COMPSCI 1101 SIR JAN ( LAST TERM )
4.9(8)
Card Sorting
1/60
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 10:30 PM on 3/12/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
1
New cards
A ____ is a named, independent section of C code that performs a specific task and optionally returns a value to the calling statement.
function
2
New cards
By using that identifier in another part of the program, you can execute the statements contained in the function. This is known as _____.
calling the function
3
New cards
A function is ____. A function can perform its task without interference from or interfering with other parts of the program
independent
4
New cards
A function ______. A task is a discrete job that your program must perform as part of its overall operation, like sending a line of text to a printer.
performs a specific task
5
New cards
A function can _____. When your statement calls a function, the statements a function contains are executed. If you want them to, these statements can pass information back to the calling program.
return a value to the calling statement
6
New cards
There are two types of functions in C Programming
Standard Library functions (built-in)
User-defined functions (custom)
User-defined functions (custom)
7
New cards
The _____ are built-in functions in C programming.
standard library functions
8
New cards
These functions are defined in header files.
standard library functions
9
New cards
The ____ and ____ functions are defined in the stdio.h header file.
printf()
scanf()
scanf()
10
New cards
The ____function is defined in the math.h header file.
sqrt()
11
New cards
LIST THE 5 REASONS WHY FUNCTION USED IN PROGRAMMING
Function code is reusable.
\
Functions make programs smaller.
\
Functions make programs easier to write.
\
Functions lead to improved commenting and readability.
\
Functions make programs easier to maintain
\
Functions make programs smaller.
\
Functions make programs easier to write.
\
Functions lead to improved commenting and readability.
\
Functions make programs easier to maintain
12
New cards
The first line of a function is called function ____
prototype declaration.
13
New cards
It tells the compiler four things about the function:
( list the four things about the function)
( list the four things about the function)
Its data type
Its name
The argument it takes
Who can call it
Its name
The argument it takes
Who can call it
14
New cards
Like an operand and expression, a _____ also has a data type associated with it.
FUNCTIONS
15
New cards
The data type of a function is the data type of the value it ___.
returns
16
New cards
If the data type is omitted it defaults to_____
int.
17
New cards
Every function must have a_____. Following the rules of identifiers.
name
18
New cards
There can be only one function named ____in a program.
main
19
New cards
The expression following ____is evaluated and its value becomes the return value of the function.
return
20
New cards
The value passed by the function call statement is called an ____
argument.
21
New cards
The arguments passed into a function are known as the function’s _____
parameters.
22
New cards
when passing an argument in function, We passed the _____ not its name.
variable’s value
23
New cards
The C language provides a convenient mechanism whereby the results of a function may be returned to the calling routine.
RETURNING VALUES
24
New cards
The syntax of this (RETURNING VALUES) construct is:
return expression;
25
New cards
This statement indicates that the function is to return the value of the expression back to the calling function
RETURNING VALUES
26
New cards
There are two ways to pass parameters to functions:
They are known generically as “_____” and “______”.
They are known generically as “_____” and “______”.
call by value AND call by reference
27
New cards
In C, all arguments are passed “_______”. This means that each argument passed to a function is evaluated, and its value is passed into the function.
call by value
28
New cards
In a call by_____, instead of passing the value of the argument into the function, a reference to (i.e. the memory address of) the value is passed into the function.
reference
29
New cards
LIST THE DIFFERENT KINDS OF USER DEFINED FUNCTIONS BASED ON OUR NEEDS
1) Non-returning functions without parameters
2) Non-returning functions with parameters
3) Returning functions without parameters
4) Returning functions with parameters
2) Non-returning functions with parameters
3) Returning functions without parameters
4) Returning functions with parameters
30
New cards
NON-RETURNING FUNCTIONS WITHOUT PARAMETERS SYNTAX
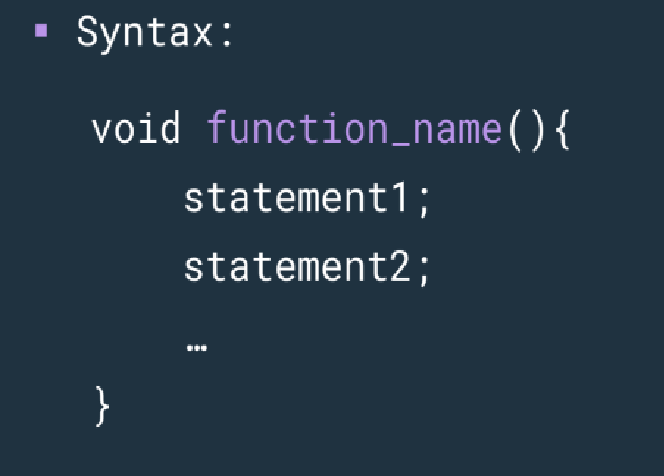
31
New cards
NON-RETURNING FUNCTIONS WITH PARAMETERS SYNTAX
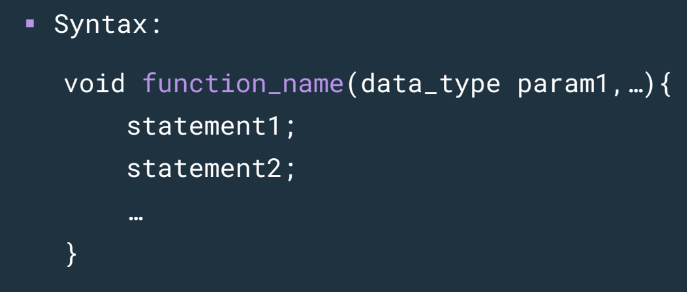
32
New cards
RETURNING FUNCTIONS WITHOUT PARAMETERS
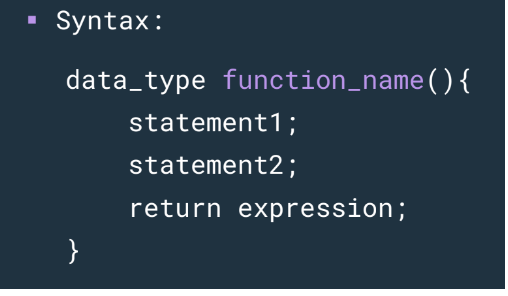
33
New cards
RETURNING FUNCTIONS WITH PARAMETERS

34
New cards
An outer block variable name is valid in an inner block unless the block redefines
FUNCTION VARIABLES
35
New cards
If an existing variable name is redefined in an inner block, or a new variable name is defined in an inner block, the variable is valid only within that block and is “___” from an outer block.
hidden
36
New cards
the scope of a local variable is the function in which it is ___
defined.
37
New cards
variables that are declared within the bounds of a function or block are referred to as_____
local variables or internal variables..
38
New cards
Variables may also be declared outside of any function block, in the same source file. They are referred to as___
global variables or external variables.
39
New cards
By using recursion in returning functions, it is necessary to use ____ for different outcomes.
multiple return statements
40
New cards
An_____ is a group of memory locations related by
the fact that they have the same identifier and
data type.
the fact that they have the same identifier and
data type.
array
41
New cards
____ provides the capability for the
programmer to define a set of ordered data items.
An array is just the same to a list.
programmer to define a set of ordered data items.
An array is just the same to a list.
C language
42
New cards
Array must be____ before they are used.
declared
43
New cards
▪ Giving a name to an array takes also the rules _____ in identifiers.
of naming convention
44
New cards
Declaration of an array involves ___the data type of values that will be stored (int, char, float, double) and ___ also the maximum number of elements (dimension) that will be stored.
declaring
indicating
45
New cards
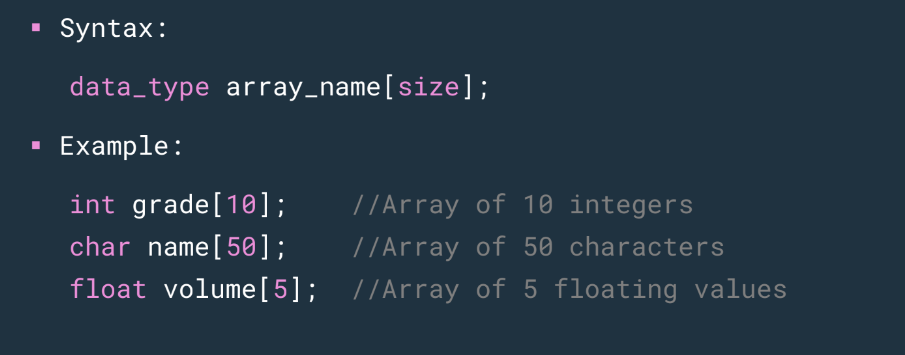
syntax of array
46
New cards
Each element of the array can be referenced by means
of a number called the_____.
of a number called the_____.
index or subscript
47
New cards
The index must be an____ or an ____
integer
integer expression.
integer expression.
48
New cards
In C, the first element is indexed with____
0 (zero).
49
New cards
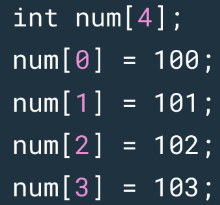
To access or reference a single element of an array,
we state the array name followed by a number in
______.
we state the array name followed by a number in
______.
square brackets
50
New cards
If an array uses an expression as a____, the
value of the expression is evaluated first to
determine the subscript.
value of the expression is evaluated first to
determine the subscript.
subscript
51
New cards
An____ array element can be used just like
variable.
variable.
individual
52
New cards
Array _____can also be used in calculations.
They are also operands.
They are also operands.
elements
53
New cards
Like variables, arrays can also be _____
initialized
54
New cards
This is done by listing the initial _____ of the array.
values
(initializers)
(initializers)
55
New cards
The values in the list are separated by ____, and
the entire list is enclosed by_____.
the entire list is enclosed by_____.
commas
parentheses
parentheses
56
New cards
If there is not enough values, elements are set to___
0
57
New cards
C allows to define an array without ____the number of elements (no dimension).
specifying
58
New cards
When this is done the size of the array is
determined____, based on the number of
____.
determined____, based on the number of
____.
automatically
initialized elements
initialized elements
59
New cards
C has no___to prevent the
computer from referring to an element that does not
exist.
computer from referring to an element that does not
exist.
array bounds checking
60
New cards
Storing individual values in each array element requires accessing ____array elements
individual
61
New cards
Size of array is usually passed to a____
function