PHM 321, Drug structures, identification, function recall
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
What structure is this?
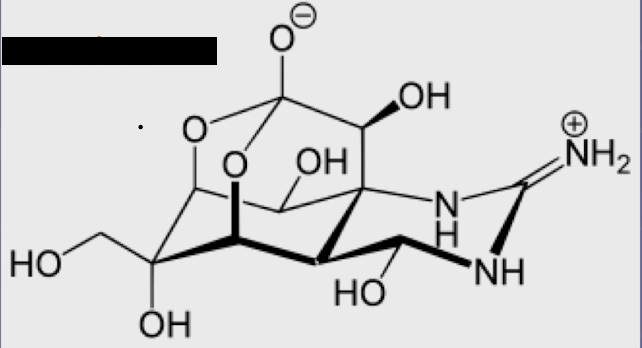
Tetrodotoxin
What structure is this?
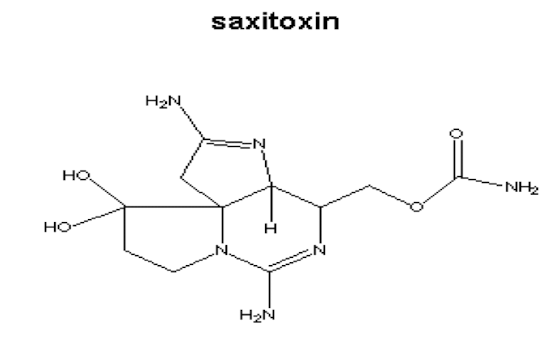
Saxitoxin, sodium channel blocker, leads to paralysis and respiratory depression
What structure is this?
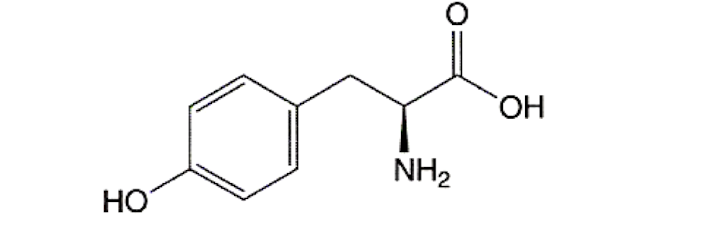
Tyrosine
What structure is this?
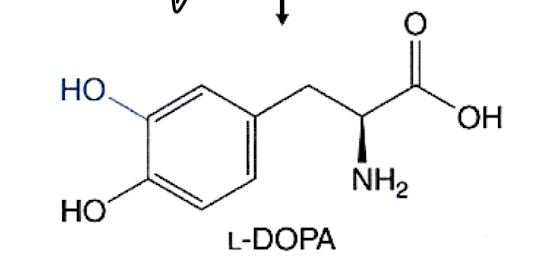
L-DOPA
What structure is this?
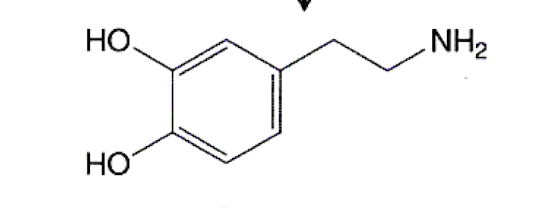
Dopamine
What structure is this?
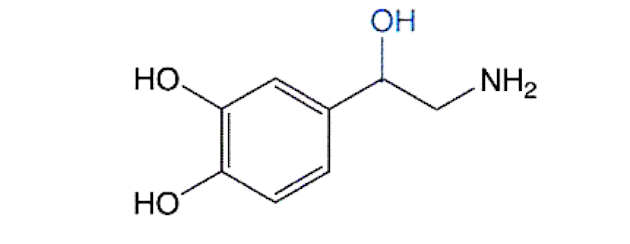
Norepinephrine
What structure is this?
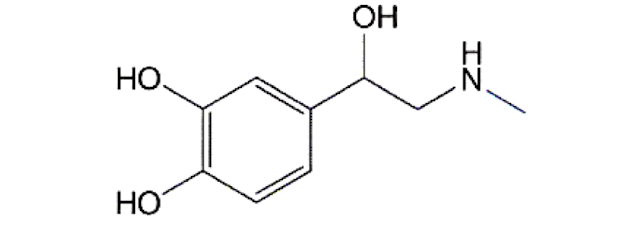
Epinephrine
What structure is this?
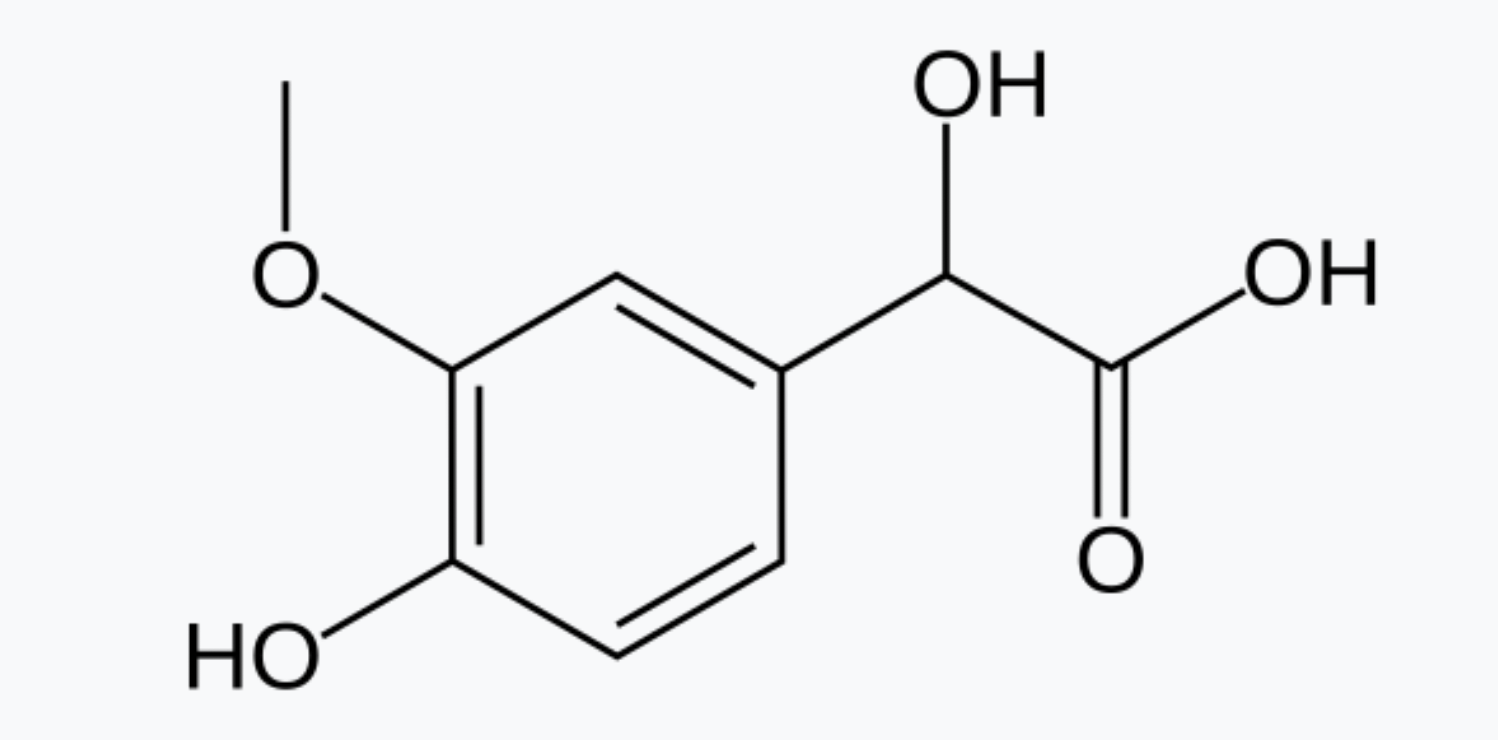
VMA
Vanillylmandelic acid, major metabolite of NE in urine.
Function of alpha-1 receptors
Mixed (both inhibitory and excitatory)
VSM contraction - increase BP
GSM contraction - urine retention
ISM Relaxtion - decreased motility
Liver - Glycogenolysis and gluconeogenosis
Function of alpha-2 receptors
Inhibitory
Pancreas - Beta cell - decrease insulin secretion from pancreas
Platelet - Increased platelet aggregation - decreased BF
Nerve - Decrease NE release - inhibition of adenylyl cyclase
VSM - contraction - minor
Function of Beta-1 receptors (all Gs bound)
Excitatory
Heart - Chronotropy and Inotropy (increased heart rate and force of contraction)
Increased AV Node conduction
Renal Juxtaglomerular cells - increased renin - RAAS , increase BP through vasoconstriction and sodium retention
Function of Beta-2 receptors
SM Relaxation
Support alpha-1 in liver functions
Beta-3 functions
Brown adipose lipolysis in neonatal years
What structure is this?
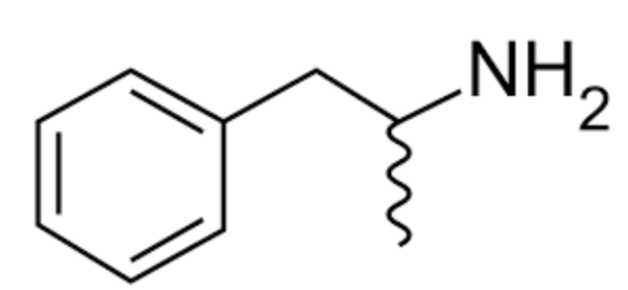
General Amphetamine structure
Chemical name for pemoline
2-amino-5-phenyl-2-oxazolin-4-one
Chemical name for phendimetrazine
3,4-dimethyl-2-phenylmorpholine
Chemical name for methylphenidate
methyl-𝛼-phenyl-2-piperidine-acetate
What structure is this?
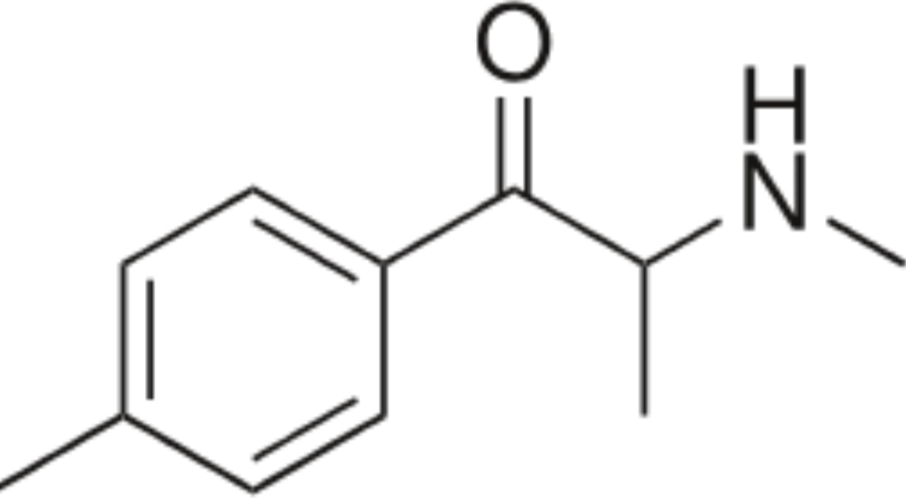
Methylone
What structure is this?
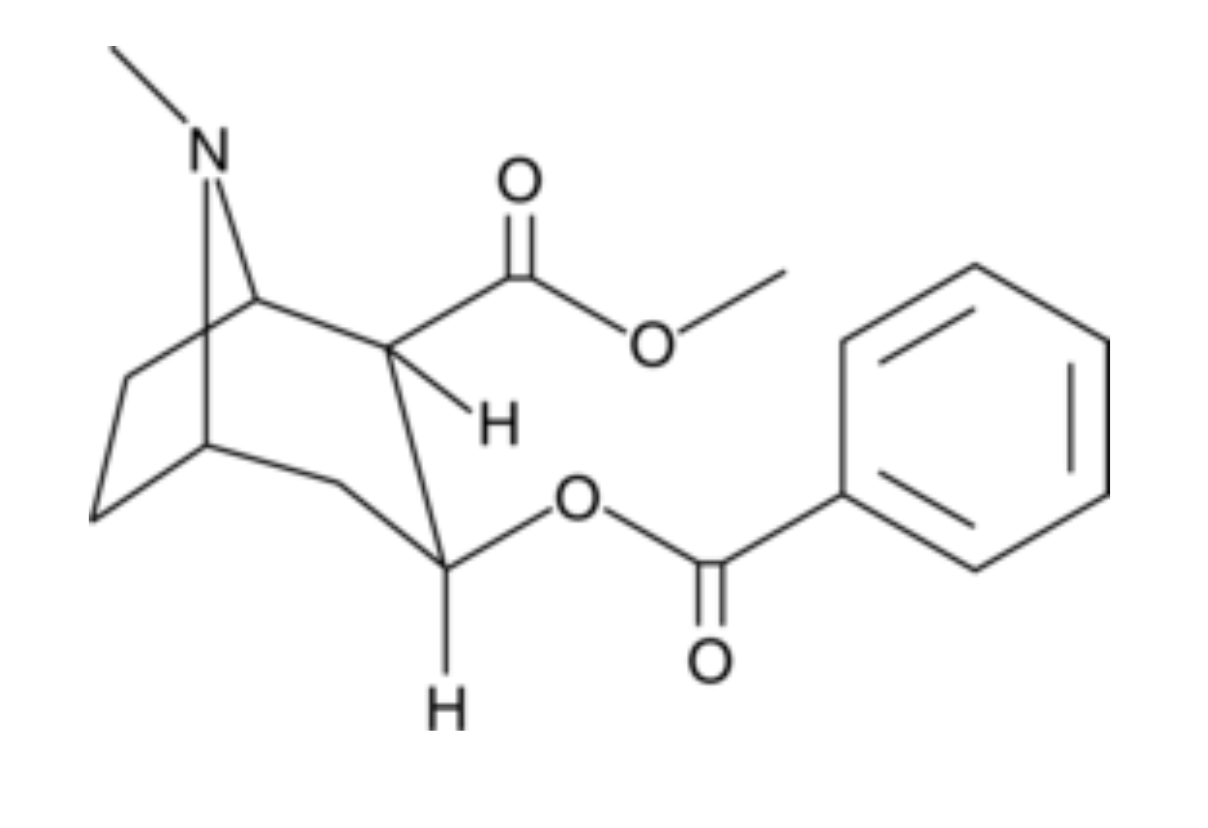
Cocaine
What structure is this?
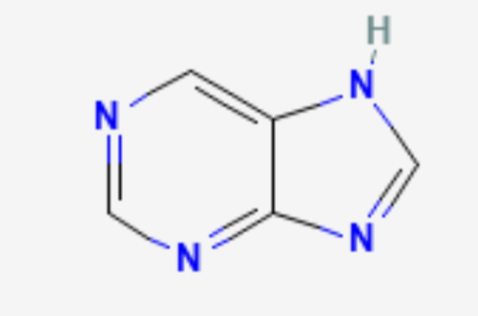
Purine
What structure is this?
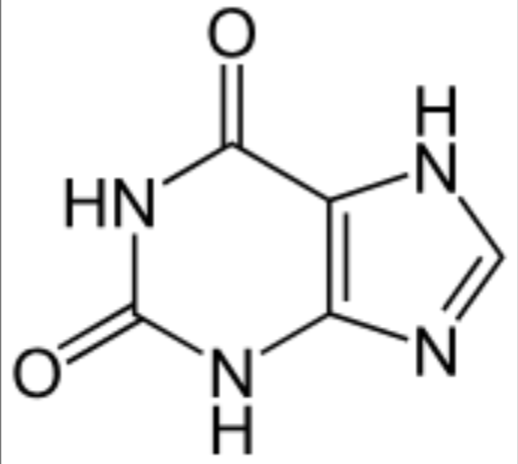
Xanthine
What structure is this?
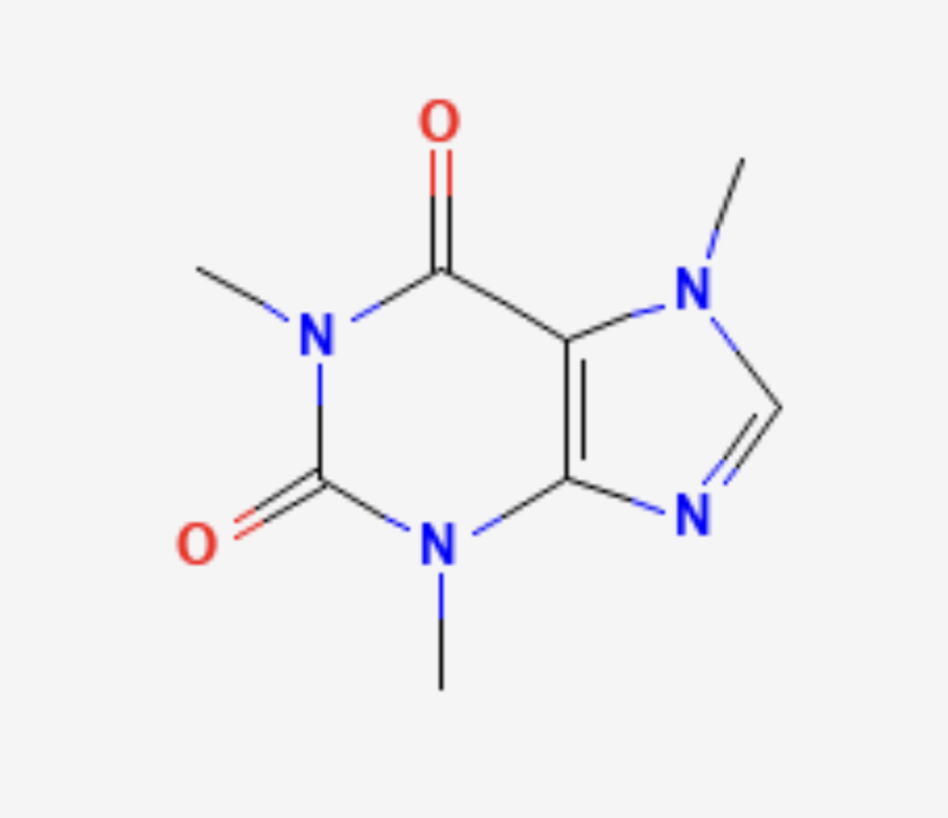
Caffiene
What structure is this?
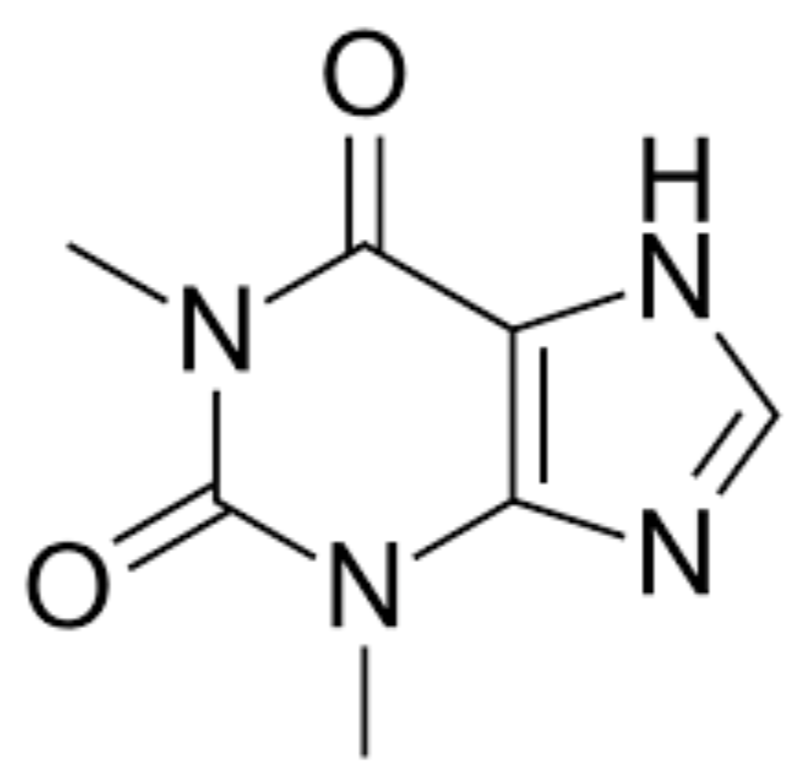
Theophylline
What structure is this?
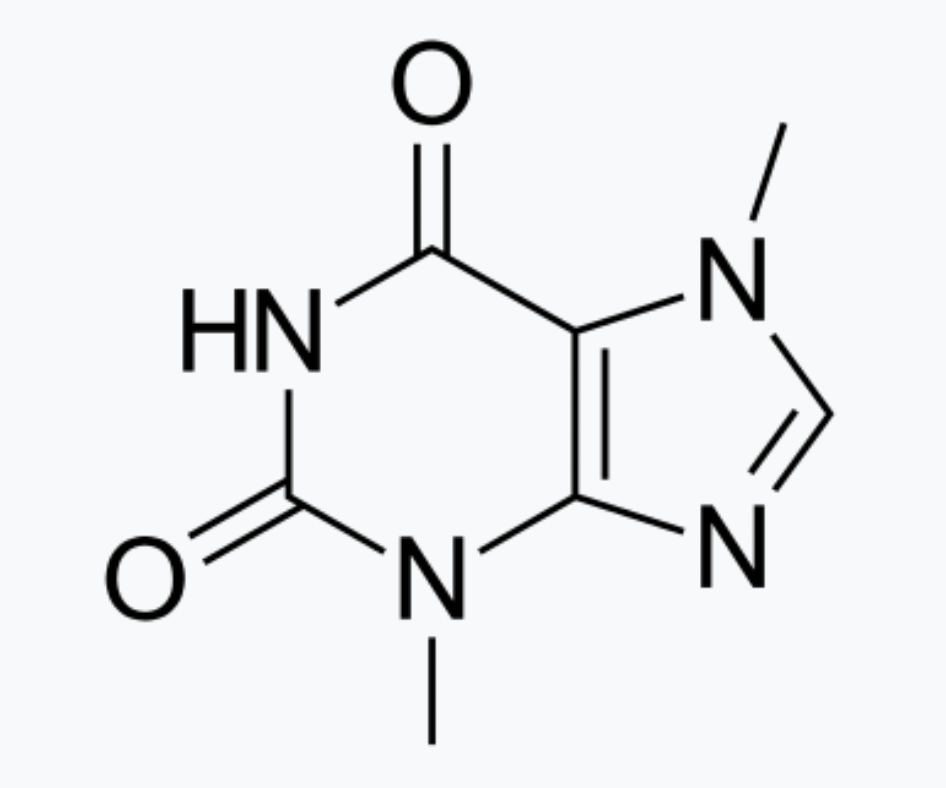
Theobromine
What structure is this?
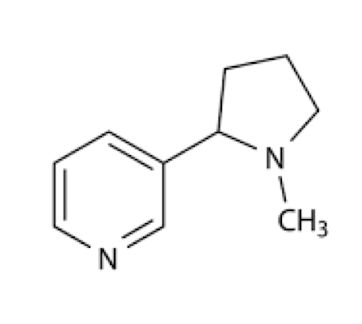
Nicotine
Where are M receptors found
CNS
autonomic, PLC simulation, Aden. Cyc. inhibition, K+/Ca2+ channels regulation
Where are N receptors found
SNS + PNS, Post synaptic excitatory synapses
Function of M1 receptors
Late EPSP - increased chance of triggering action potential
CNS - arousal, attention, pain reduction (analgesia)
Function of M2 receptors
SA Node - slowed depolarization, slowed hyper polarization
AV Node - decreased conduction velocity
Atrium - decreased refractory period, decreased contractile force
Function of M3 receptors
SM - contraction
Function of M4 receptors
inhibits adenylyl cyclase
Modulate DA release, involved in motor control
Function of M5 receptors
Stimulate PLC for cerebral vasodilation
Nicotinic M vs N receptors
M - NM endplate depolarization (contraction), muscle contraction
N- Autonomic, post ganglionic neuron firing, catecholamine secretion
What is this structure?
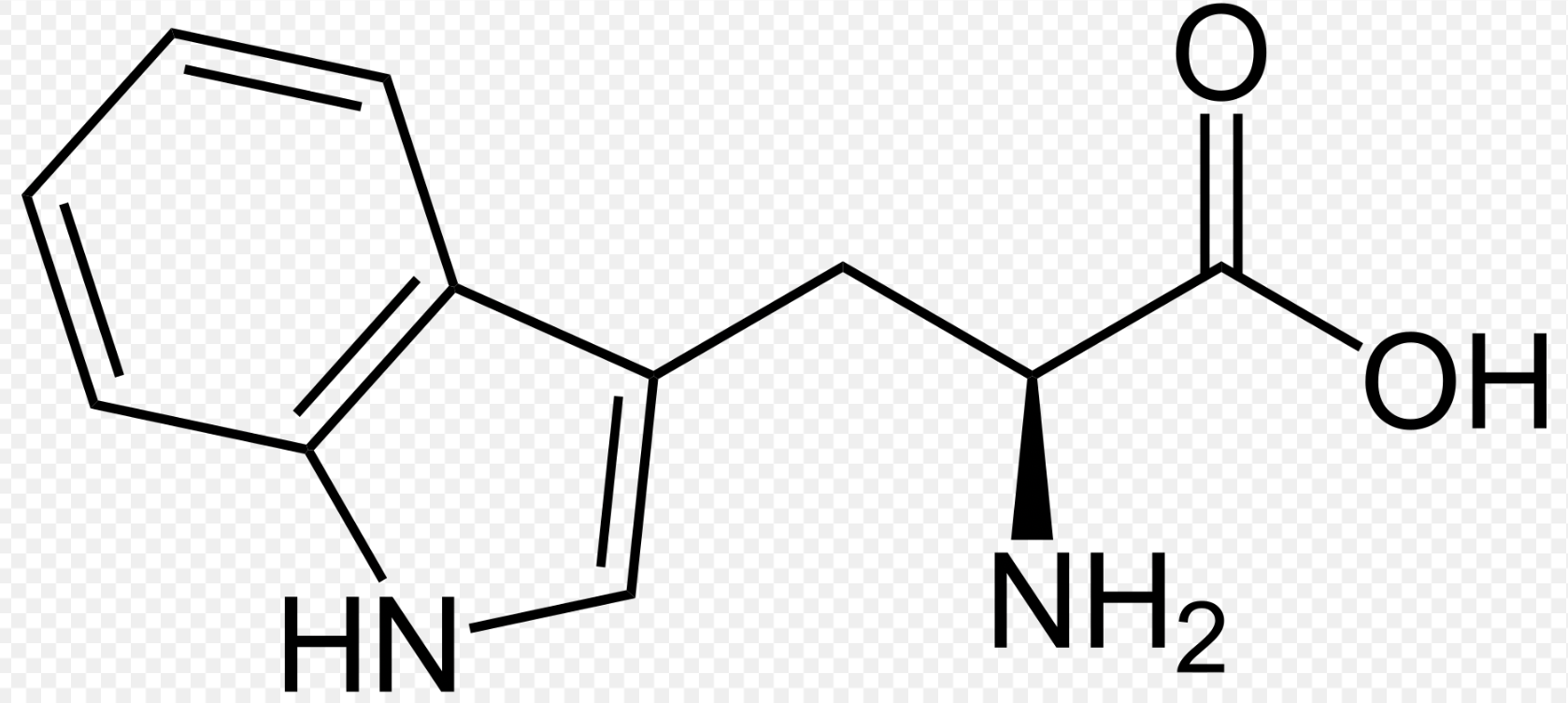
Tryptophan
What is this structure?
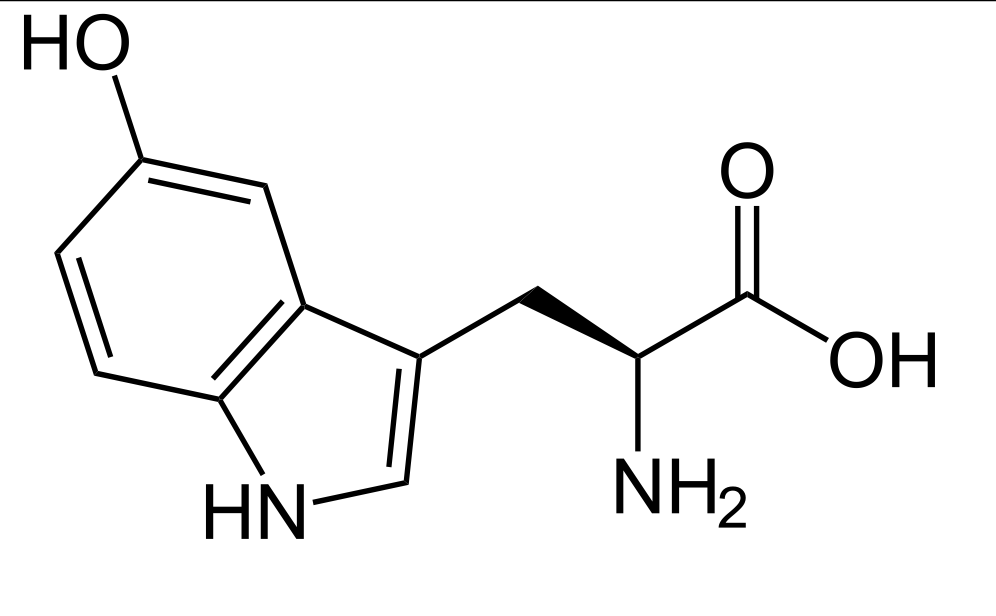
5-hydroxytryptophan
What is this structure?
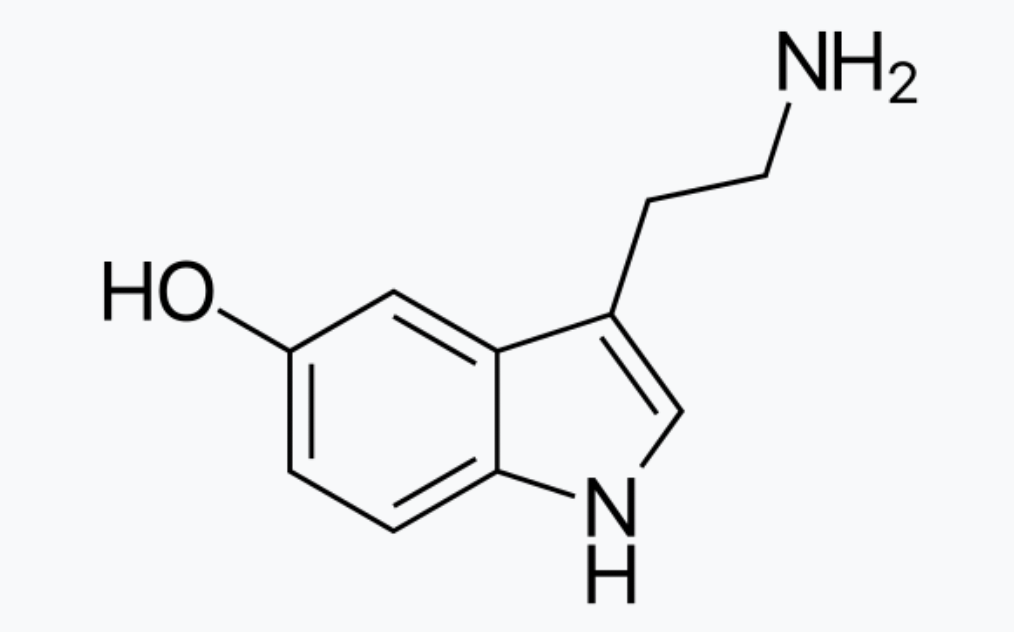
5-hydroxytriptamine or serotonin
What is this structure?
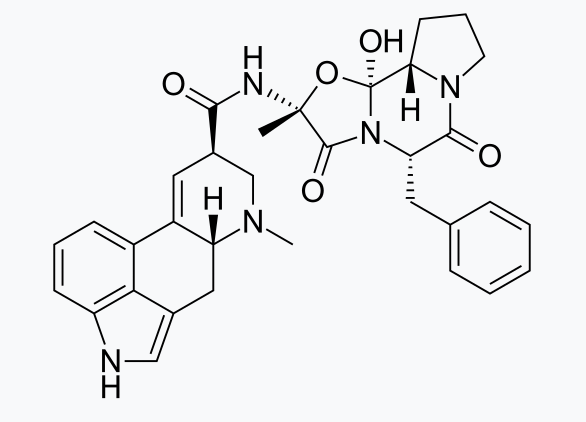
Ergotamine
What is this structure?
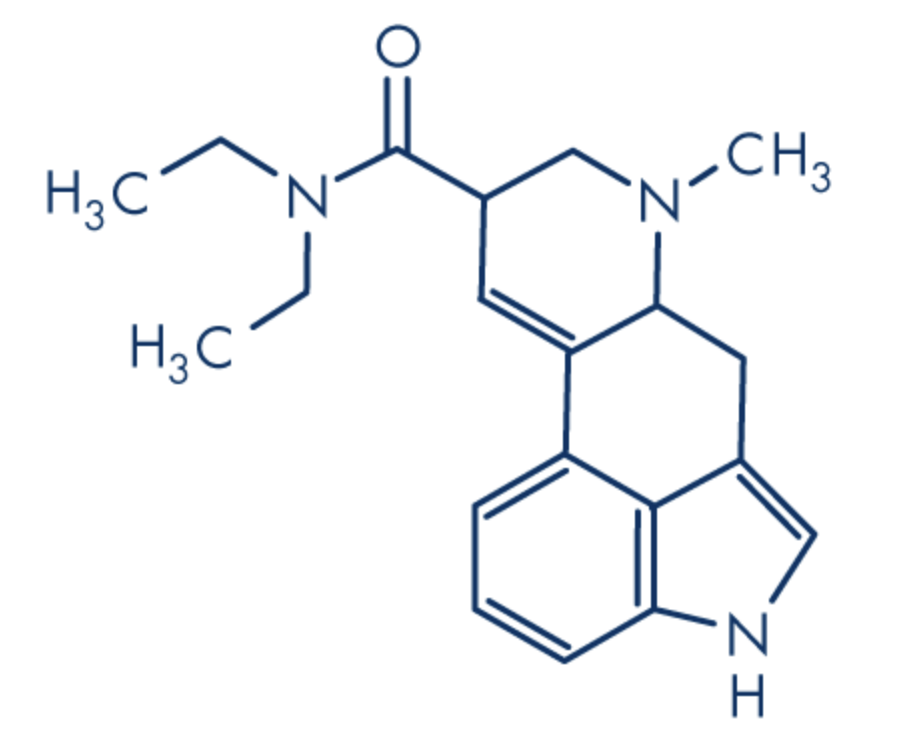
LSD, Lysergide
What is this structure?
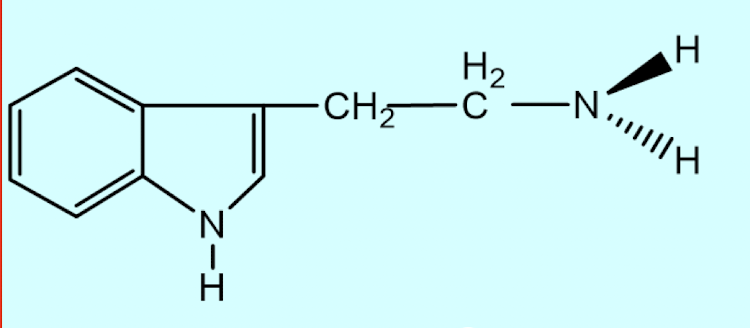
Tryptamine
What is this structure?
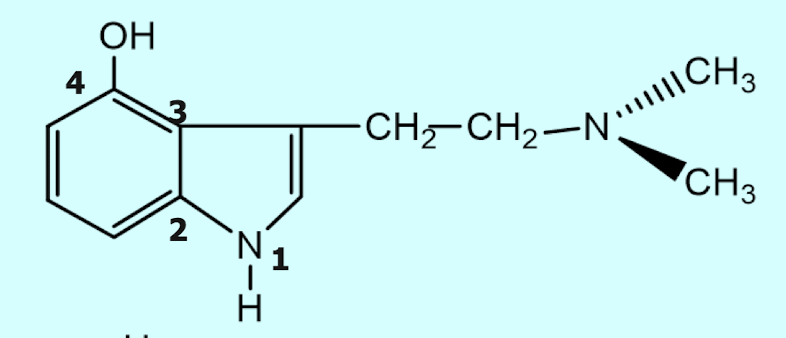
Psilocin - 4-hydroxydimethyltryptamine
What structure is this?
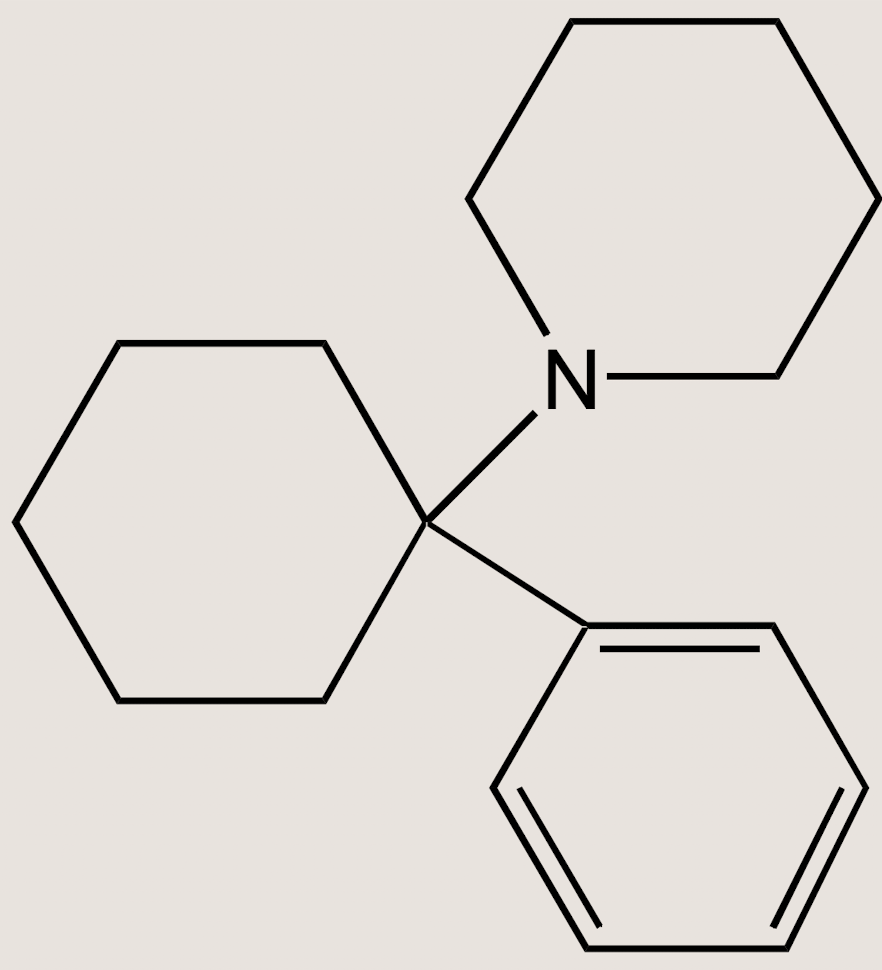
PCP, 1-phenylcyclohexyl piperdine
What structure is this
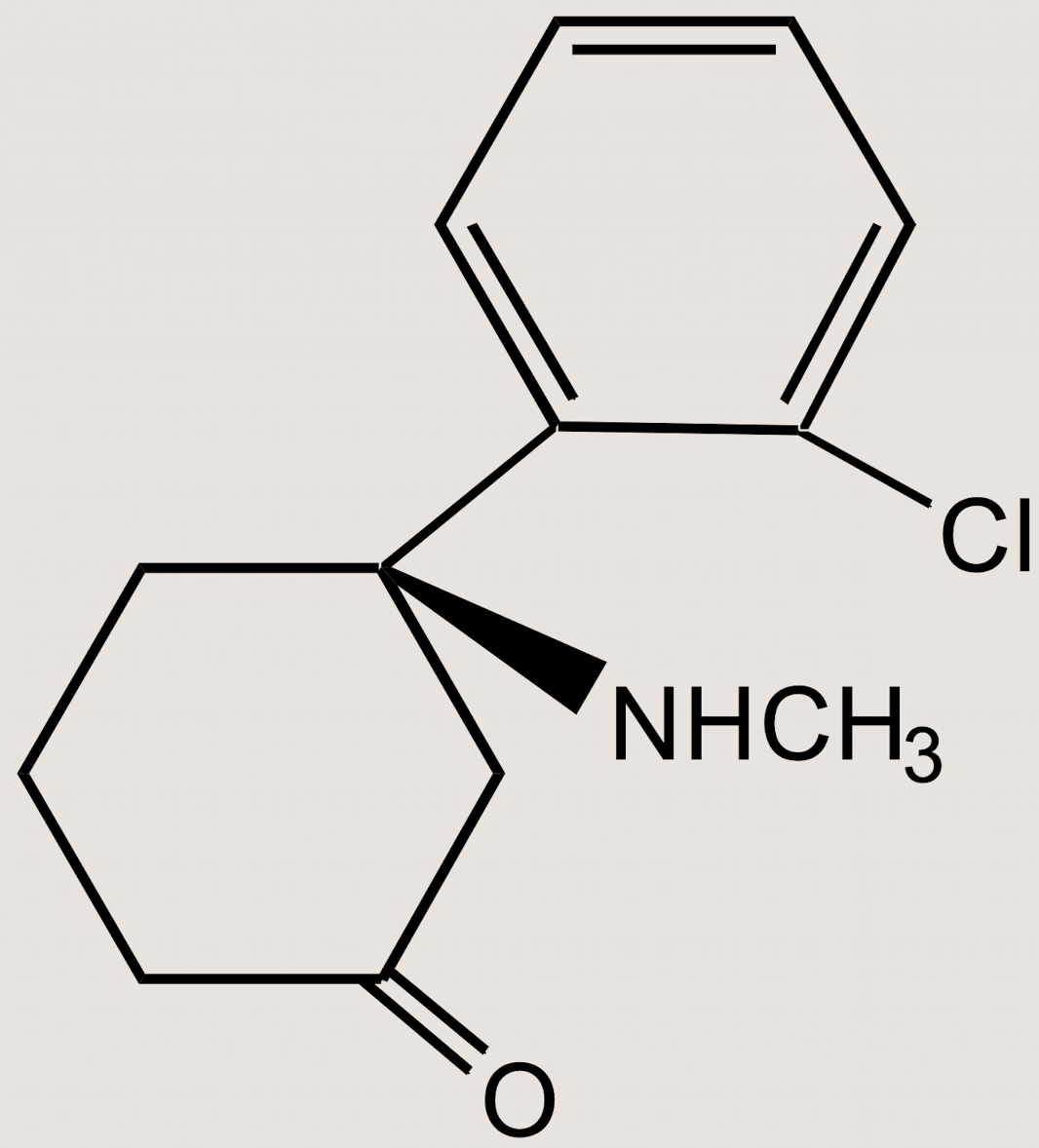
Ketamine, 2-(ortho-chlorophenyl)-2-methylamino-cyclohexanone HCl