EPSY Final
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
Academic Language
specialized vocab, concepts, strategies, reading, writing in specific subject (learned in 6-9 years)
Balanced Bilingualism
equal fluency in both languages (with academic knowledge)
code switching
changing dialects depending on environment
critical period
a specific window in dual language learning and accurate pronunciation (early childhood
cultural deficient model
a (racist) view that a person lacks certain abilities to achieve because of their cultural background
dialect
variety of a language spoken by particular group
Part of collective identity
Differences in pronunciation/grammar are not mistakes or errors
complex, logical, and rule governed
emergent learning
The skills and knowledge usually developed in the preschool years, foundation of reading and writing
2 categories of skills for learning reading
Understanding sounds and codes
Know letter names, sounds of each letter
Know that words are made of sounds
Oral language skills
Expressive and receptive vocabulary
Knowledge of syntax, able to understand/tell stories
english as a second language (ESL)
classes devoted to teaching these students english
english learners (ELs)
heritage language not english
funds of knowledge
the essential cultural practices and bodies of knowledge that are embedded in the daily practices and routines of families
genderlects
Girls
More talkative, affilative in speech
More likely to cooperate, caring
Boys
More competitive, talk about rights/justice
American boys interrupt more than girls
Differences may not apply across cultures
generation 1.5
STUDENTS WHO ARE U.S. RESIDENTS OR CITIZENS BUT WHOSE FIRST OR HOME LANGUAGE WAS NOT ENGLISH
heritage language
spoken at home or by other family members
Often lost bc family emigrate to different countries
limited English proficient (LEP)
students just learning english
melting pot
Expected to assimilate into american culture in past decades (this metaphor)
metalinguistic awareness
Explicit understanding of language and how it works
Begins to develop around 5 and continues
Emergent literacy (tiers to learning to read)
monolingual
a person only knowing/ proficient in one language
overregularize
apply new rule or syntax or grammar where the rules doesn’t apply
Foots, holded
pragmatics
Context based knowledge
When, where, how and whom to speak
Children know to use simplier language to younger children
receptive vocabulary
the words an individual understands, either when heard or read, regardless of whether they can use them in their own speech (“input”)
semilingual
lack of proficiency in any language
sensitive periods
optimal time for bilingual language and reading exposure and mastery (for second language learning)
sheltered instruction
offers support to students (english learners) through visual aids, adapted reading materials and tasks, and catering to their language-related requirements
structured English immersion
teaching student in only English
syntax
subject-verb-object word order
absence seizure
Very brief, involving small part of brain
Americans with disabilities act of 1990 (ADA)
landmark civil rights law enacted that prohibits discrimination against individuals with disabilities in various areas of public life, including employment, transportation, public accommodations, and telecommunications.
articulation Disorders
production difficulties (substitution, distortion, omission of sounds)
Attention-deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
Pervasive pattern of inattention, impulsivity and/or hyperactivity that is more frequent and severe
than is typically observed in individuals at a comparable level of development
• Not just inattention, also hyperfixation, difficulty changing tasks
• Drug Treatment Controversy
• Those who are not medical professionals should refrain from suggesting pharmaceutical
treatment
• Fabiano et al. meta‐analysis “Our results suggest that efforts should be redirected from debating
the effectiveness of behavioral interventions (e.g., time out, self‐regulation, shaping) to
dissemination, enhancing, and improving the use of these programs in community, school, and
mental health settings.”
• Students benefit from approaches that combine motivational training with
instruction in learning and memory strategies and behavior modification
Autism Spectrum Disorder
Added to IDEA in 1990
• Range of mild to severe (Asperger’s no longer a separate disorder)
• Less than 1/3 have intellectual impairment; 10% extraordinary abilities
• More boys than girls (80%)
• Disorder of social communication and repetitive/restrictive behaviors
Automaticity
the ability to perform tasks or activities without conscious thought or effort, usually due to extensive practice or learning.
Cerebral Palsy
range of motor or coordination difficulties due to brain damage; spasticity and secondary handicaps
Convergent Thinking
focuses on reaching one well-defined solution to a problem
Creativity
imaginative, original thinking or problems
Any subject can be approached in creative ways
Assessing creativity: verbal and graphic tests
Divergent thinking =, coming up with possible solutions
Uncommon convergent thinking–single solution
Scores based on originality, fluency, flexibility of ideas
Indicators of creativity in students: curiosity, adaptability, high energy. Humor, nonconformity, interest in complex/mysterious
Crystallized Intelligence
Intelligence is composed of two separate abilities
Depends upon exposure
Acquired skills and knowledge of facts, how to apply in environment
Culturally appropriate applications
Fluid Intelligence
intelligence is composed of two separate abilities (mental efficiency)
Nonverbal and culture free
Problem solving, abstract thinking, reasoning
Inherent and increases until 20s
Deviation IQ
compared to average performance of others in that age group – relative to mean
Divergent Thinking
coming up with possible solutions
Emotional and Behavioral Disorders
IDEAs definition: emotional disturbances as innaporpriate behavior, unhappiness or depression, fears and anxiety trouble with relationships
Overlap with high incidence disablities category
Respond to this with structure and organizaiton, schedules, and activities+rules
Emotional Intelligence
Epilepsy
seizures caused by abnormal electrical discharges in the brain; require teachers help to avoid
Focus:
Generalized tonic-clonic
Absence
Fluency Disorders
stuttering
Flynn Effect
IQ Scores have been rising since the early 1900s
To keep 100 as the average, tests become more difficult
Re-norming
Free, Appropriate public education (FAPE)
guarantee to be accommodated by public schools receiving federal government funds
Generalized Intelligence (g)
Intelligence is explained by one main ability (general intelligence)
Performance on tasks also includes specific abilities
Across domains, explains high correlation between performance on a broad range of cognitive tasks (reading, writing, math)
Criticism: “g” doesnt offer much in terms of explaining specific abilities we have and difference that can exist but them
Spearman (1927)
One ability
Gifted and Talented students
Competency in one or more domains
3 part conception of giftedness: above-average general ability, high creativity, high motivation to achieve
Origin of gifts: nature, hard work, parents’ investment in development of child's gift
Gifted in math, music, visual arts–enhanced development of right side of brain
Problem with gifted adolescents: depressed, bored, frustrate, isolates
May be viewed as show-offs, impatient
Focal onset seizure
brief seizures, occuring in one are of brain
handicap
a disadvantage or impairment that makes it difficult for someone to perform certain activities
identity-first reference
language that refers to the person/ proper noun before the disability (person with a wheelchair)
Individualized Education Program (IEP)
Present level of performance, annual goals (also short‐term goals), services to be provided (when/where/what), extent of participation in required testing; when older ~ transition plan
Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA)
Prior to 1975 student w disabilities were not served in public schools
Class action lawsuits being filled in states over acces to education
Passage of federal education law
Principles
Free and appropriate public education (FAPE)
Zero reject: all means all
Obligation to “child find”
insight
the sudden realization of a solution to a problem, often described as an "aha!" or "eureka!" moment. It's a cognitive process where individuals quickly and clearly grasp the solution without extensive trial and error or overt problem-solving steps.
intellectual disabilities
Disability characterized by significant limitations in both intellectual
functioning and adaptive behavior as expressed in conceptual, social, and practice adaptive skills
• Generally IQ score below 70 + adaptive behavior deficits (MR)
intelligence
Theoretical construct: unobservavble/ hypothetical/ abstract
Most theories about the same nature of intelligence include in their definition
Capacity to learn
Ability to take in information from our environment and make it “part of what we know”
The total knowledge the person has acquired
The ability to adapt successfully to new situations and environments
intelligence quotient (IQ)
Mental age, later termed IQ (ratio of mental age to chronoloigcla age)
learning preference
Individual preferences for particular learning modes and environments
learning styles
Approaches to learning and studying
Research does not support idea that matching learning style to instruction/studying has any effect on achievement
Least restrictive environment
As much as possible considered best practice (principle of IDEA)
legally blind
20/200 vision; severely restricted peripheral vision
• Special materials/equipment aid in classroom functioning
• Room arrangement must accommodate student’s safety
low vision
Limited to close objects; read large print
mainstreaming
the practice of placing students with special needs into regular general education classrooms for a portion of the day or for specific subjects, based on their individual skills and needs
response to intervention (RTI)
Systematic process of assessing and providing appropriate
instruction/support for students with learning problems
• Main goal: Effective research‐based instruction and support as soon as
possible, before students fall behind
• Second goal: Systematic documentation of interventions tried
• May be used to determine who needs more intensive learning support
• Commonly used three‐tiered system to reach RTI goals
• Tier 1 schoolwide, grade‐level research‐based instruction
• Tier 2 targeted supplemental instruction in classroom
• Tier 3 intensive support by specialists
restructuring
section 504
Section 504– part of vocational rehabilitation act of 1973
Prevents discrimination against people with disabilities in any progras funded with federal money
Covers children with conditions not covered in IDEA
medical /health: diabetes, drug addiction, severe allergies
Stuednts with attention disorders
procedures/ plans developed by individual schools
Protections extend beyond schools (library, restaurants, stores, transportation, theaters)
spasticity
a neurological condition characterized by stiff or rigid muscles due to increased muscle tone and exaggerated reflexes
theory of multiple intelligences
Intelligence is the ability to solve problems and create products or outcomes taht are valued by culture
Little research support, “talents” overlap
tonic-clonic seizure
severe, involved both sides of brain
transition programming
the process of preparing students with disabilities for life beyond high school
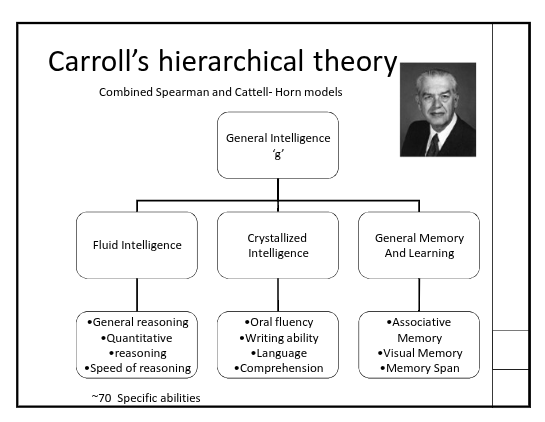
triarchic theory of successful intelligences
Fluid Intelligence, crystallized Intelligence, and general memory+learning (associated memory, visual memory, memory span)
zero reject
all means all (principle of IDEA) every child must be accommodated
voicing problems
inappropriate pitch, quality, loudness or intonation
learning disabilities
• In general ~ performance below what would expect given their other abilities. Not intellectual
disability, emotional problems or educational disadvantages; normal vision, hearing and language.
• Most commonly difficulty with reading, followed by math computation
• Early identification critical
IDEA “a disorder in one or more of the basic psychological processes involved in understanding or
using language, spoken or written, that may manifest itself in imperfect ability to listen, think, speak,
write, spell or do mathematical calculation”
cognitiive intelligence
information processing (review)
Focusing attention, emotional self- regulation, impulse inhibition
neuroscience intelligence
plasticity; some brains better than others at forming new connections
Pygmalion Effect
is a psychological phenomenon where higher expectations for someone lead to improved performance. In essence, believing in someone's potential and communicating that belief can positively influence their behavior and achievements.
Language development
Sounds and pronunciation
By age five, most children have mastered the sounds of native language
Vocab and meaning
By age 6, most can understand 20,000 words and can use 26000
Cognitive skills develop, understanding abstract ideas and hypothetical situations
Inside-out skills
(letter sound)
Translate written symbols into spoken words
Outside-in skills
(language comprehension)
Applying knowledge of information outside the particular printed words being read
Additive bilingualism
keep first language and add another
Substracitve bilingualism
add second language, lose first
Movement management
keeping lessons and the group moving at an appropriate (and flexible) pace, with smooth transitions and variety
Overlapping
keeping track of several activities at the same time
Individuals, small groups, at computers
With-it-ness
awareness of what going on in the classroom (eyes in the back of your head)
Prevent minor disruptions from escalating
No timing errors (waiting too long to deal with a problem)
No target errors (blaming wrong student)
“I” message
clear and assertive, non-accusatory statement of how something os affecting you
Verbal intervention to change students behavior
“I feel” “I cant focus”
Assertive discipline
clear, firm, unhostile response
clearly , condifdently state what you expect
Ignore excuses, accusations, promises to change
Teach responsible behavior
authentic assessments
central tendency
Mean: Arithmetical average
• May not be a score anyone earned, affected by outliers
• Median: Middle score in a ranked list (half above, half below)
• Mode: most frequently occurring score
criterion referenced
Scores are compared to a given criterion or standard
of performance
• E.g., scoring above 80% on driver’s test means you pass
• Should tell teacher exactly what students can or cannot
do
formative assessment
occurs before or during instruction to aid in planning
and diagnosis
• Non-evaluative, supportive, timely, specific
• A pretest is one example of a formative assessment
• Determine what students know, not graded
summative assessment
At the end of instruction
• Level of accomplishment (e.g., final exam)
measurement
quantitative description of an event or characteristic using numbers
• How much, how often, or how well
• Characteristics summarized into a score, amount, rank
• Only one part of assessmen
norm referenced
Norms for determining meaning of a given score
• Different types of norm groups
• Class or school
• School District
• National Sample
• Useful for determining overall or levels of
achievement
• Can’t tell you who is ready for more advanced work
assessment
Broader than testing and measurement, procedures used to obtain
information about student performance
• Good assessment uses multiple measurements, tests, and sources of information
grade-equivalent score
Indicate how closely a students’ performance matches average scores for a given grade
(Separate norm groups by grade)
• Often misinterpreted
• Does not indicate instructional leve
authentic assessments
Students apply skills and abilities in real-life situations (example: use fractions to double a recipe)
performance assessments
Any form of assessment that requires students to carry out an activity or produce a product in order to demonstrate learning
pretest
one example of a formative assessment
• Determine what students know, not graded
standard deviation
how widely scores vary from the mean
• Large SD ~ scores spread out in distribution
• Small SD ~ scores clustered around mean
• Range: distance between highest and lowest score
blooms taxonomy
classification of educational outcomes
Benjamin bloom and colleagues developed taxonomy in 1950s
cognitive outcomes
memory and reasoning