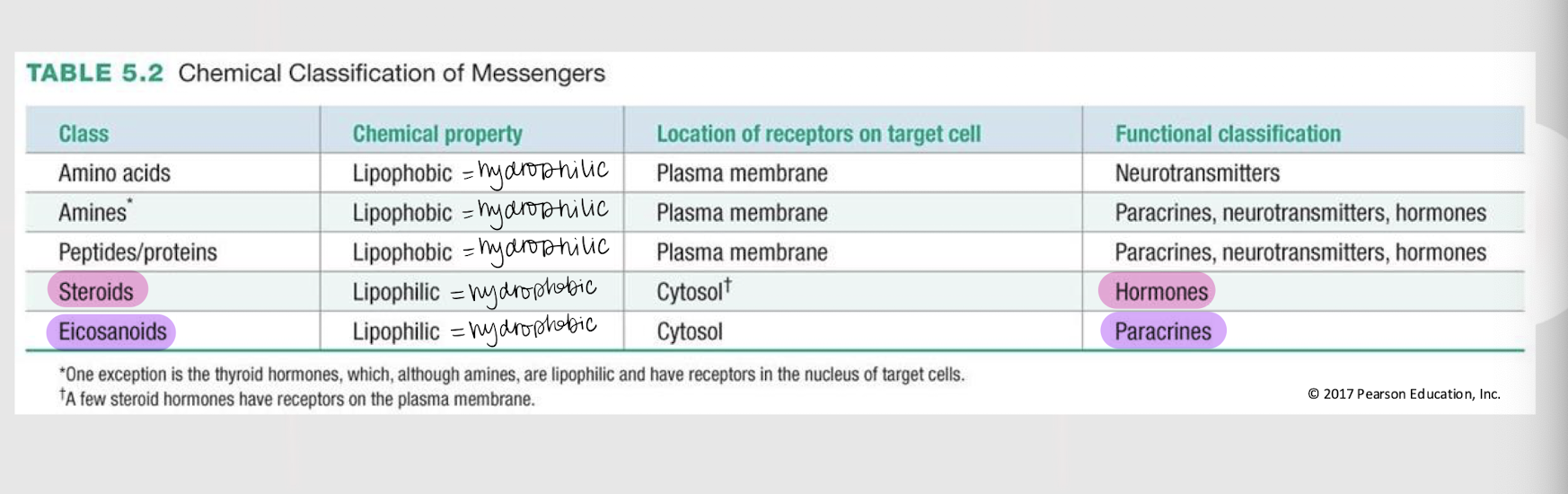
plasma membrane
If a chemical messenger is lipophobic / hydrophilic, where are its receptors found in the target cell?
cytosol
If a chemical messenger is lipophilic / hydrophobic, where are its receptors found in the target cell?
steroid
If a chemical messenger is functionally classified as a hormone, what is its general class?
eicosanoid
If a chemical messenger is functionally classified as a paracrine, what is its general class?
amines, peptides/proteins
If a chemical messenger is functionally classified as a paracrine, neurotransmitter or hormone, what is its general class?
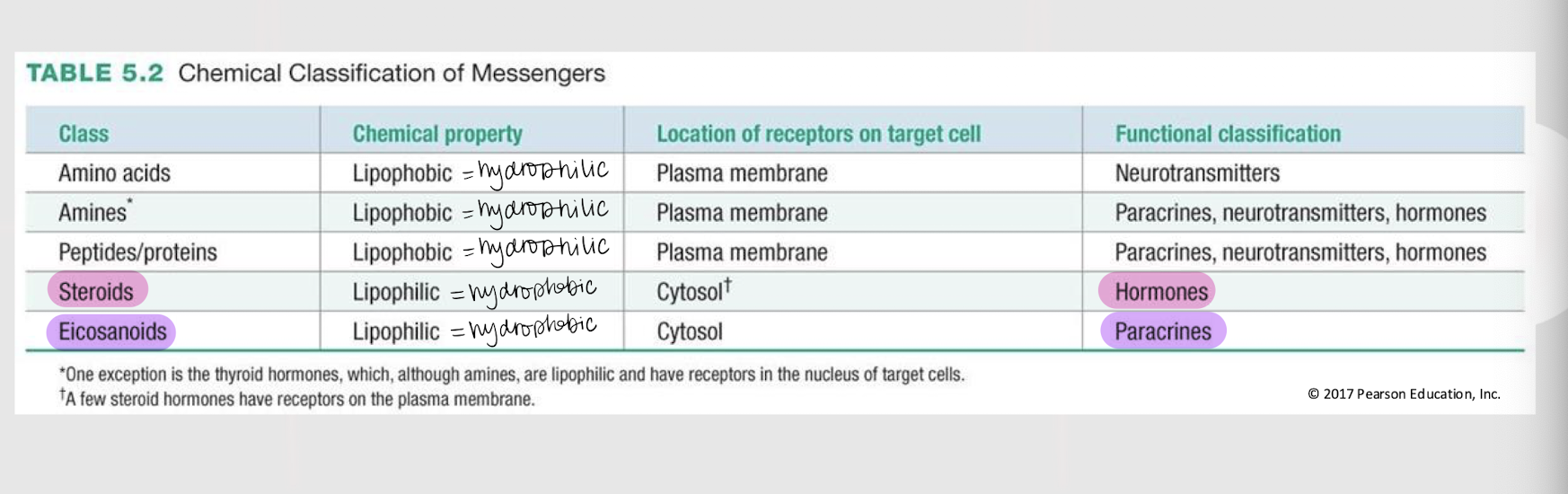
amino acids
If a chemical messenger is functionally classified as a neurotransmitter, what is its general class?
glutamate, aspartate, glycine, GABA
What 4 amino acids function as neurotransmitters in the CNS?
dopamine, norepinephrine, epinephrine
What are the 3 catecholamines?
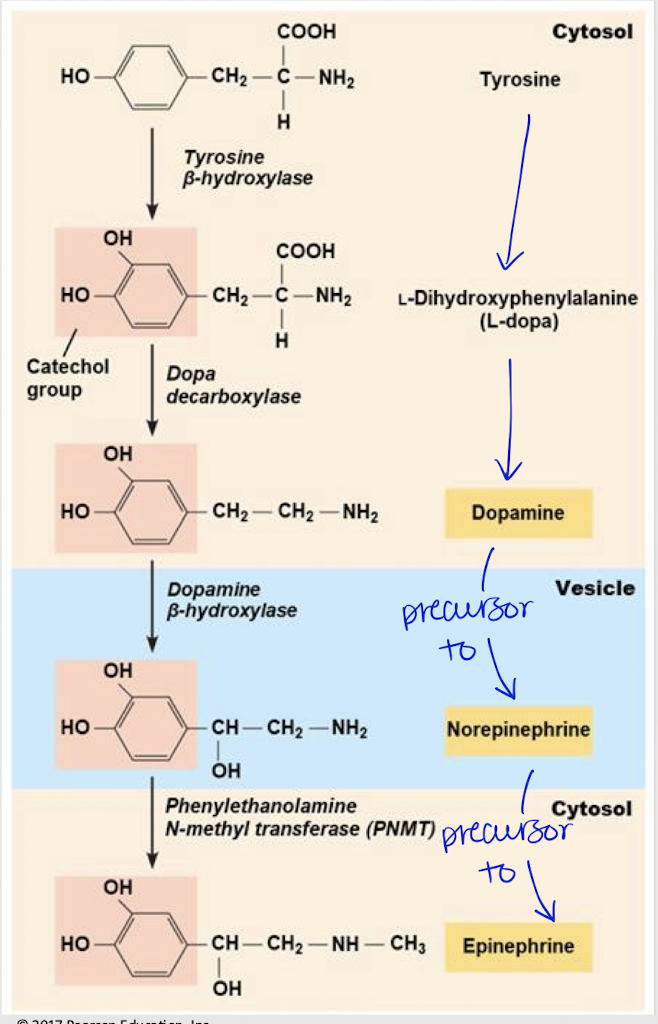
dopamine, epinephrine
Catecholamine synthesis — ________ is a precursor to norepinephrine, which is a precursor to ________.
neurotransmitter
Dopamine acts as a…
neurotransmitter
Norepinephrine acts as a…
hormone
Epinephrine acts as a…
neurotransmitter
Serotonin acts as a…
paracrine
Histamine acts as a…
thyroid hormone
The ONLY amine messenger that is lipophilic (receptor located on cell nucleus) is…
amine messengers
The catecholamines (i.e. dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine), serotonin, histamine, and thyroid hormones are all ______ ________ w/ their receptors located on the plasma membrane (EXCEPT thyroid hormones).
amine group
Identify: -NH2
cytosol
Where are amine messengers (except thyroid hormones) synthesized?
peptides/proteins, amines, and amino acids
3 types of hydrophilic/lipophobic messengers w/ receptors located on the plasma membrane
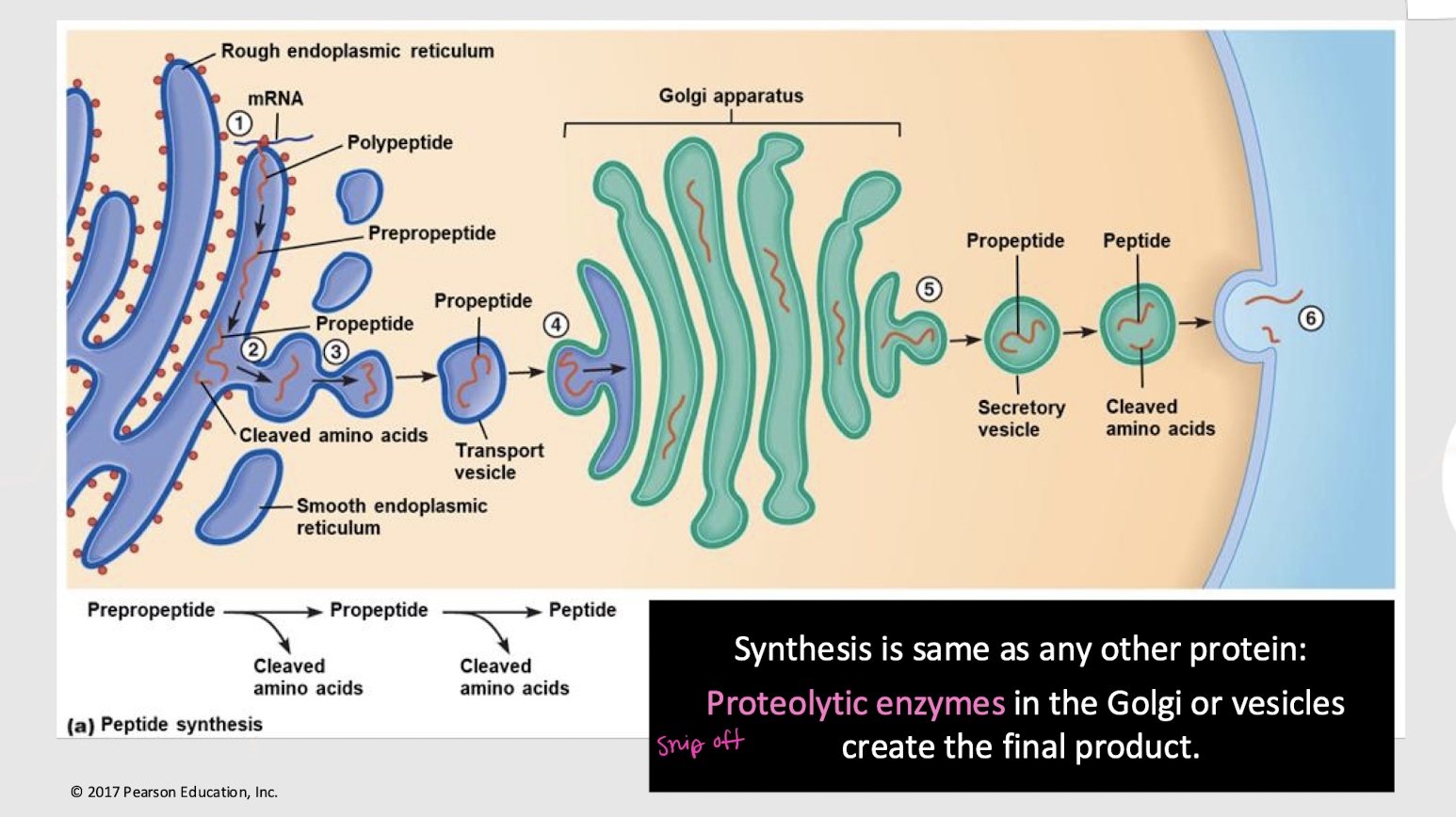
cleaved; Golgi; exocytosed
In peptide/protein synthesis, polypeptides are ________ by proteolytic enzymes to form active peptides, which travel via transport vesicles to the _______ and are then _________.
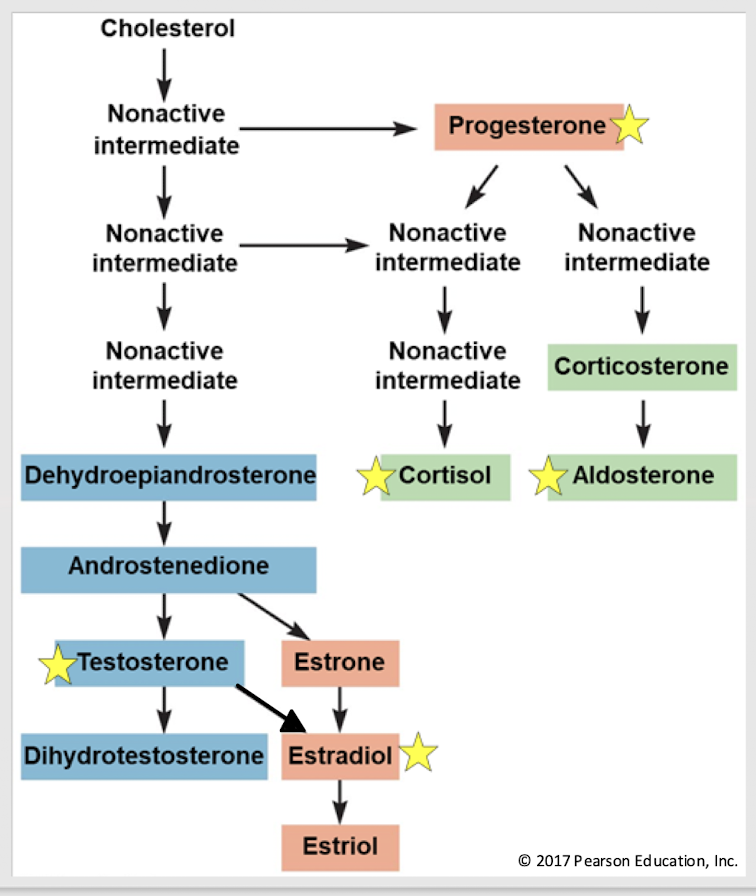
steroid messengers
Messengers derived from cholesterol that ALWAYS function as hormones and are lipophilic, w/ their receptors located (mostly) in the cytosol.
SER or mitochondria; released immediately
Where are steroids synthesized? Are they stored in the cells where they’re made or are they released immediately?
eicosanoid messengers
Paracrine messengers derived from arachidonic acid (a fatty acid) and that are lipophilic/hydrophobic, w/ their receptors located in the cytosol.
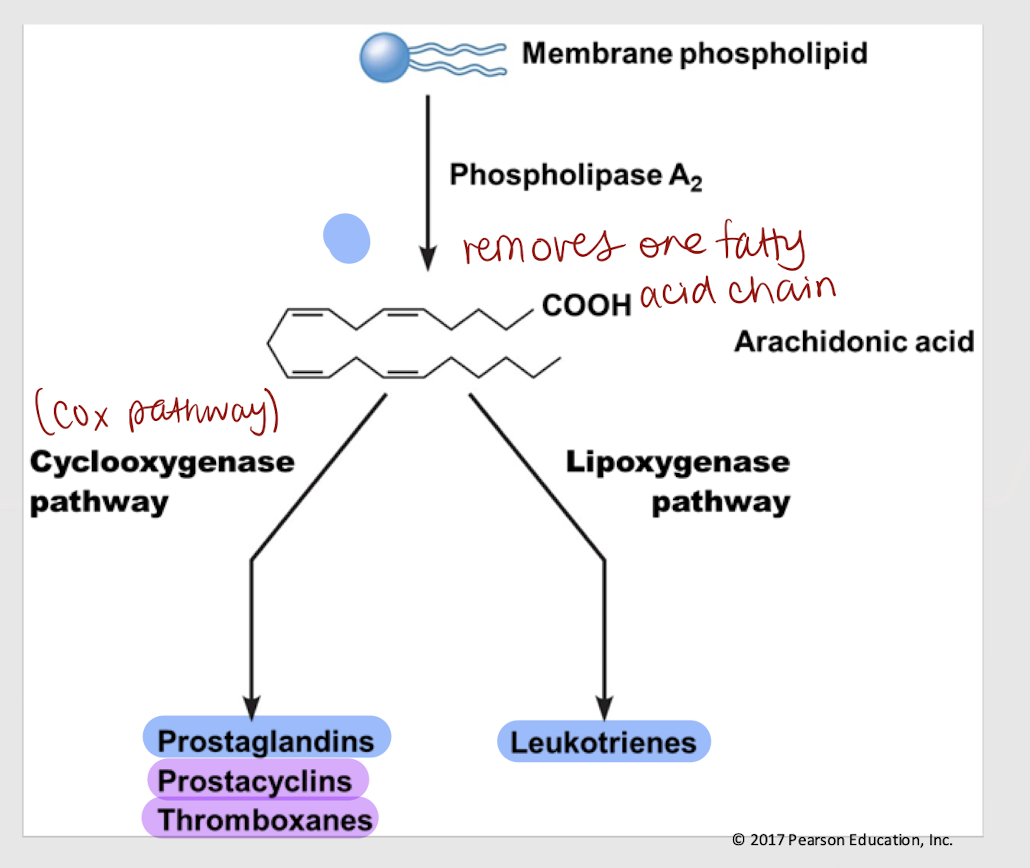
arachidonic acid; membrane
In eicosanoid synthesis, phospholipase A2 removes _______ _______ (a fatty acid chain) from a _______ phospholipid.
inflammatory and pain pathways
Eicosanoids — Are leukotrienes & prostaglandins involved in inflammatory and pain pathways, or blood clot formation?
blood clot formation
Eicosanoids — Are prostacyclins & thrombaxanes involved in inflammatory and pain pathways, or blood clot formation?
aspirin; COX
_______ is an NSAID that non-selectively blocks all ____, leading to negative effects, such as becoming more prone to stomach ulcers.
An alternative to this are COX-2 selective inhibitors.
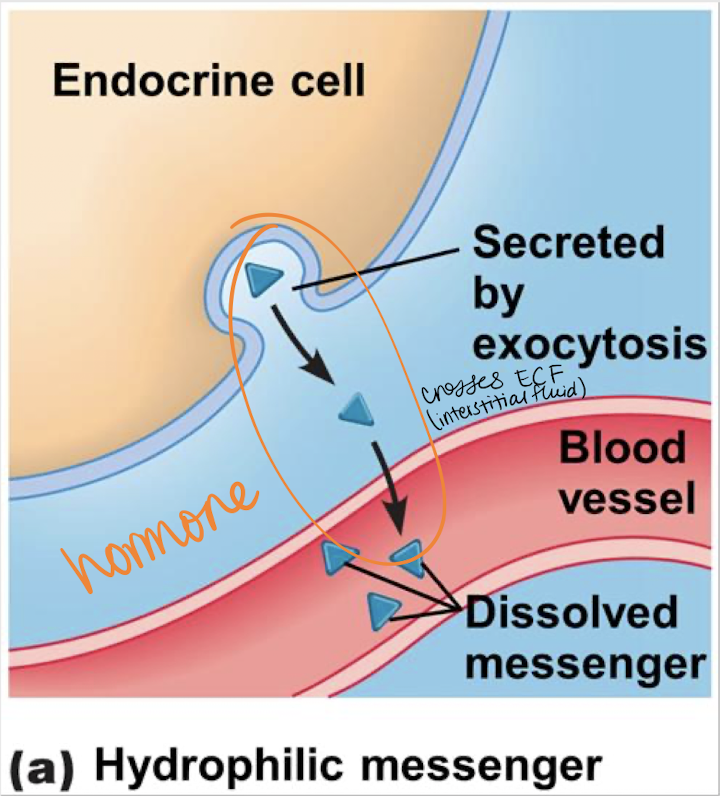
hydrophilic; exocytosis
________ (lipophobic) messengers are secreted by _________ and are able to dissolve in blood.
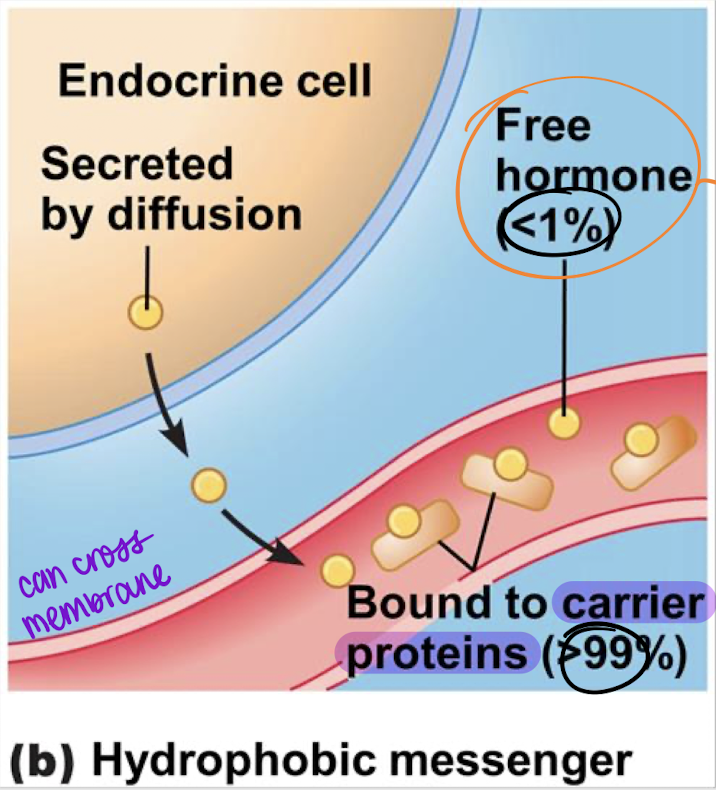
Lipophilic; diffusion; carrier; hormone
________ (hydrophobic) messengers are secreted by ________ and either bind to _______ proteins or remain a free _______.
free hormones
______ ________ are not bound to carrier proteins b/c as they travel through the blood, they will need to bind to their receptors and they can’t be bound to a carrier protein and receptor simultaneously.
clumping; evenly
Lipophilic proteins must be bound to carrier proteins to prevent ________ and instead be _______ distributed in the blood.
reversibly; to maintain ratio (<1% free hormones, >99% bound to carrier proteins)
Do lipophilic messengers bind reversibly or irreversibly to carrier proteins in the blood? Why?
True
True or False: Receptors are specific to a class of messenger and have different affinities for specific chemical messengers within a class.
False
True or False: Target cells have only one type of receptor.
messengers
Factors that affect messenger + receptor binding — concentration of ?
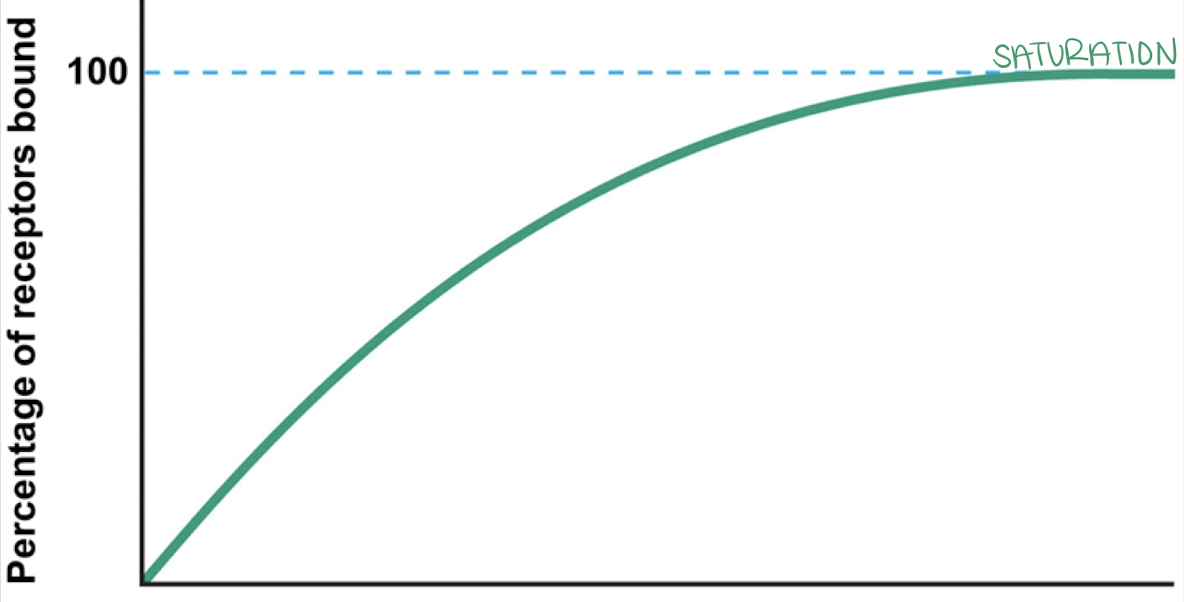
receptors
Factors that affect messenger + receptor binding — concentration of ?
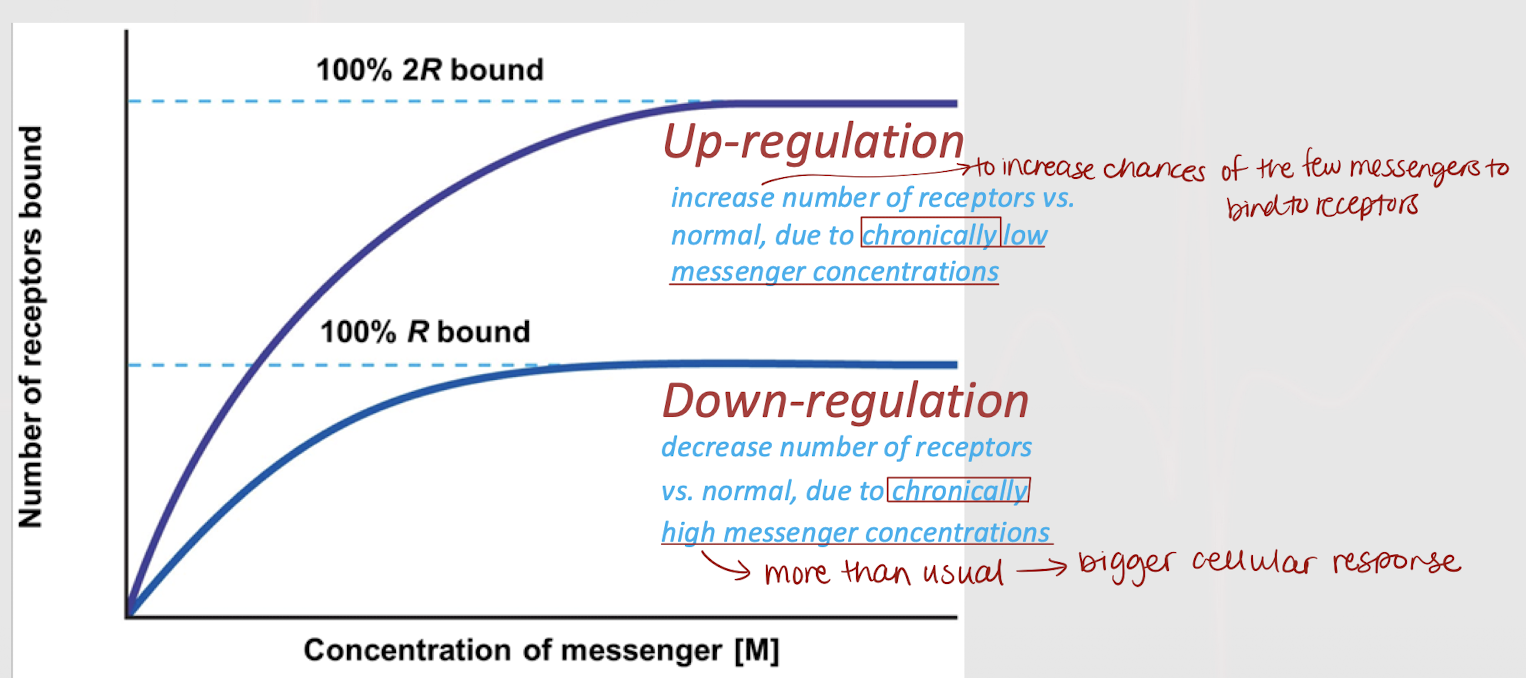
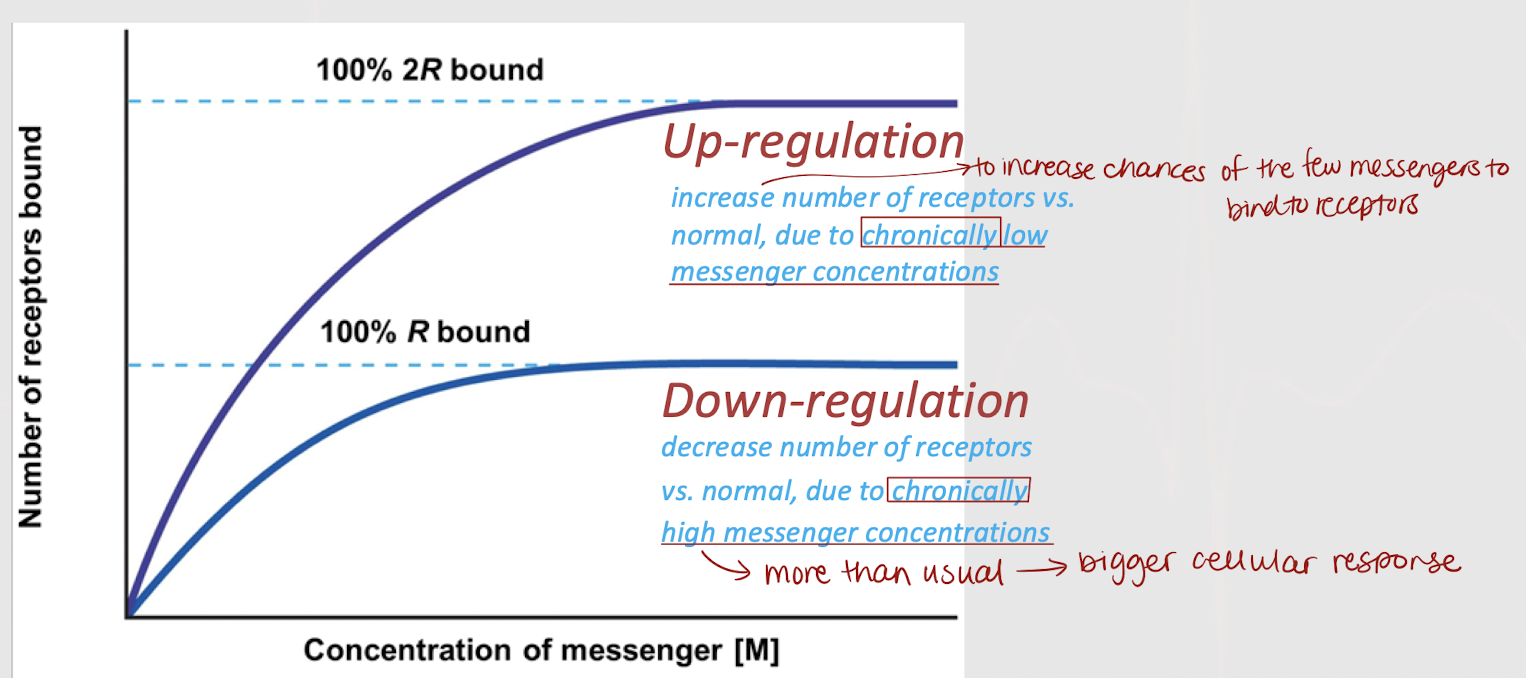
up-regulation
An increase in number of receptors (higher than normal), due to chronically low messenger concentrations. Done to increase the chances of messengers to bind to the receptors.
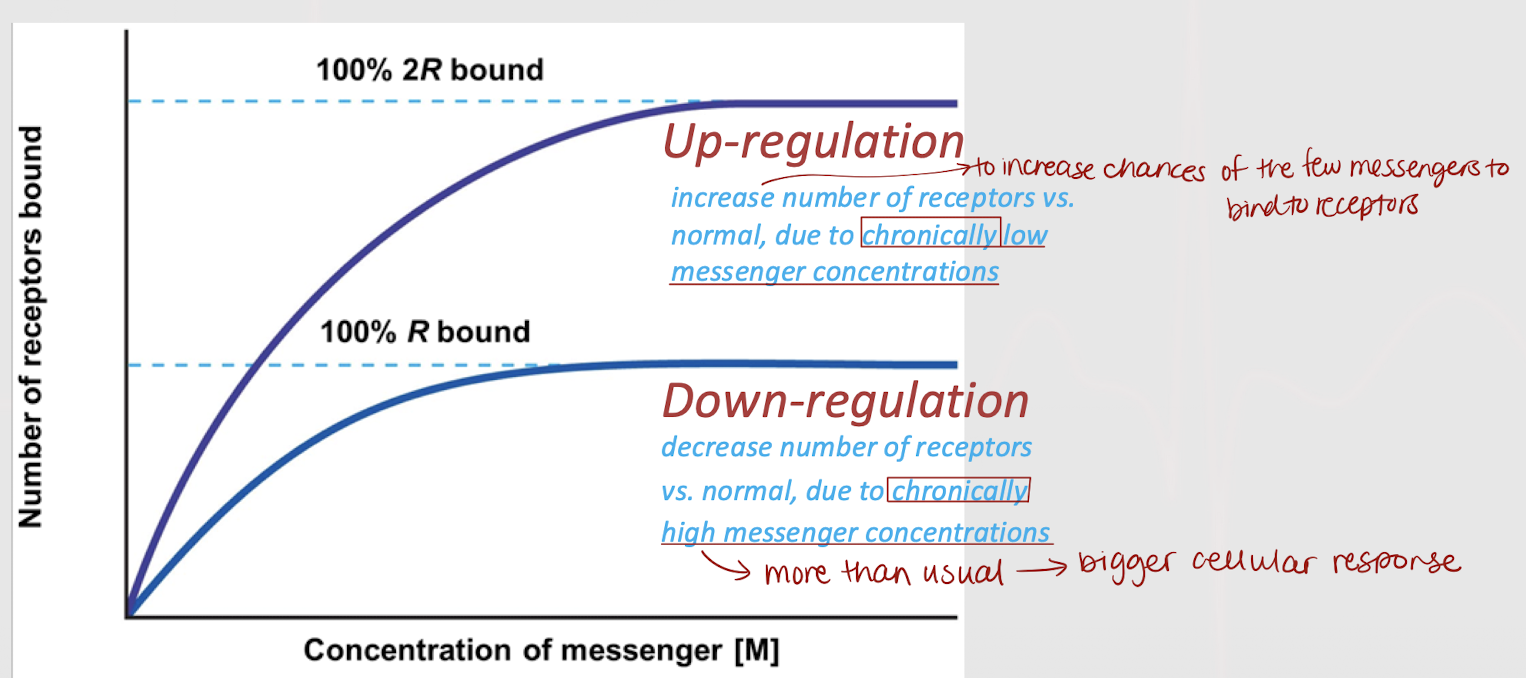
down-regulation
A decrease in number of receptors (lower than normal), due to chronically high messenger concentrations. Done to prevent a potentially bigger cellular response.
receptor affinity
Factors that affect messenger + receptor binding — ?
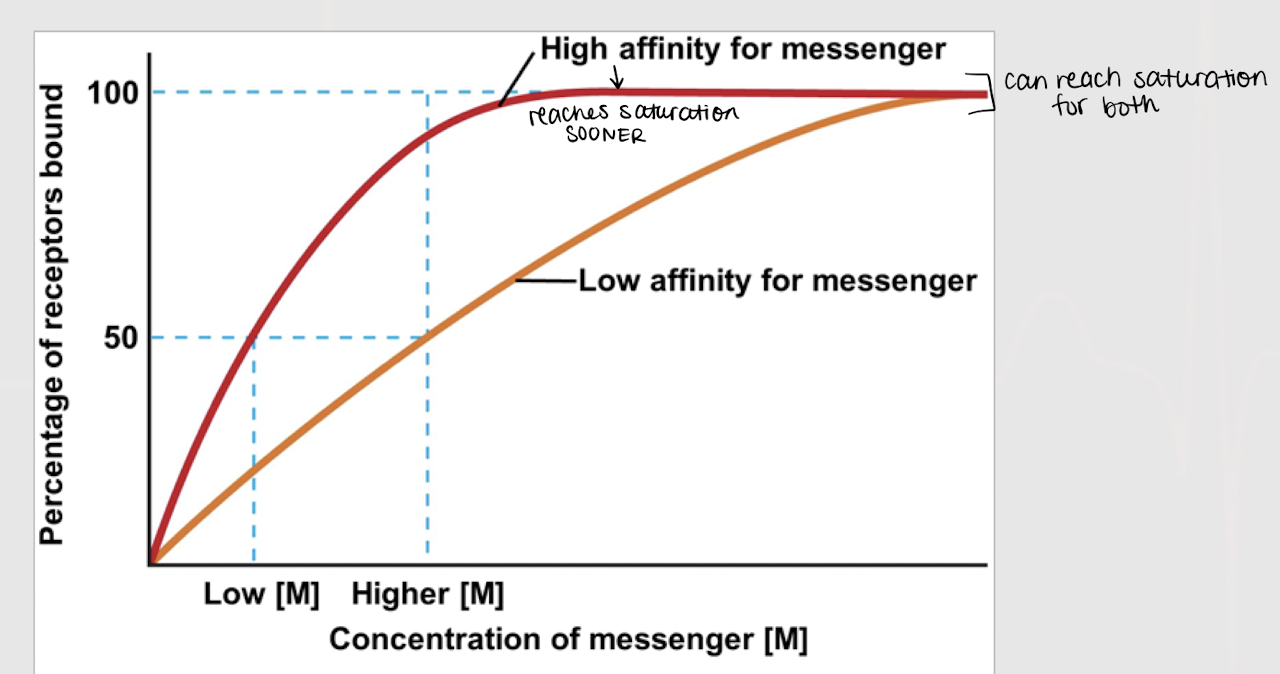
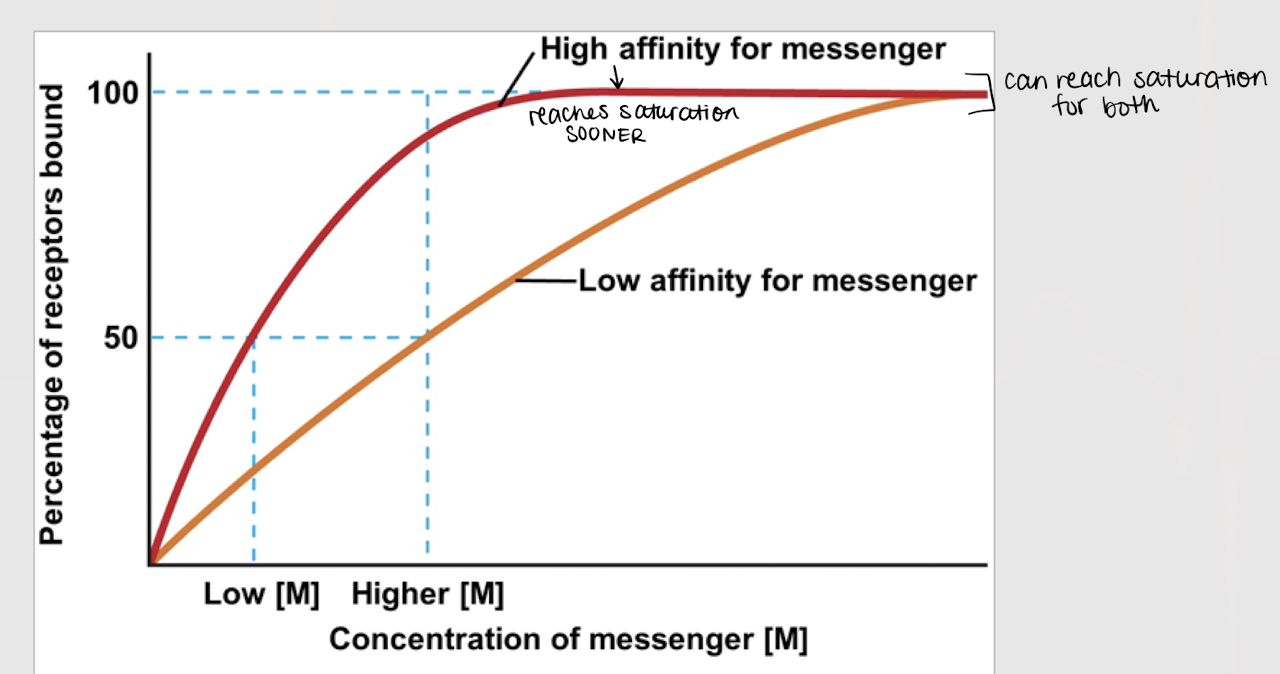
saturation
The higher the receptor affinity, the faster it will reach…
agonists
Ligands that cause cellular response when receptor binding occurs
antagonists
Ligands that prevent cellular response when receptor binding occurs. Compete w/ agonist molecules for receptor binding sites.
adrenergic receptors; ß2; agonist
Epinephrine binds to __________ _________, specifically, ____ receptors (which are abundant in the heart). It acts as an _______, causing faster/harder contractions.
antagonists; epinephrine; BP
ß-blockers are ß2-__________, not allowing _________ to bind to the receptors in the heart, causing it to beat slower and w/ less force, thereby lowering ____.
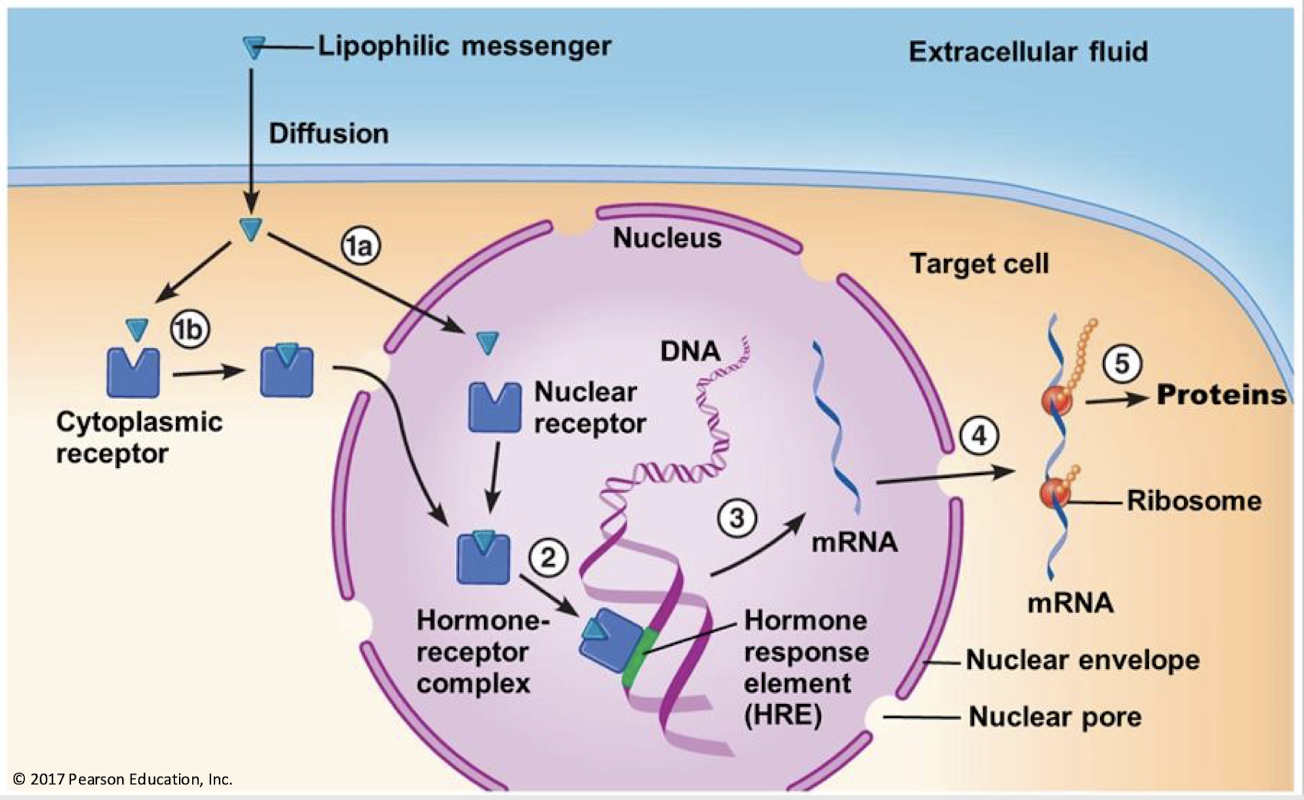
lipophilic; cytosol; nucleus
If a receptor is intracellular, it means the messenger is _________ (hydrophobic). The receptor can be either in the _______ or _______.
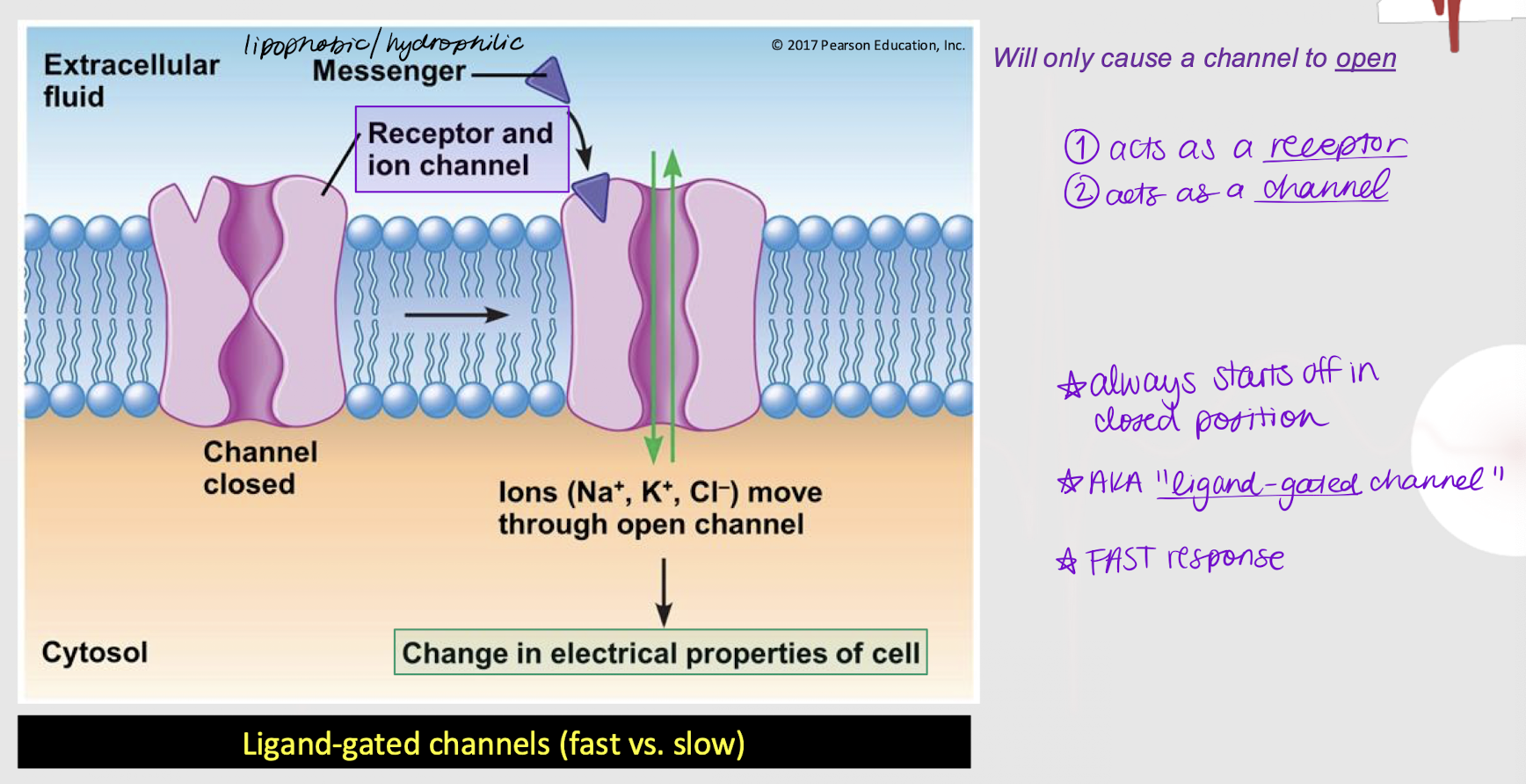
lipophobic; open
If a membrane-bound receptor is a channel-linked receptor (ligand-gated channel), it means the messenger is _________ (hydrophilic). The messenger will cause the channel to ______.
closed
Is a channel-linked receptor always open, closed, or either?
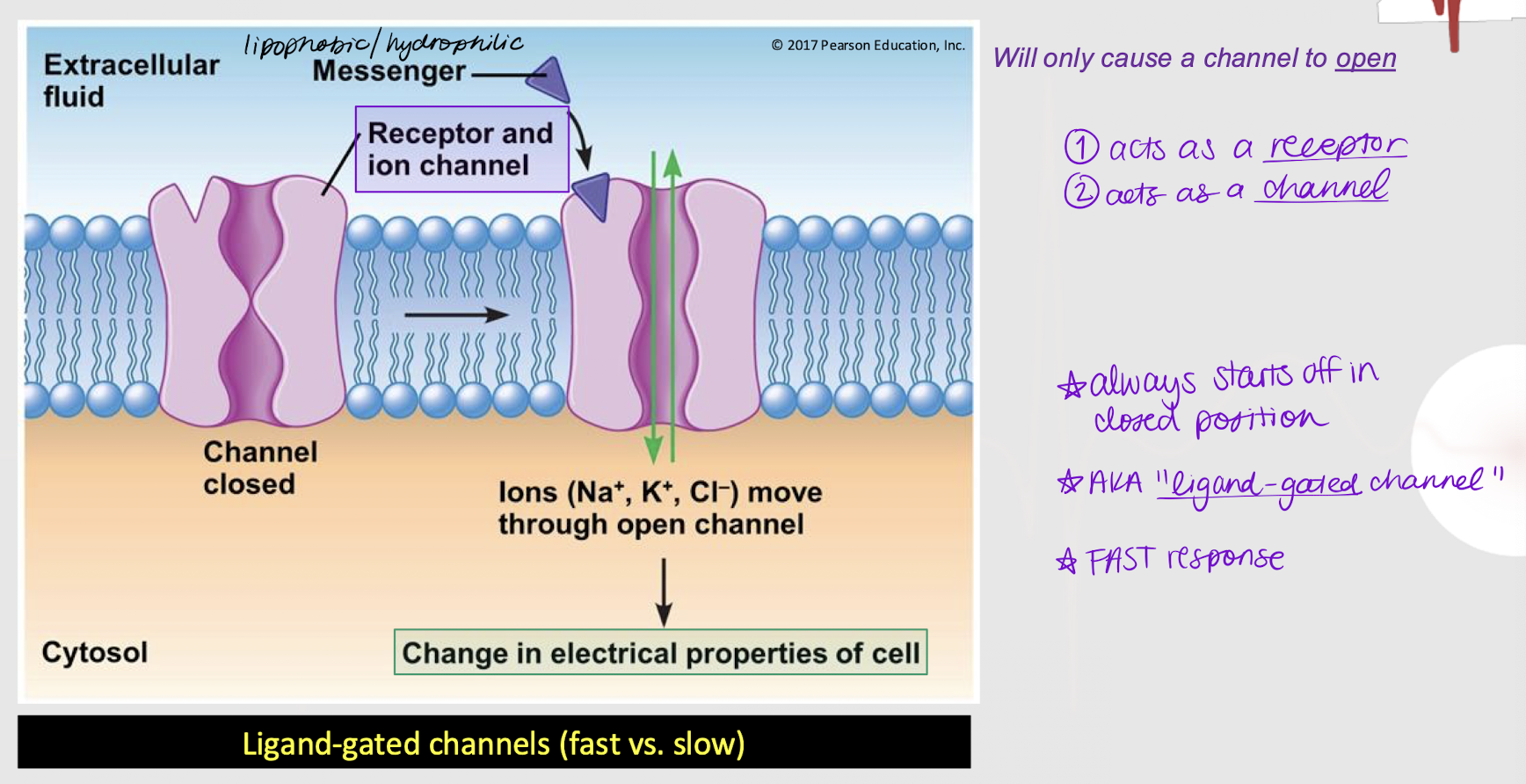
True
True or False: A channel-linked receptor can act both as a receptor and a channel.
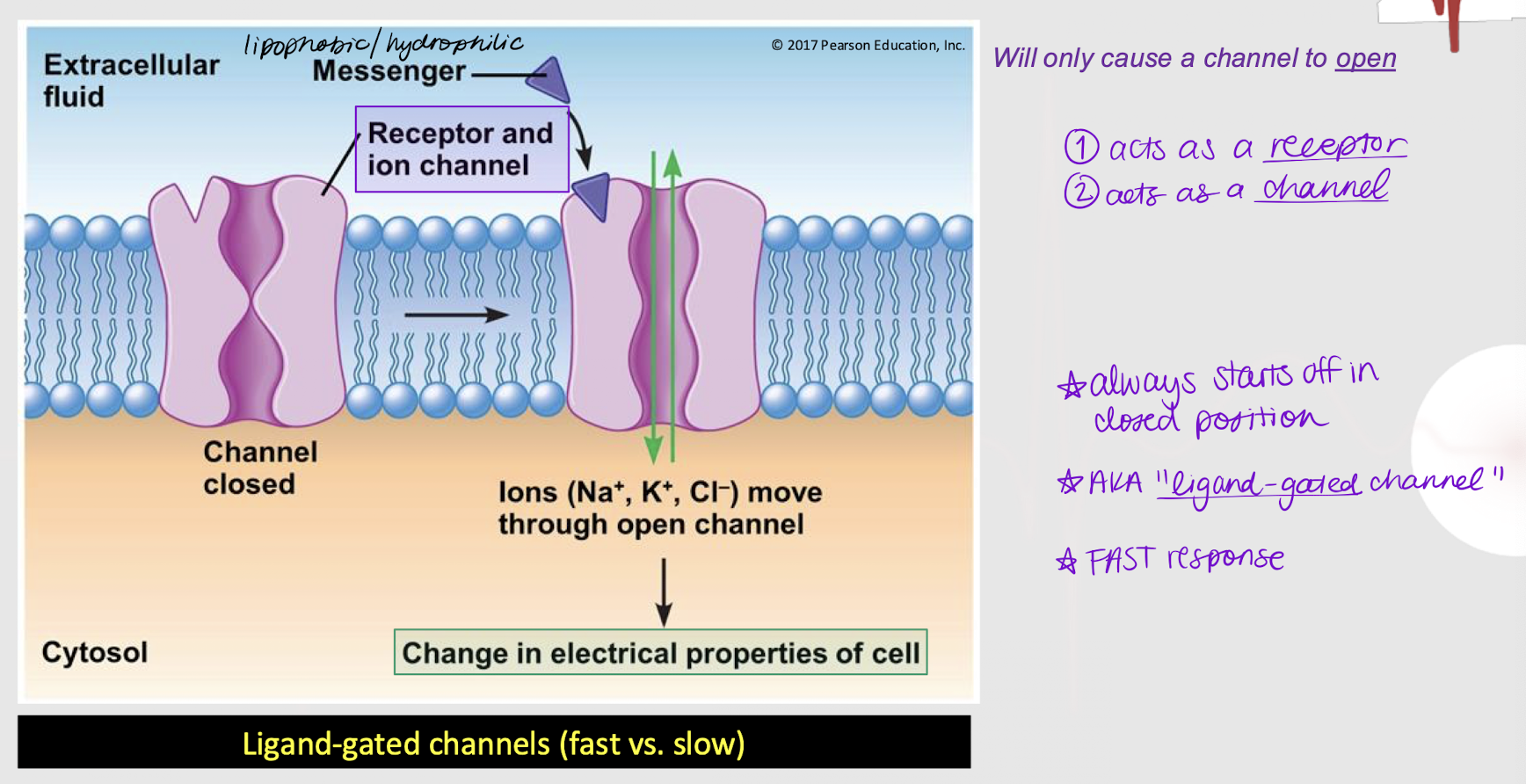
fast response
Does a channel-linked receptor (ligand-gated channel) induce a fast or slow response?
intracellular; second messenger; quickly
Channel-linked receptors (ligand-gated channels) can interact w/ ________ proteins for varied response. For example, when calcium enters a cell through the channel, it can act as a ________ ________.
Effects occur ______ but binding is brief, so overall effects are short-lived.
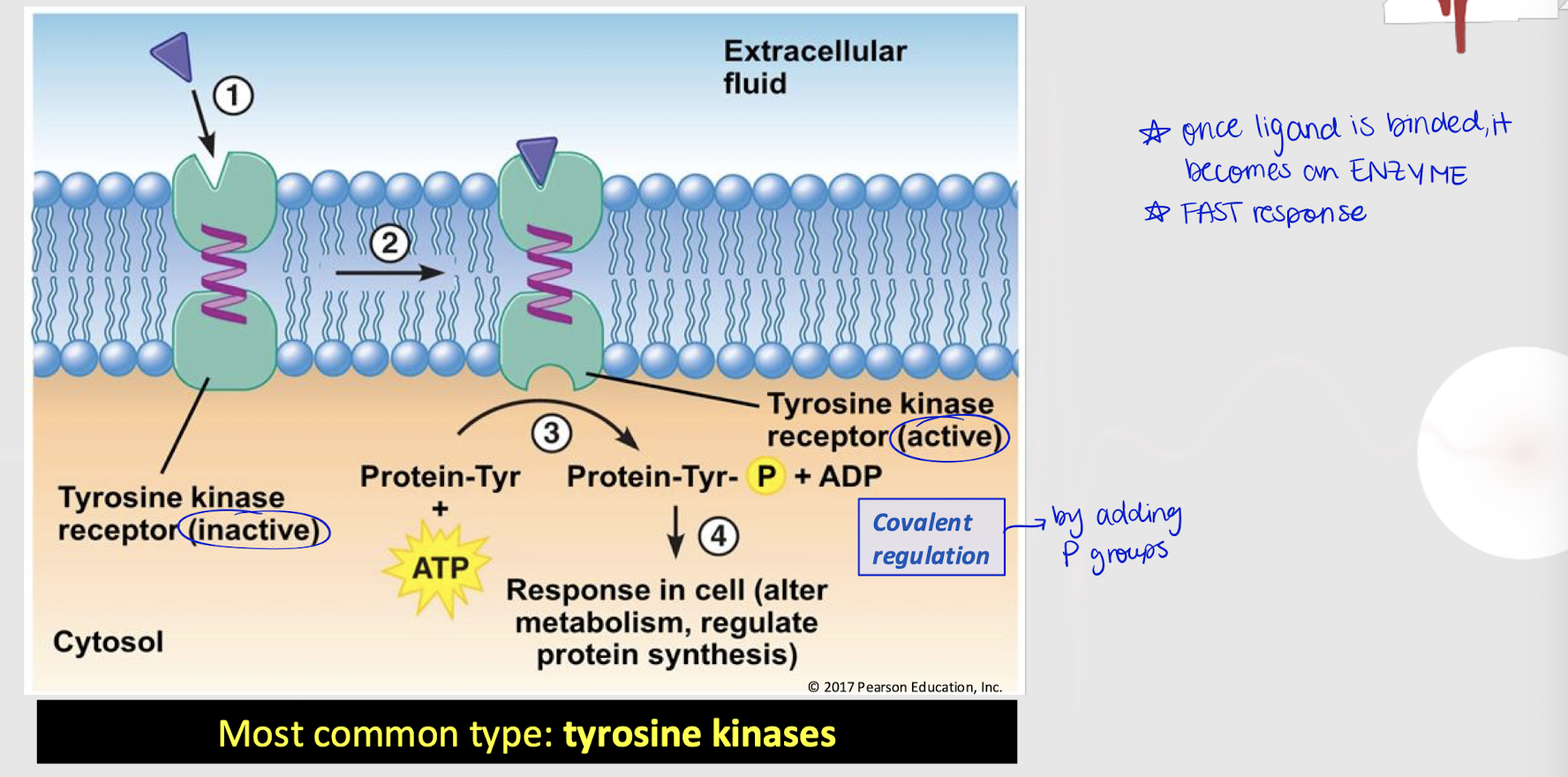
enzyme-linked receptor
Membrane-bound receptor that gets activated when a ligand binds to it (fast response), leading to a series of biochemical reactions inside the cell (e.g. covalent regulation).
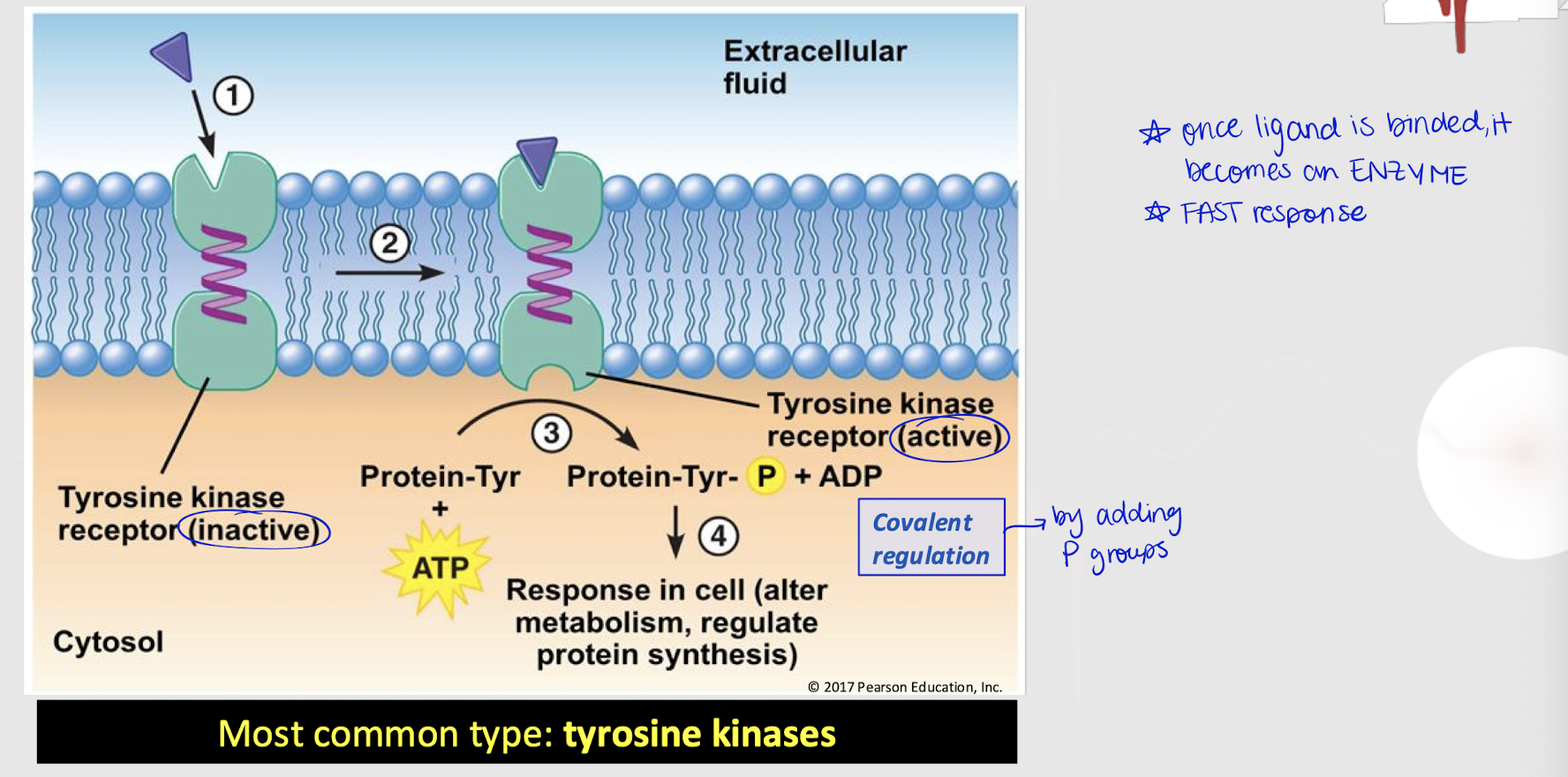
tyrosine kinases
What is the most common type of enzyme-linked receptor involved in cellular signaling?
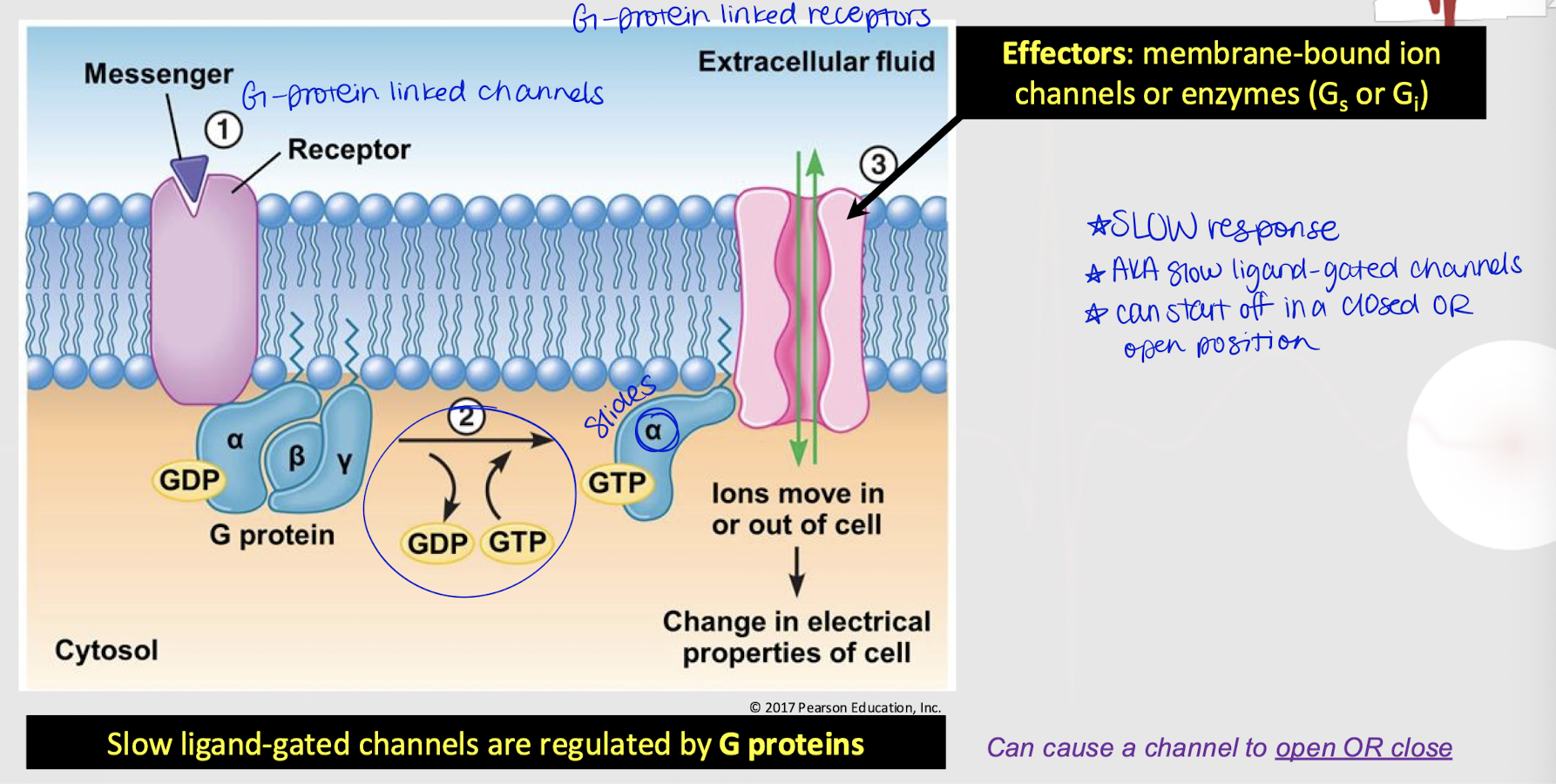
G-protein linked receptor
Membrane-bound receptor that activates a G-protein when a ligand binds, initiating a signaling cascade via second messengers within the cell, thereby having a slow response.
either
Is a G protein-linked receptor always open, closed, or either?
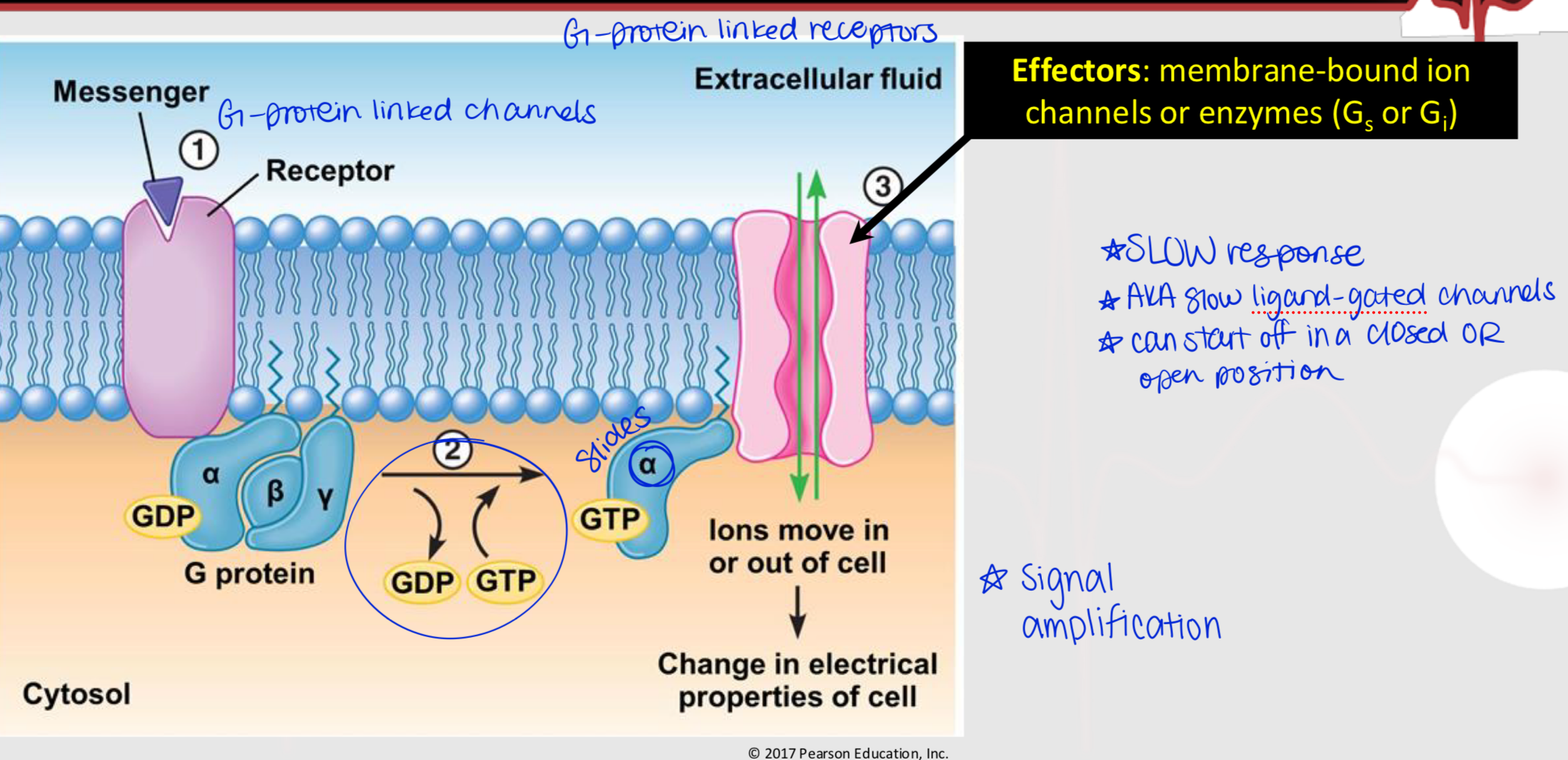
effectors
In G-protein linked receptors, membrane-bound ion channels or enzymes (i.e. Gs and Gi)
enzymes
Activation of G-protein regulated _________ result in the production or activation of a second messenger
cAMP, cGMP, DAG, IP3, calcium
What are the 5 major second messengers?
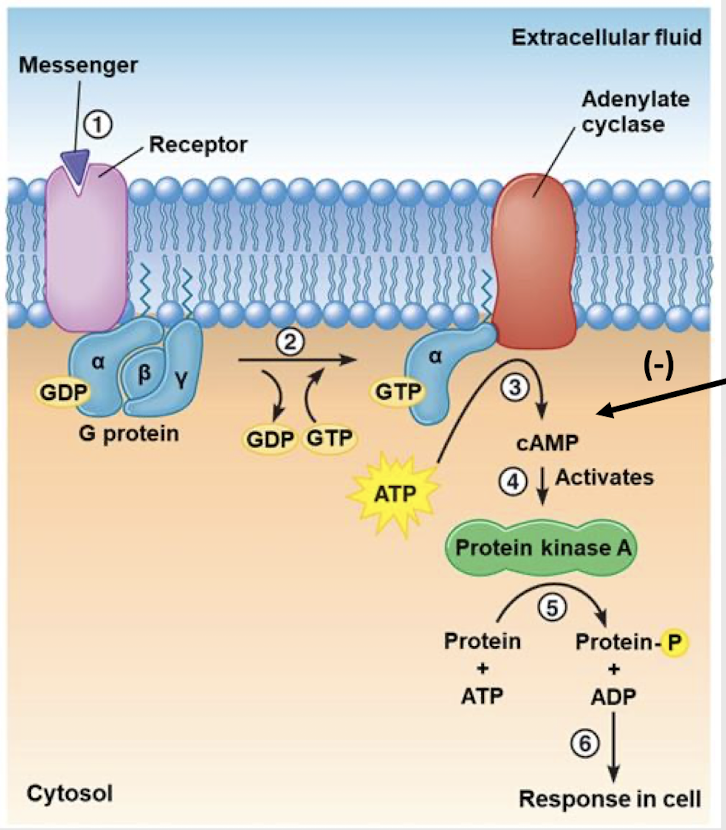
inhibits; cAMP; increase
Caffeine ________ the enzyme cAMP phosphodiesterase, which degrades _______, causing an _______ of it due to its lack of degradation.
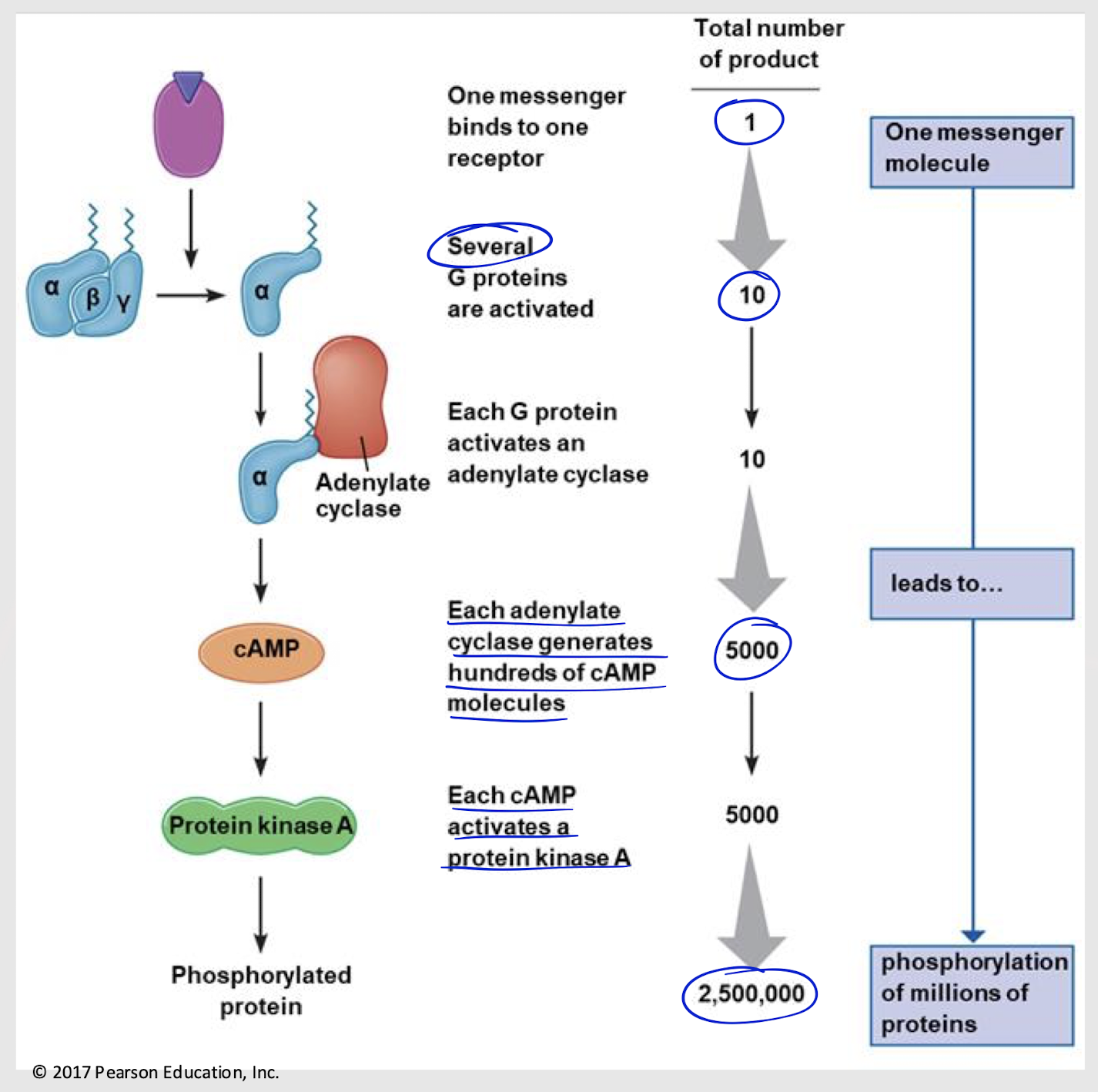
signal amplification
The process by which a single signaling molecule leads to the production of many secondary messengers, resulting in a larger cellular response.